The Universe's Most Common Water is a Hot Mess
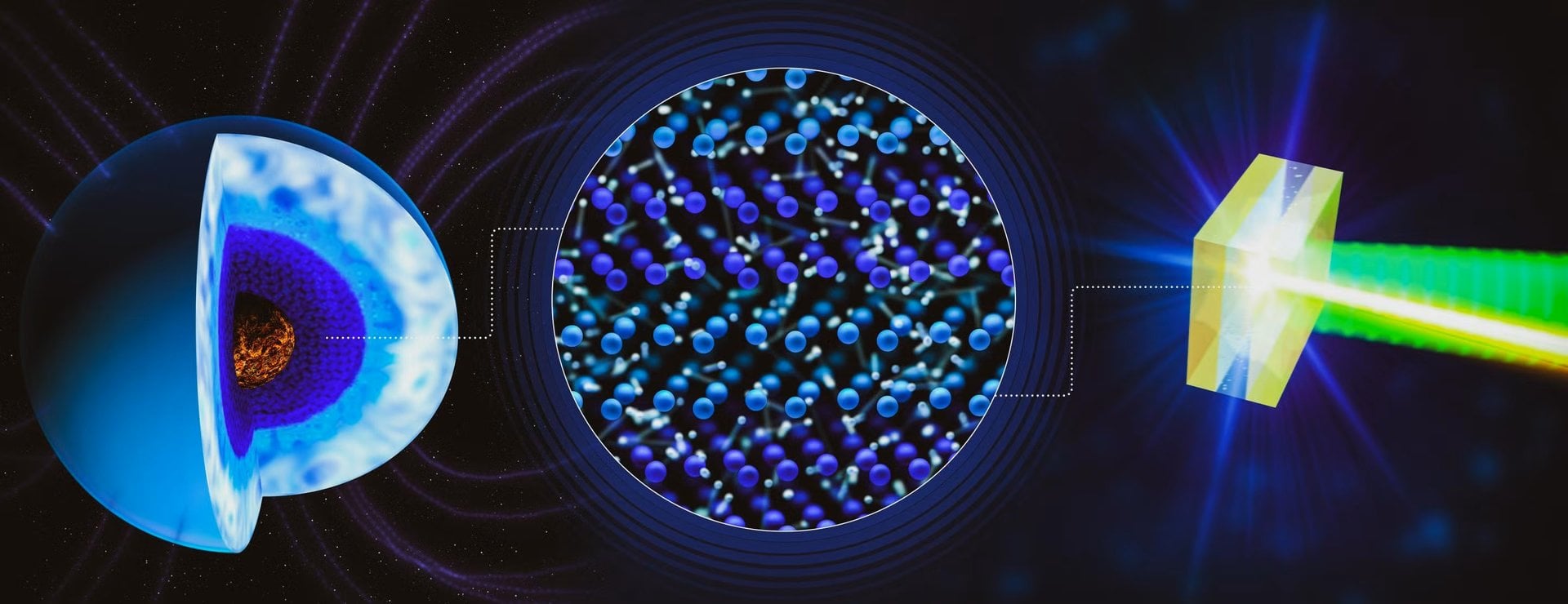
Inside the cores of ice giant planets, the pressure and temperature are so extreme that the water residing there transitions into a phase completely unfamiliar under the normal conditions of Earth. Known as “superionic water”, this form of water is a type of ice. However, unlike regular ice it’s actually hot, and also black. For decades, scientists thought that the superionic water in the core of Neptune and Uranus is responsible for the wild, unaligned magnetic fields that the Voyager 2 spacecraft saw when passing them. A series of experiments described in a paper published in Nature Communications by Leon Andriambariarijaona and his co-authors at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and the Sorbonne provides experimental evidence of why exactly the ice causes these weird magnetic fields - because it is far messier than anyone expected.
 Universe Today
Universe Today