Evan Gough
Evan Gough is a science-loving guy with no formal education who loves Earth, forests, hiking, and heavy music. He's guided by Carl Sagan's quote: "Understanding is a kind of ecstasy."
Recent Articles
-

-

Peering Into the Energetic Turbulence Around Supermassive Black Holes
February 10, 2026Astronomers used the XRISM x-ray satellite to observe two supermassive black holes in two separate galaxy clusters. Researchers know that SMBH have powerful effects on star formation and galaxy evolution. The observations reveal new details in how it all works.
-

A Dense Clump Of Dark Matter, Not A Supermassive Black Hole, Could Reside In The Milky Way's Center.
February 09, 2026There's been widespread agreement that a supermassive black hole resides in the Milky Way's Center. But that may not be true. Researchers say that a dense clump of fermionic dark matter can also explain the motions of stars and gas clouds in the region. Crucially, it can also explain the famous Event Horizon Telescope image of the SMBH.
-
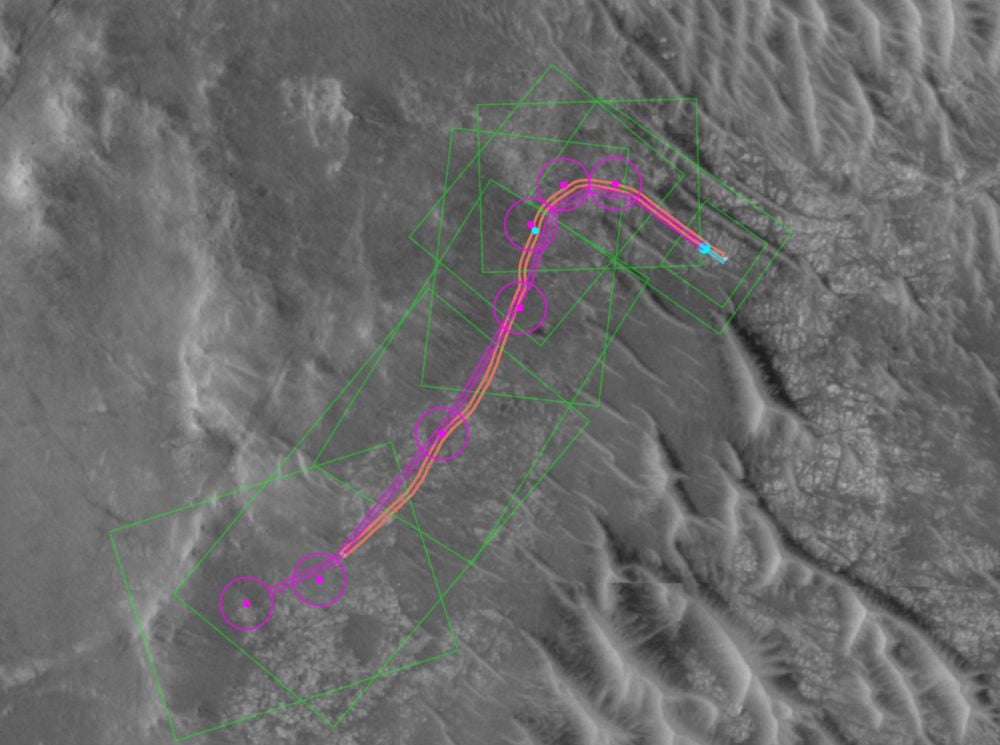
NASA Let AI Drive The Perseverance Rover For Two Days
February 09, 2026NASA has taken another step towards greater autonomy for planetary exploration rovers. In December, the space agency used AI to generate waypoints for Perseverance's route on two separate days. The rover drove more than 450 meters without human input.
-
Is There A Link Between Primordial Black Holes, Neutrinos, and Dark Matter?
February 05, 2026In 2023, a subatomic particle called a neutrino crashed into Earth with such a high amount of energy that it should have been impossible. In fact, there are no known sources anywhere in the universe capable of producing such energy—100,000 times more than the highest-energy particle ever produced by the Large Hadron Collider, the world's most powerful particle accelerator. However, a team of physicists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently hypothesized that something like this could happen when a special kind of black hole, called a "quasi-extremal primordial black hole," explodes.
-
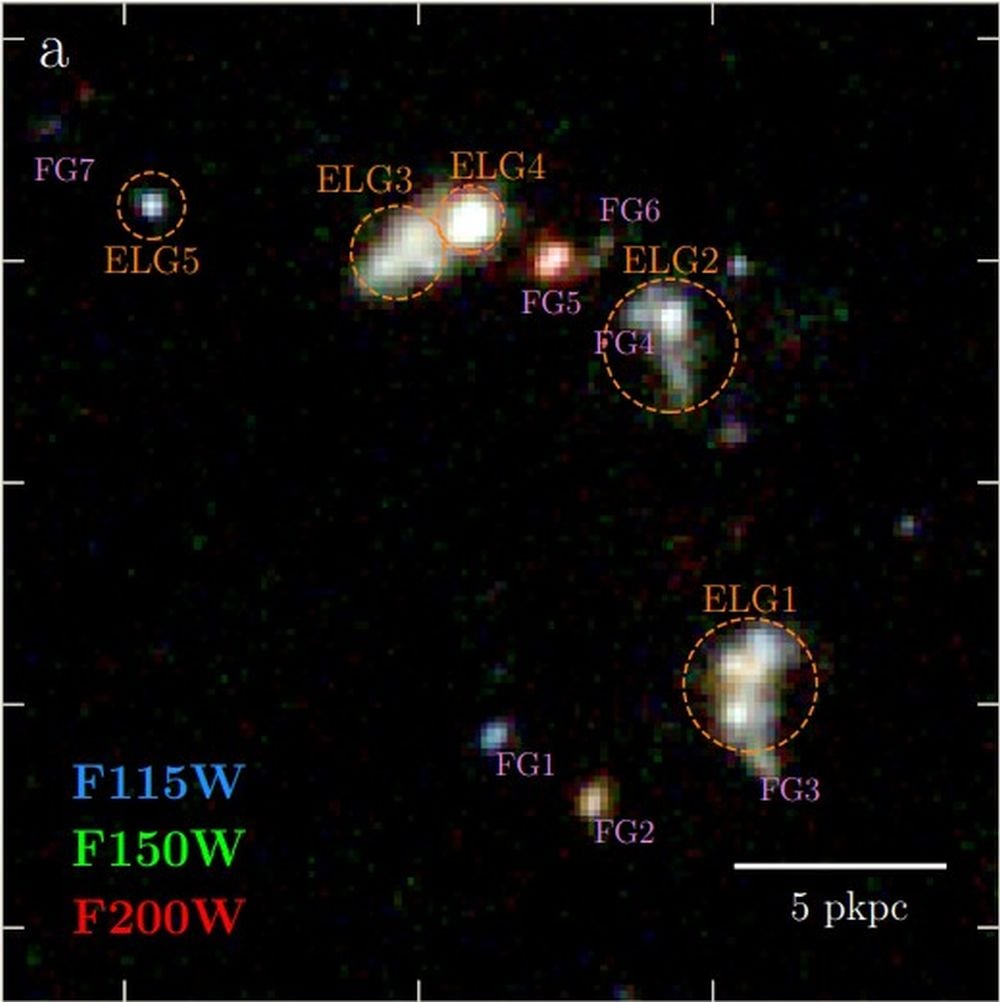
Cosmic Collision: The JWST Found An Early 5-Galaxy Merger
February 04, 2026The JWST found a system of at least five interacting galaxies only 800 million years after the Big Bang. The discovery adds weight to the growing understanding that galaxies were interacting and shaping their surroundings far earlier than scientists thought. There's also evidence that the collision was redistributing heavy elements beyond the galaxies themselves.
-

Red Giant Stars Can't Destroy All Gas Giants. Some Are Hardy Survivors
February 03, 2026Astronomers haven't found many gas giants orbiting white dwarfs. But is that because they're so difficult to spot? Or is it because their survival rate is so low? New research probes the issue.
-

The Magnetic Superhighways That Drive Galaxy Evolution
February 02, 2026Arp 220 is a well-known pair of galaxies that are merging. New ALMA observations of polarized light reveal the complex and powerful magnetic fields that shape the process.
-
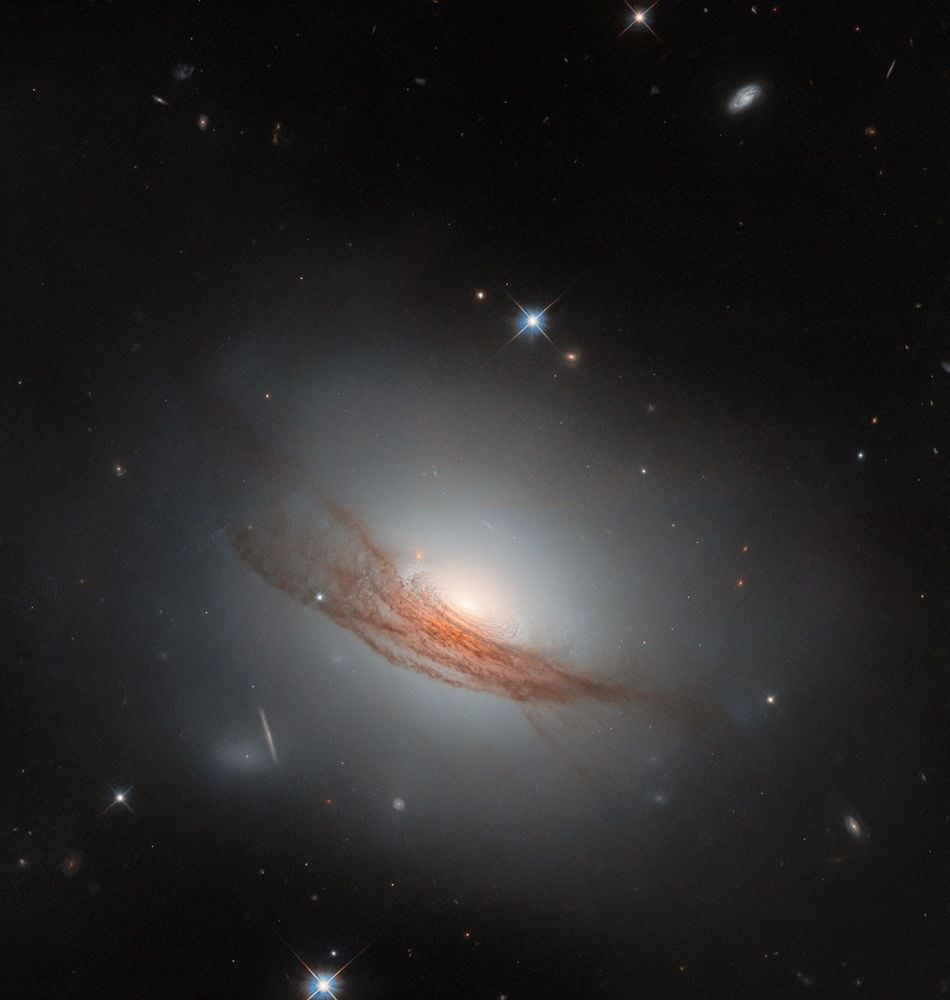

Hubble And The Fingerprints Of An Ancient Merger
February 02, 2026This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows NGC 7722, a lenticular galaxy about 187 million light-years away in the constellation Pegasus. This “lens-shaped” galaxy sits in between more familiar spiral alaxies and elliptical galaxies in the galaxy classification scheme. The dark, dramatic dust lanes are the fingerprints of an ancient galaxy merger.
-

"Red Geyser" Galaxies Have Plenty of Star-Forming Gas But Don't Form Stars
January 30, 2026Red Geysers are an unusual class of galaxy that contain only old stars. Despite having plenty of star-forming gas, Red Geysers are quenched. Astronomers have mapped the flow of gas in these galaxies and figure out why they're dormant.
-
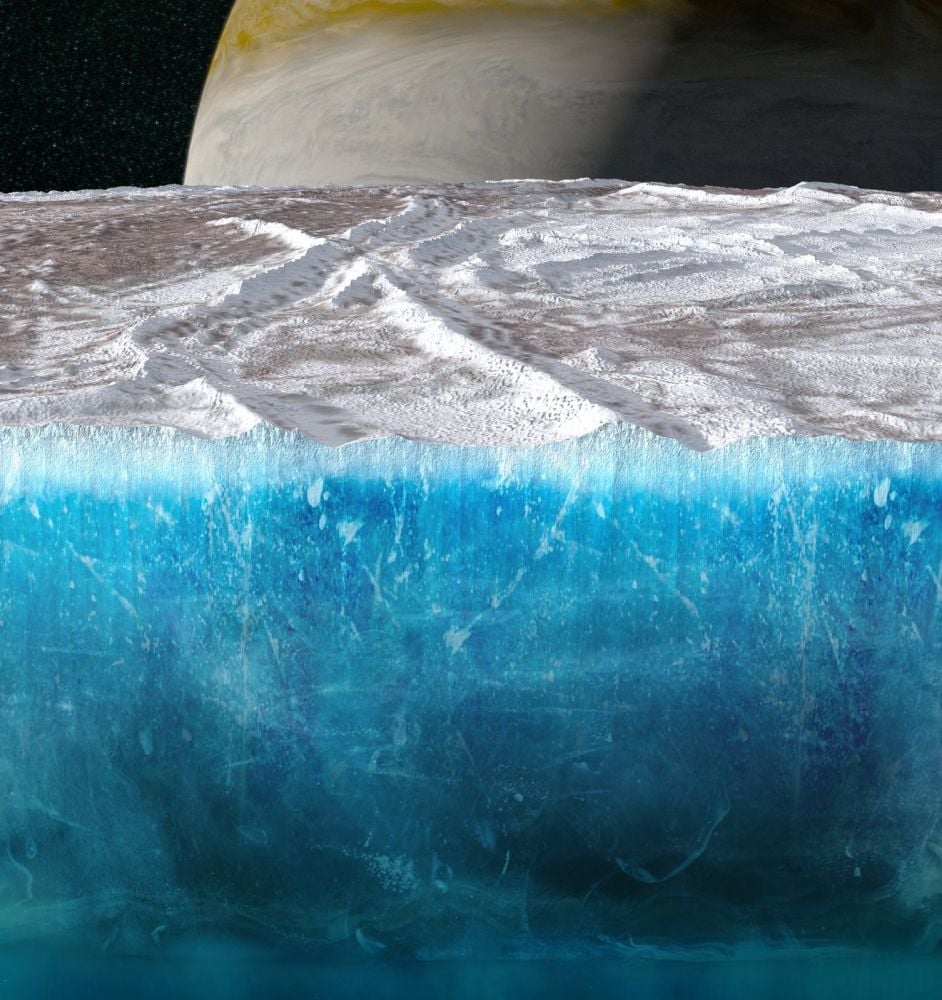

New Measurements of Europa's Ice Shell Taint the Icy Moon's Potential Habitability
January 30, 2026Jupiter's icy moon Europa is a tantalizing target in the search for habitability in our Solar System. Its thick, global ice sheet overlies a warm, salty, chemically-rich ocean. But for life to exist in that ocean, nutrients need to find their way from the surface to the ocean. New research says that may be very difficult.
-

Finding A Frozen Earth In Old Data
January 29, 2026Finding Earth-like planets is the primary driver of exoplanet searches because as far as we know, they're the ones most likely to be habitable. Astronomers sifting through data from NASA's Kepler Space Telescope have found a remarkably Earth-like planet, but with one critical difference: it's as cold as Mars.
-
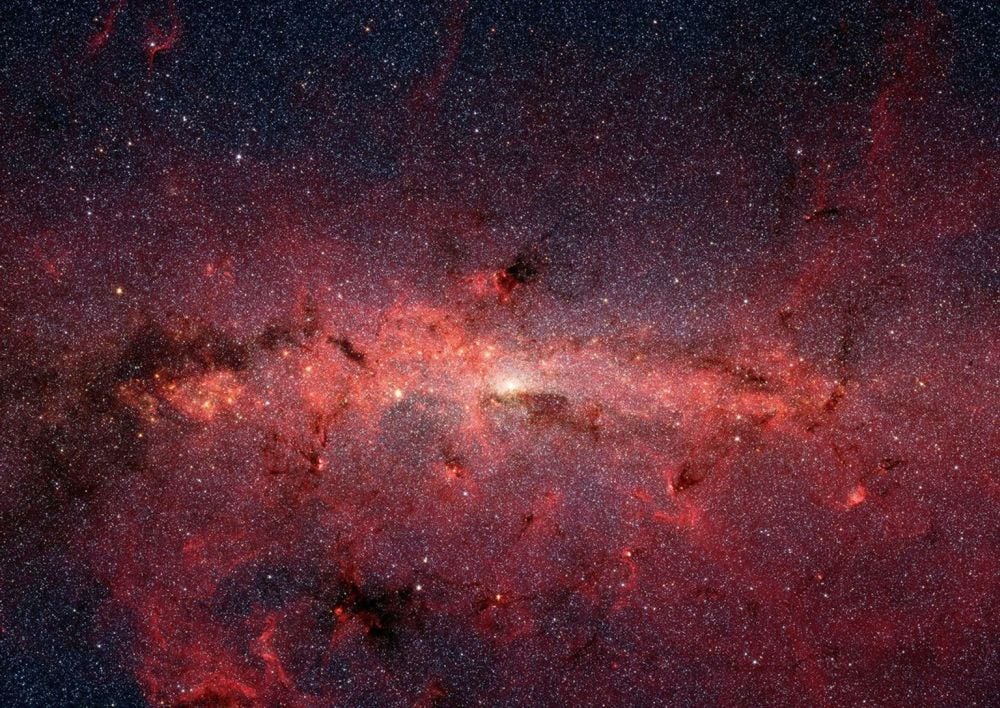

The Milky Way's Center is a Difficult Target, But It Can't Deter the Roman Telescope
January 29, 2026The Milky Way's Galactic Center and Bulge are shrouded in thick dust and tightly-packed with stars. It's a tough region to observe, but the Nancy Gracy Roman Space Telescope is built for the task. Its Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey will find more than 100,000 exoplanets, along with stars, black holes, neutron stars, and even rogue planets.
-
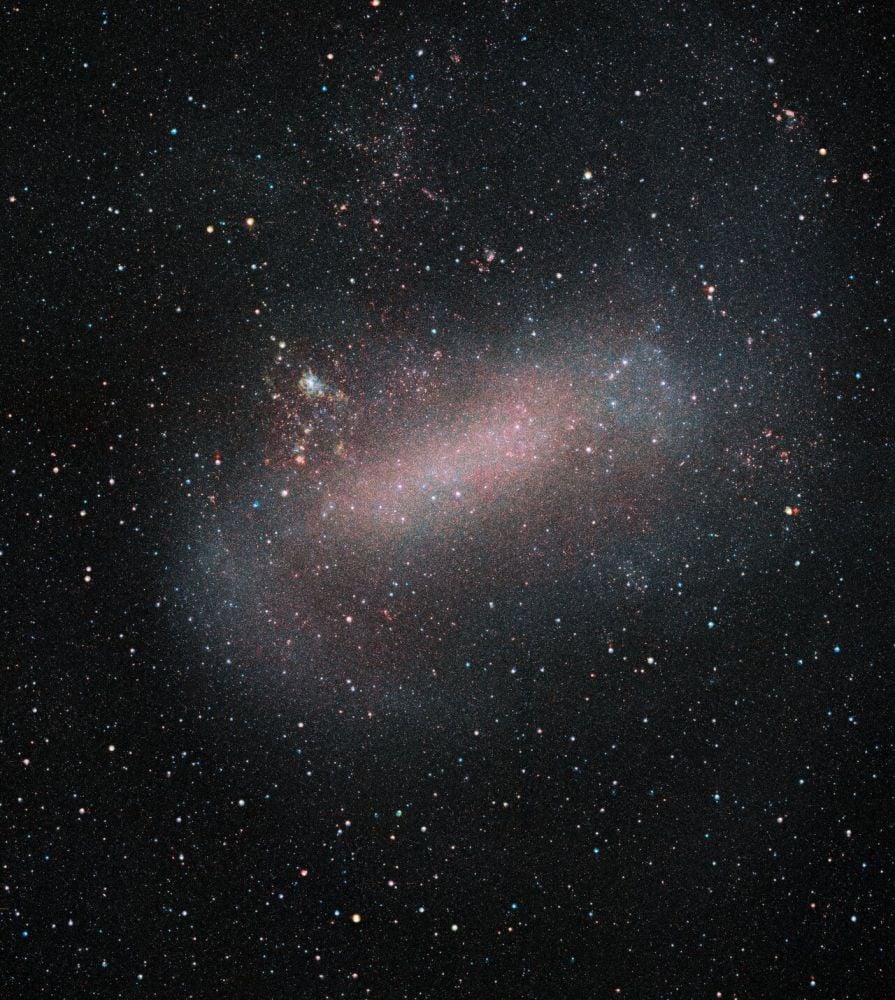

Do Dwarf Galaxies Merge In The Milky Way's Halo?
January 28, 2026Our current understanding of the Cosmos shows that structures emerge hierarchically. First there are dark matter densities, then dwarf galaxies. Those dwarfs then merge to form more massive galaxies, which merge together into even larger galaxies. Evidence of dwarf galaxy mergers is difficult to obtain, but new research found some in the Milky Way's halo.
-
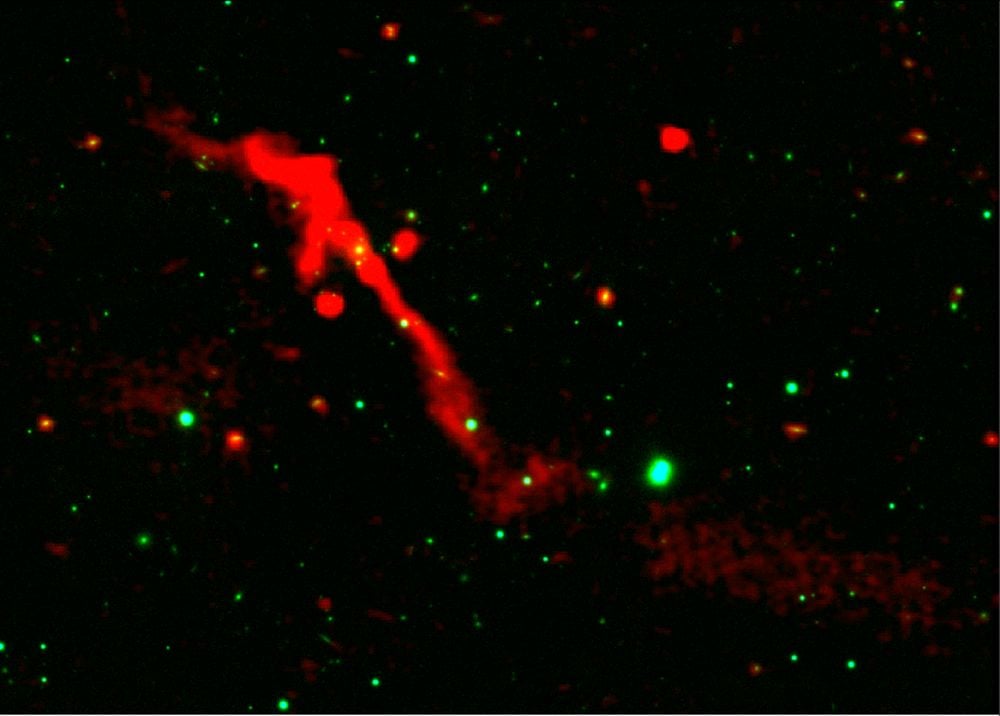
Intermittent Black Hole Jets Are Like A 'Cosmic Volcano'
January 27, 2026Supermassive black holes grow larger by accreting matter. When they're actively accreting matter they're called active galactic nuclei (AGN). AGN are the most luminous sources of persistent radiation in the Universe, yet they turn on and off as the SMBH passes through quiet and active phases. Astronomers have found one that is just turning on its powerful jets after a long period of dormancy.
-
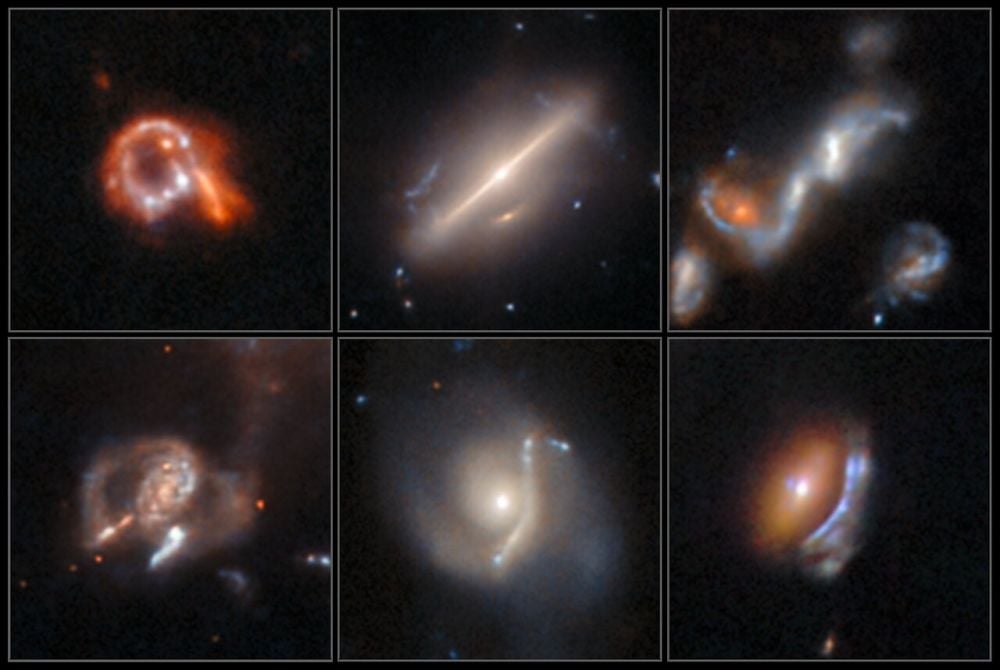

Researchers Use AI To Find Astronomical Anomalies Buried In Archives
January 27, 2026AI faces strong skepticism due to its potential for misuse, its drain on resources, and even its potential dumbing down of students. But new results illustrate its uses. A team of astronomers have used a new AI-assisted method to search for rare astronomical objects in the Hubble Legacy Archive. The team sifted through nearly 100 million image cutouts in just two and a half days, uncovering nearly 1400 anomalous objects, more than 800 of which had never been documented before.
-
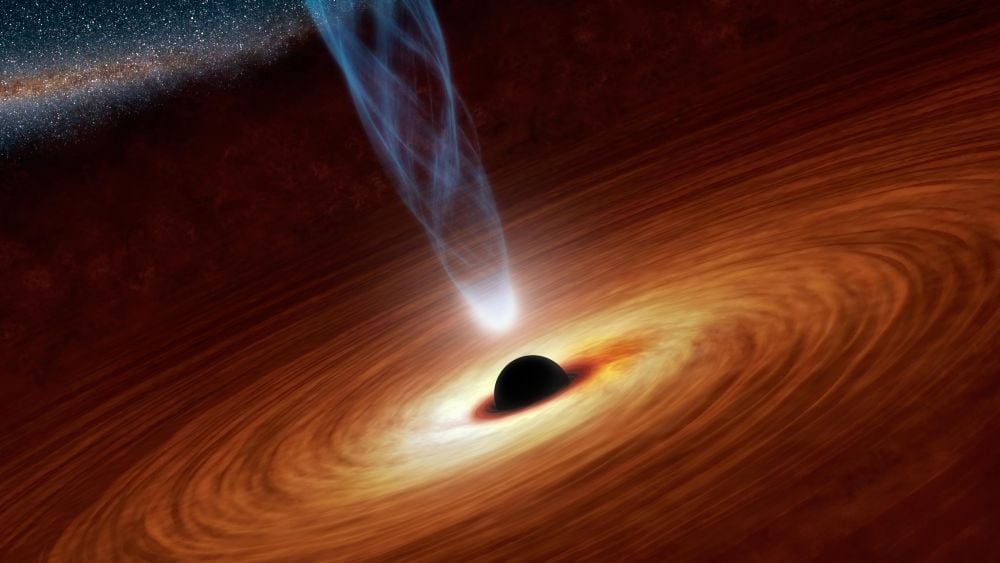

This Rapidly Growing Black Hole Is Challenging Super-Eddington Accretion
January 27, 2026Why are SMBH in the early Universe so massive? According to astrophysical models, these extraordinarily large SMBH haven't had time to become so massive. Super-Eddington accretion might explain it, but can it explain a very unusual early SMBH recently discovered?
-
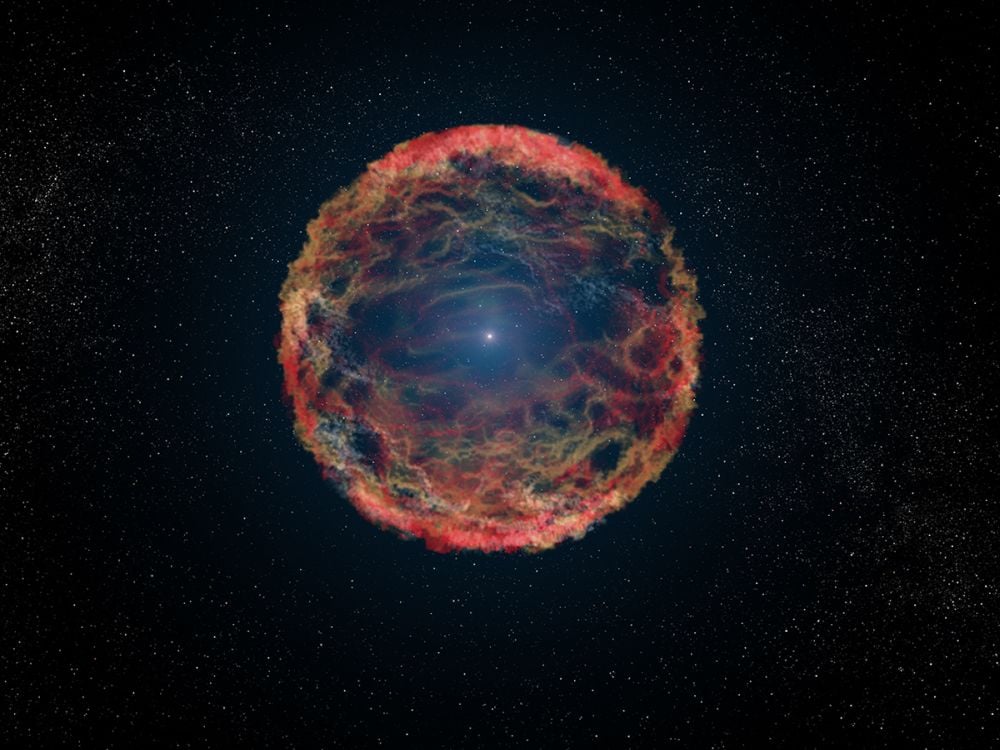

The Rubin Observatory Will Rapidly Detect More Supernovae
January 27, 2026It's been about one millennia since humans directly observed a core-collapse supernova in the Milky Way. That's strange, since there should be 1 or 2 every century. By working with neutrino detectors, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory should be able to detect far more supernovae.
-
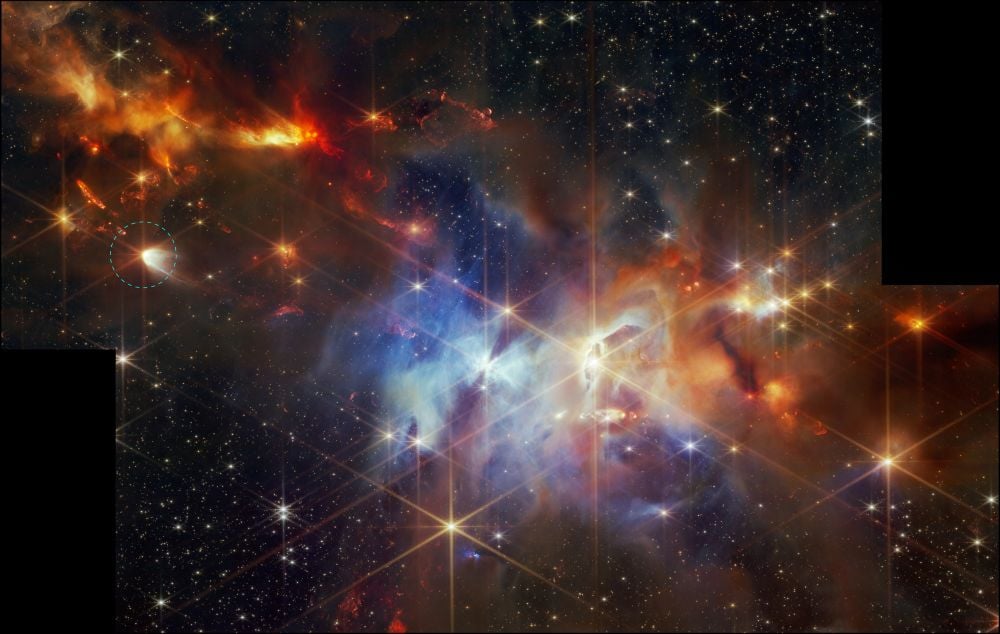

Icy Comets Get A Contribution From Stellar Furnaces
January 26, 2026Icy comets contain common crystals that can only be formed in extreme heat. But comets reside in the frigid outer reaches of the Solar System. How did these materials form, and how did they find their way into the Solar System's cold fringes?
-
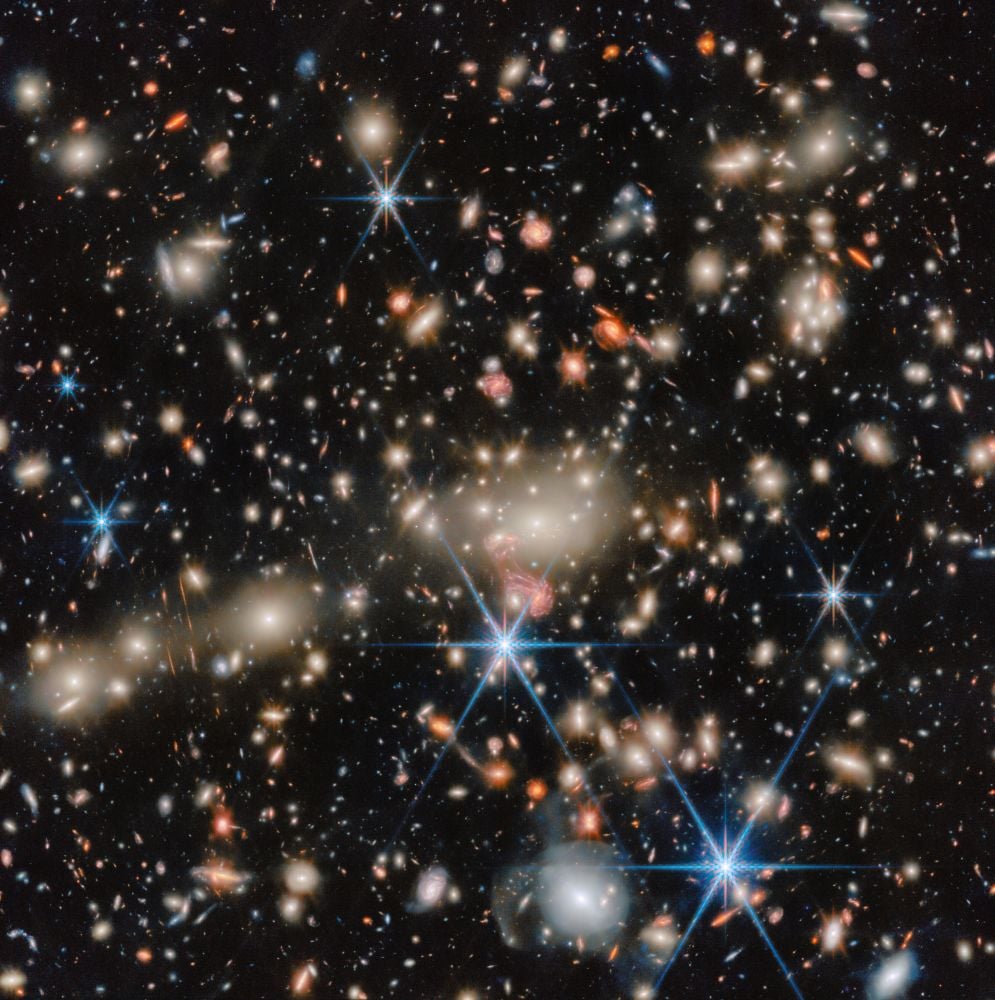

An Almost-Famous Galaxy Cluster Is The JWST's Picture Of The Month
January 23, 2026Gravitational lensing is a powerful tool that brings impossibly distant galaxies into reach. The JWST uses galaxy clusters and their overpowering to magnify background galaxies that are otherwise beyond our observational capabilities. One cluster, named MACS J1149.5+2223, is 5 billion light-years away and holds at least 300 galaxies, probably many more. It's been chosen as the JWST's Picture Of The Month.
 Universe Today
Universe Today