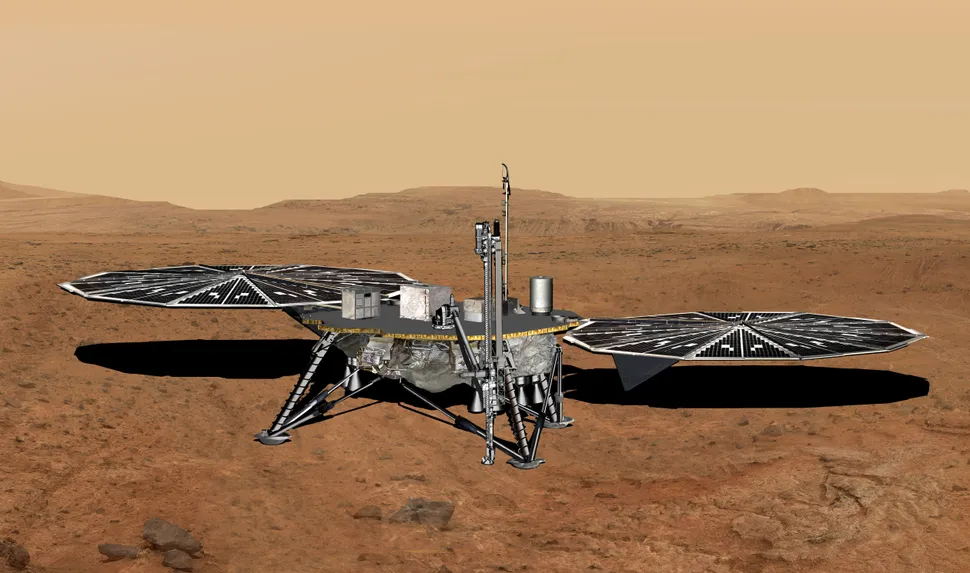
Searching for life on Mars has been an explicit goal of the astrobiological community for decades. However, they have not really had the resources to effectively do so, and they might be running out of time. Crewed missions to Mars are planned for as little as 15 years from now (though those timelines might be changing…again), and by the time that happens it may be too late to separate Martian life from unintentionally transplanted Earth-life. According to a group of researchers from the Agnostic Life Finding Association, there is one final chance to detect Martian life before it is irreversibly contaminated - the Mars Life Explorer (MLE). But to do its job properly, it’s going to need an upgrade.
Continue reading
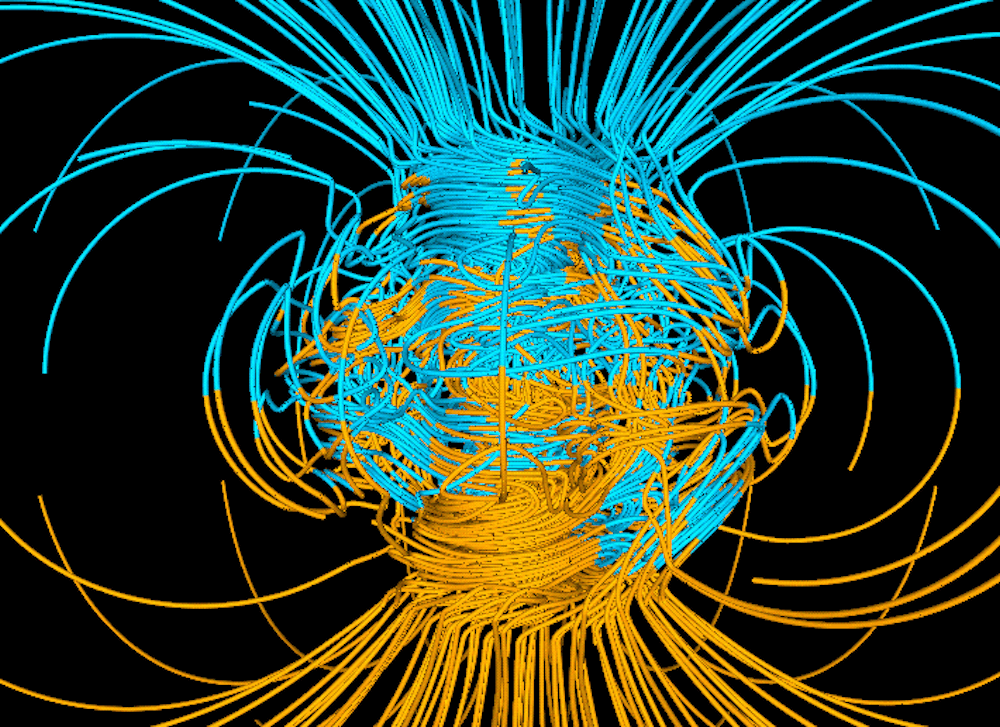
Scientists have finally solved a billion year old mystery that explains how life on Earth survived its earliest and most vulnerable stages. Using powerful computer simulations, researchers have proved that our planet's completely liquid core could generate the magnetic field that acts as an invisible shield against deadly cosmic radiation. This groundbreaking discovery reveals that Earth has been protecting life far longer than previously thought, creating a safe haven where the first complex molecules could form and evolve without being destroyed by high energy particles from space.
Continue reading
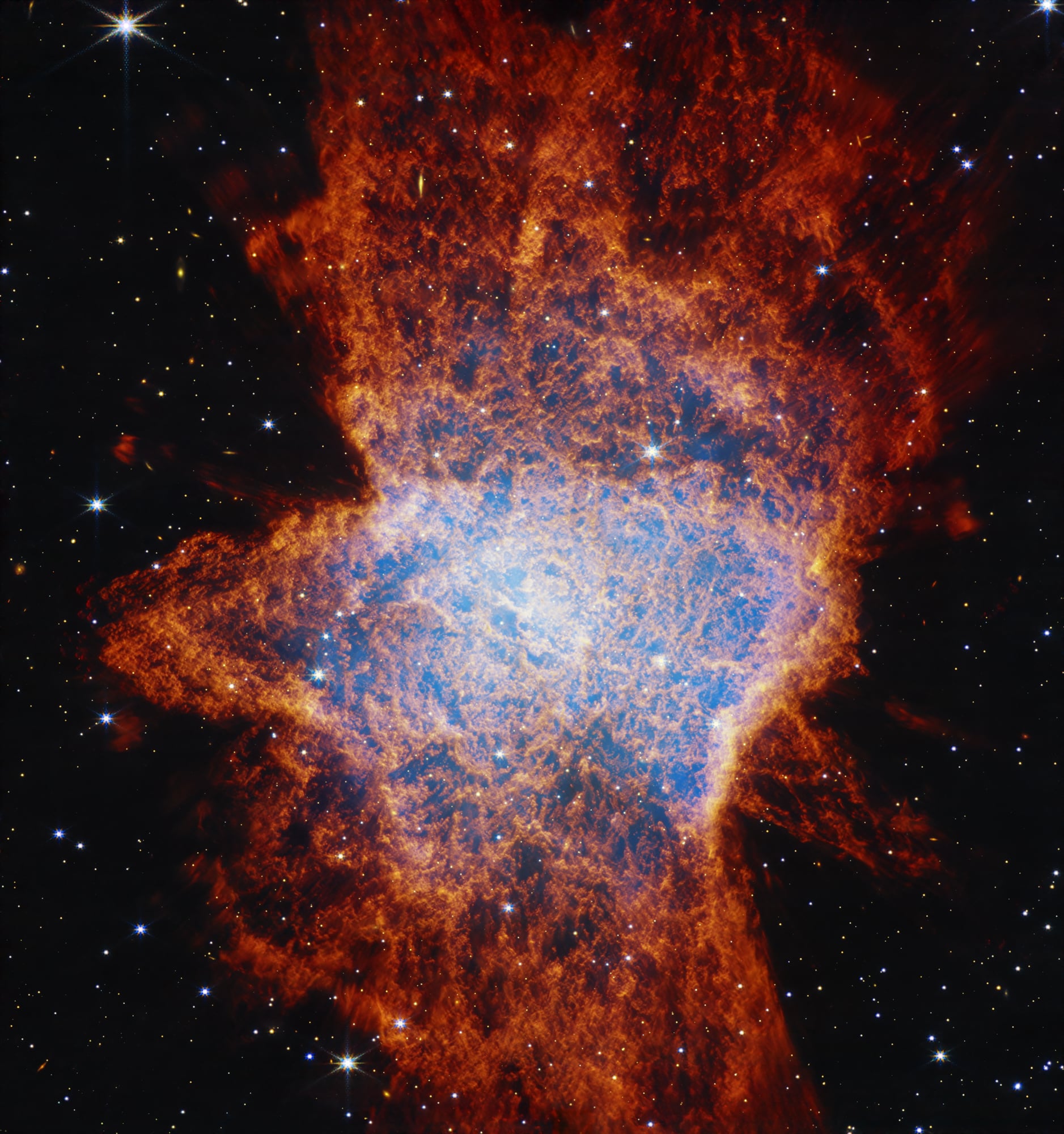

The James Webb Space Telescope’s latest look at a planetary nebula, NGC 6072, provides new insights into the lifecycle of stars. This could help astronomers predict what will happen to our Sun during its final days as well.
Continue reading
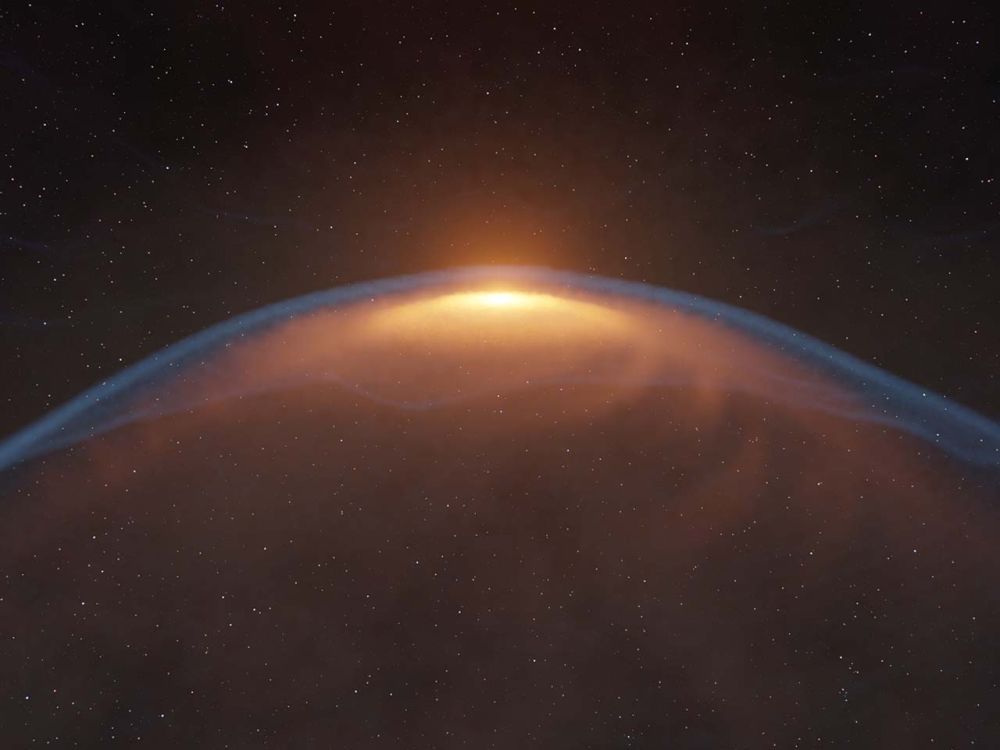

A jet from a young star created an expanding bubble that collided with the star's protoplanetary disk. Astronomers have found these explosive bubbles before, but never one that's collided with the disk. What does this mean for planet formation?
Continue reading
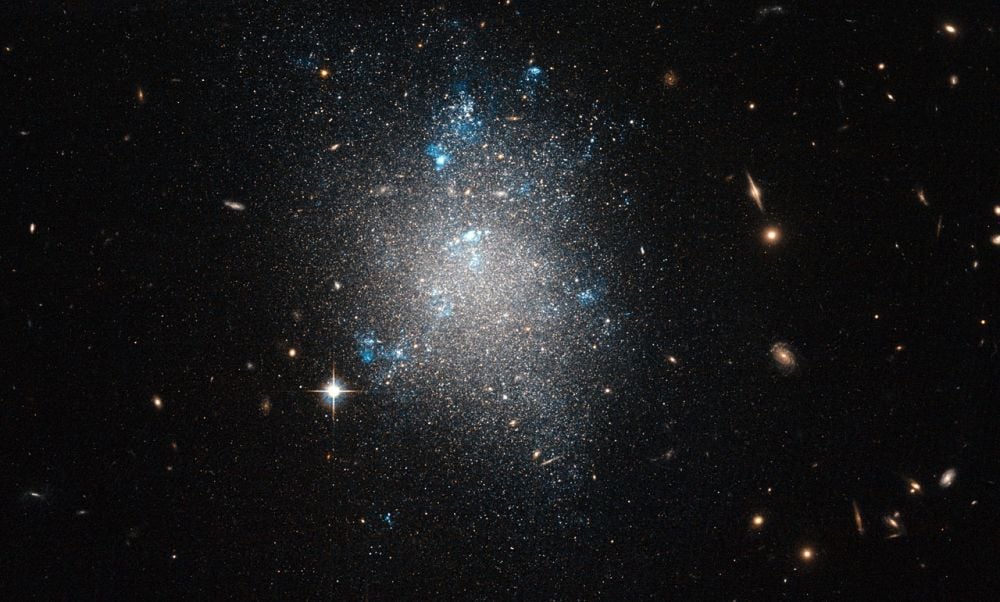

Massive galaxies like the Milky Way have smaller satellite galaxies that are tidally disrupted and absorbed. Astronomers think this is how galaxies assemble hierarchically. New research examines galaxies much less massive than the Milky Way to see if they also have their own, much less massive satellites.
Continue reading
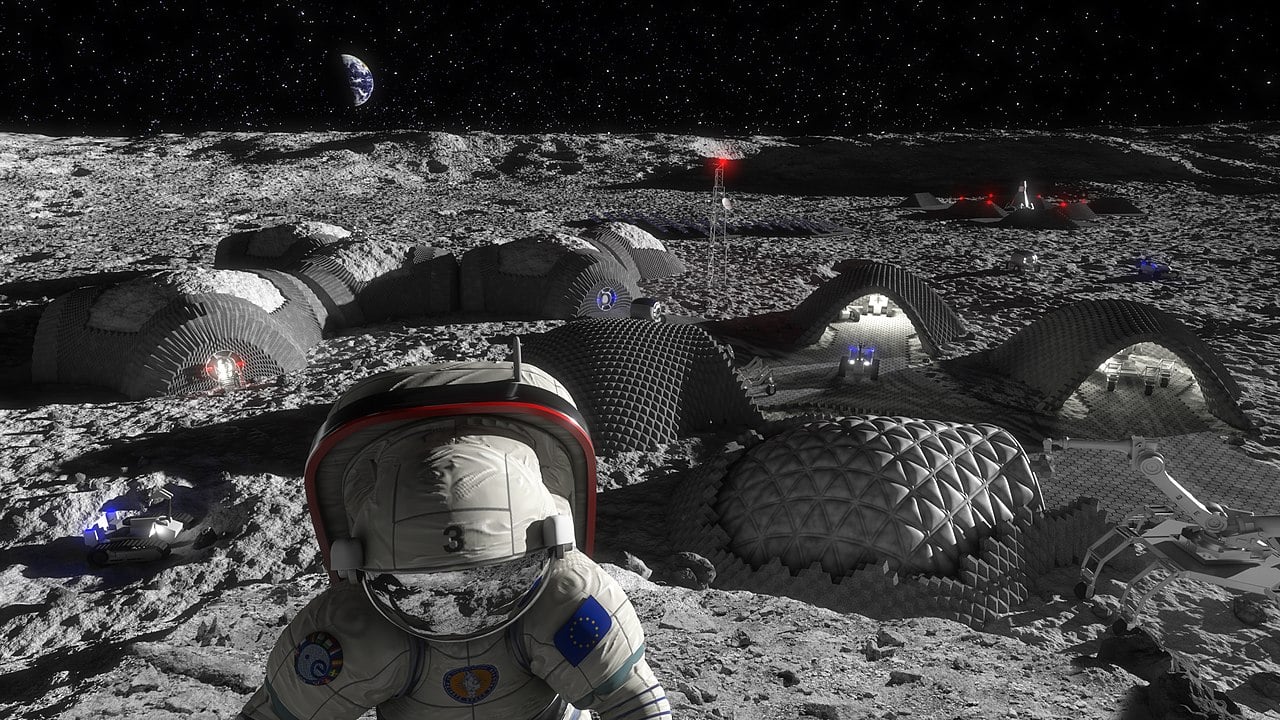
Imagine building an entire city on the Moon using nothing but sunlight and lunar soil! Chinese scientists have made this science fiction dream a reality by creating a revolutionary machine that acts like a solar powered 3D printer, melting lunar soil at temperatures exceeding 1,300°C to create strong construction bricks. This technology could transform space exploration by eliminating the need to transport heavy building materials from Earth, making lunar bases not only possible but affordable.
Continue reading
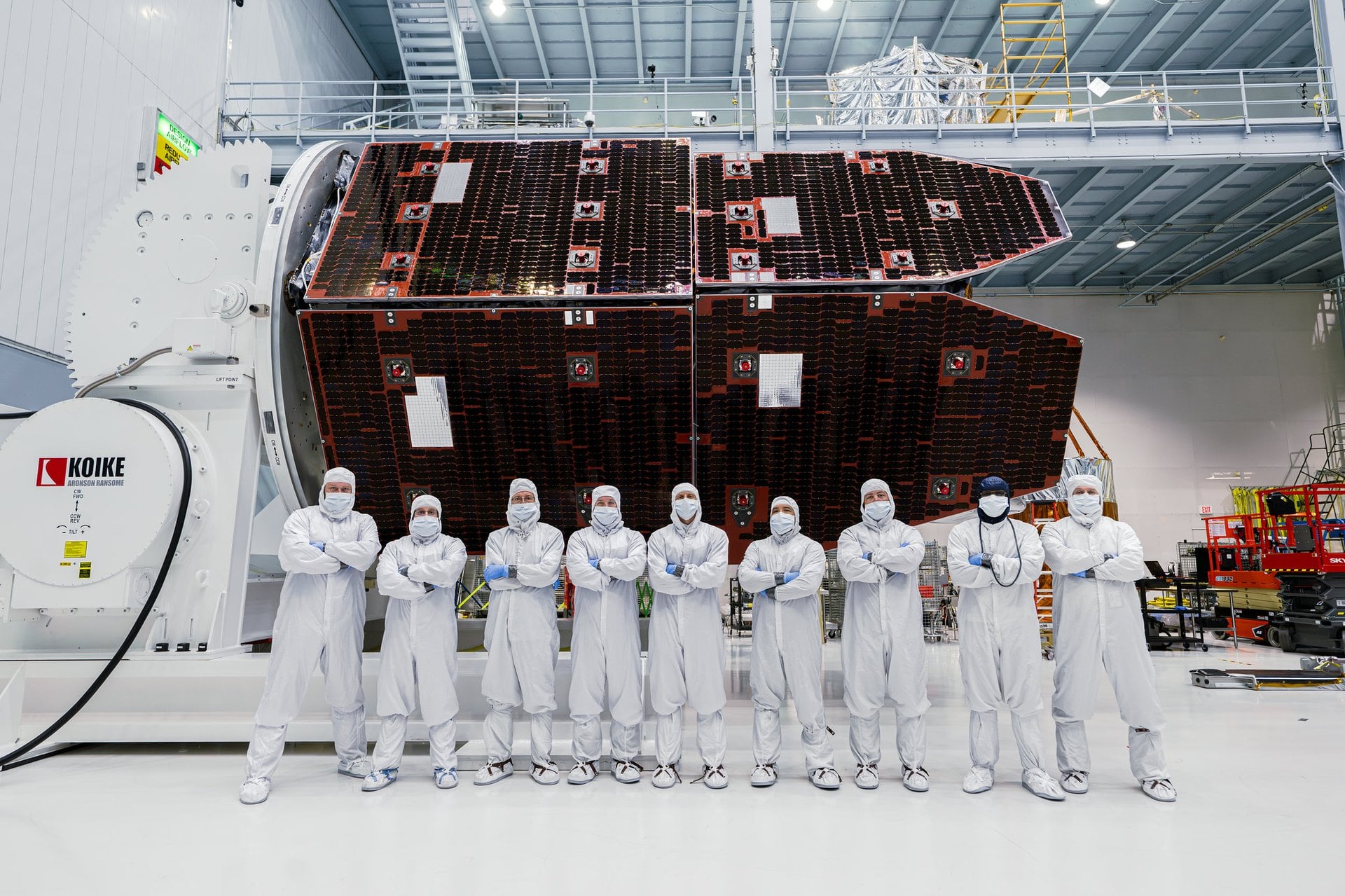

Technicians have successfully installed two sunshields onto NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope’s inner segment. Along with the observatory’s Solar Array Sun Shield and Deployable Aperture Cover, the panels (together called the Lower Instrument Sun Shade), will play a critical role in keeping Roman’s instruments cool and stable as the mission explores the infrared universe. […]
Continue reading
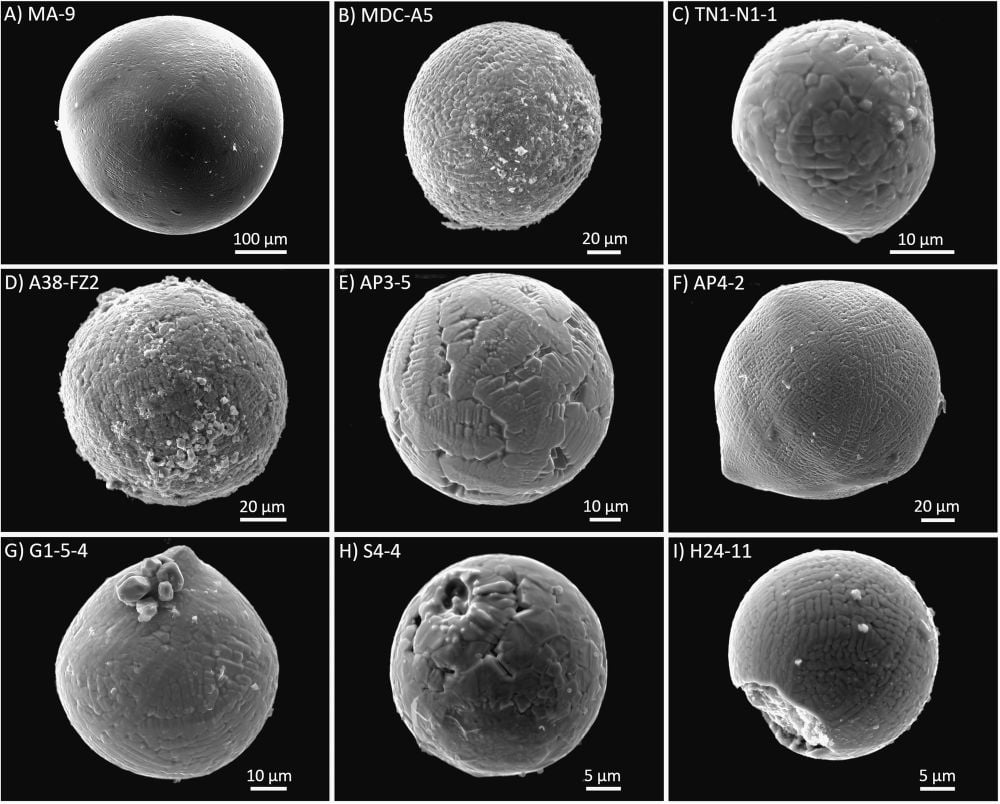
Earth has endured, and been shaped by, a constant rain of material from elsewhere in the Solar System. Some of the material was large, like the Chicxulub asteroid that ended the dinosaur's reign. But most of it is in the form of tiny micrometeorites. Those tiny rocks hold clues to Earth's ancient atmosphere.
Continue reading
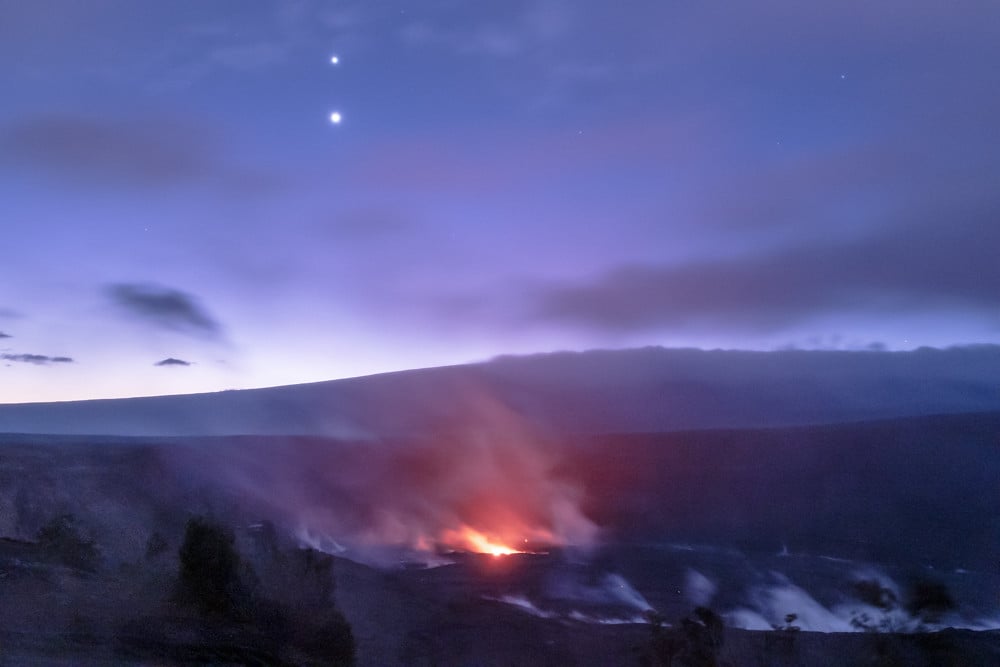

August sees all of the naked eye worlds excepting Mars hiding in the dawn. Set your alarm, and you can uncover Mercury through Saturn all in the dawn twilight sky, crowned with a fine close conjunction of Jupiter and Venus on Tuesday, August 12th. You can see the changing scene each morning starting this weekend, as the two get ever closer from one morning to the next.
Continue reading
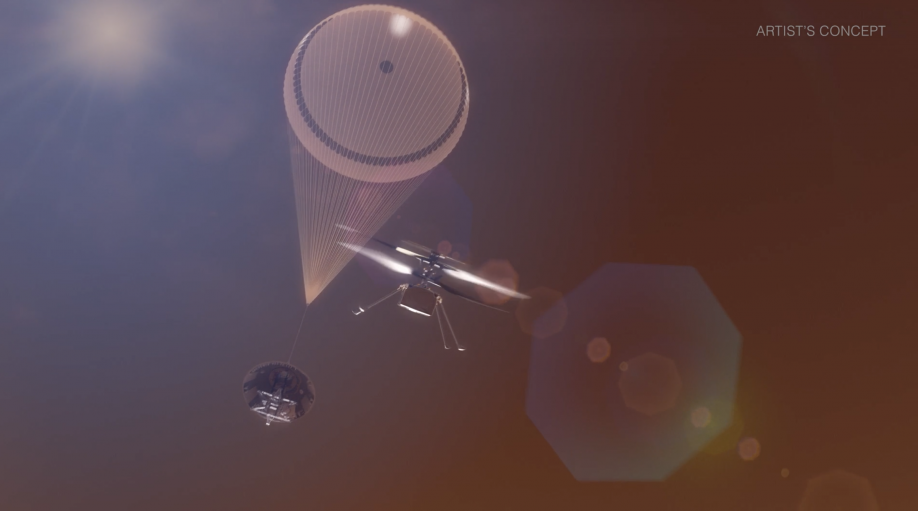
Ingenuity marked a number of milestones in space exploration. Arguably most importantly, it proved that powered flight was possible on another planet. However, it did have some limitations, such as being tied to the Perseverance rover and there only being one copy of the helicopter itself. AV Inc, one of the sub-contractors for Ingenuity, hopes to fix those problems with a proposed new mission called Skyfall that would involve six helicopters and no rover.
Continue reading
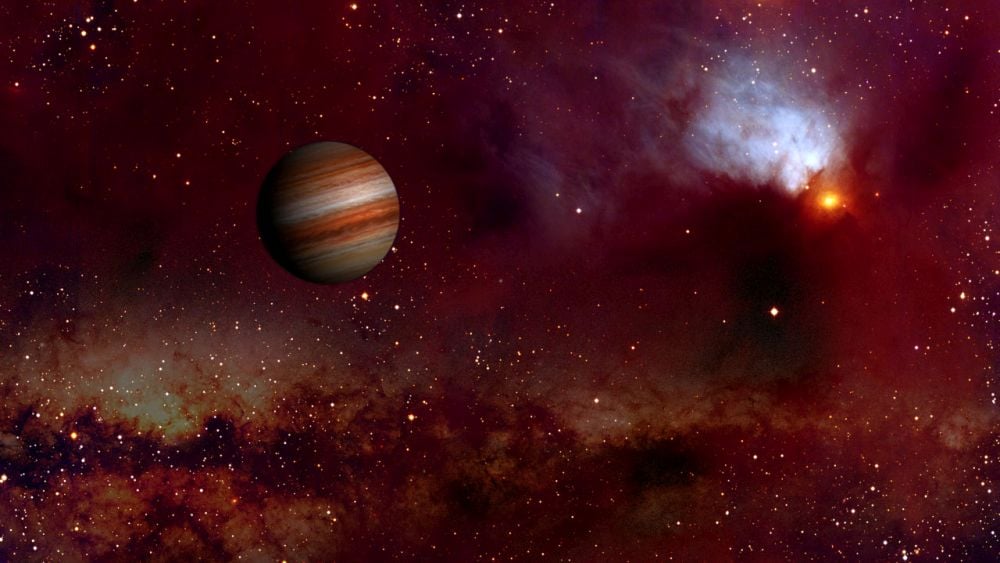

New research from the University of St Andrews has found that giant free floating planets have the potential to form their own miniature planetary systems without the need for a star.
Continue reading
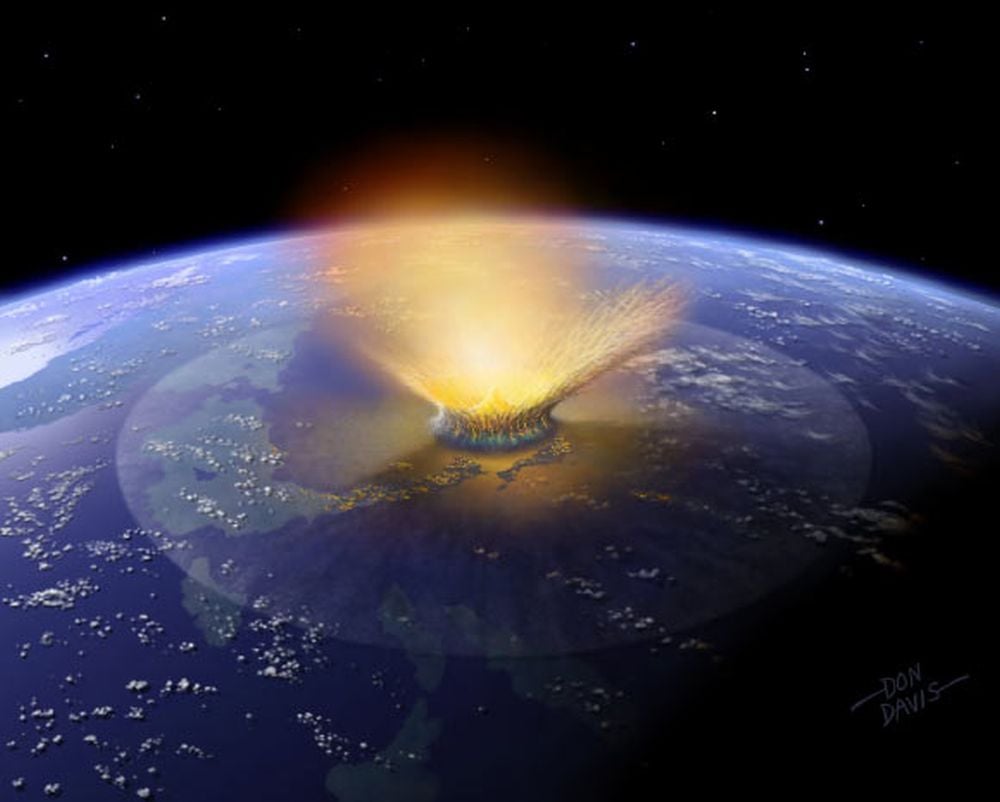

Earth's history was shaped by the bombardment of icy and rocky bodies. These impacts delivered volatiles and organic compounds to the planet. They also brought water, helping Earth become the life-supporting planets it is today. Could the same thing happen on exoplanets?
Continue reading
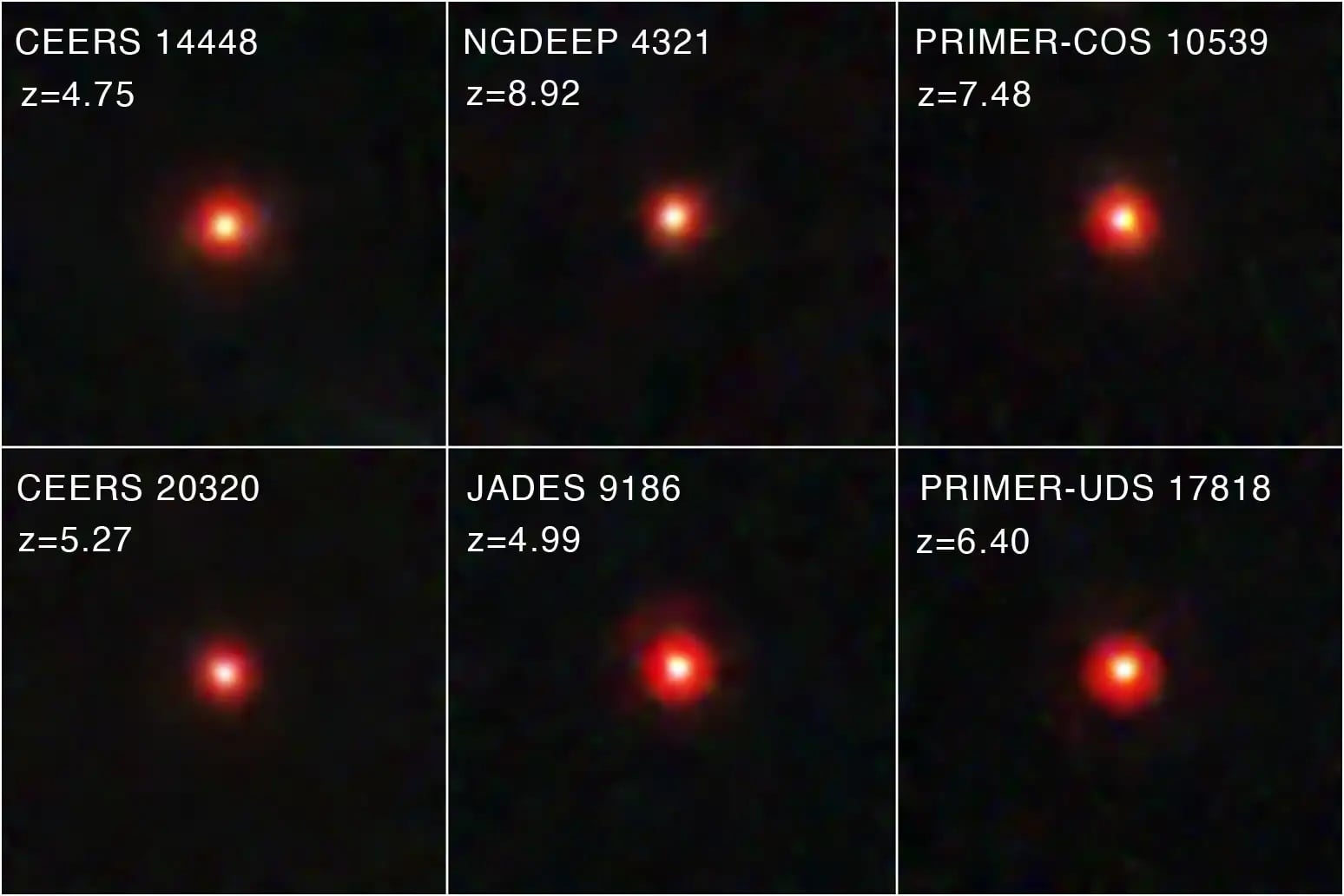

Little Red Dots are thought to be young supermassive black holes at the center of early galaxies. That would make them young versions of Active Galactic Nuclei. But Little Red Dots don't emit much x-ray light, and we're starting to learn why.
Continue reading
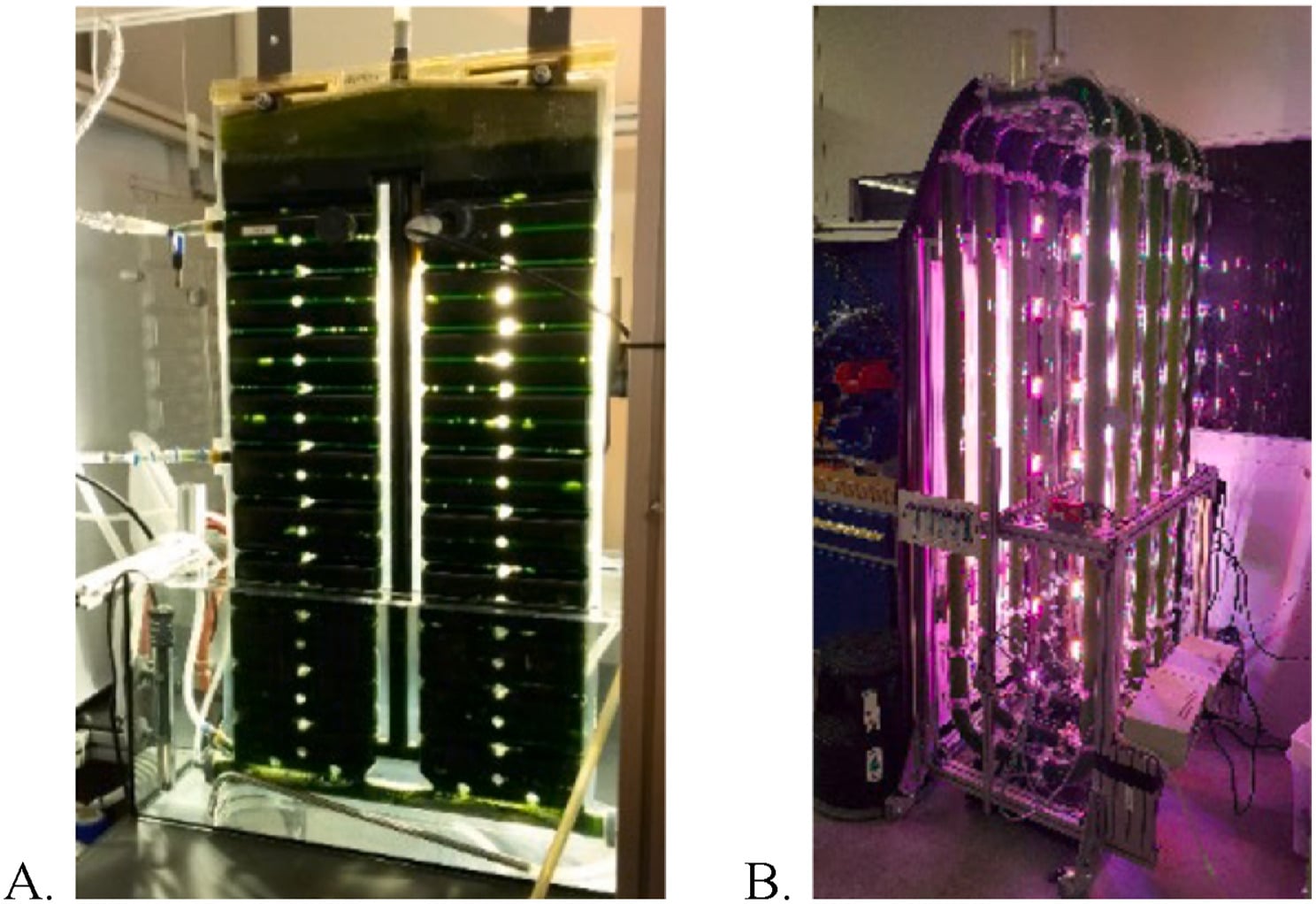
Astronauts exploring the Moon will need all the help they can get, and scientists have spent lots of time and plenty of money coming up with different systems to do so. Two of the critical needs of any long-term lunar mission are food and oxygen, both of which are expensive to ship to the Moon from Earth. So, a research team from the Technical University of Munich spent some of their time analyzing the effectiveness of using local lunar resources to build a photobioreactor (PBR), the results of which were recently published in a paper in Acta Astronautica.
Continue reading
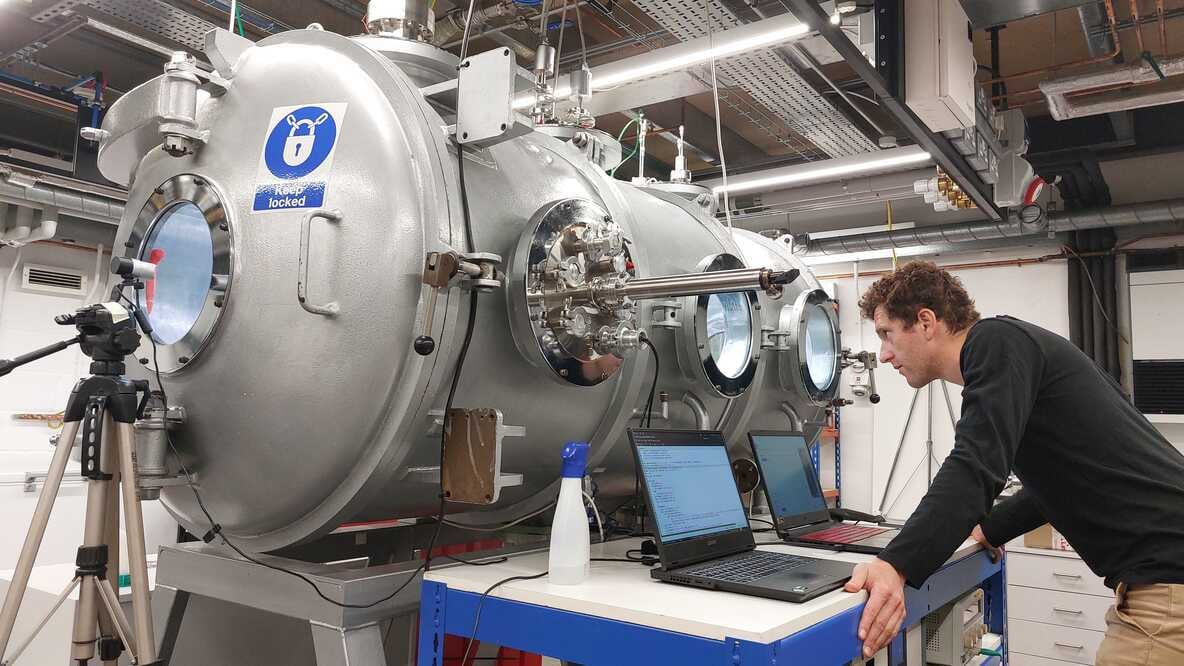

Many objects in the outer Solar System contain large amounts of water ice, leading to a thick icy shell surrounding an ocean of liquid water. This water behaves like lava on Earth, reshaping their surfaces through a process called cryovolcanism. To better understand this process, researchers have created a low-pressure chamber that simulates the near-vacuum conditions on the surfaces of worlds like Europa and Enceladus. They could watch water create features we see across the Solar System.
Continue reading
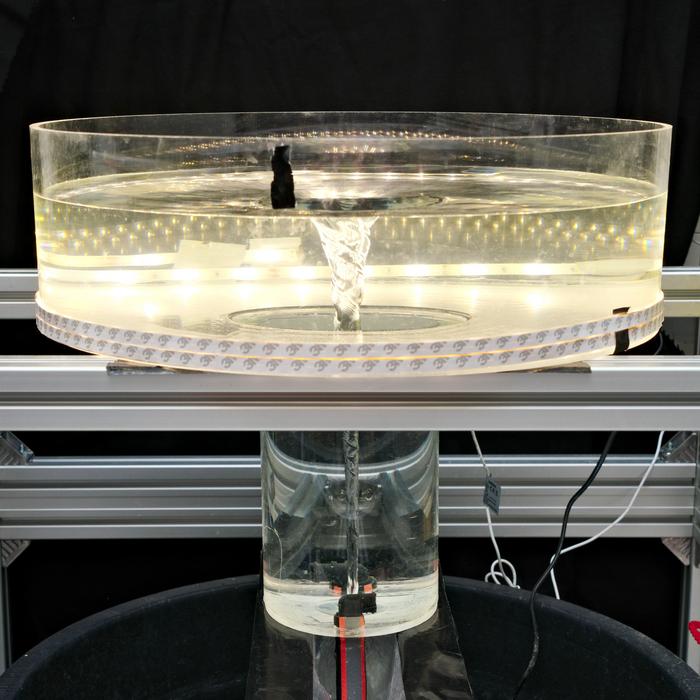

Sometimes the easiest way to understand the physics of a phenomenon is to make a physical model of it. But how do you make a model of a system as large as, say, a protoplanetary disc? One technique, suggested in a recent paper in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Letters by researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics and the University of Griefswald, would be familiar to any grade schooler who took a science class - spin water around in a circle really fast.
Continue reading
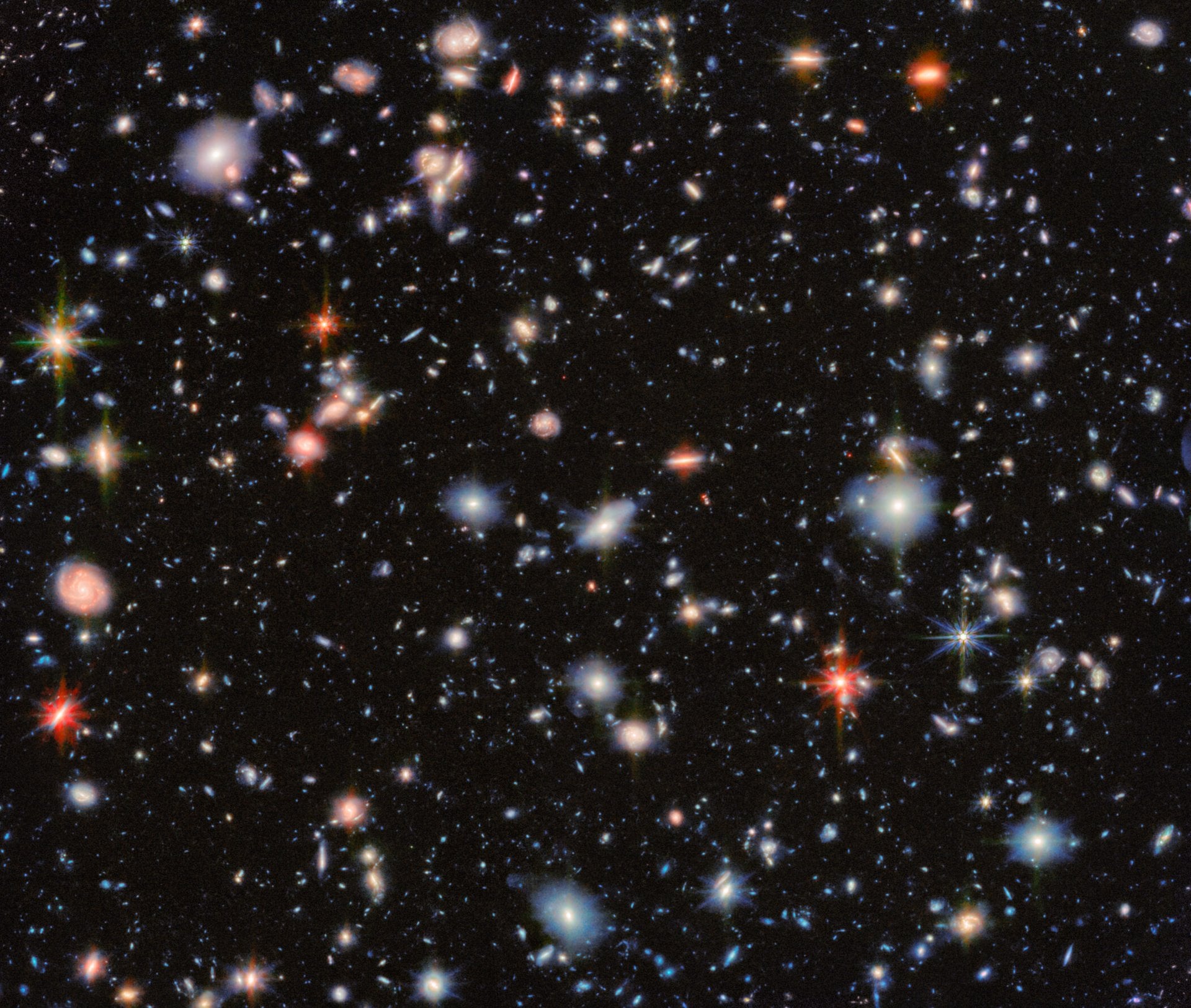

This image from the James Webb Space Telescope revisits one of the most iconic regions of the sky, the Hubble Ultra Deep Field. The result is a detailed view of thousands of distant galaxies, some dating back to the earliest periods of cosmic history.
Continue reading

If you have any doubts about the objectives of the program, just check out their logo: a stylized crescent moon with two footprints in the middle.
Continue reading

In the northern hemisphere, we're getting on to enjoying summer time which traditionally includes vacationing. Typically, vacations are a time to pause from work and remember life's possibilities beyond work. Now, perhaps you, the vacationer, want to rekindle a brief fling you had with science or maybe begin a new science tryst. Ersilia Vaudo's book "The Story of Astrophysics in Five Revolutions" could be just the impetus necessary for such a diversion.
Continue reading
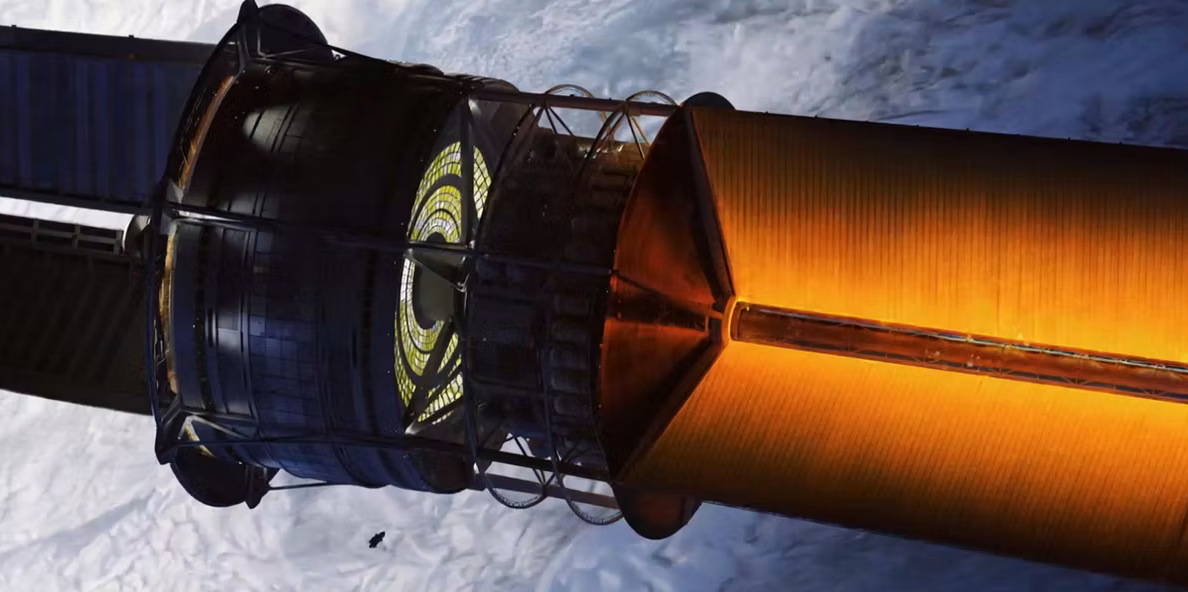

The UK-based not-for-profit company Initiative for Interstellar Studies (i4is) has announced the winners of the Project Hyperion Design Competition, a global challenge that called upon interdisciplinary teams to envision generation ships designed for a 250-year journey to Proxima b. The teams designed habitats of such a spacecraft that would allow a society to sustain itself and flourish in a highly resource-constrained environment.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today


















