
Understanding how life started on Earth means understanding the evolution of chemistry in the Solar System. It began in the protoplanetary disk of debris around the Sun and reached a critical point when life appeared on Earth billions of years ago. Close to the Sun, the chain of chemical evidence is broken by the Sun's radiation. But further out in the Solar System, billions of kilometres away, some of that ancient chemistry is preserved.
Continue reading
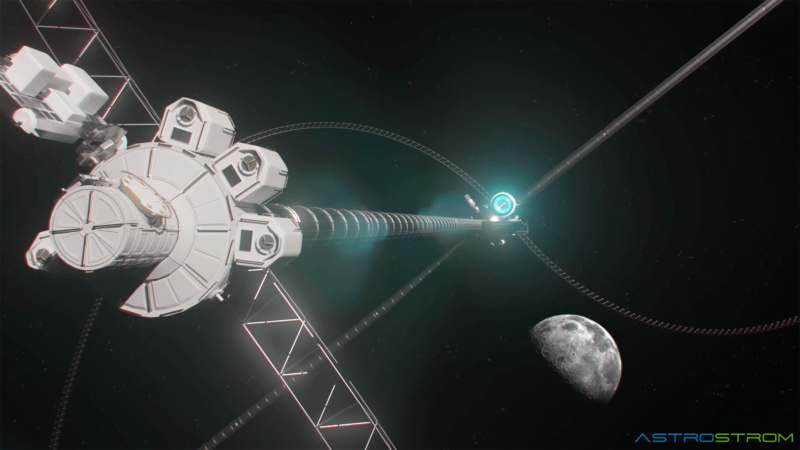

Space-based solar power (SBSP) has long been the dream of many space enthusiasts and energy economists. However, the reality of economic constraints has long left any practice projects on the ground. There has been plenty of discussion about how to lower the cost of entry to build the kind of space-based solar power satellite described by John Mankins in his books and articles. However, even with the advent of lower costs to orbit thanks to reusable rockets, the economic case for SBSP is still not great simply due to the sheer amount of mass required to get into orbit. Unless we get that mass from somewhere else, with a smaller gravity well. Astrostrom, which means something like "Star current" in German, is an organization based in Switzerland that hopes to make space-based solar power a reality.
Continue reading
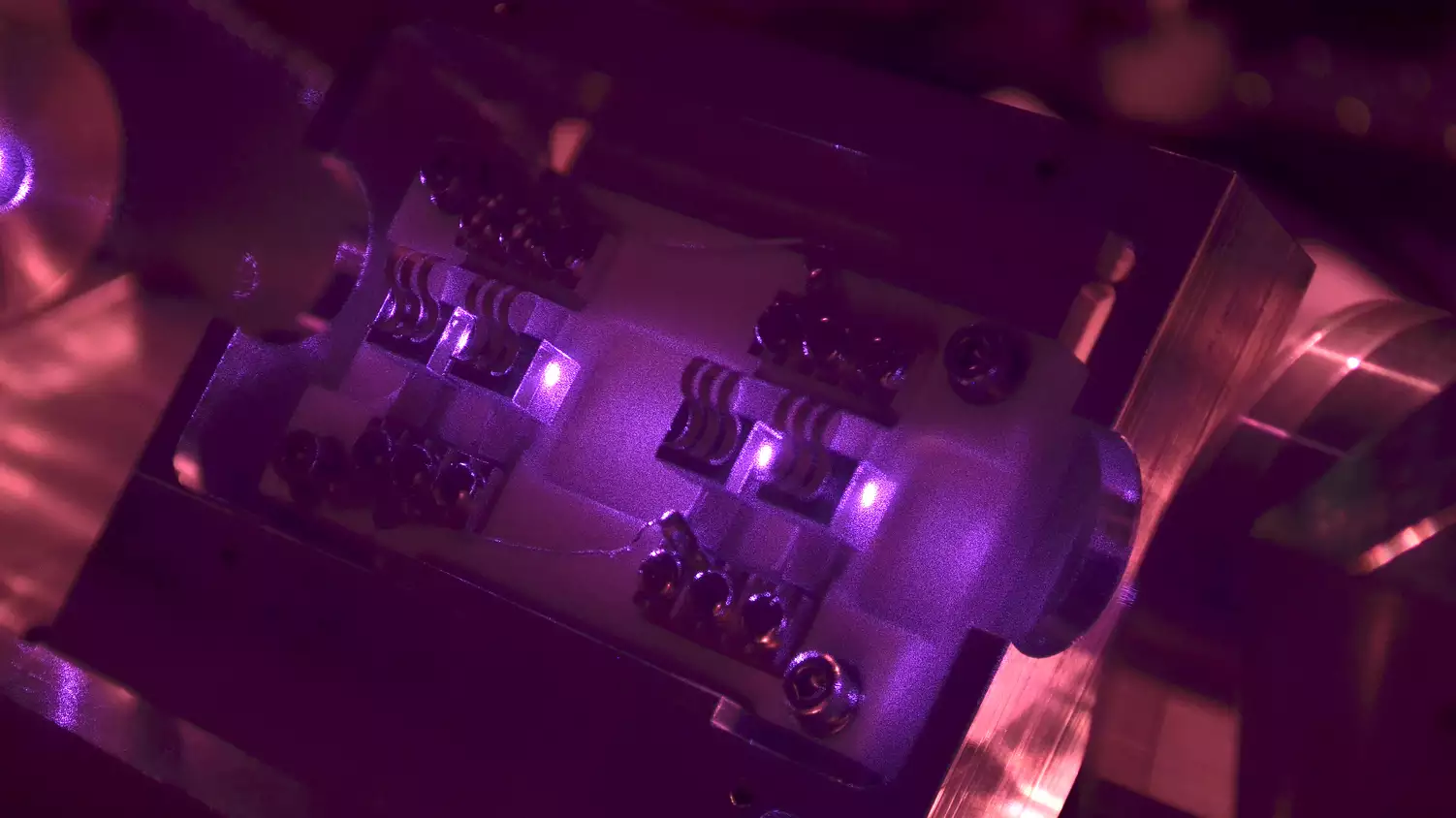
Astronomy has entered the age of gravitational waves. While there are plenty of differences between gravitational wave astronomy and typical waves of the electromagnetic spectrum, they share one similar feature: frequency. While we have detectors for a wide range of electromagnetic frequencies, gravitational wave detectors only focus on a narrow band of relatively low-frequency signals. That will change with the upgrade of the GEO600 gravitational wave detector located at the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics.
Continue reading

We know that our Milky Way galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole (SMBH) in its center. Astronomers think most spiral galaxies do, and that SMBHs coexist and co-evolve with their host galaxies. However, they haven't been able to find them in all spirals. M83, the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy, has always been puzzling because scientists haven't seen any evidence of an SMBH in its center. The JWST may have finally found some.
Continue reading
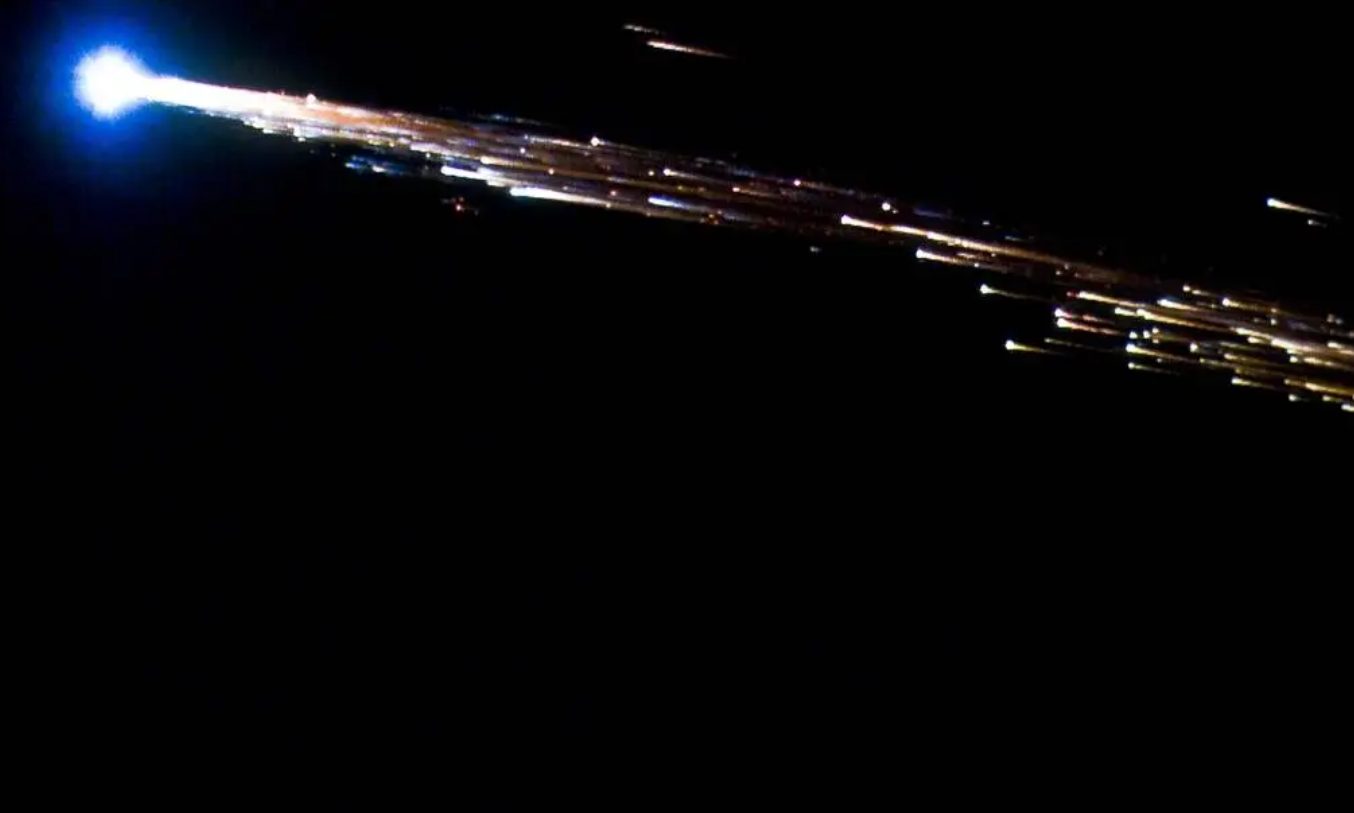

It's one straight out of the history books. After over 50 years in space, the late Soviet Union's Kosmos-482 mission is set to reenter the Earth's atmosphere, early next month. Stranded in Earth orbit, there are just a few weeks remaining to see this enigmatic relic of a bygone era.
Continue reading
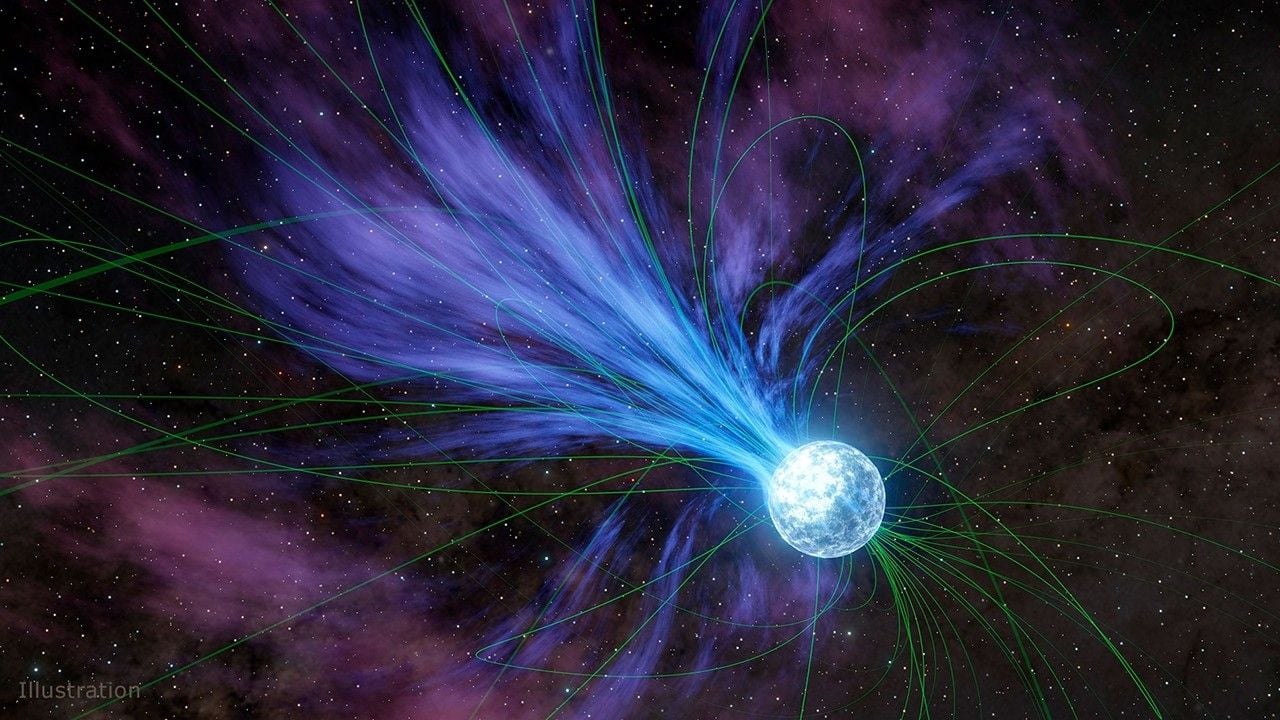

Where do the heavy elements in the Universe come from? While we know they are formed in colliding neutron stars and likely in supernova explosions, astronomers have now identified a surprising additional source: magnetars. These highly magnetised neutron stars emit powerful flares, which may result from neutrons fusing into heavier elements. This process could explain the presence of elements like gold early in the Universe's history.
Continue reading

What probes can be used to explore the depths of Jupiter's icy moon, Europa, and other ocean worlds throughout the solar system? This is what a recent study presented at the 56th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference hopes to address as a team of researchers participated through the Ocean Worlds Reconnaissance and Characterization of Astrobiological Analogs (ORCAA) project to investigate how cryobots could be used to explore the oceans of other worlds in our solar system.
Continue reading

Stars don't exist in isolation. They have siblings and exist in clusters, associations, and groups. The ESA's Gaia mission found an unusual group of stars rapidly leaving its birthplace behind and dispersing into the wider galaxy. While that's not necessarily unusual behaviour, it is for such a large group. Could supernovae explosions be responsible?
Continue reading
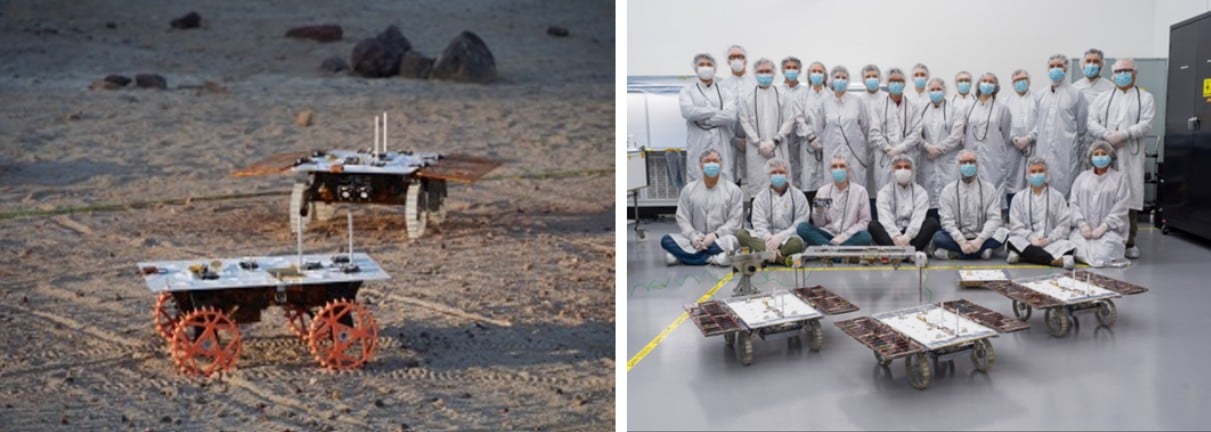

Getting missions to land successfully on the Moon has been difficult. Recent missions, such as IM-1 and IM-2, which the private company Intuitive Machines completed, have been qualified successes at best, with both landers settling at unintended angles and breaking parts of them off along the way. Such experiences offer excellent learning opportunities, though, and NASA is confident that a third time might be a charm for a flawless mission. There will be a lot riding on IM-3, the third Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) mission, including a set of rovers and ground station for a NASA experiment called the Cooperative Autonomous Distribution Robotic Exploration (CADRE), which recently passed its Verification and Validation (V&V) test for one of it's most essential parts. This software architecture handles tasks for each rover and binds them into a cohesive whole.
Continue reading
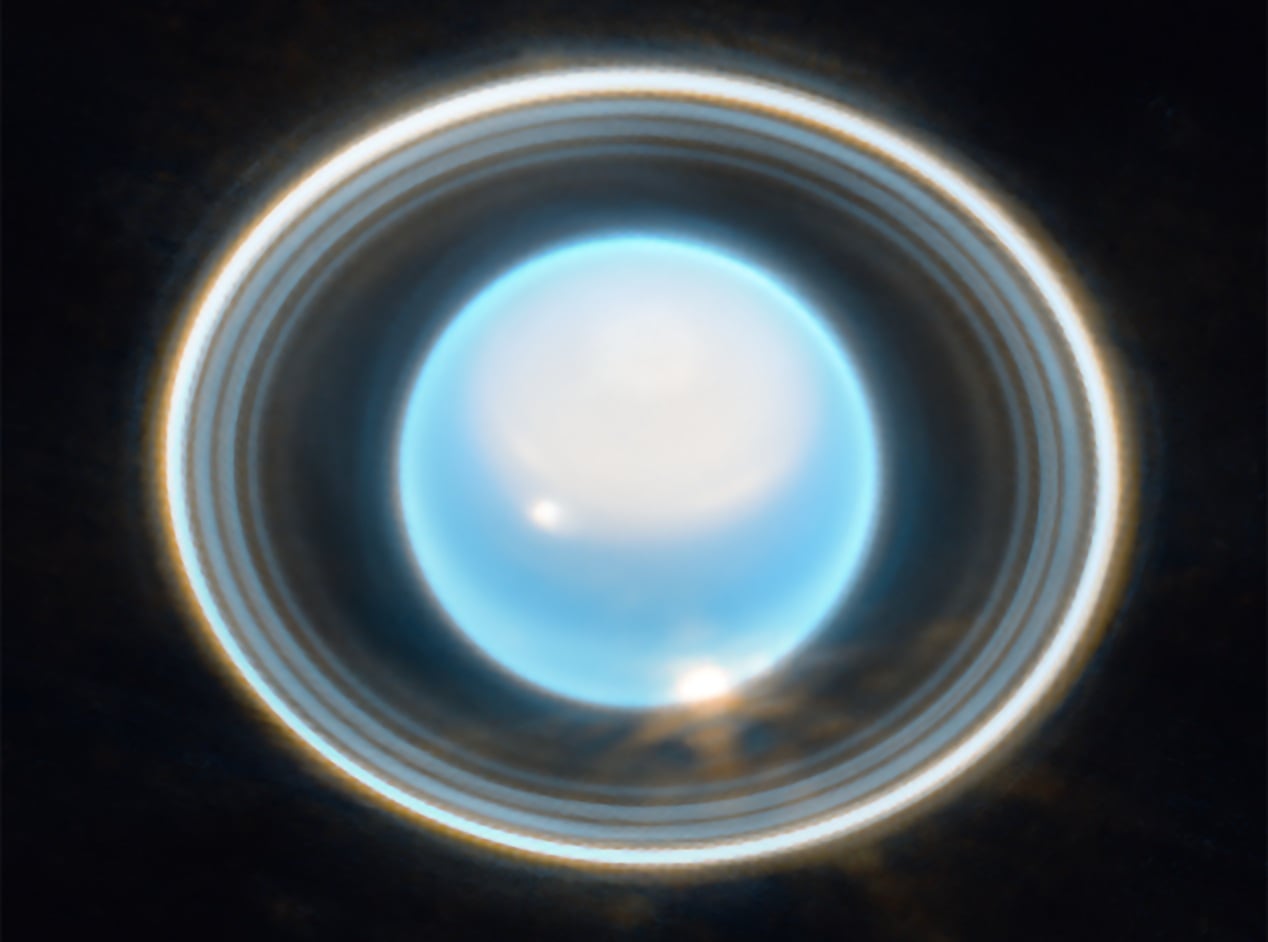

A rare stellar occultation, which happens only once every 30 years, allowed astronomers to observe Uranus and learn more about the composition of its atmosphere and rings.
Continue reading
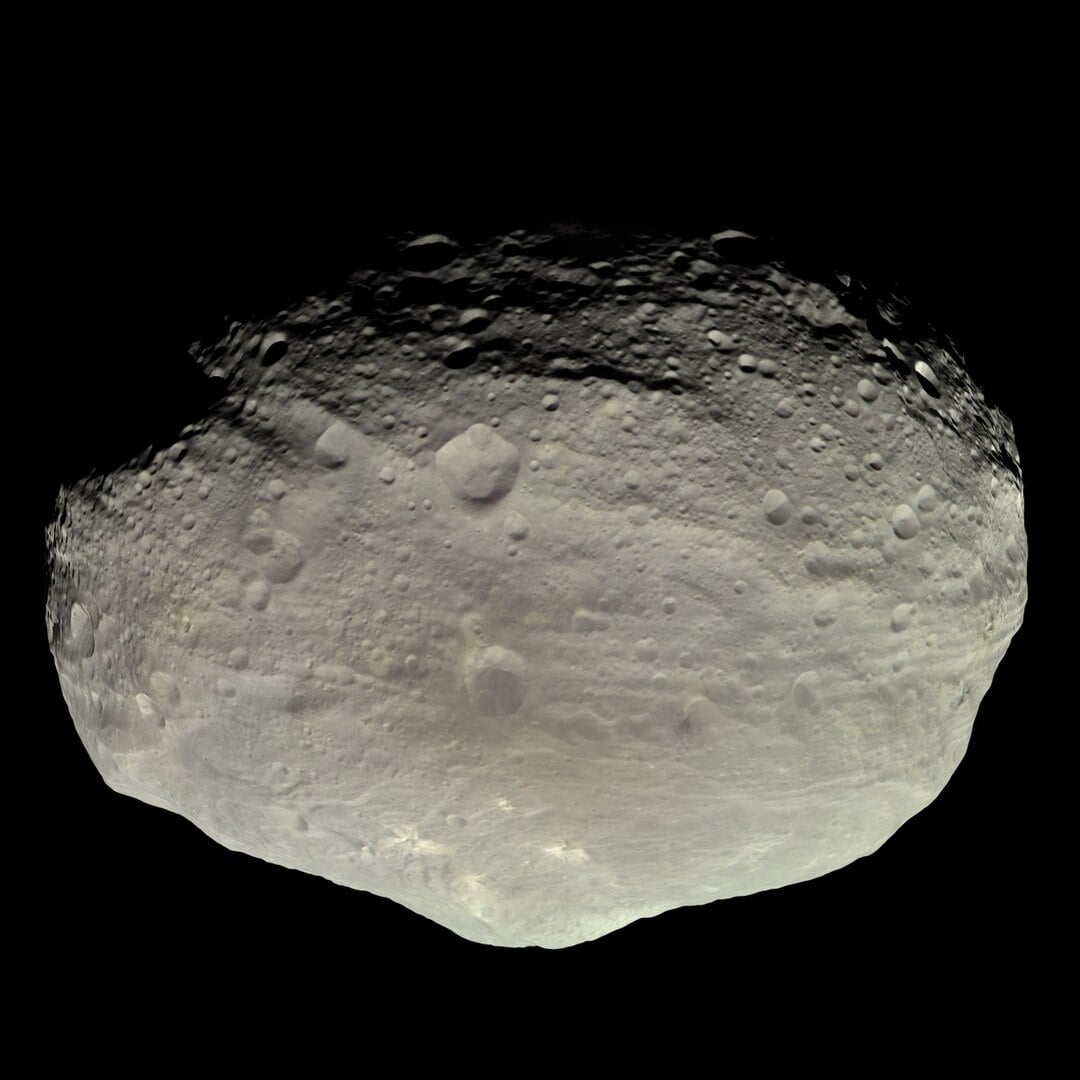

As the second-largest object in the main asteroid belt, Vesta attracts a healthy amount of scientific interest. While smaller asteroids in the belt are considered fragments of collisions, scientists think Vesta and the other three large objects in the belt are likely primordial and have survived for billions of years. They believe that Vesta was on its way to becoming a planet and that the Solar System's rocky planets likely began as protoplanets just like it. But new research is casting doubt on that conclusion.
Continue reading

What will a human experience while standing on the surface of Saturn's largest moon, Titan, even with the protection of a pressurized spacesuit? This is what a recent study presented at the 56th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference hopes to address as William O'Hara, who is the Executive Director of Explore Titan investigated what physical attributes a human will experience when standing on Titan's surface. This study has the potential to help scientists, engineers, mission planners, and the public better understand the risks associated with sending humans to far-off worlds for long periods of time and how to develop technologies to mitigate these risks.
Continue reading
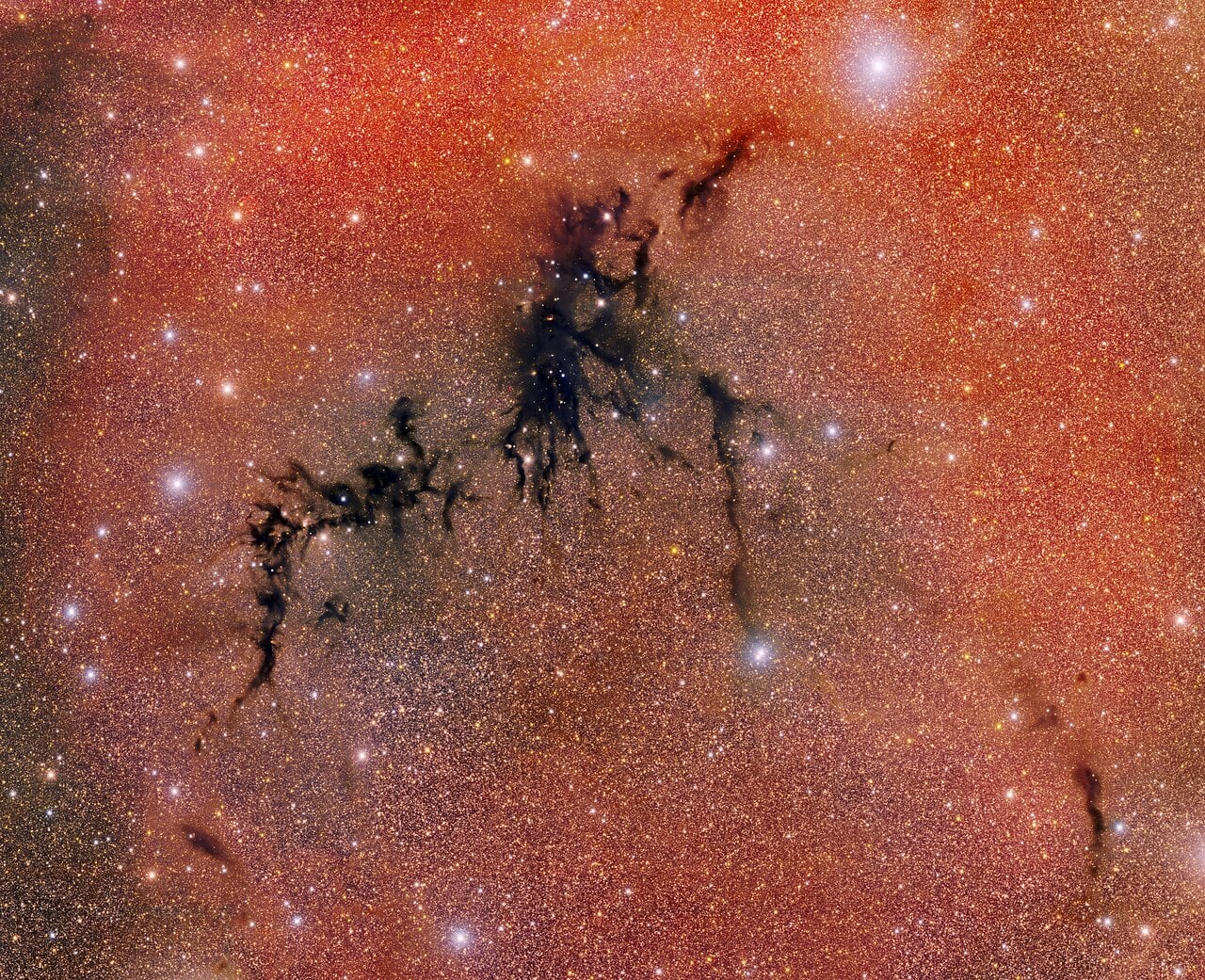

Star birth is a process hidden inside dense crèches of gas and dust. Yet, if you know what to look for, you can see the products of this essential cosmic process across the sky. The Circinus West molecular cloud is a starbirth crèche some 2,500 light-years away. It boasts everything from dark nebulae to protostellar objects and newborn stars to the faint ghosts of stars that have already died.
Continue reading
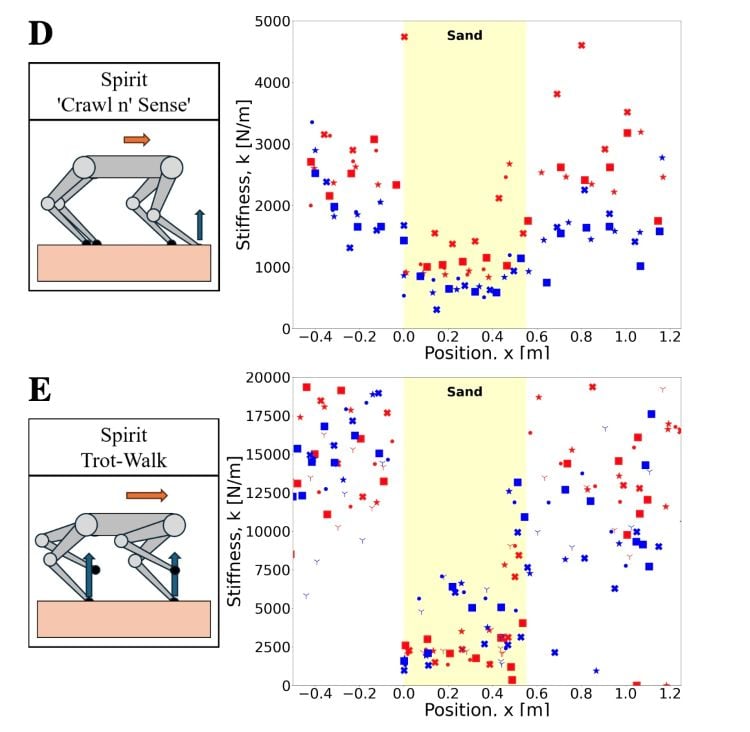
How can walking robots deliver more efficient in-situ robotic exploration on the Moon compared to other types of robots? This is what a recent study presented at the 56th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference hopes to address as a team of researchers from the University of Southern California (USC) discussed the benefits of using legged robots for lunar exploration regarding gait speed (walking speed). This study has the potential to help engineers, scientists, mission planners, and astronauts develop novel robotic designs to conduct more efficient science and mission objectives on future Moon surface missions.
Continue reading
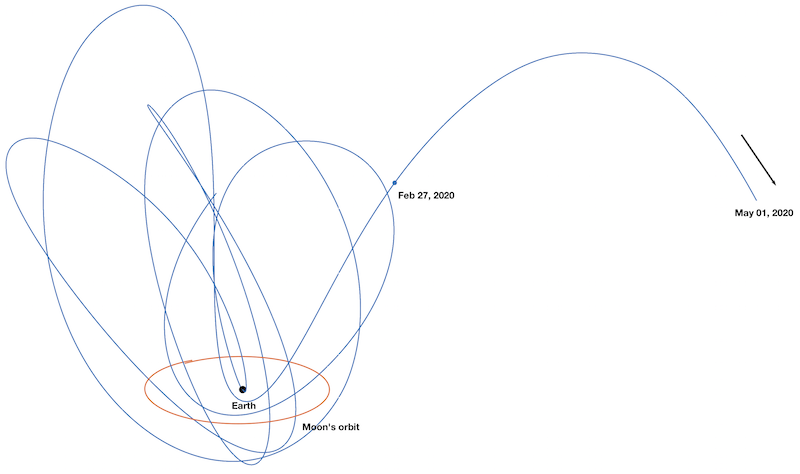
Earth has a number of companions in space; of course the Moon is the most well known but there are a host of smaller objects that visit us, complete a few orbits then head off again. A team of astronomers have detected four objects like this and have performed spectroscopic analyses on them. They found that their surface composition is similar to eh Moon suggesting that it's a major source of these temporary satellites instead of the asteroid belt.
Continue reading

The Orion Nebula is a fabulous example of a vast cloud of electrically charged gas which is emitting bright radiation. If the atoms in the gas are cool enough though, they can form giant molecular clouds that obscure light, these are known as dark nebula. A team of astronomers have now found an enormous cloud of molecular hydrogen in our own cosmic backyard just 300 light years away. The cloud contains 3,400 times the mass of the Sun and if we could see it, it would stretch nearly 40 times the width of the Moon across the sky.
Continue reading
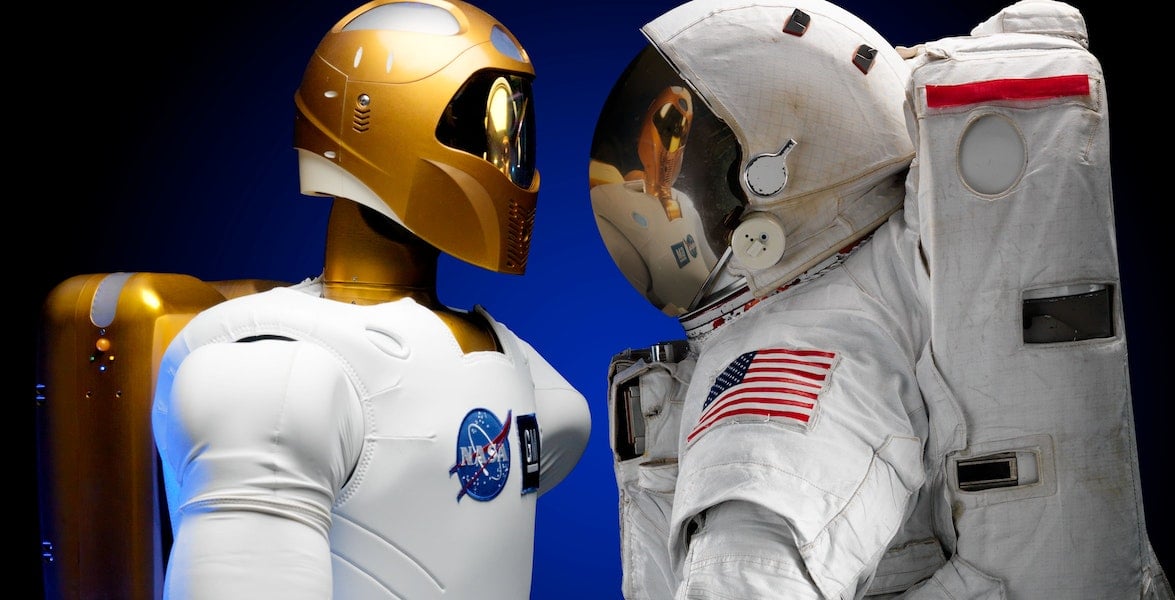
How do robots feel in space? This is both a practical and possibly an existential question. Still, today, we'll focus on the practical side by looking at a review paper from Hadi Jahanshahi and Zheng Zhu of York University in Canada that discusses different tactile sensor types and their advantages and disadvantages for use in space.
Continue reading
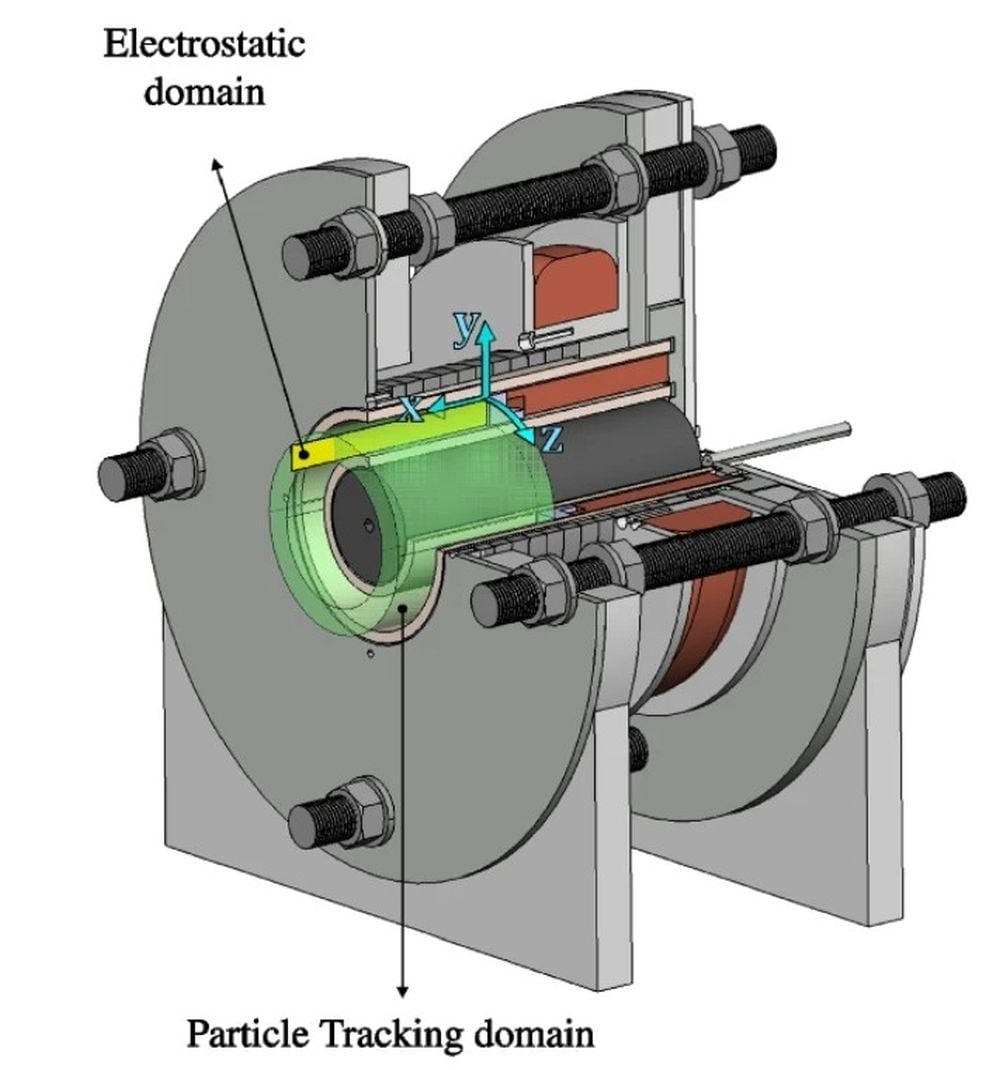
Ion drives are renowned for their efficiency. They're extremely efficient compared to chemical rockets, so they're preferred for deep space missions where propellant supplies are critical. New research shows how they could run on simple water, making them even more efficient.
Continue reading
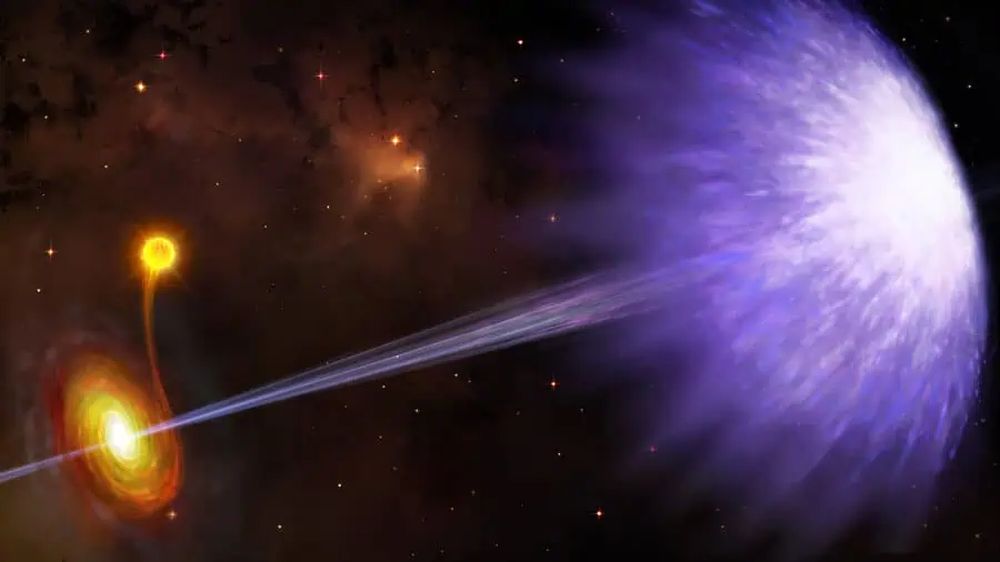

It's nearly impossible to overstate the effect supermassive black holes have on their host galaxies. When actively accreting matter, they release colossal amounts of energy as winds, jets, and radiation that shape their surroundings. But stellar mass black holes also shape their surroundings with energetic jets.
Continue reading

Nothing wows new observers like seeing Saturn for the first time. I always check out the ringed planet if it's visible, and telescopes down the line at any star party will invariably be pointed Saturn-ward to a chorus of 'oh's' and 'ah's'…. but 2025 gives you another reason to gaze at Saturn, as its largest moon Titan completes a series of rare shadow transits.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today


















