Evan Gough
Evan Gough is a science-loving guy with no formal education who loves Earth, forests, hiking, and heavy music. He's guided by Carl Sagan's quote: "Understanding is a kind of ecstasy."
Recent Articles
-

-

No Supernova Needed. This Star Collapsed Directly Into A Black Hole
February 19, 2026Theory says that, under the right conditions, massive stars can collapse directly into black holes without exploding as supernovae. But observational evidence of the phenomenon has been hard to get. Now astronomers have found some sequestered in archival data.
-

Another Early Universe Surprise From The JWST: A Jellyfish Galaxy
February 19, 2026Astronomers have found a candidate Jellyfish Galaxy only about 5 billion years after the Big Bang. This is earlier than expected, since the ram pressure stripping responsible for it wasn't thought to be possible so early in the Universe's history. The galaxy could explain the puzzling "Red Nugget" galaxies, but first it has to be confirmed.
-
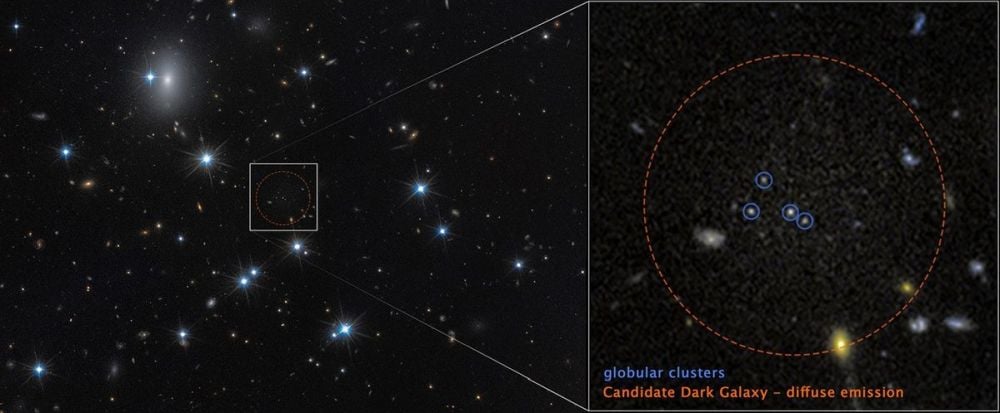

Hubble and Euclid Team Up To Identify A Dark Matter Galaxy
February 19, 2026We know galaxies by their powerful illumination, generated by multitudes of stars. But some galaxies can be very dim. These are hypothesized to be dark galaxies, or dark matter galaxies. They're theoretical, and only candidates have been identified, but researchers may have confirmed the very first one.
-

How Supermassive Black Holes Stifle Star Formation In Neighbouring Galaxies
February 18, 2026We know that supermassive black holes can inhibit star formation in their galaxies. But new research and JWST observations show that the most luminous quasars can actually suppress star formation in neighbouring galaxies. SMBH may have played a more pronounced role in shaping the early Universe than previously thought.
-

A Pulsar Near The Milky Way's Galactic Center Is A Perfect Set-up To Test General Relativity
February 18, 2026The Milky Way's center is densely-packed with stars and there should be abundant pulsars there. But for some reason, we can't find them. New research presents a candidate pulsar in the GC. It's close enough to the Milky Way's supermassive black hole that it can test Einstein's General Relativity. But first, it has to be confirmed.
-
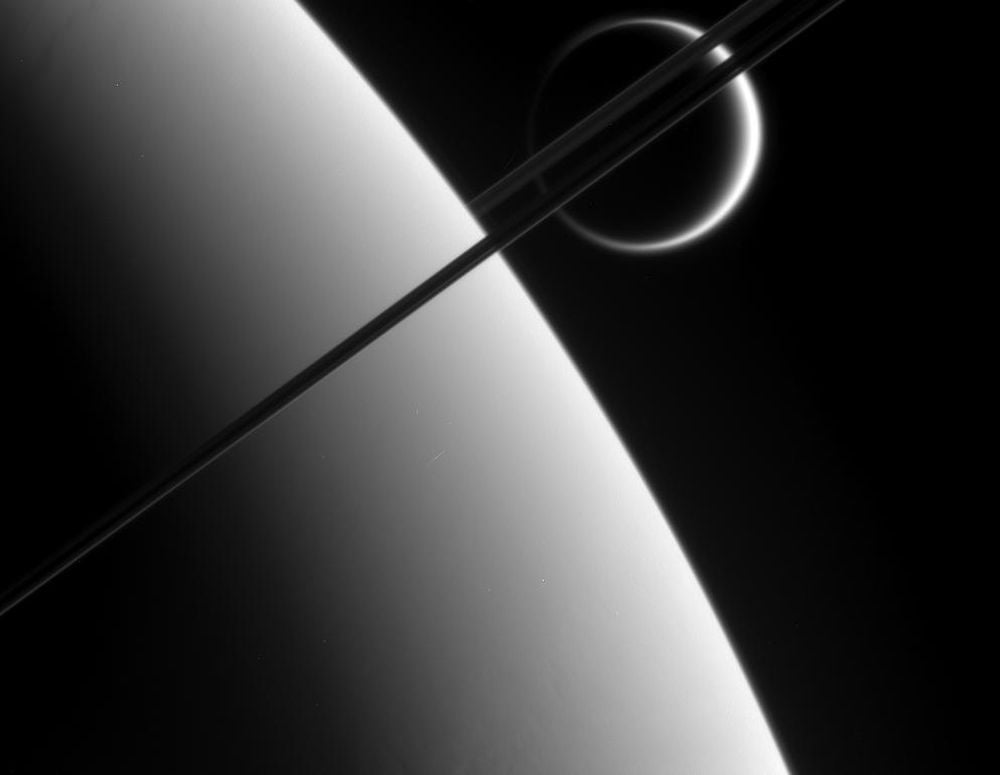

An Ancient Merger Could Have Created Titan and the Debris Created Saturn's Rings
February 17, 2026New research presents a timeline for recent (astronomically speaking) events in the Saturnian system. It shows that Titan collided with a proto-Hyperion, and the collision smoothed Titan's surface while some of the debris accreted onto a new Hyperion and also created Saturn's rings. The research can also explain some of the Saturnian system's other unusual characteristics.
-

Very Few Planets Have the Right Chemistry for Life
February 16, 2026A complex web of interrelated factors make Earth a life-supporting planet, and some of those factors are chemical. New research shows how oxygen abundance regulates the availability of the important chemicals phosphorous and nitrogen on planets, and that few planets get it right. While discouraging, it could help us optimize our search for habitable worlds.
-
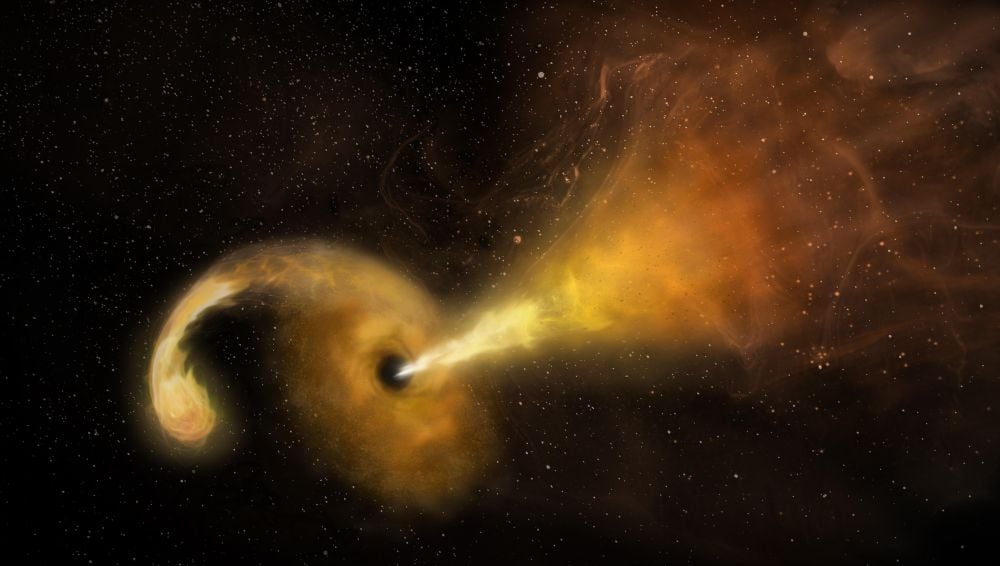

Look Out Alderaan. This Black Hole Is More Destructive Than The Death Star
February 12, 2026Several years ago, an automated sky survey spotted a distant supermassive black hole that tore apart a star. The star that got too close, and the resulting tidal disruption event released a lot of energy. But the SMBH is exhibiting a strong case of cosmic indigestion, and has been burping out the remains of the star for four years. And it keeps getting brighter and brighter.
-
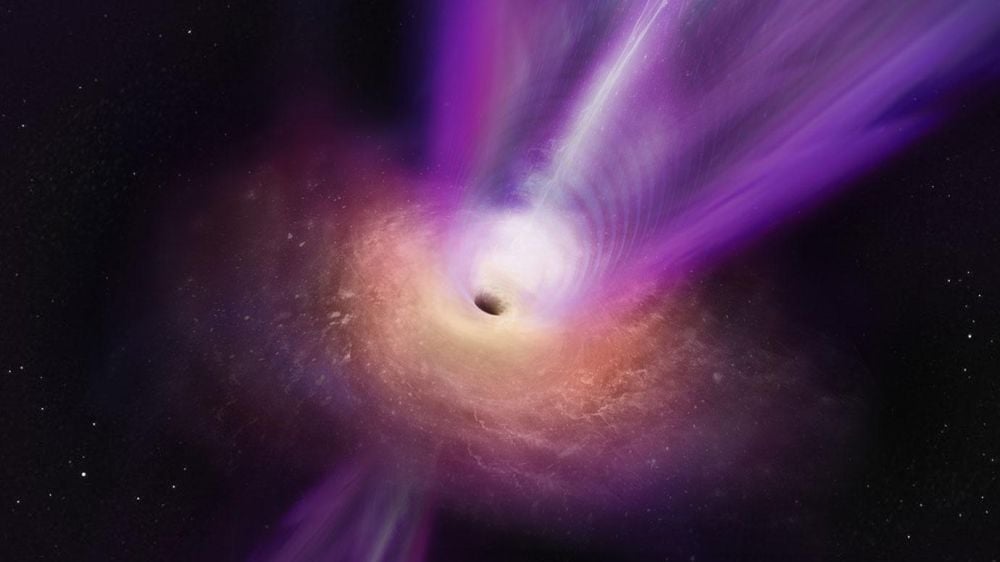

Peering Into the Energetic Turbulence Around Supermassive Black Holes
February 10, 2026Astronomers used the XRISM x-ray satellite to observe two supermassive black holes in two separate galaxy clusters. Researchers know that SMBH have powerful effects on star formation and galaxy evolution. The observations reveal new details in how it all works.
-

A Dense Clump Of Dark Matter, Not A Supermassive Black Hole, Could Reside In The Milky Way's Center.
February 09, 2026There's been widespread agreement that a supermassive black hole resides in the Milky Way's Center. But that may not be true. Researchers say that a dense clump of fermionic dark matter can also explain the motions of stars and gas clouds in the region. Crucially, it can also explain the famous Event Horizon Telescope image of the SMBH.
-
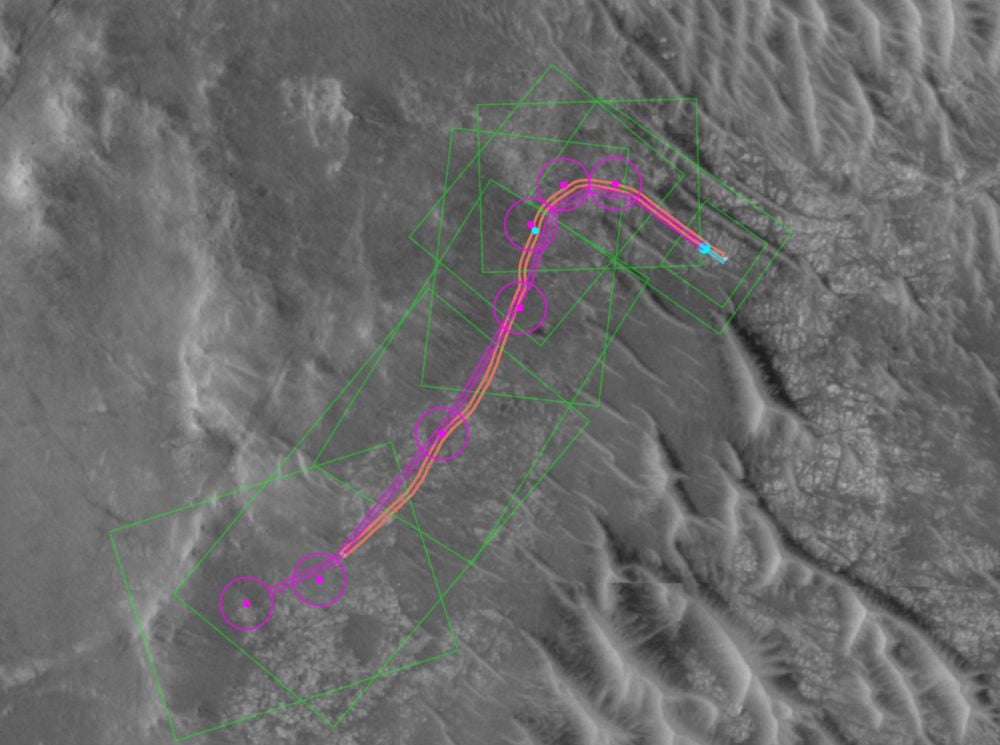
NASA Let AI Drive The Perseverance Rover For Two Days
February 09, 2026NASA has taken another step towards greater autonomy for planetary exploration rovers. In December, the space agency used AI to generate waypoints for Perseverance's route on two separate days. The rover drove more than 450 meters without human input.
-
Is There A Link Between Primordial Black Holes, Neutrinos, and Dark Matter?
February 05, 2026In 2023, a subatomic particle called a neutrino crashed into Earth with such a high amount of energy that it should have been impossible. In fact, there are no known sources anywhere in the universe capable of producing such energy—100,000 times more than the highest-energy particle ever produced by the Large Hadron Collider, the world's most powerful particle accelerator. However, a team of physicists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently hypothesized that something like this could happen when a special kind of black hole, called a "quasi-extremal primordial black hole," explodes.
-
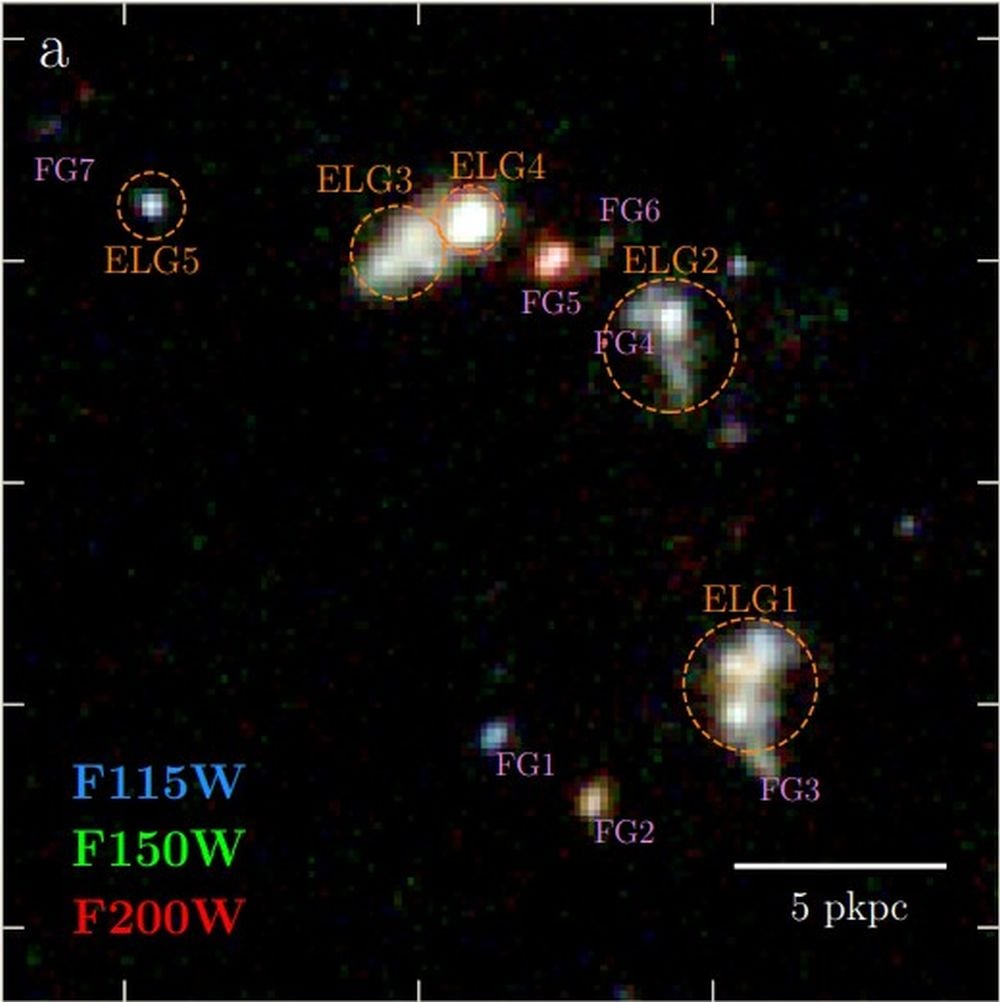
Cosmic Collision: The JWST Found An Early 5-Galaxy Merger
February 04, 2026The JWST found a system of at least five interacting galaxies only 800 million years after the Big Bang. The discovery adds weight to the growing understanding that galaxies were interacting and shaping their surroundings far earlier than scientists thought. There's also evidence that the collision was redistributing heavy elements beyond the galaxies themselves.
-
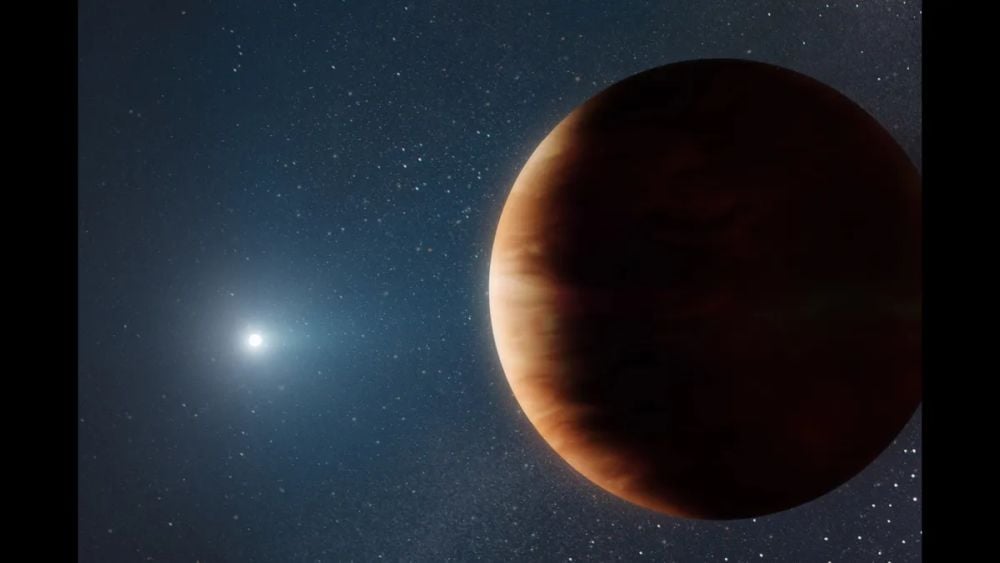

Red Giant Stars Can't Destroy All Gas Giants. Some Are Hardy Survivors
February 03, 2026Astronomers haven't found many gas giants orbiting white dwarfs. But is that because they're so difficult to spot? Or is it because their survival rate is so low? New research probes the issue.
-

The Magnetic Superhighways That Drive Galaxy Evolution
February 02, 2026Arp 220 is a well-known pair of galaxies that are merging. New ALMA observations of polarized light reveal the complex and powerful magnetic fields that shape the process.
-
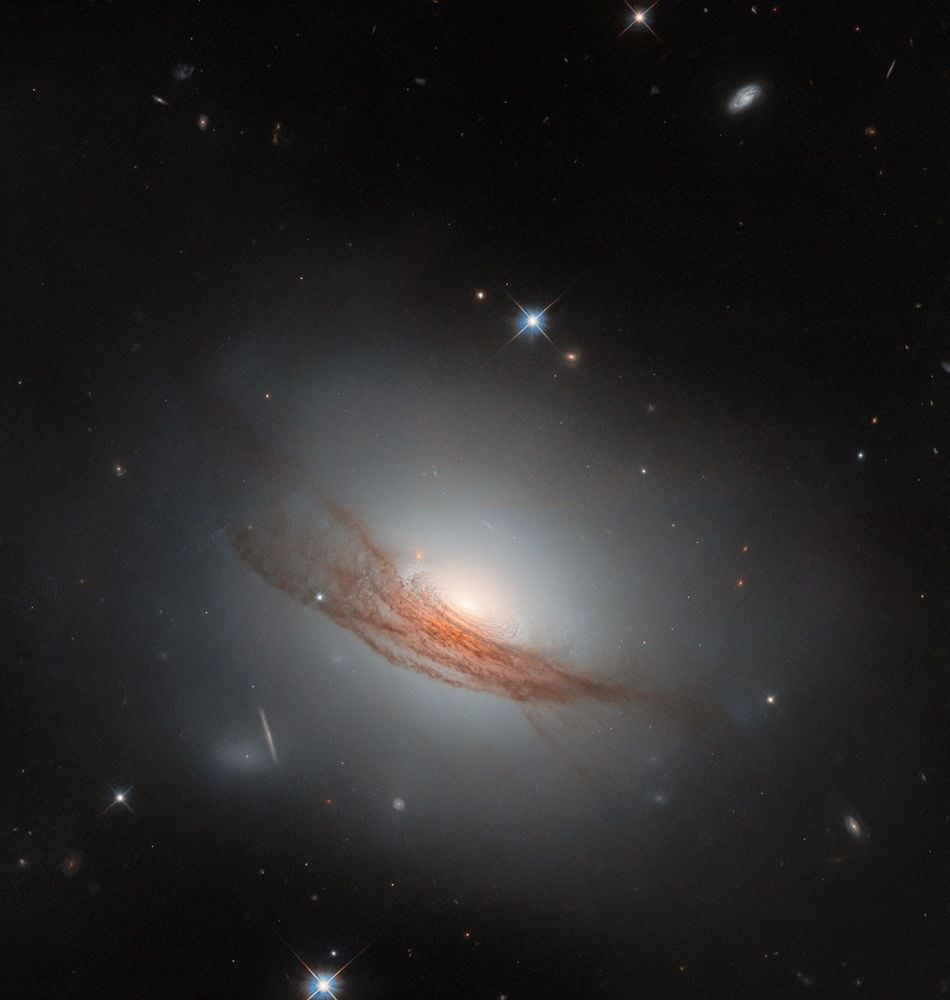

Hubble And The Fingerprints Of An Ancient Merger
February 02, 2026This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows NGC 7722, a lenticular galaxy about 187 million light-years away in the constellation Pegasus. This “lens-shaped” galaxy sits in between more familiar spiral alaxies and elliptical galaxies in the galaxy classification scheme. The dark, dramatic dust lanes are the fingerprints of an ancient galaxy merger.
-

"Red Geyser" Galaxies Have Plenty of Star-Forming Gas But Don't Form Stars
January 30, 2026Red Geysers are an unusual class of galaxy that contain only old stars. Despite having plenty of star-forming gas, Red Geysers are quenched. Astronomers have mapped the flow of gas in these galaxies and figure out why they're dormant.
-
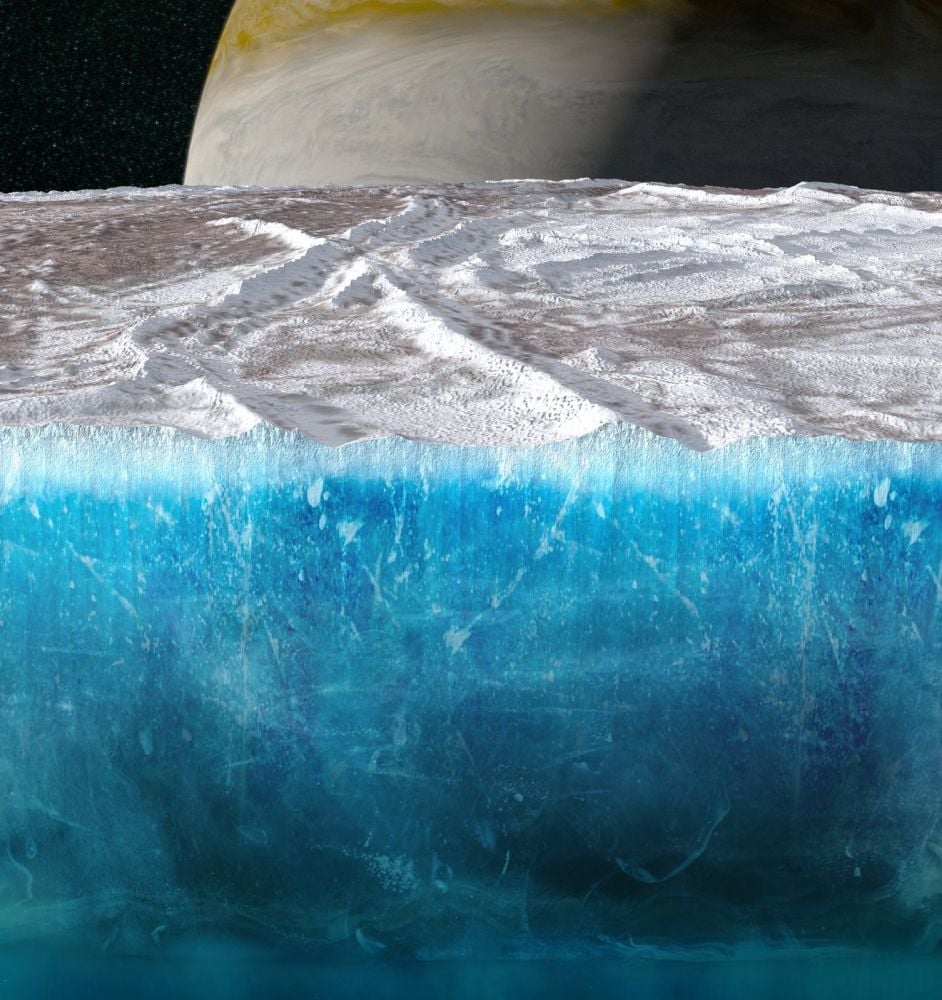

New Measurements of Europa's Ice Shell Taint the Icy Moon's Potential Habitability
January 30, 2026Jupiter's icy moon Europa is a tantalizing target in the search for habitability in our Solar System. Its thick, global ice sheet overlies a warm, salty, chemically-rich ocean. But for life to exist in that ocean, nutrients need to find their way from the surface to the ocean. New research says that may be very difficult.
-
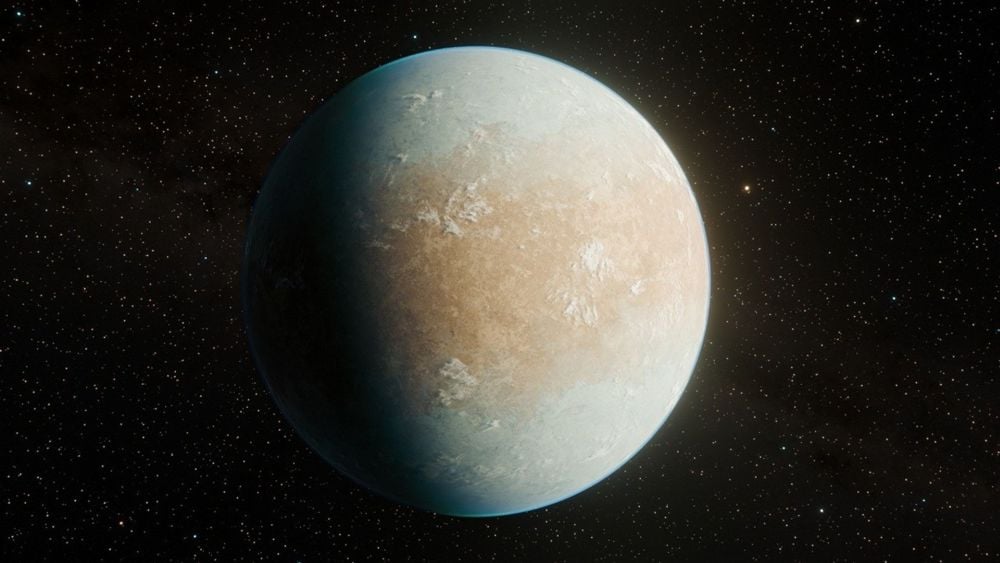

Finding A Frozen Earth In Old Data
January 29, 2026Finding Earth-like planets is the primary driver of exoplanet searches because as far as we know, they're the ones most likely to be habitable. Astronomers sifting through data from NASA's Kepler Space Telescope have found a remarkably Earth-like planet, but with one critical difference: it's as cold as Mars.
 Universe Today
Universe Today