
Black holes, regions of space where gravity is so intense that even light cannot escape, have captivated astronomers for decades. Some are the result of stellar death while others sit at the hearts of quasars, galaxies that shine so brightly they can be spotted from billions of light years away. Understanding how these supermassive black holes grow so massive, so quickly, has been one of the great puzzles of modern astrophysics, however, a new observation using cutting edge technology has just thrown a spanner in the works.
Continue reading
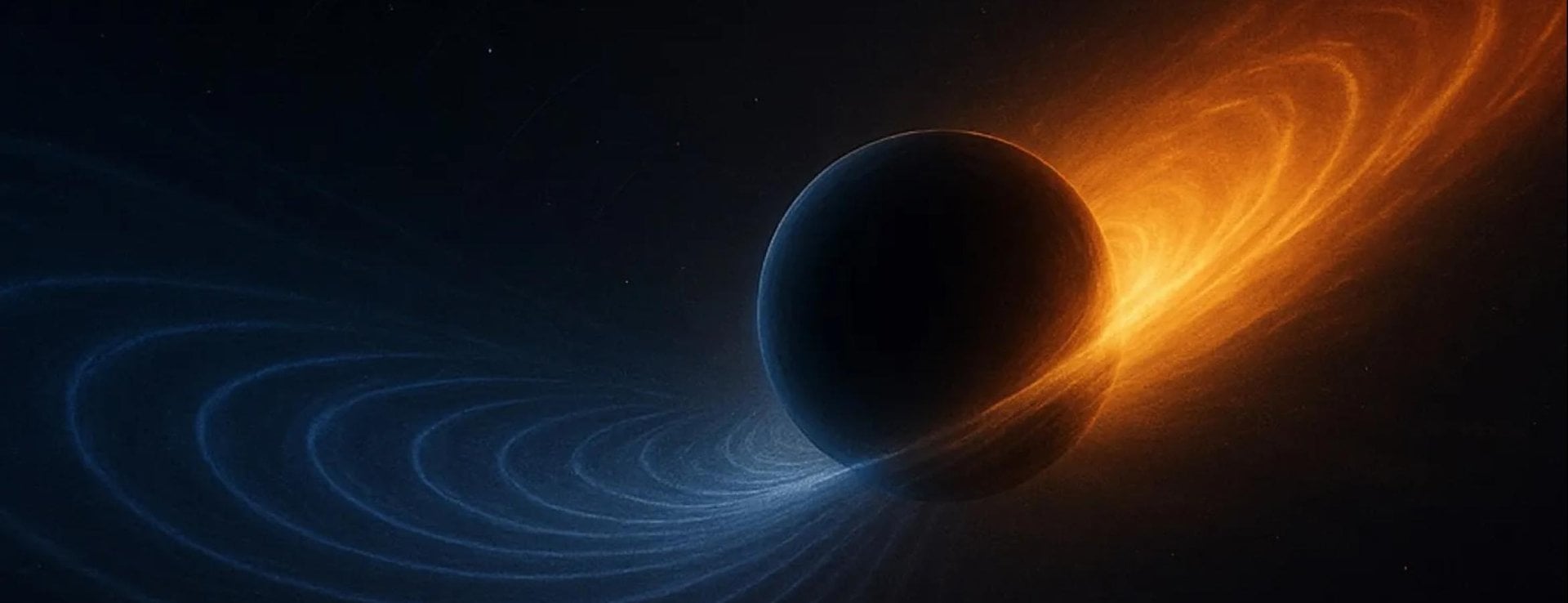

Black hole mergers are some of the most violent events in the universe. Just how violent is becoming more clear in part due to a new paper published in Nature Astronomy. For the first time, it tracks the “recoil” that the newly formed black hole gets from asymmetric gravitational waves that are released during the merger. Turns out they are strong enough to “kick” the new, supermassive combined black hole into motion at a speed of thousands of kilometers a second.
Continue reading

Venus has often been called Earth’s sister planet however there are stark differences between them. Among the similarities are a number of geological features and lava tubes are just one example. These natural tunnels form when the surface of a lava flow cools and solidifies while hot lava continues to flow beneath. They are common in Iceland and Hawaii and now, for the first time they have been found on Venus too.
Continue reading
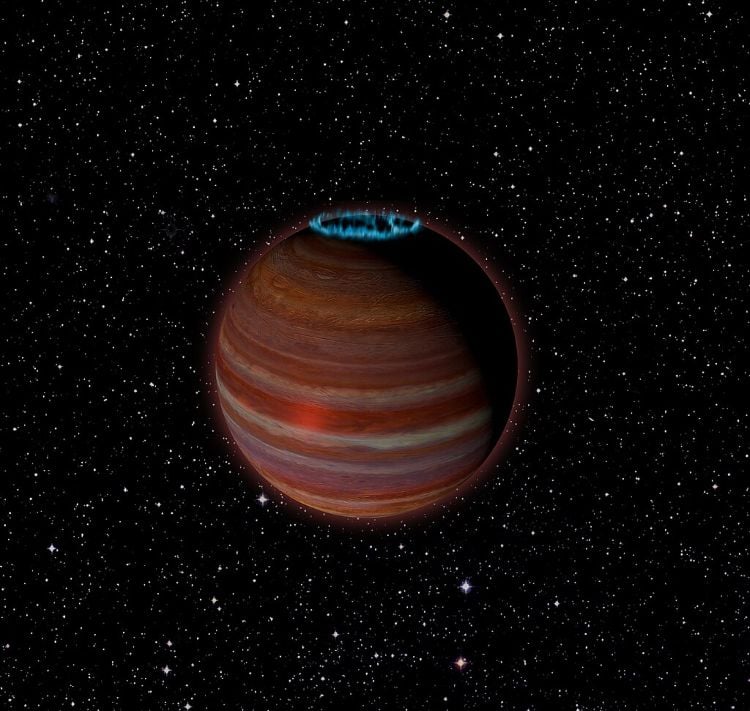

What can auroras on a rogue planet teach astronomers about planetary formation and evolution? This is what a recent study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated the atmospheric composition of a nearby rogue planet, including its atmospheric temperature and auroras. This study has the potential to help astronomers better understand rogue planets, along with additional planetary atmospheric formation and evolutionary traits.
Continue reading
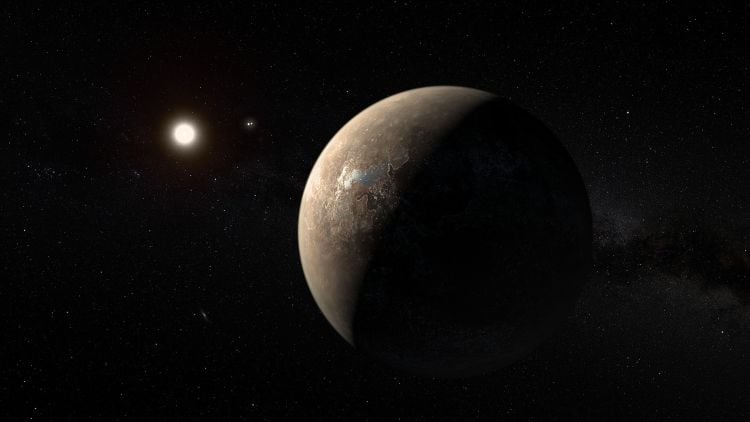

What new methods can be employed to help astronomers distinguish the light from an exoplanet and its host star so the former’s atmosphere can be better explored? This is what a recent study accepted to Astronomy & Astrophysics hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated how a novel and proposed telescopic instrument that could be capable of characterizing exoplanet atmospheres in new and exciting ways. This study has the potential to help scientists develop novel tools for examining exoplanets and whether they could possess life as we know it, or even as we don’t know it.
Continue reading
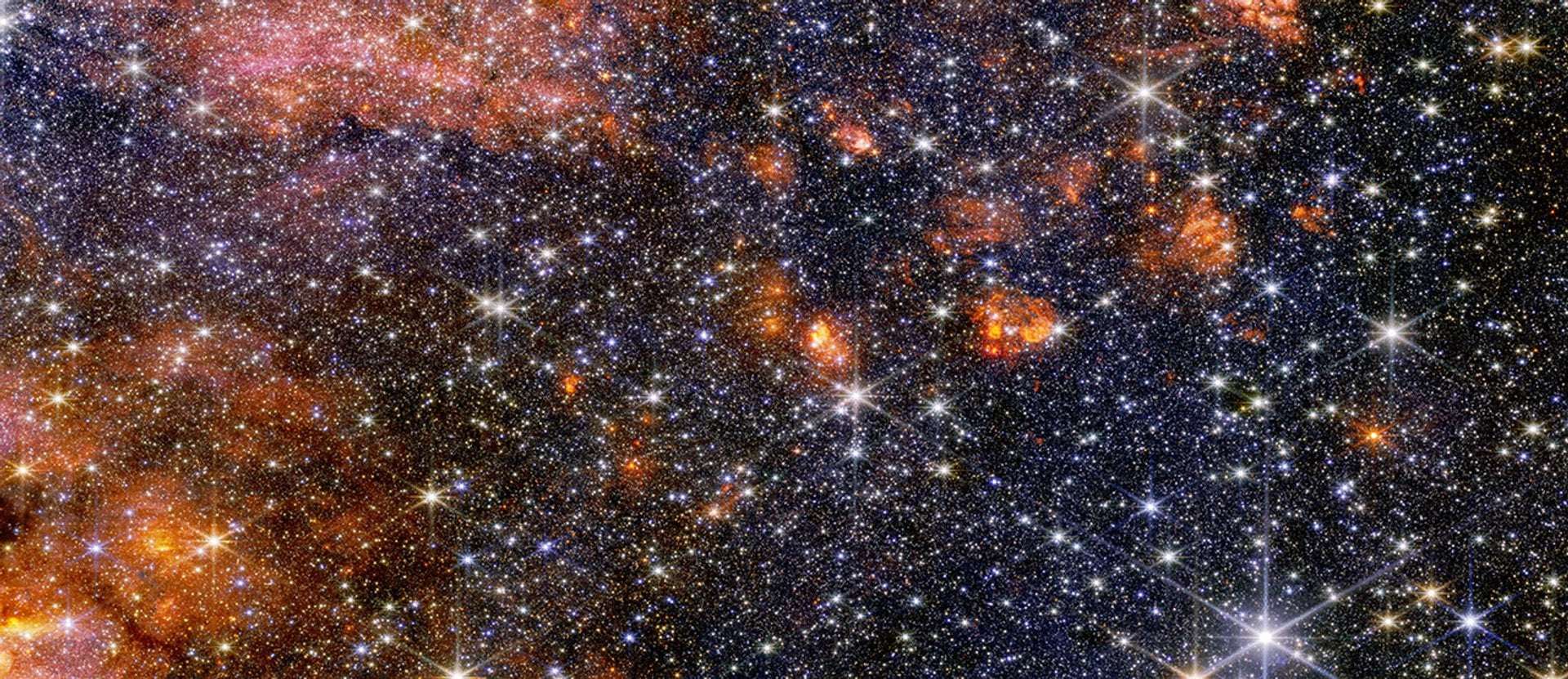

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has revealed a colorful array of massive stars and glowing cosmic dust in the Sagittarius B2 molecular cloud, the most massive and active star-forming region in our Milky Way galaxy.
Continue reading
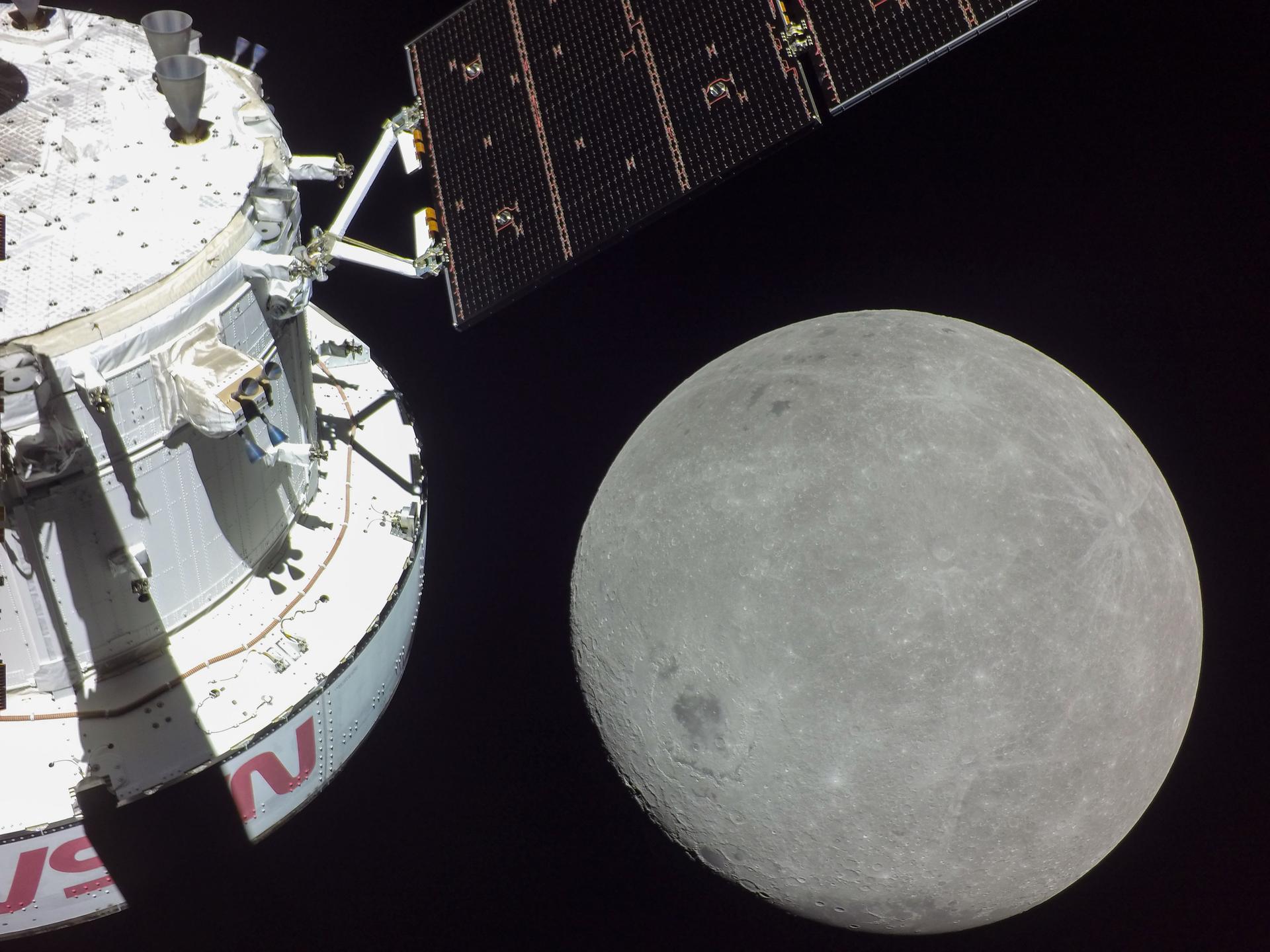
NASA announced that Artemis II, the first crewed mission to the Moon since the Apollo Era, will launch by February 2026. The crew has named their spacecraft "Integrity" to honor the efforts those working tirelessly to realize NASA's long-awaited return to the Moon.
Continue reading
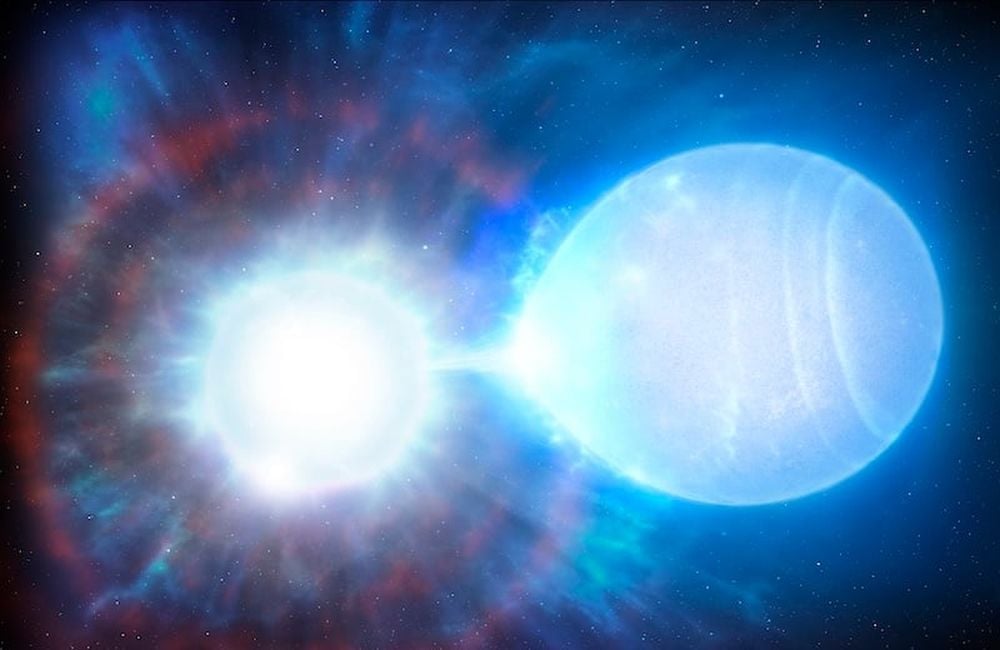

A new article published in The Astrophysical Journal explores a new theory of how Type Ia supernovae, the powerful stellar explosions that astronomers use to measure distances across the universe, might be triggered. Traditionally, these supernovae occur when a white dwarf star explodes after interacting with a companion star. But this explanation has limitations, leaving open questions about how these events line up with the consistent patterns astronomers actually observe.
Continue reading

A study of Saturn's atmospheric structure using data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has revealed complex and mysterious features unseen before on any planet in our Solar System. The results were presented last week by Professor Tom Stallard of Northumbria University, at the EPSC-DPS2025 Joint Meeting in Helsinki.
Continue reading
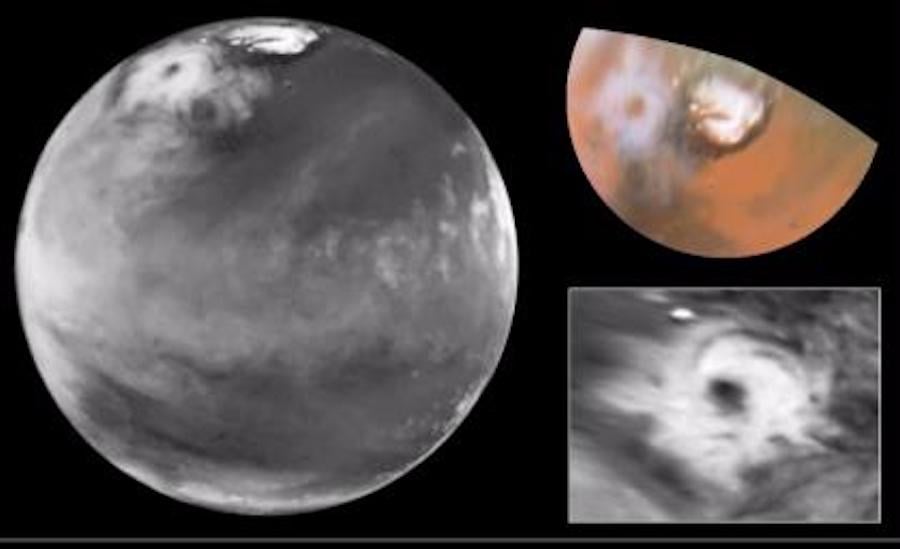
Mars holds a special place in my heart being the second planet I saw through a telescope. It’s probably fair to say that it’s held a special place for many as we continue to explore the fascinating world that is the red planet. Scientists studying Mars have recently uncovered a seasonal phenomenon that could change our understanding of the potential for it to support life. Their discovery, a swirling polar vortex that forms of the Martian north pole every winter.
Continue reading
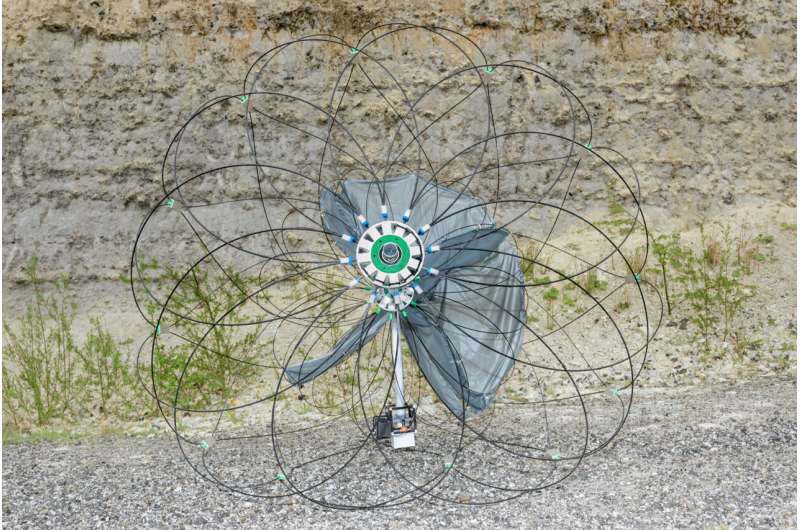

Tumbleweeds offer iconic visual depictions of desolate landscapes. Though typically associated with the American West, the most common type of tumbleweed actually originated in Europe, and is known scientifically as salsola targus, or more commonly as Russian thistle. So its only fitting that a team led by European scientists has some up with an idea based on the tumbleweed’s unique properties that could one day have groups of them exploring Mars.
Continue reading
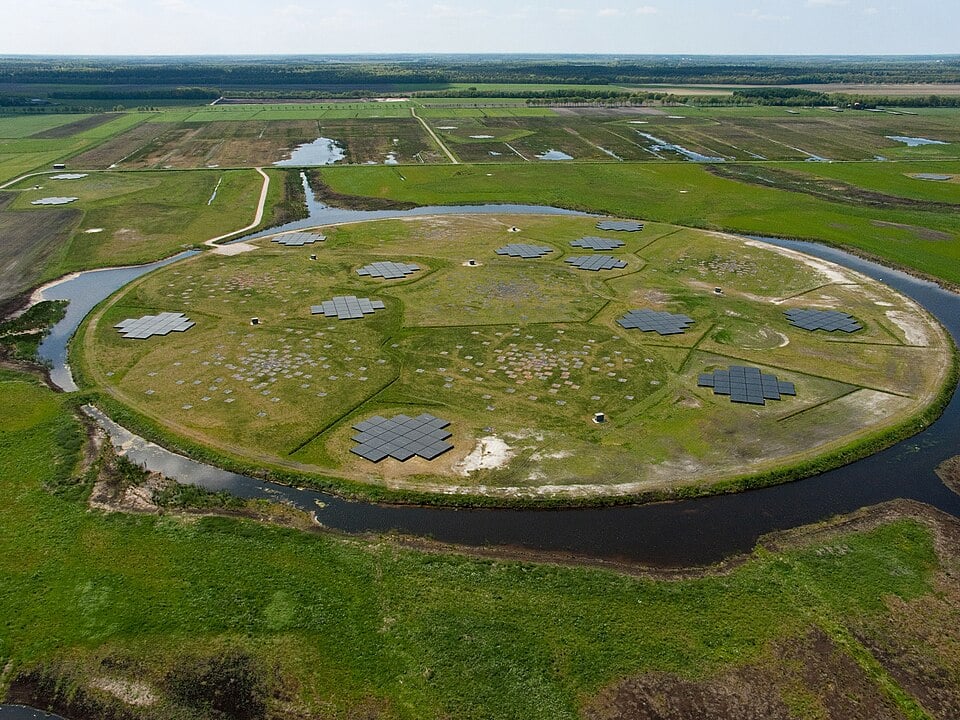

Visual observations have, over the years had to battle light pollution, weather, aircraft and even satellite constellations. Radio observations have until recently, been reasonably well protected however in their attempt to preserve the “quiet skies” a team of radio astronomers have secured a significant victory. For the first time, they've joined forces with the International Special Committee on Radio Interference, a committee that sets global standards for preventing electronic interference.
Continue reading
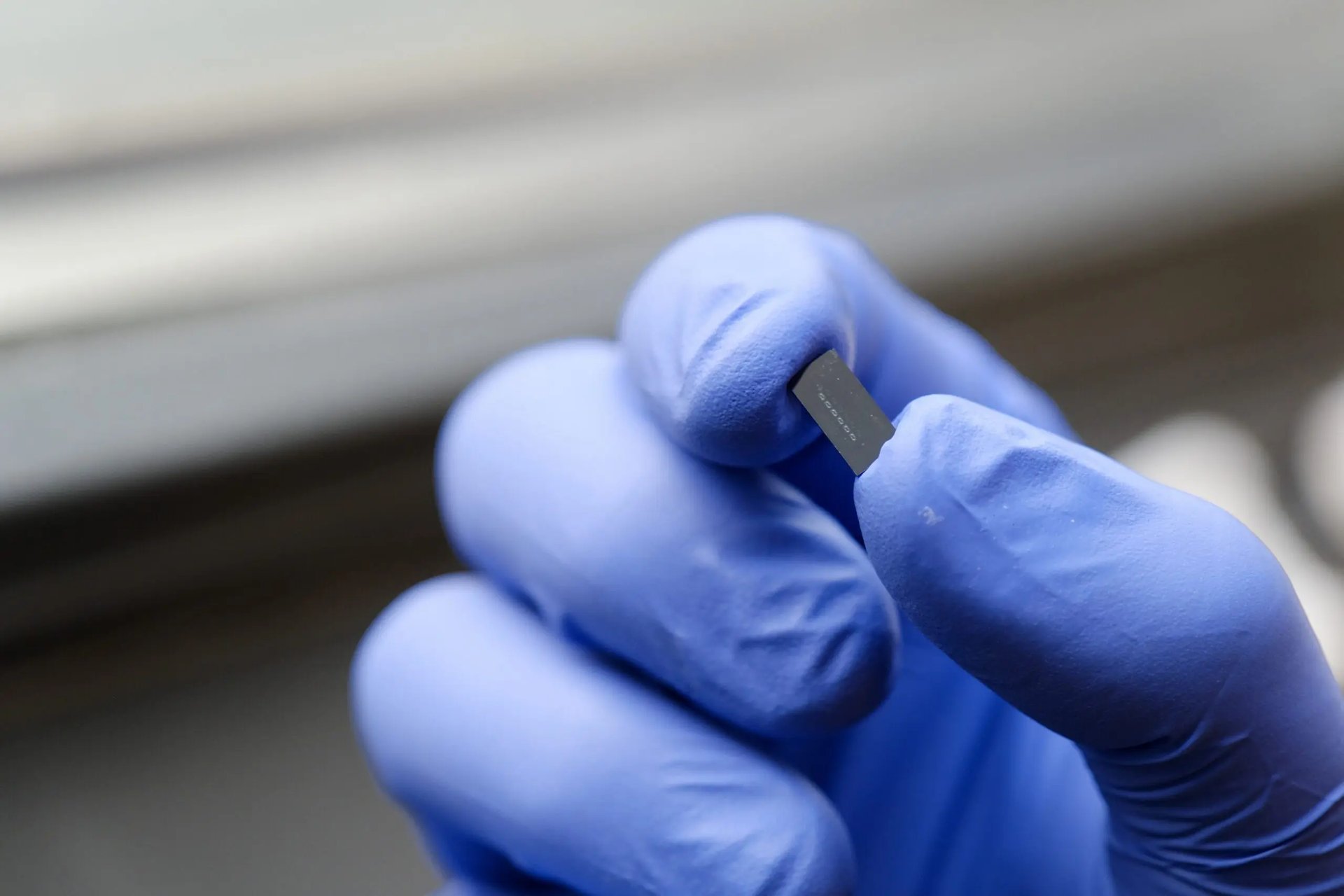

Are we alone in the universe? It’s a question that has plagued us since the ancient Greeks posed it for the first time in the 5th century and since then we have tried all manner of ways to reach out to our alien cousins….if they exist. We have fixed golden plaques to space probes, beamed messages out from radio telescopes and in 2012 even sent 10,000 ‘X’ (formerly twitter) messages out to three star systems with the hashtag #ChasingUFOs! A new tool has been developed, rather mundane compared to these other examples, which is no bigger than a soft drink can and could detect signs of life on alien worlds with unprecedented precision.
Continue reading
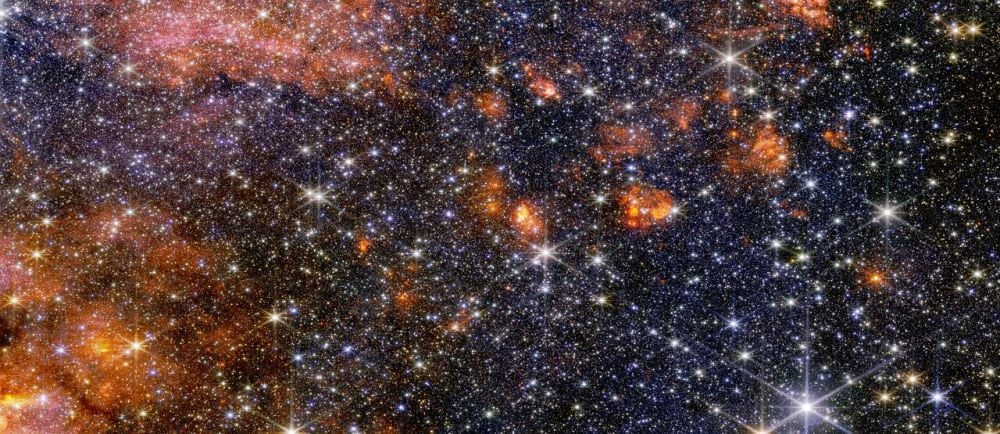

The JWST examined the most vigorous star-forming region in the entire galaxy. It's called Sagittarius B2, and while astronomers have studied it in detail, no other telescope reveals its details the way the JWST can.
Continue reading
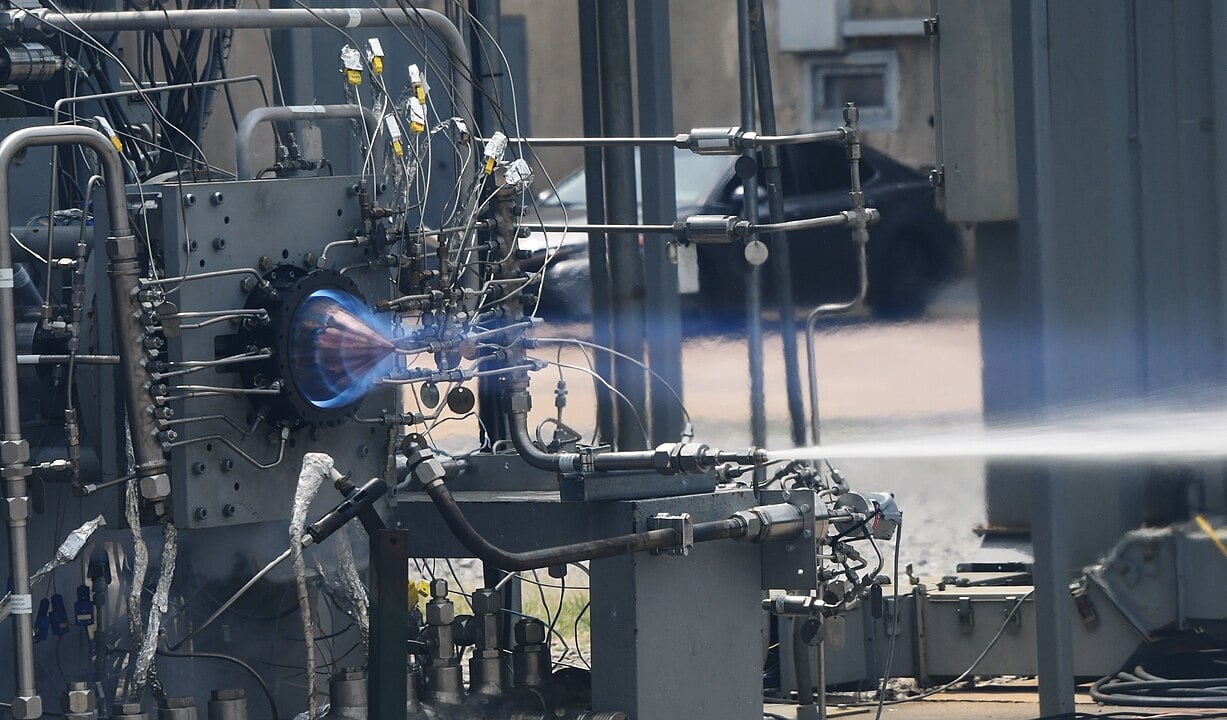

Imagine an engine with no moving parts that runs on continuous explosions. I’m actually sure I one saw a hilarious video of such a device some years ago but alas, am unable to find it and share. Still, the image of the poor occupants being constantly pressed into their seats and accelerated in a series of explosions is likely to be quite a long way from the reality of the new Rotation Detonation Engine. The team of researchers Lehigh University are behind the idea and have just received $2 million to solve the biggest challenge standing in its way, finding materials to build the thing out of that are tough enough to survive the punishment.
Continue reading
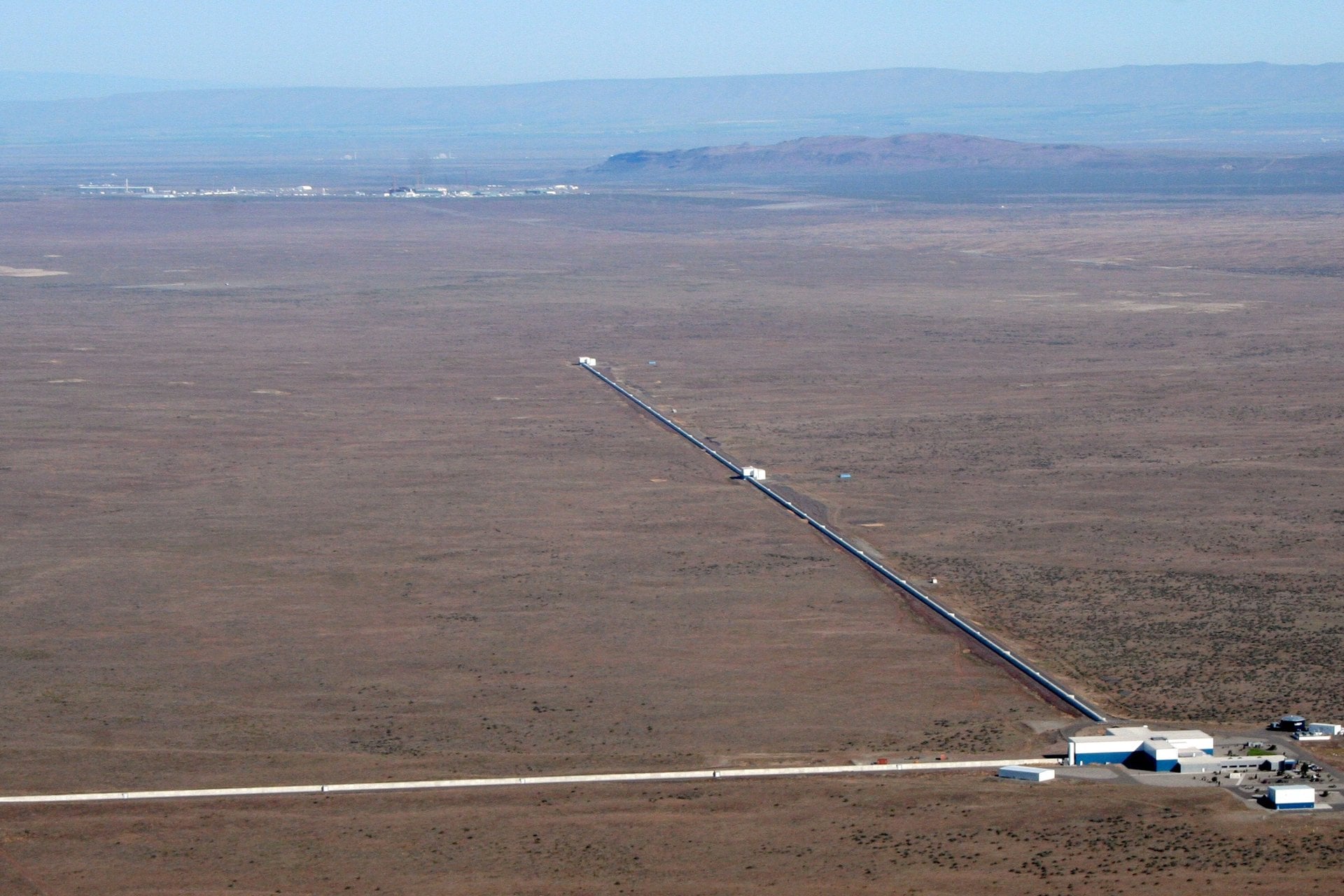

Interference from human activity has always been a sticking point in astronomical observations. Radio astronomy is notoriously sensitive to unintentional interference - hence why there are “radio silent” zones near telescopes where cell phones are banned. But gravitational wave astronomy is affected to an even worse degree than radio astronomy, according to a new paper by Reed Essick of the University of Toronto, and it’s not clear there’s much we can do about it.
Continue reading
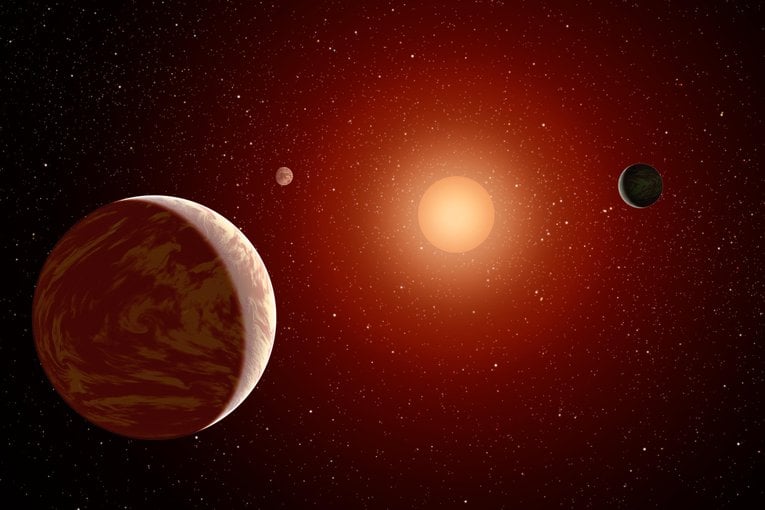
What can exoplanets orbiting M-dwarf stars teach scientists about planetary formation and evolution? This is what a recent study submitted to the American Astronomical Society journals hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated the possibility of exo-Titans, exoplanets with atmospheres comprised of nitrogen and methane like Saturn’s moon Titan, orbiting M-dwarf stars, which are smaller and cooler than our Sun. this study has the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of exoplanets orbiting M-dwarf stars and whether they could possess life as we know it.
Continue reading
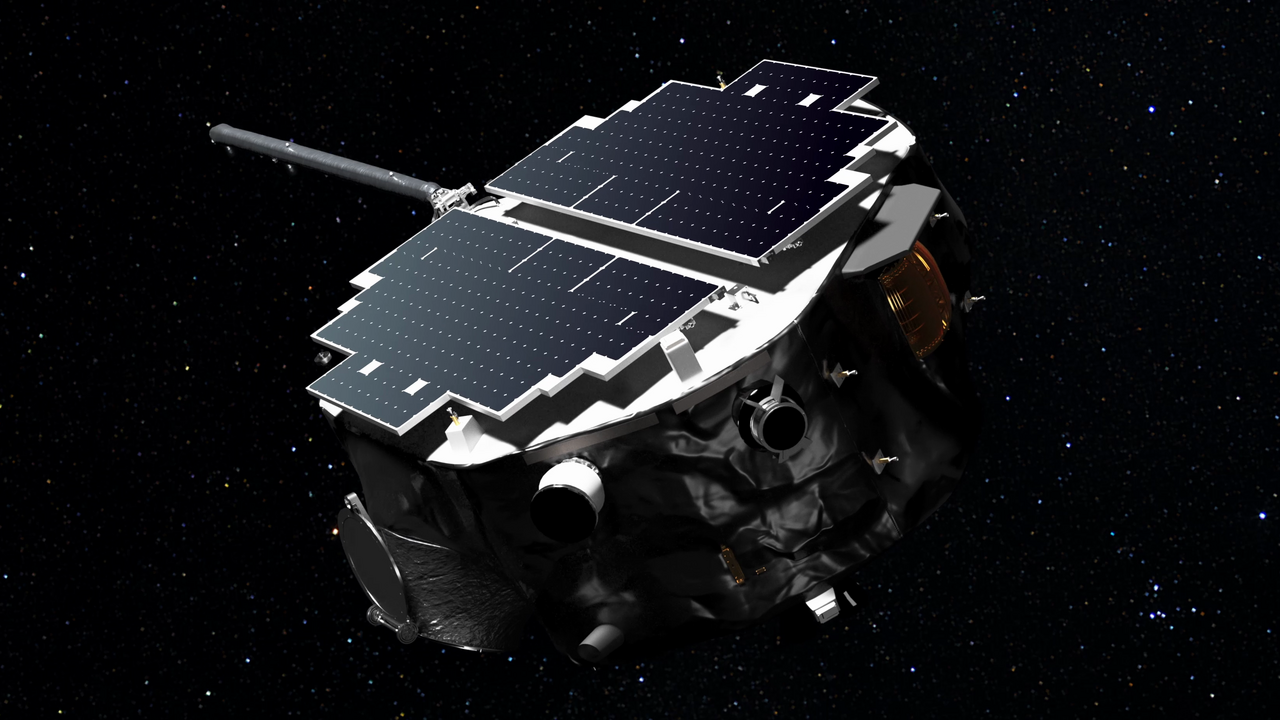

When astronauts head out into space they are protected from deadly radiation by their spacecraft and on space walks, their space suit. Back on Earth, we too are protected but by an invisible bubble that’s known as the heliosphere. The heliosphere has been subjected to numerous studies over the years but NASA’s newest mission is set to give us the most detailed of it map ever created.
Continue reading
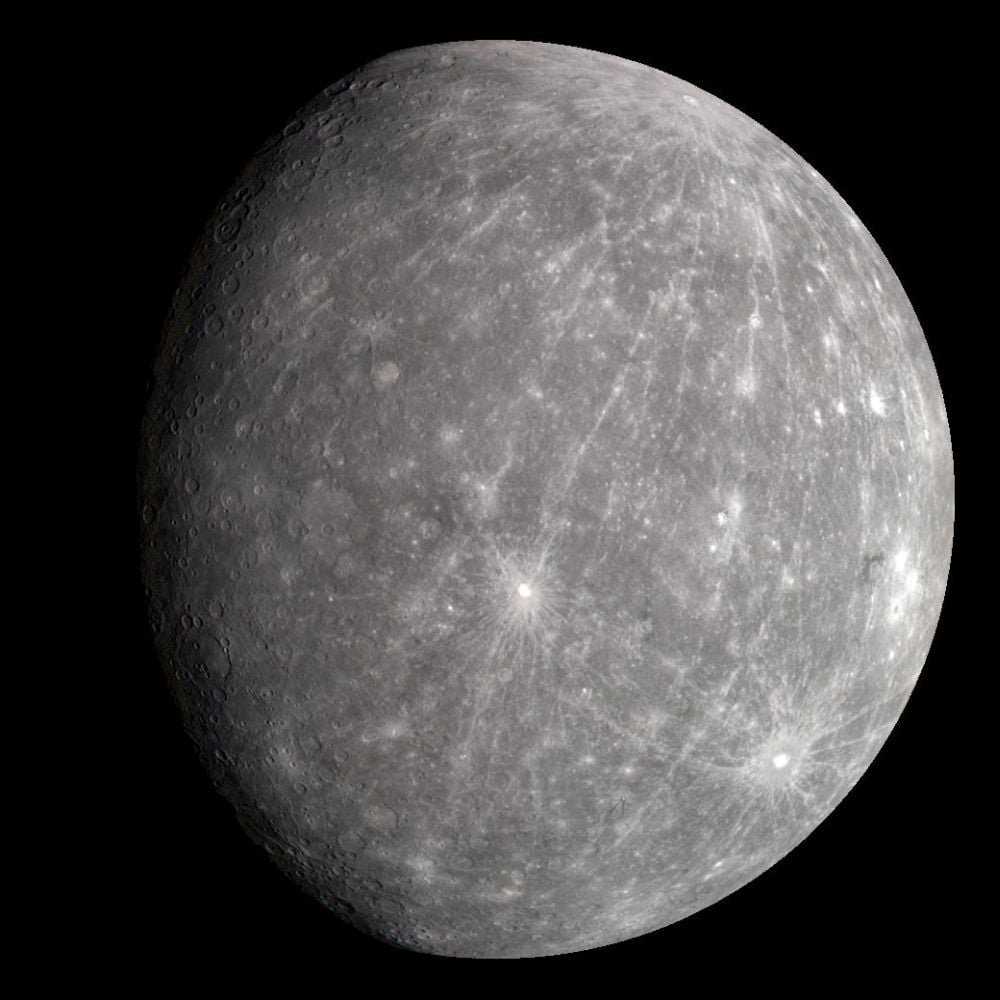

Mercury's large metallic core is 70% of its mass, which is way more than the other rocky planets. Scientists have wondered if a collision with a much larger body stripped away much of its mantle and crust, and Mercury is only the remnant core of a once much larger planet. New simulations show that's not quite what happened.
Continue reading
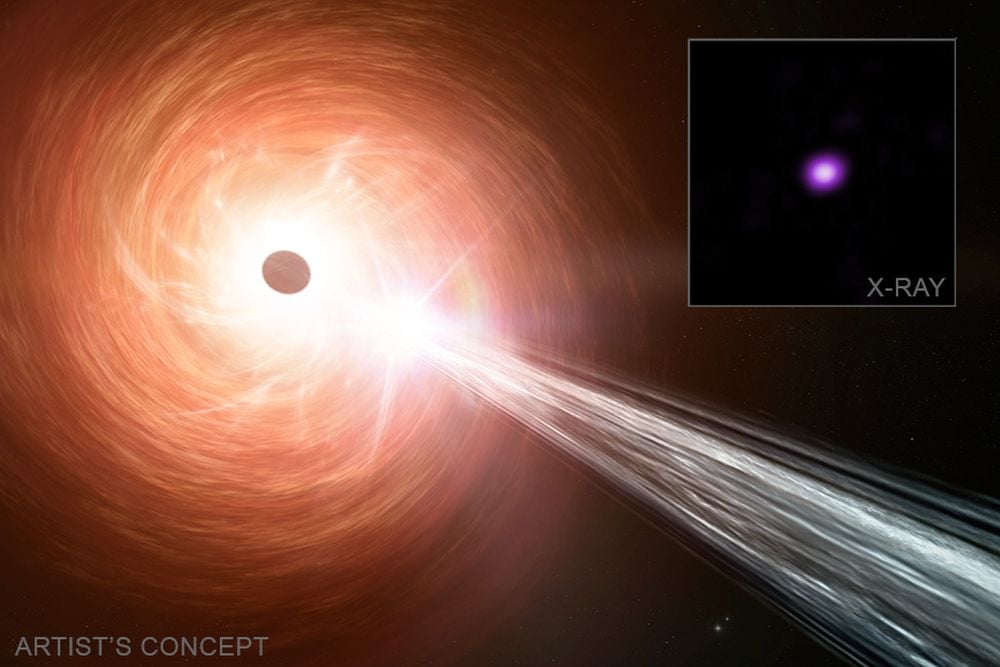

NASA's Chandra X-ray space telescope has found a black hole that's growing at an extremely rapid pace. The telescope is seeing the black hole, which has about one billion solar masses, when the Universe was less than one billion years old. Studying its rapid accretion could explain how some black holes become so massive so soon after the Big Bang.
Continue reading

Continue reading

What is the meaning of life? Even the best of us couldn’t hope to answer that question in a universe today article. But there are those who would try to “constrain” it, at least in terms of physics. A new paper from Pankaj Mehta of Boston University of Jané Kondev of Brandeis that was recently pre-published on arXiv looks at how the fundamental constants of physics might be applied to life as we know it - and even life as we don’t know it yet. Their idea doesn't necessarily give the answer to the ultimate question, but it does tie two seemingly disparate fields nicely together.
Continue reading

Exoplanets aren’t the only objects floating around other stars - they likely have comets and asteroids as well. Even some of the exoplanets themselves will have “exomoons”, at least according to our current understanding of the physics of planetary formation. However, we have yet to find any of these other objects conclusively, though there has been some hint at the presence of exomoons in the last ten years. A new paper from astronomers at the European Southern Observatory (ESO), recently pre-published on arXiv, suggests a way in which we might be able to finally detect the presence of an exomoon - using a technique that is also commonly used to find exoplanets themselves.
Continue reading
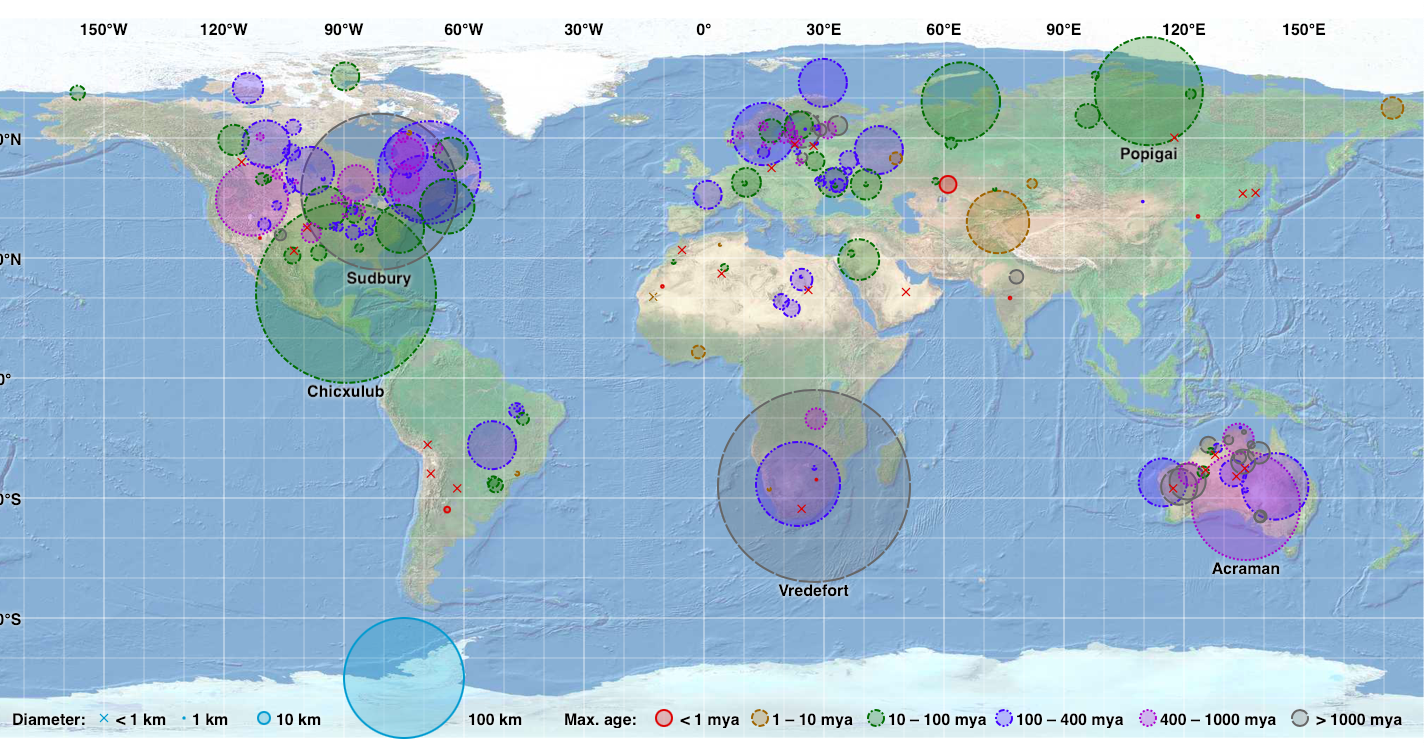
A team of scientists in south Australia have discovered tiny pieces of glass that tell the story of a catastrophic event that happened 11 million years ago, an asteroid impact so massive it should have left a crater the size of a major city, yet mysteriously, no one has found it. This discovery represents only the sixth known tektite field ever identified on Earth. The glassy fragments, scattered across the landscape are forcing scientists to reconsider what they know about ancient asteroid impacts and the geological features they leave behind.
Continue reading
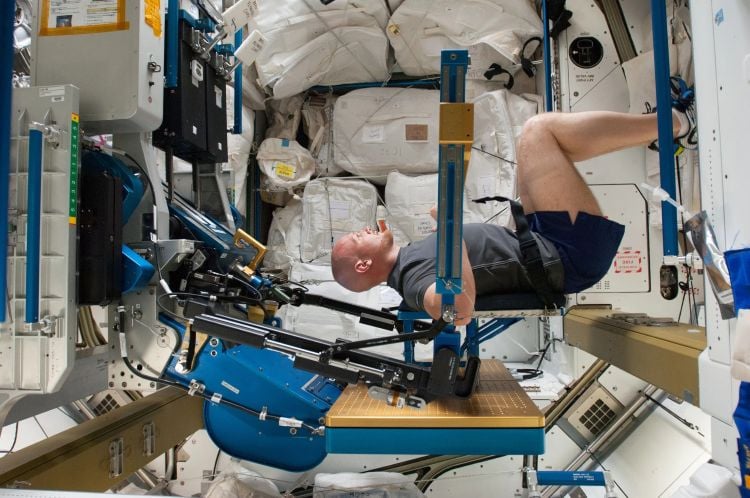

How does spaceflight influence sarcopenia, which is a common age-related muscle decline, specifically for elder adults? This is what a recent study published in Stem Cell Reports hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated how microgravity influences muscle cell function. This study has the potential to help scientists, mission planners, astronauts, and the public better understand the long-term health impacts of microgravity on muscle decline and the steps that can be taken to mitigate it.
Continue reading
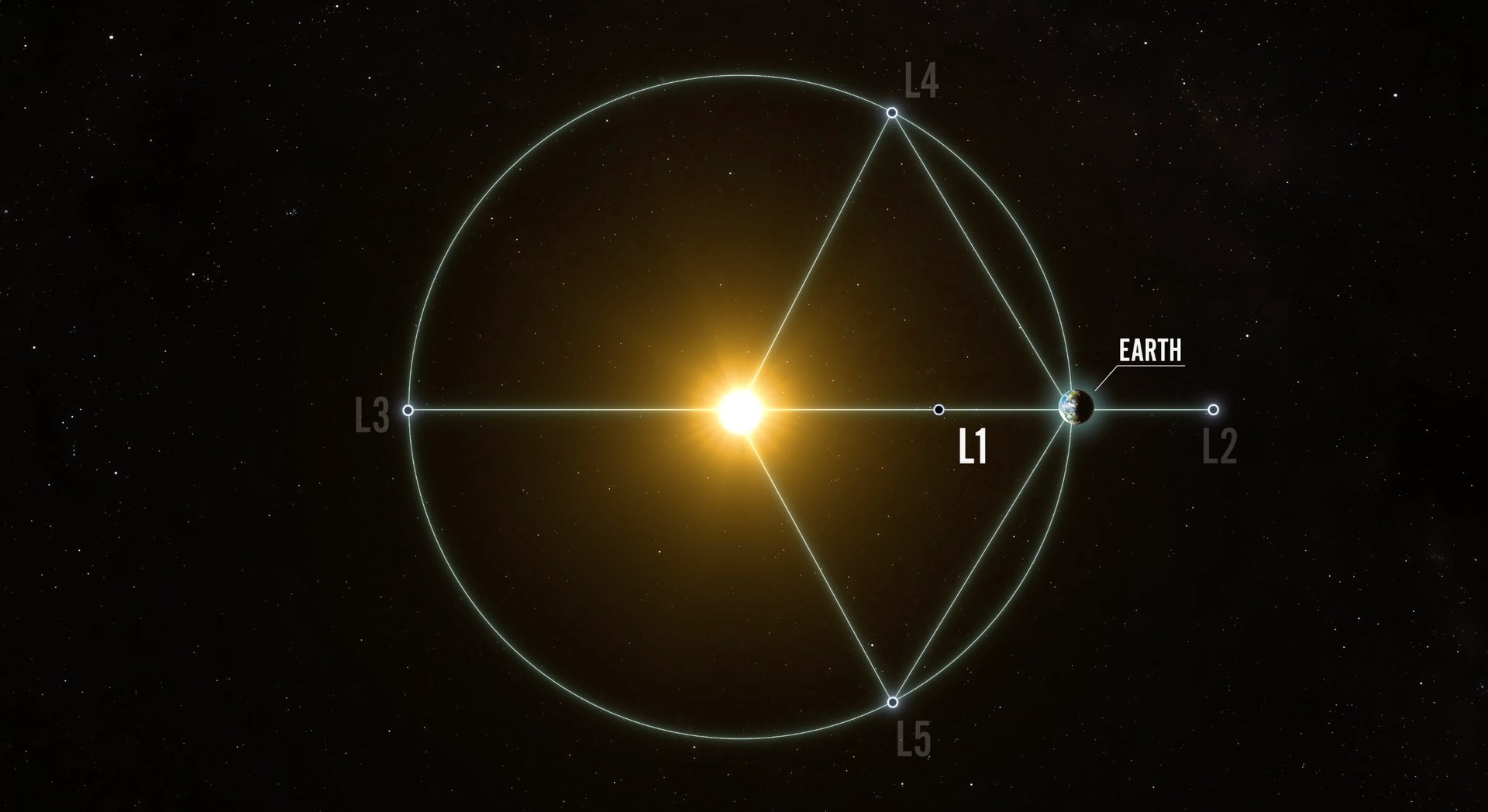
Some NASA missions are designed for very specific tasks, but all of them help feed into our understanding of our universe, and in some cases our pale blue dot, work. A new mission to study one of the more esoteric parts of the atmosphere is scheduled to launch today, and over the next 2-3 years will monitor the outer reaches of our planet’s atmosphere.
Continue reading
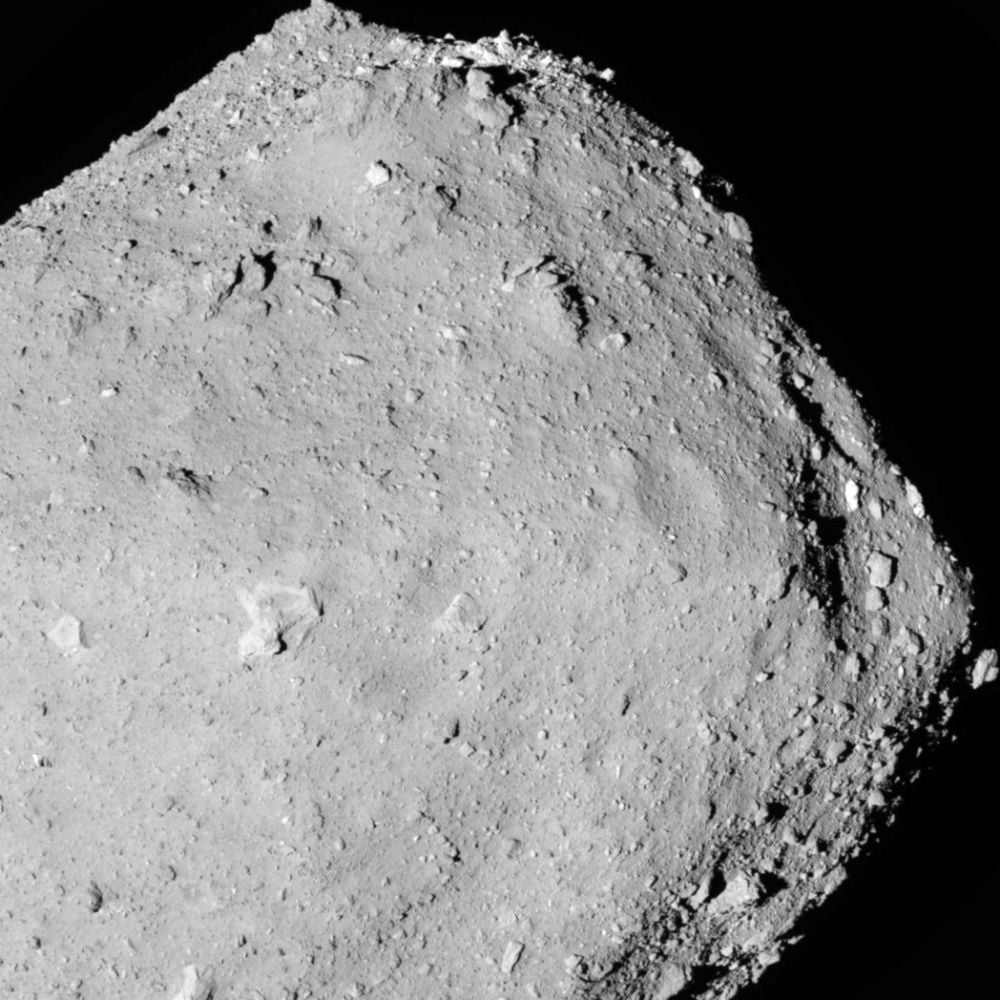

Researchers working with a sample from asteroid Ryugu discovered that water flowed on the asteroid almost one billion years after it formed. The finding suggests that carbon-rich asteroids could've delivered far more water to Earth than thought.
Continue reading

A team of researchers from Kent have demonstrated that it is possible to grow tea in lunar soil as part of a wider field of work to explore how future astronauts living and working on the moon can grow their own food.
Continue reading

A new study, based on years of precise data from telescopes such as the Dark Energy Survey in Chile, above, suggests that the mysterious force known as dark energy may be evolving over time rather than constant.
Continue reading

Earth’s History Written in the Stars: Zircon Crystals Reveal Galactic Influence
kerryhensley45577
Tue, 09/16/2025 - 10:27
Earth’s History Written in the Stars: Zircon Crystals Reveal Galactic Influence
https://www.curtin.edu.au/news/media-release/earths-history-written-in-the-stars-zircon-crystals-reveal-galactic-influence/
Continue reading

The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) conducted the termination procedure for the Venus Climate Orbiter “Akatsuki” (PLANET-C) starting at 9:00 AM on September 18, 2025 (JST), thereby ending the probe's operations.
Continue reading
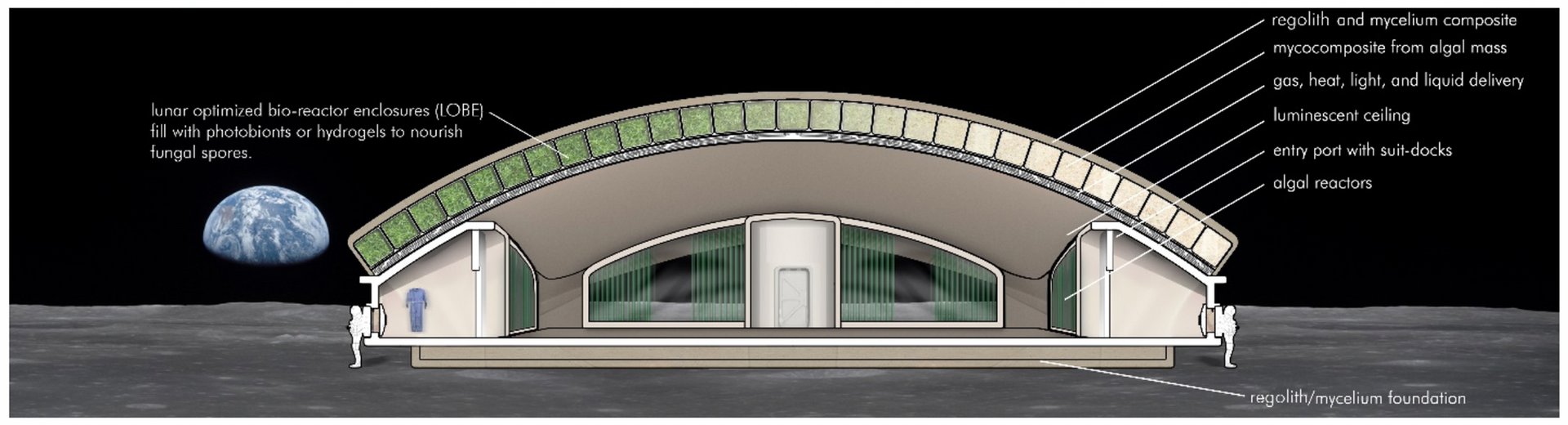
Let’s say you’ve picked the perfect spot for building a settlement on Mars. But this opens up some pretty nasty questions. Building…what? And building….with what?
Continue reading
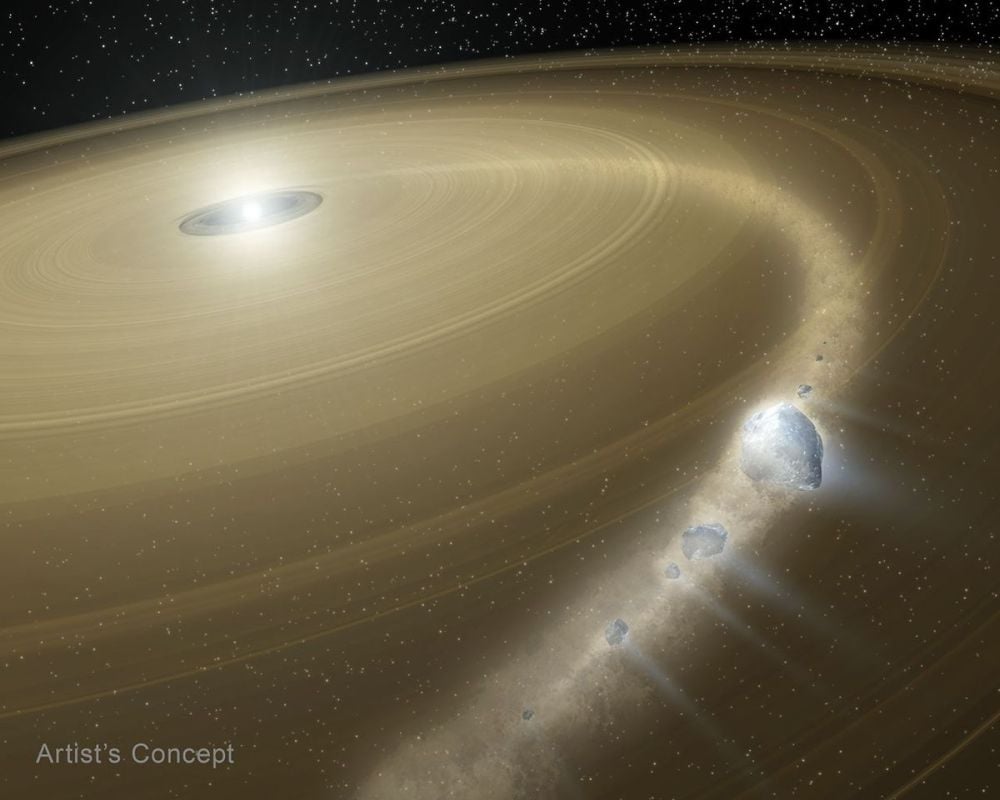
The Hubble Space Telescope has spotted a white dwarf that's devouring a chunk of an icy body. It suggests that even in distant solar systems, icy bodies from the distant reaches can deliver water to planets in the inner solar system.
Continue reading

Let’s say you’re in charge of a Mars mission. Okay boss, where do we land?
Continue reading

arXiv:2509.12351v1 Announce Type: new Abstract: Near-Earth asteroid 2024 YR4 was discovered on 2024-12-27 and its probability of Earth impact in December 2032 peaked at about 3% on 2025-02-18. Additional observations ruled out Earth impact by 2025-02-23. However, the probability of lunar impact in December 2032 then rose, reaching about 4% by the end of the apparition in May 2025. James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observations on 2025-03-26 estimated the asteroid's diameter at 60 +/- 7 m. Stu...
Continue reading
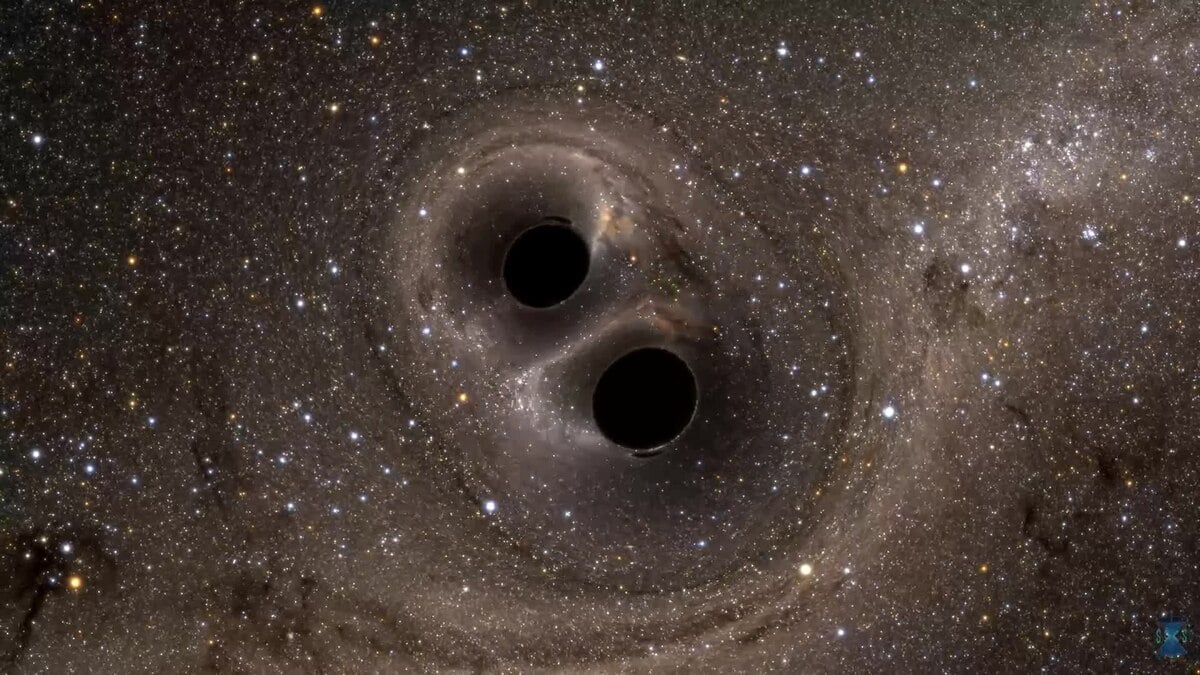

When two black holes collide and merge, they release gravitational waves. These waves can be detected by sensitive instruments on Earth, allowing scientists to determine the mass and spin of the black holes. The clearest black hole merger signal yet, named GW250114 and recorded by LIGO in January 2025, offers new insights into these mysterious objects.
Continue reading

NASA says we now know of 6,000 confirmed exoplanets. At first there was just a trickle of discoveries. But the pace has quickened and shows no signs of slowing down.
Continue reading
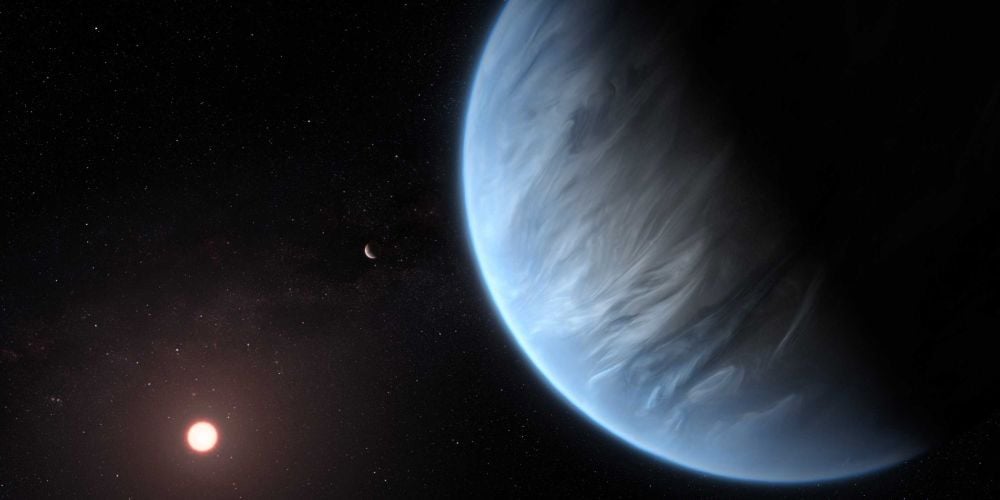

New research shows that the purported water world K2-18b isn't a marine world with a deep ocean. In fact, so-named Hycean worlds may not exist at all. But on the bright side, Earth's water content may not be unusual.
Continue reading
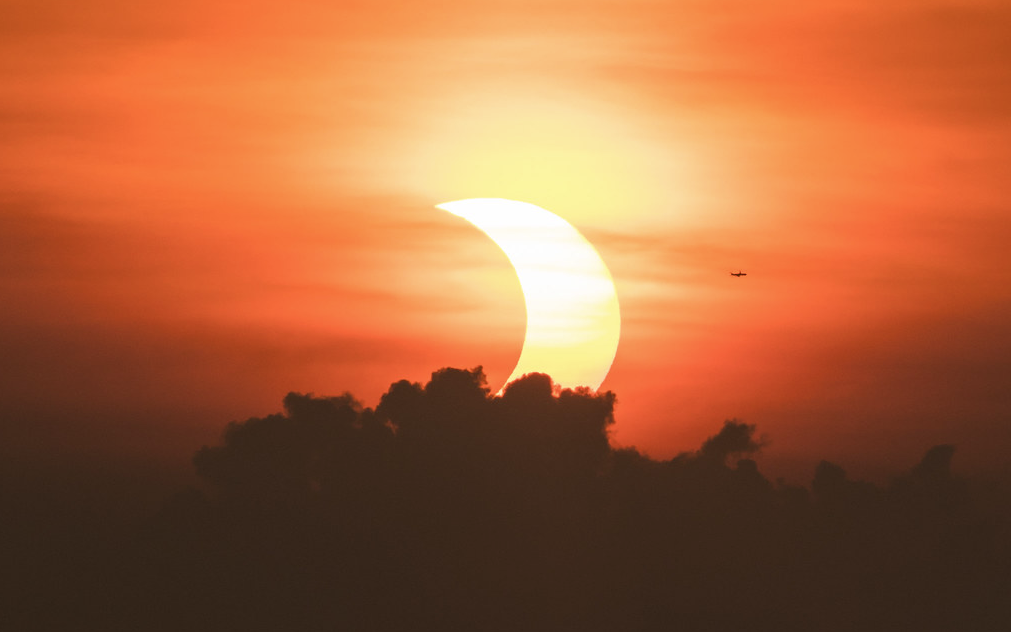

Subtle astronomical events can still produce memorable scenes, hidden away in distant locales. Such a spectacle goes down on Sunday/Monday, September 21st/22nd, with a partial solar eclipse. Although the eclipse only skims the southernmost portion of the South Pacific, viewers along the eastern coast of Australia, Antarctica and all of New Zealand will see an unforgettable sight, as a partially-eclipsed Sun rises out of the sea.
Continue reading
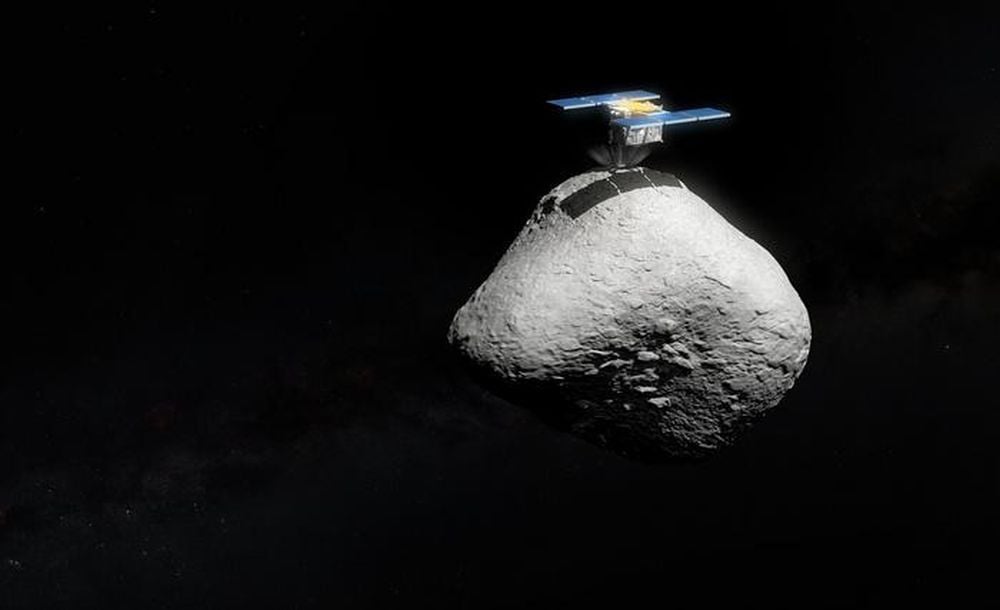

Hayabusa 2 may need to alter its visit to its next target. VLT observations show that the asteroid 1998 KY26 is three times smaller than thought and spinning much more rapidly.
Continue reading
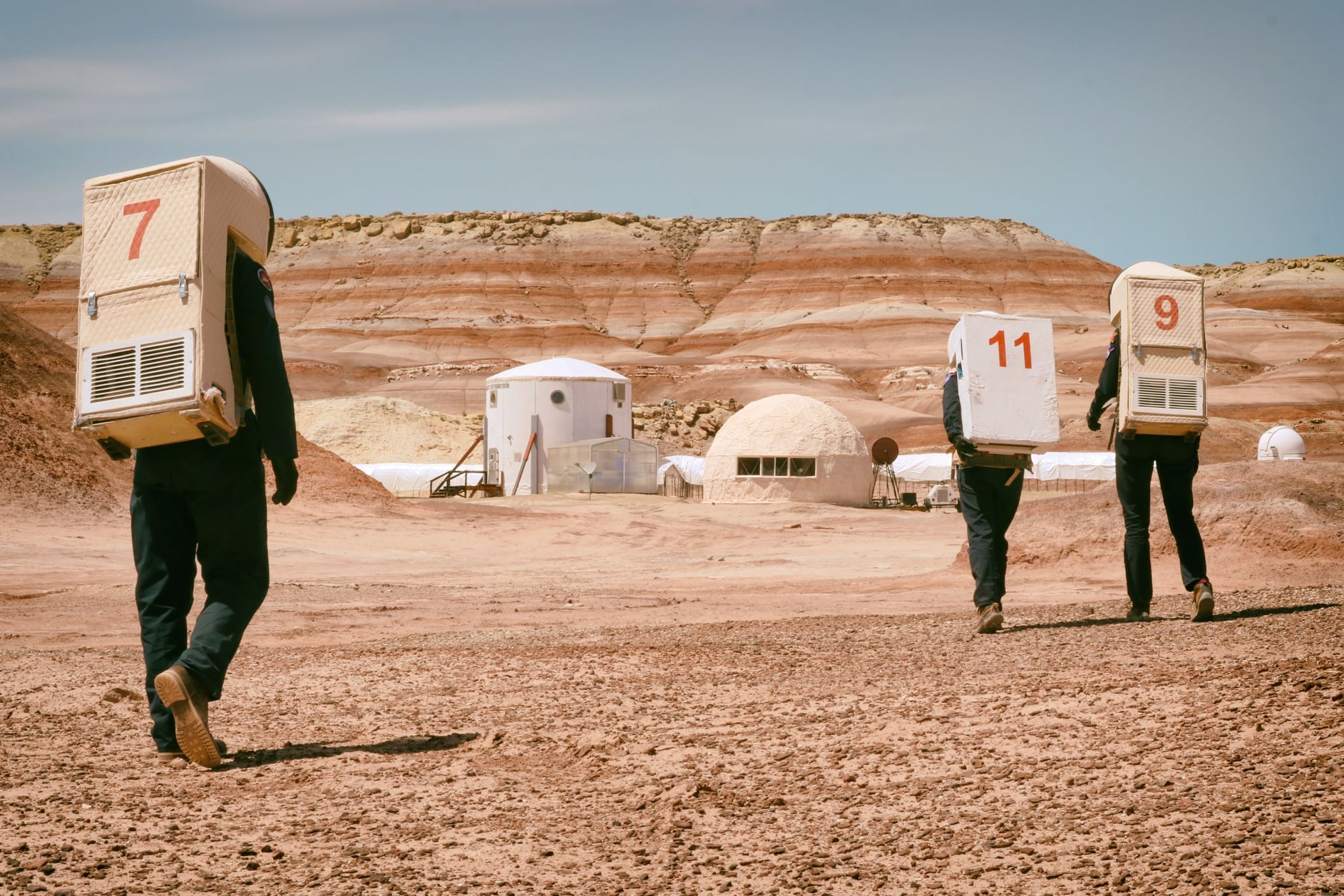

Before we get to Mars, we’re going to have to practice. And develop radical leaps in technology, but also practice.
Continue reading

Exoplanet surveys are useful for more than just astrobiology or increasing the tally of known planets in other solar systems. They can also help us understand the evolution of planetary systems themselves. That’s what a new paper from researchers led by astronomers at the University of Geneva and published in Astronomy & Astrophysics attempts to do - by looking at a large population of “exo-Neptunes” they are attempting to understand the intricacies of how planetary systems are formed.
Continue reading
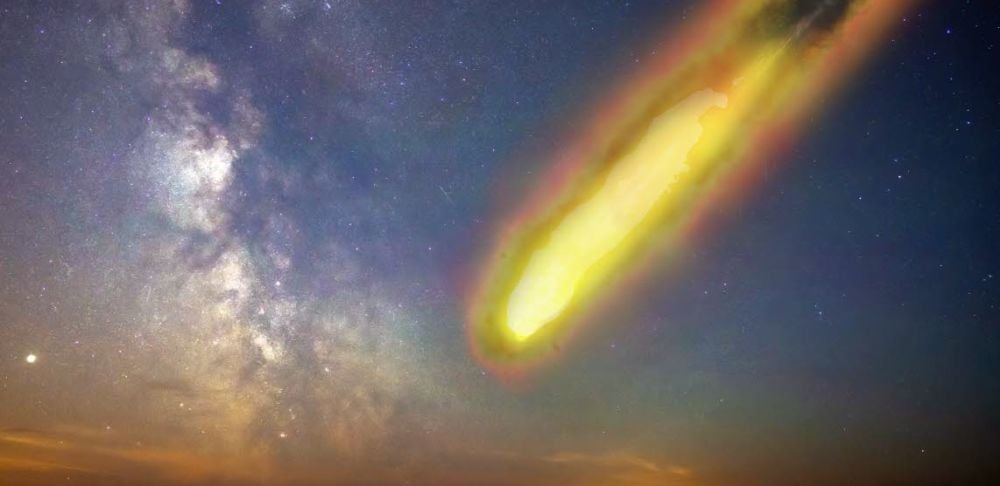

Researchers have dated the appearance of microbial life in a 78 million year old impact crater. Life colonized the fractured hydrothermal system the impact created, and thrived for millions of years. It could do the same on other worlds.
Continue reading
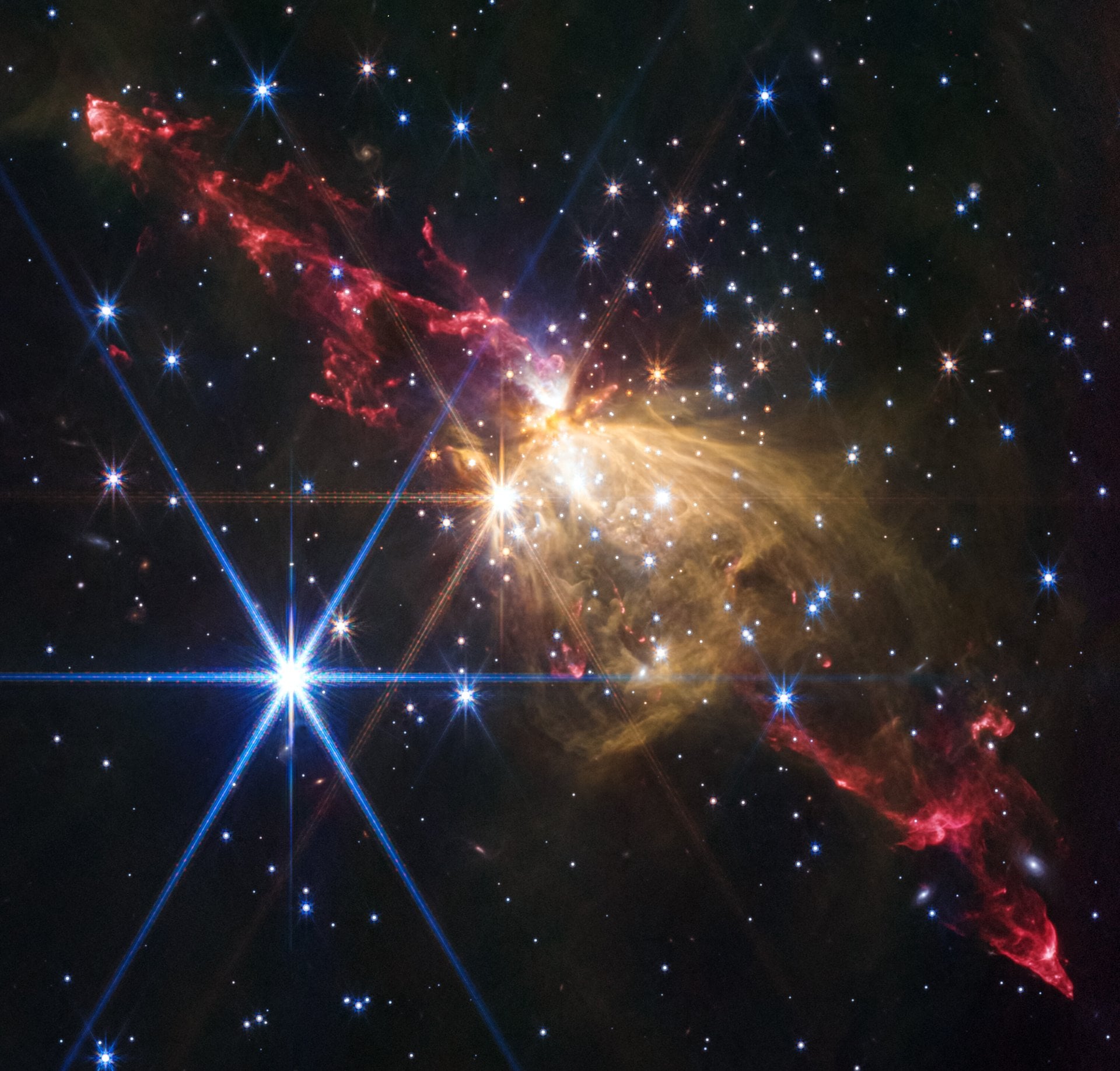

NASA's James Webb Space Telescope recently imaged an extremely large and symmetric protostellar jet at the outskirts of our Milky Way galaxy. From tip to tip, this protostellar jet is 8 light-years across, about double the distance from our Sun to its closest neighboring star system, Alpha Centauri.
Continue reading

You know, if you take away the lack of air and water, the weaker Sun, the lower gravity, and the toxic soil, Mars isn’t all that bad of a place to live.
Continue reading

It seems like most of the planets have fled the evening scene. But that’s about to change this week. Saturn reaches opposition on Sunday, September 21st, passing closest to the Earth at just over 8.5 Astronomical Units (AU) or 1.3 billion kilometers distant, and rising opposite to the setting Sun. This marks the best time to view the ringed world, as it dominates the night sky from sunset until sunrise.
Continue reading
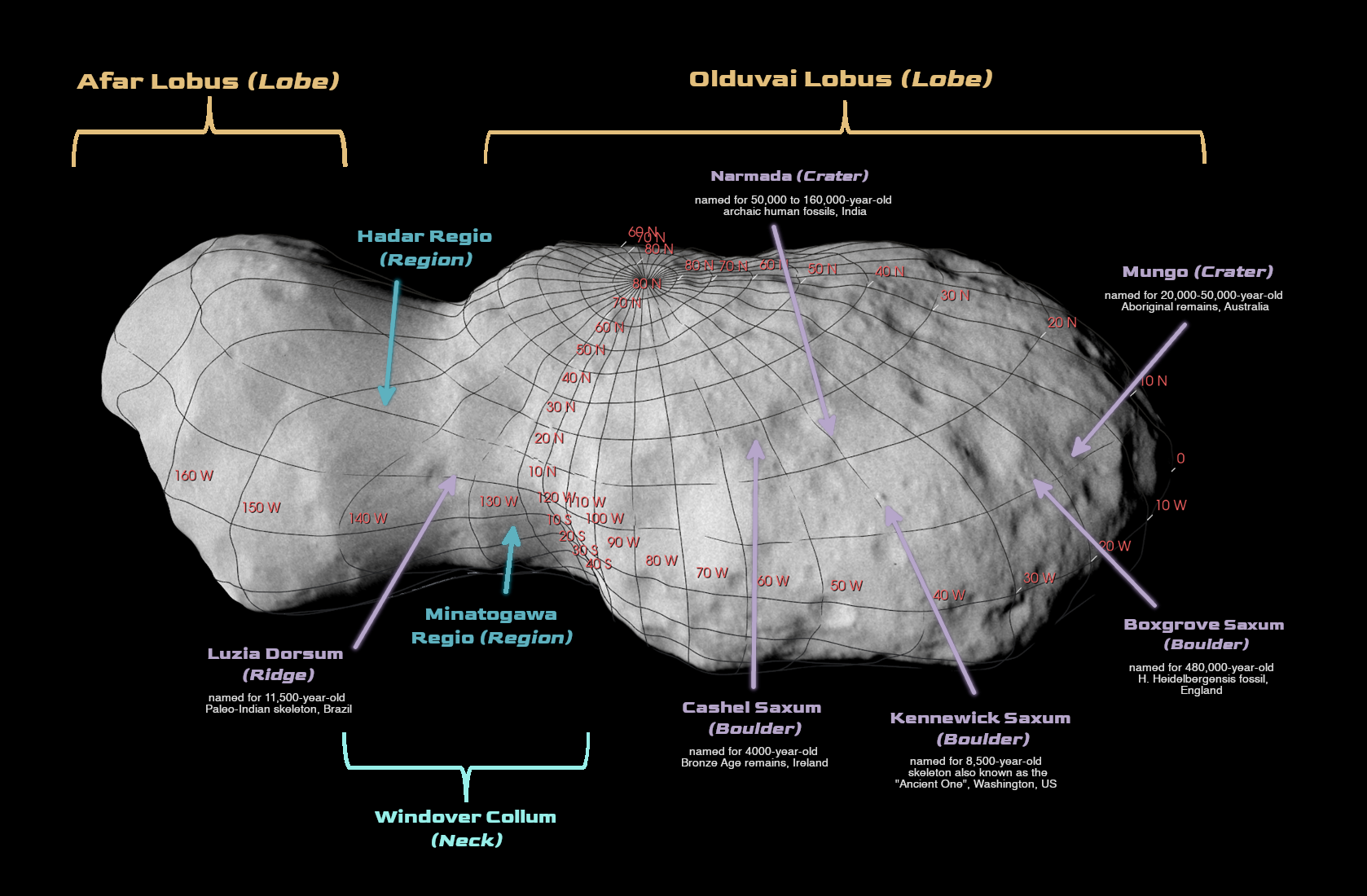
When considering the unnamed major features of all the moons, asteroids, and comets in our solar system there are still a lot of places out there that need proper names. That means the International Astronomical Union (IAU), the non-governmental body responsible for naming astronomical objects, has its work cut out for them. Recently they tackled a relatively easy challenge by approving a series of names on the asteroid Donaldjohnson, the first and only target of NASA’s Lucy mission in the main asteroid belt. With those names come a whole new way to talk about one of the asteroids that humanity has studied most closely thus far.
Continue reading
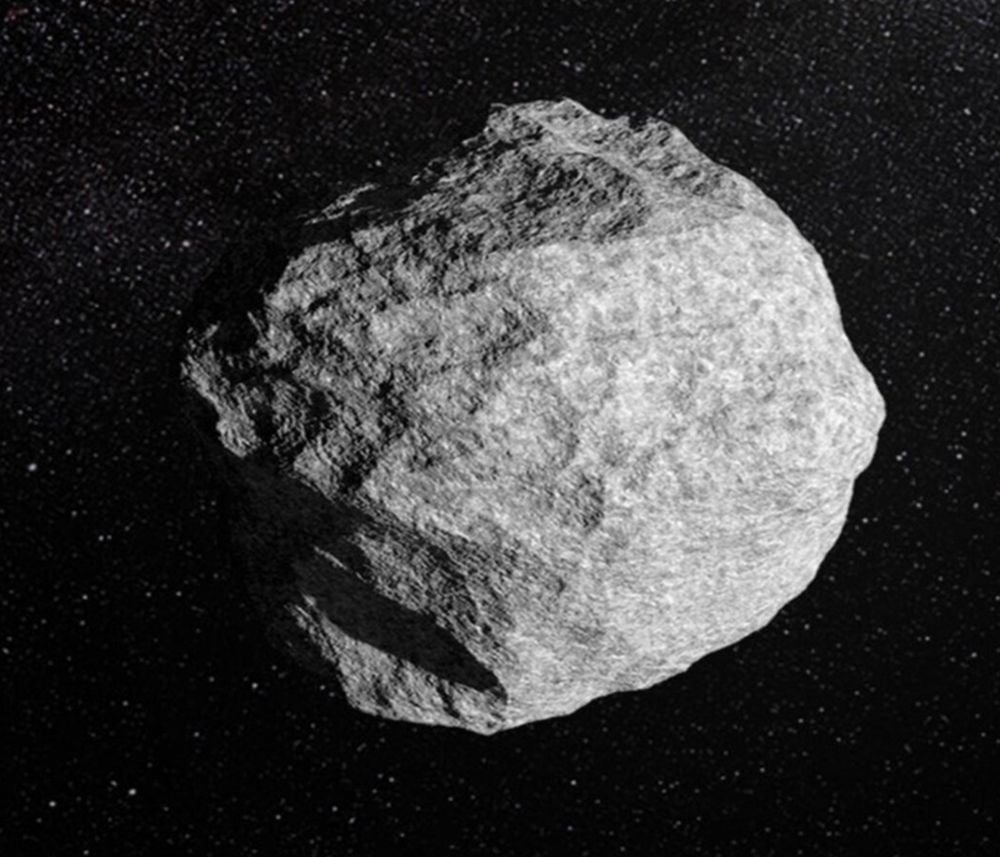

Earth has a new co-moving neighbour. It's a new member of the group of asteroids that follow Earth-like orbits and are called quasi-satellites. Together, they constitute an asteroid belt.
Continue reading

Here we fly through Gaia’s new 3D map of stellar nurseries. This new map includes 3D-views of the Gum Nebula, the North American Nebula, the California Nebula, and the Orion-Eridanus superbubble. It allows us to fly around, through, and above these areas containing stellar nurseries. At the end of the animation, we arrive at our Sun.
Continue reading
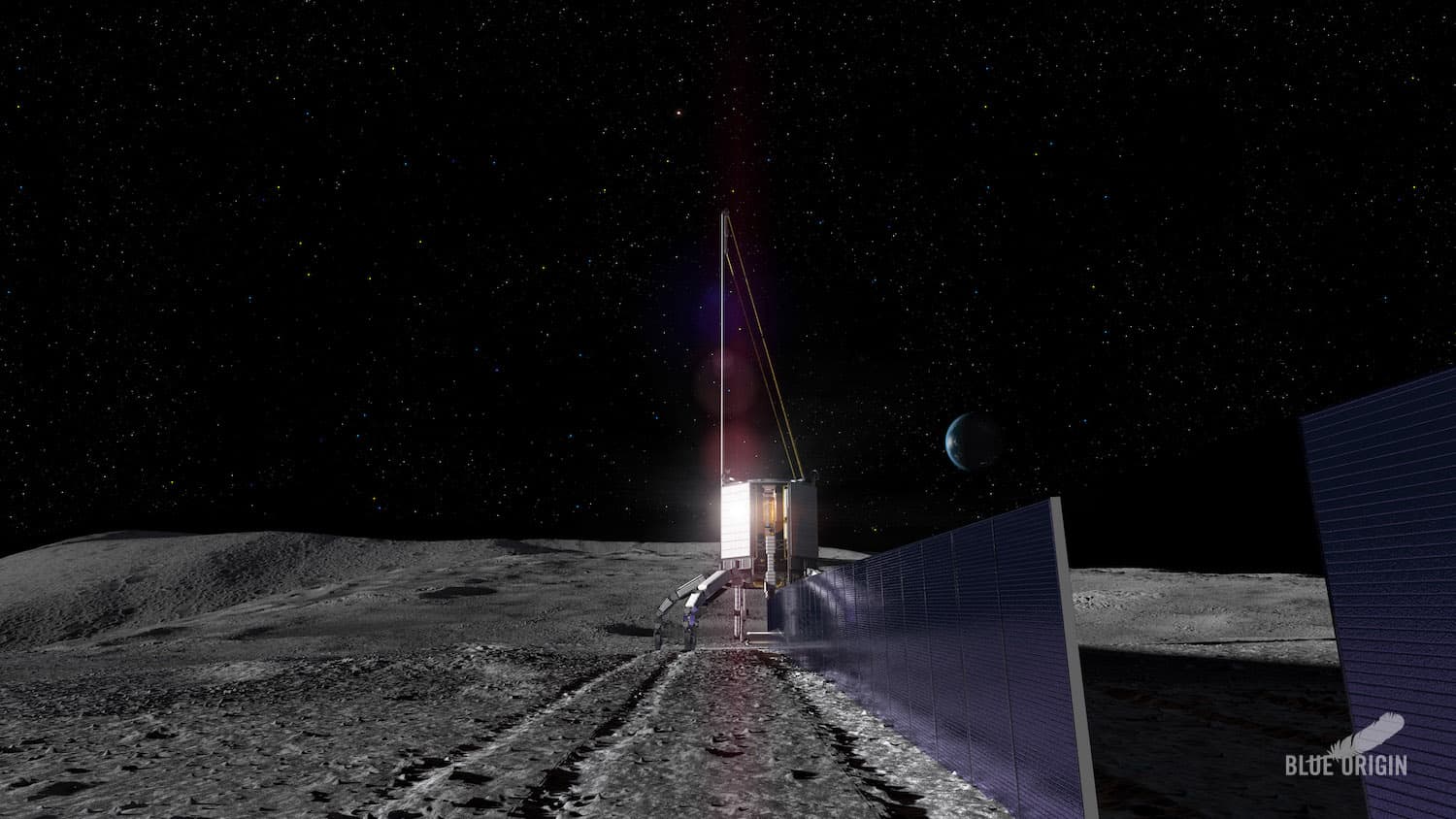
Blue Origin's breakthrough in-space resource utilization system aims to turn lunar regolith into solar arrays, metals, and breathable and propellant-grade oxygen, enabling sustainable robotic and human Moon missions and future Mars exploration.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today
















































