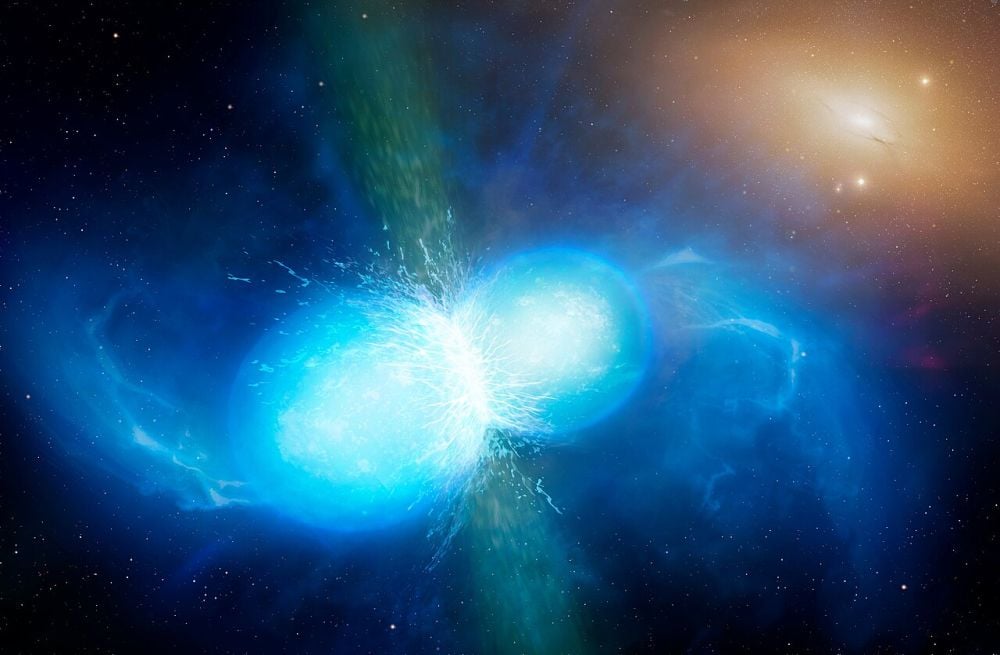

A neutron star merger is an extraordinary event. It features extremely powerful, chaotic magnetic fields that generate extremely energetic photons. Supercomputer simulations show that the extreme gamma-ray photons created in the mayhem can't even escape the chaos.
Continue reading

So why should we expect interstellar comets like 3I/ATLAS and 'Oumuamua and even to some extent Borisov to be different-different?
Continue reading
MIT physicists have observed the first clear evidence that quarks create a wake as they speed through quark-gluon plasma, confirming the plasma behaves like a liquid.
Continue reading
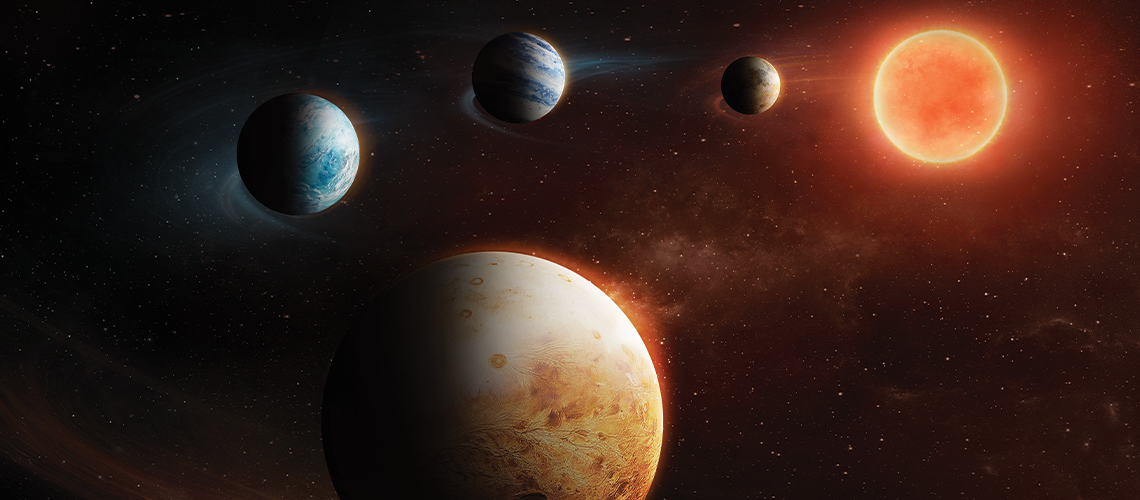

We’re starting to see just how exceptional our own solar system and its history is, as more exoplanets are discovered. A fourth exoplanet discovery in the LHS 1903 system made by ESA’s CHEOPS mission places a rocky world right where it shouldn’t be. This ‘inside-out system’ could challenge our current understanding of planetary formation.
Continue reading

Three years ago, a detector sitting on the floor of the Mediterranean Sea recorded a single subatomic particle carrying more energy than anything of its kind ever seen before. Where it came from has been a mystery ever since. Now, scientists working with the KM3NeT detector off the coast of Sicily think they may have found the culprit, a population of blazars, some of the most violent objects in the universe, each one powered by a supermassive black hole firing a jet of plasma directly toward Earth.
Continue reading

For 45 years, astronomers believed that stars like our Sun would eventually flip their rotation pattern as they aged with the poles speeding up and the equator slowing down. It was one of those theoretical predictions that seemed rock solid, written into textbooks and built into stellar models. Now, researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have run the most powerful simulations of stellar interiors ever attempted, and the theory has collapsed. Stars like the Sun, it turns out, seem to keep the same rotation pattern for their entire lives.
Continue reading

“Follow the water” has been a guiding mantra of astrobiology, and even space exploration more generally for decades. If you want to find life, it makes sense to look for the universal solvent that almost all types of life on Earth use. But what if life doesn’t actually need water to live or even evolve? A recent paper, available in pre-print on arXiv by researchers at MIT, including Dr. Sara Seager, and the University of Cardiff, proposes an alternative to water as the basis for life - ionic liquids (ILs) and deep eutectic solvents (DES). These liquids could allow life to exist in environments we had once thought were far too hot, too cold, or too barren to support life, and could dramatically change our search for it throughout the cosmos.
Continue reading

While megastructures are clearly speculative, new research shows that they can (in theory) be built in a way that ensures long-term stability. These findings can provide insight into the properties of potential technosignatures in search for extraterrestrial intelligence studies.
Continue reading

NASA telescopes have detected what could be the most distant gamma-ray burst ever detected. A merging pair of neutron stars generated when they merged and exploded as a kilonova. It happened in an unusual location: a tidal stream of debris created by a group of merging galaxies.
Continue reading

Once you start listing the properties of 3I/ATLAS, it becomes clear pretty quickly that this thing is distinctly different from any other comet we've ever seen. Here's just a small taste.
Continue reading
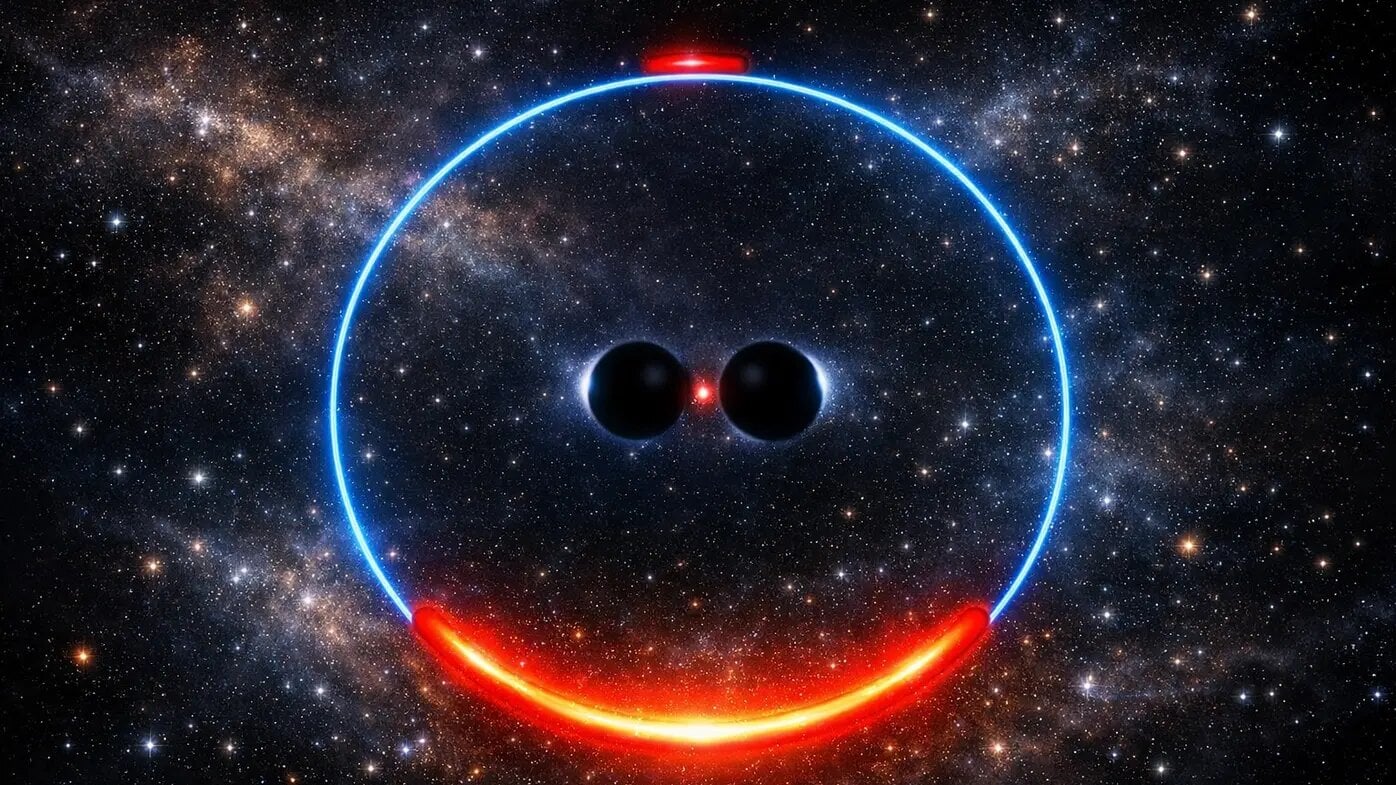
Supermassive black hole binaries can be difficult to detect in many galaxies, but a new approach could find them by looking for the regular flashes of starlight caused by the gravitational lensing of these black holes.
Continue reading
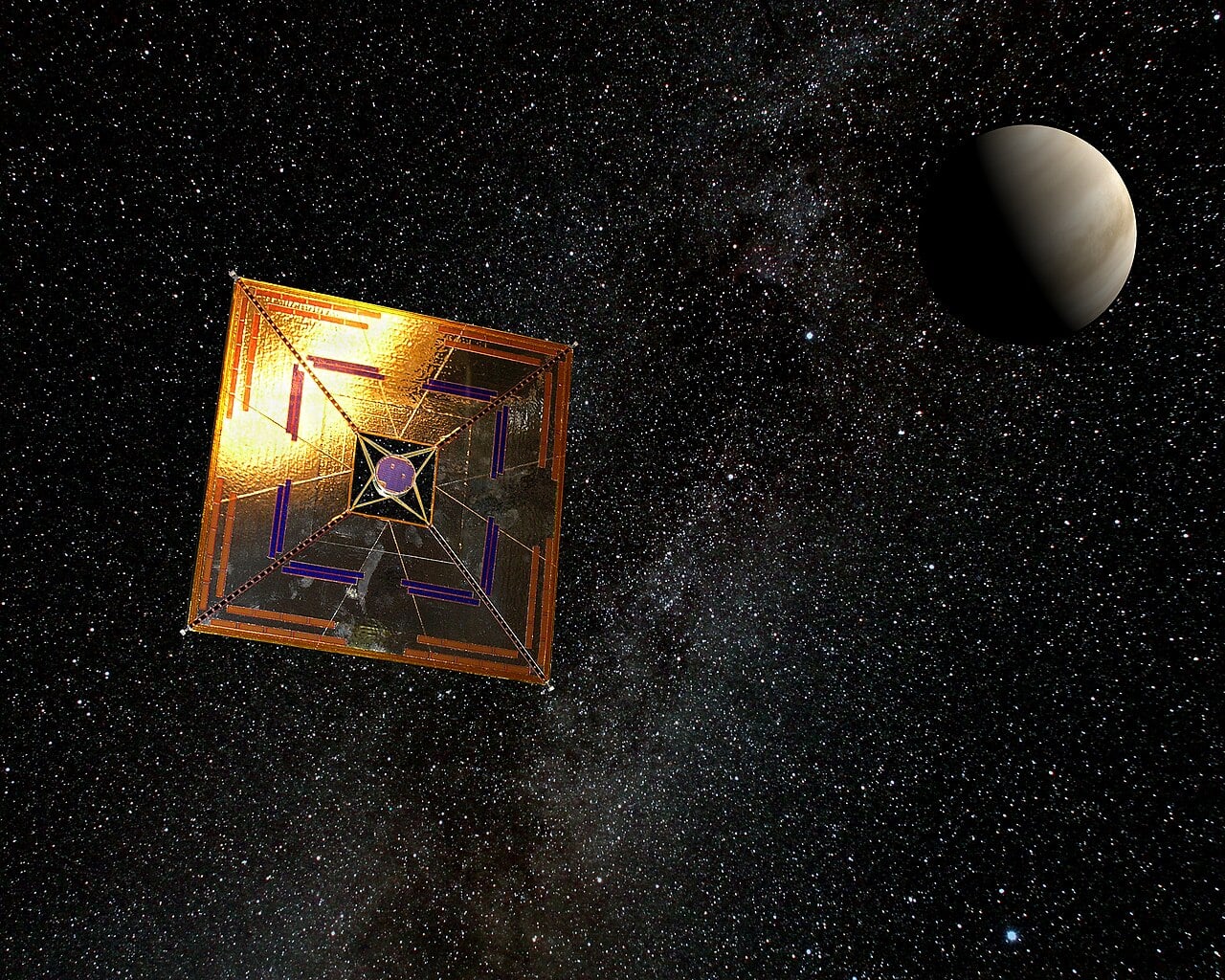
Traditional chemical rockets, though they are the most commonly used propulsion method for space exploration today, are beholden to the tyranny of the rocket equation. Every ounce of thrust they use must also start out as fuel, which means the rocket itself will have to weigh more, and weight is one of the limiting factors in how fast a propulsion system can go. So, scientists have been searching for, and actively testing, alternatives for decades. One of the most promising is the solar sail - a huge reflective sheet that uses sunlight, or in some cases a “pushing laser” to maneuver about the solar system without any onboard propellant necessary. A recent paper published in the Journal of Nanophotonics by Dimitar Dimitrov and Elijah Taylor Harris of Tuskegee University describes a new type of light sail that solves some of the major problems of existing designs.
Continue reading

China has just laid out one of its most ambitious spaceflight schedules yet and the details reveal a programme that is accelerating. Two crewed missions, a cargo resupply flight, a year long solo endurance experiment, and the first ever space station flight by astronauts from Hong Kong or Macao are all on the cards for 2026. Beyond Earth orbit, the countdown to a Chinese crewed Moon landing is ticking louder than ever. Here's what's coming up and why it matters.
Continue reading

A NASA spacecraft that spent seven years mapping Earth's invisible radiation shields has made its final journey home and it came back years ahead of schedule. Van Allen Probe A, launched in 2012 to study the powerful belts of charged particles that wrap around our planet, re-entered Earth's atmosphere in March 2026, most of it burning up in a blaze of friction and heat. What brought it down early wasn't a malfunction or a mission decision. It was the Sun and that twist in the story tells us something important.
Continue reading

When a powerful solar storm erupts, the warning system we currently rely on gives us just hours to respond, barely enough time to protect the satellites, power grids, and communication networks that modern life depends on. But a new tool developed by scientists at the Southwest Research Institute and the National Science Foundation could change that entirely, pushing advance warnings of dangerous space weather from hours to weeks. The secret lies not at the Sun's surface, but deep in its hidden interior and unlocking it has required a remarkable fusion of physics and artificial intelligence.
Continue reading

A new movie called "Project Hail Mary" tells the story of an unlikely astronaut who teams up with an alien to deal with a common cosmic threat. In the latest Fiction Science podcast, SETI astronomer Seth Shostak provides a status report on the real-world quest for alien contact.
Continue reading

For forty years, a network of telescopes has been listening to the Sun hum and scientists have finally decoded what those sounds reveal about our star's hidden interior. A new study from the University of Birmingham and Yale University has found that the Sun's internal structure quietly shifts between solar cycles, leaving measurable fingerprints deep beneath its surface. It's a discovery that could transform how we forecast space weather and its impact here on Earth.
Continue reading

Multiple mobile phones, dashcams, and dedicated meteor cameras capture a fireball over part of Europe on Sunday night. Thousands of people witnessed it, and the ESA's Planetary Defence Team is analyzing it. So far, it looks like it was a few meters in diameter. It lit up the sky, and some debris even struck some buildings in Koblenz, Germany.
Continue reading

One of the Vera Rubin Observatory's objectives is to detect incoming objects. It's decade-long Legacy Survey of Space and Time will detect one-meter class objects about to impact Earth and allow more detailed observations of them. That will help determine their impact sites with greater accuracy, allowing for more recovery.
Continue reading

Just a few days in simulated microgravity can subtly change the way women’s blood clots, sparking bigger questions about health monitoring protocols for astronauts who can spend six months or more in orbit, say Simon Fraser University researchers.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today


















