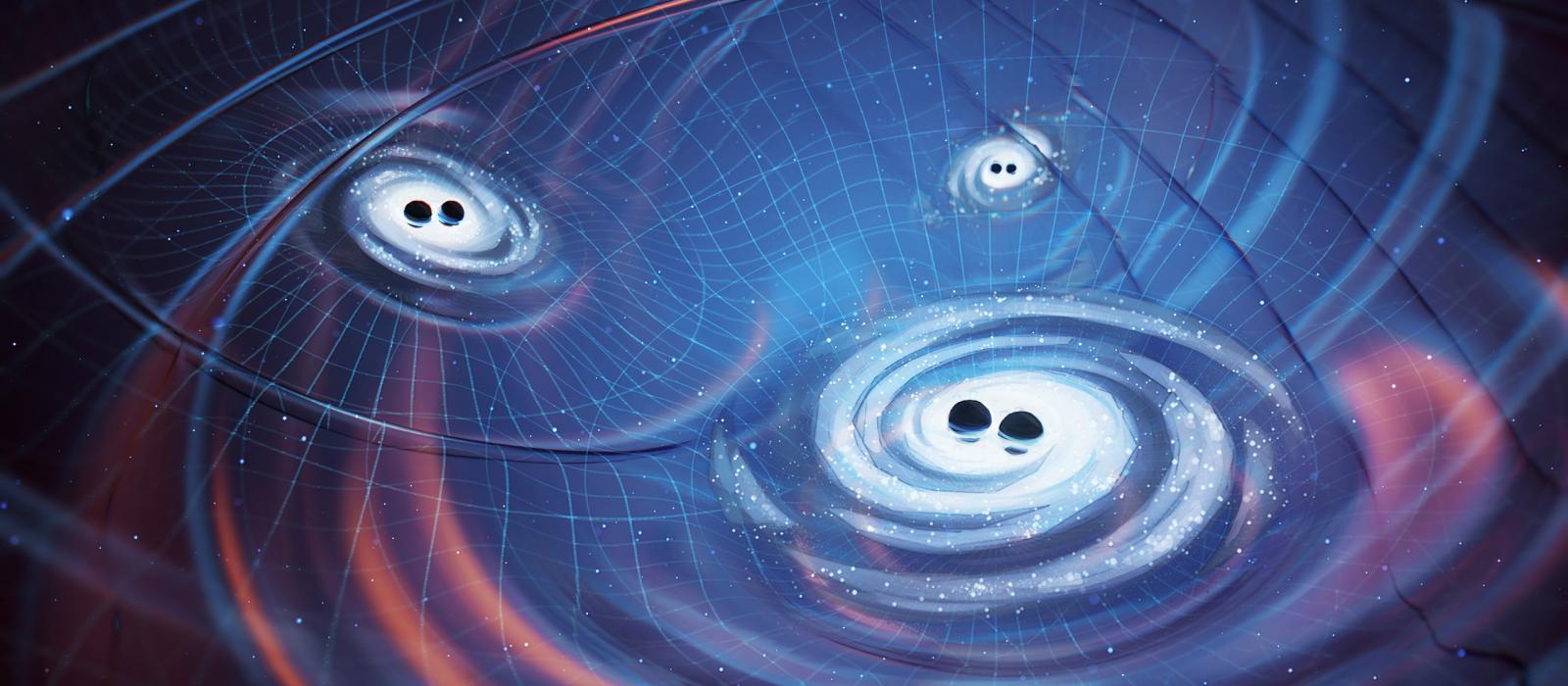
Astronomers are listening for cosmic gravitational waves in the rhythm of pulsars. But even after finding them, they will need to distinguish between cosmic waves and the more local waves of black holes.
Continue reading
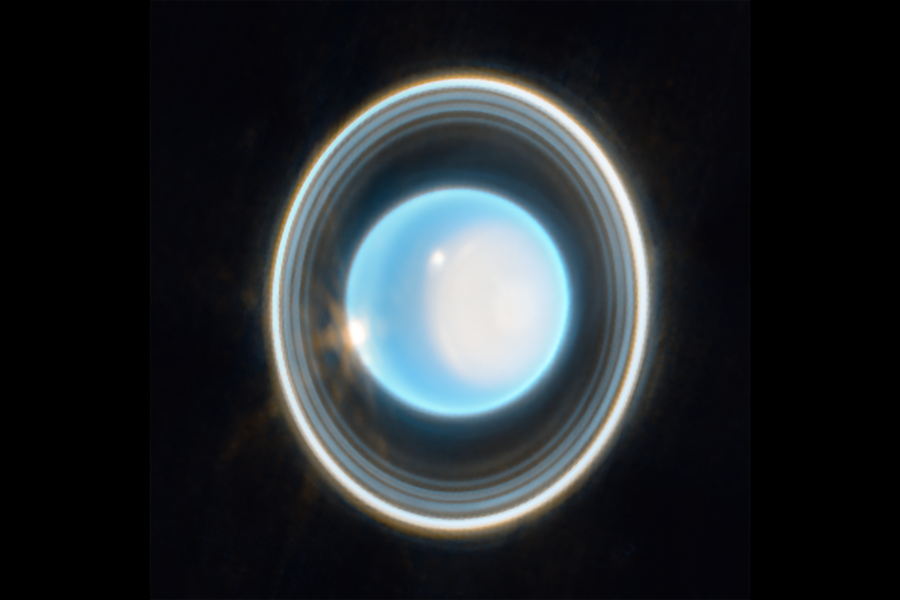

The ice giants remain some of the most interesting places to explore in the solar system. Uranus in particular has drawn a lot of interest lately, especially after the 2022 Decadal Survey from the National Academies named it as the highest priority destination. But as of now, we still don’t have a fully fleshed out and planned mission ready to go for the multiple launch windows in the 2030s. That might actually be an advantage, though, as a new system coming online might change the overall mission design fundamentally. Starship recently continued its recent string of successful tests, and a new paper presented at the IEEE Aerospace Conference by researchers at MIT looked at how this new, much more capable launch system, could impact the development of the Uranus Orbiter and Probe (UOP) that the Decadal Survey suggested.
Continue reading

Alien civilizations may evolve so quickly that they are only detectable for a blink of cosmic time, thanks to the rise of artificial intelligence.
Continue reading
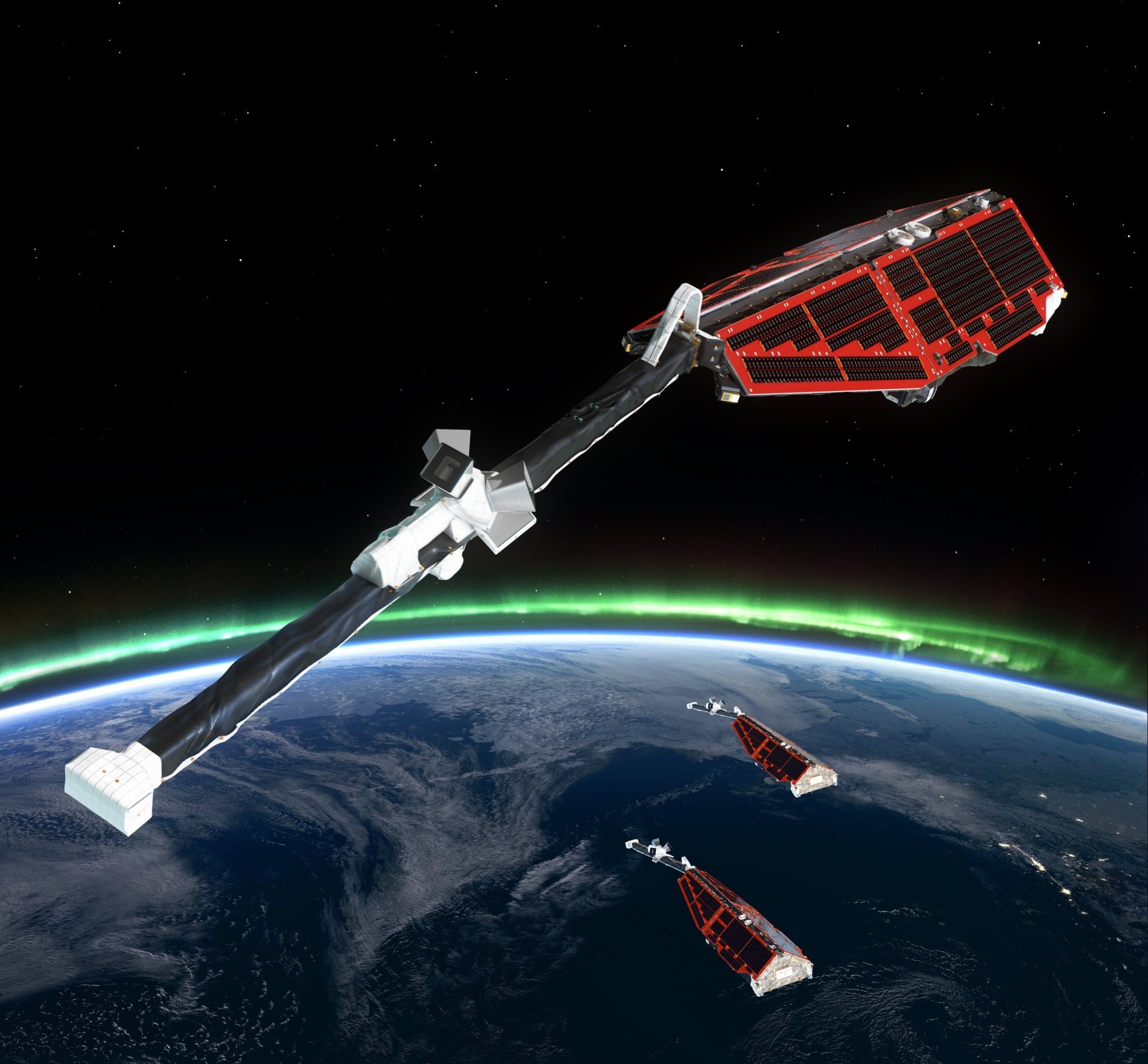

Earth is a dynamic place, both on its surface and down to its very core. The European Space Agency (ESA) recently released findings from its Swarm constellation of Earth-observing satellites highlighting this fact, documenting activity in the planet’s magnetic field during its decade plus of extended operations. One key finding shows the well-known Southern Atlantic Anomaly is expanding in size.
Continue reading
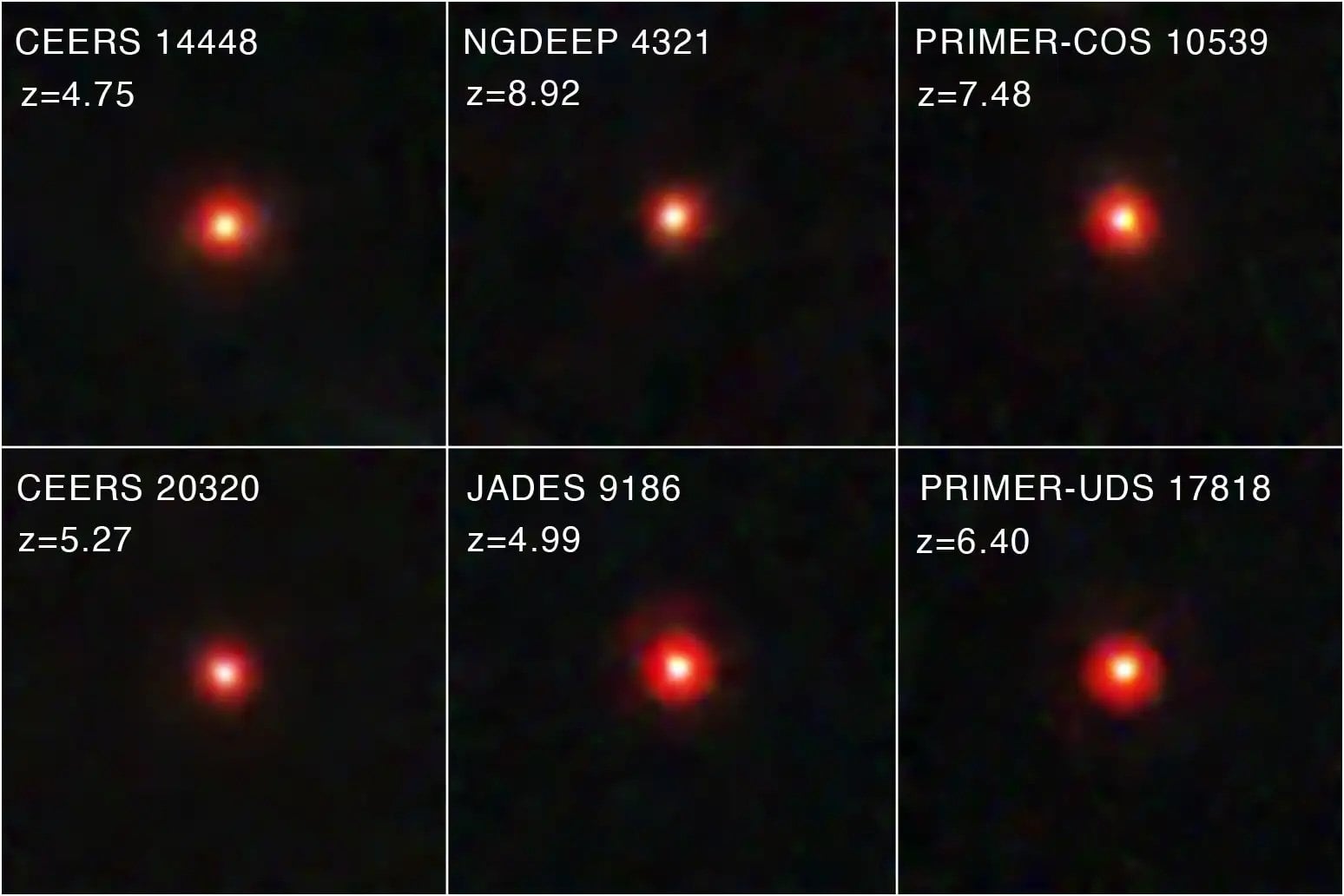

An international team of astronomers addressed the mystery of the "Little Red Dots" (LRDs) observed by Webb. They conclude that they are likely to be "black hole stars," the early seeds of supermassive black holes (SMBHs) we see at the center of galaxies today. Their findings have implications for our understanding of cosmic evolution.
Continue reading

Samples from one of the Apollo 17 drive tubes was recently opened and analyzed by Brown University researchers, who found surprising sulfur isotopes signatures inside.
Continue reading
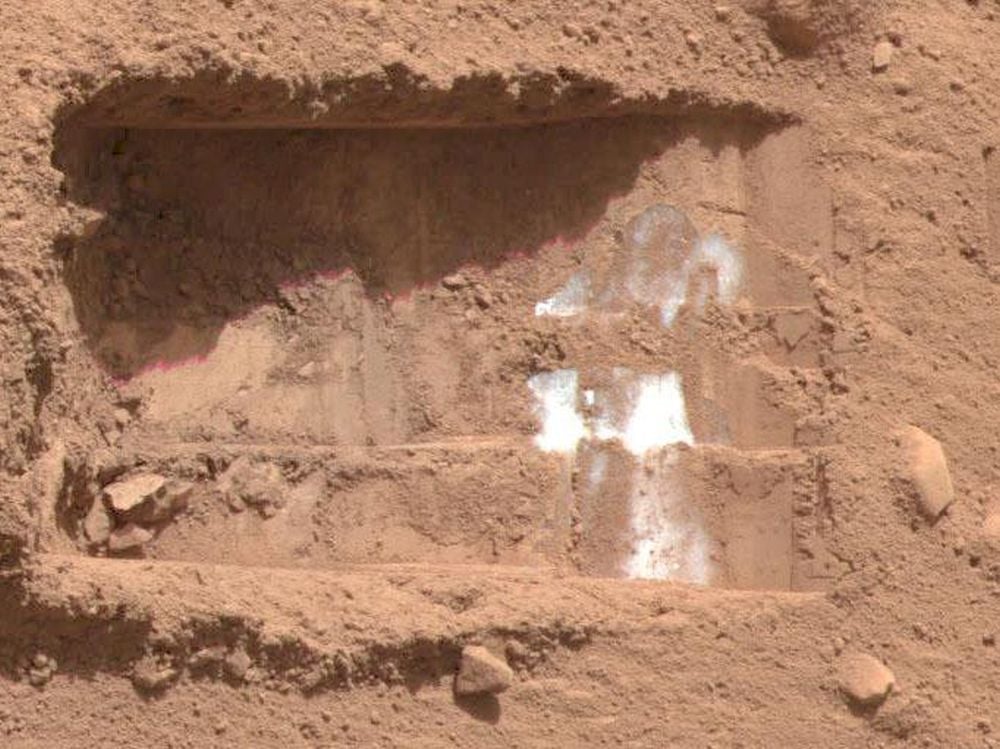

Frozen in time, ancient microbes or their remains could be found in Martian ice deposits during future missions to the red planet. By recreating Mars-like conditions in the lab, a team of researchers from NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and Penn State demonstrated that fragments of the molecules that make up proteins in E. coli bacteria, if present in Mars' permafrost and ice caps, could remain intact for over 50 million years, despite harsh and continuous exposure to cosmic radiation.
Continue reading
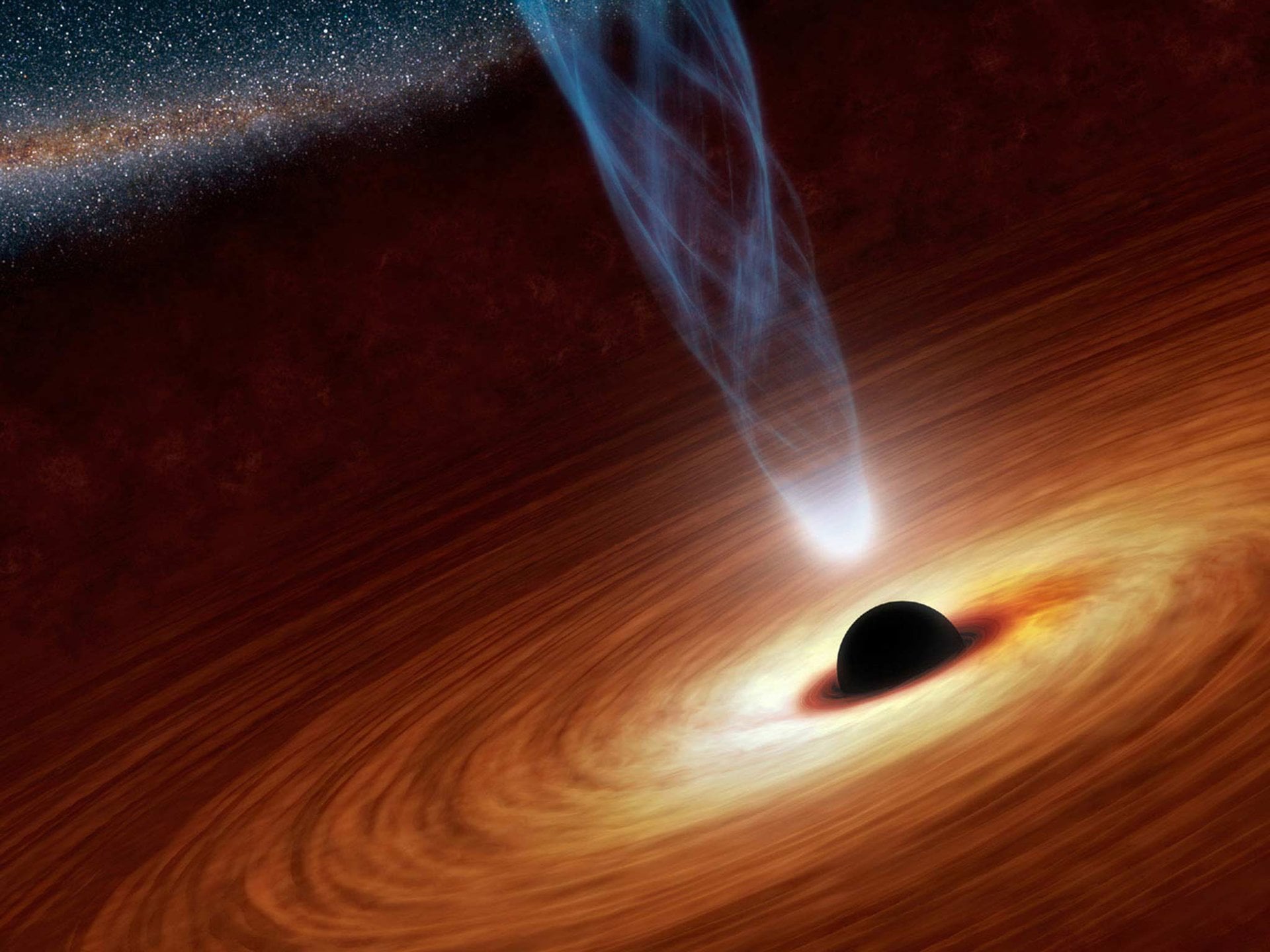

In a recent study, theoretical physicists at Goethe University Frankfurt described the origin of powerful jets emanating from the core regions of galaxies using a series of complex simulations.
Continue reading
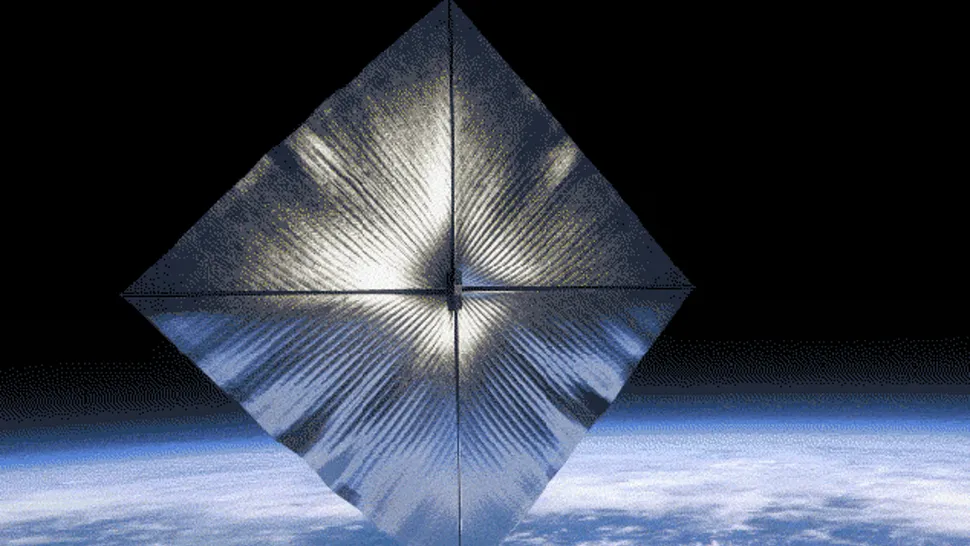
Use cases for smart materials in space exploration keep cropping up everywhere. They are used in everything from antenna deployments on satellites to rover deformation and reformation. One of the latest ideas is to use them to transform the solar sails that could primarily be used as a propulsion system for a mission into a heat shield when that mission reaches its final destination. A new paper from Joseph Ivarson and Davide Guzzetti, both of Auburn’s Department of Aerospace Engineering, and published in Acta Astronautica, describes how the idea might work and lists some potential applications exploring various parts of the solar system.
Continue reading

Rather randomly I’ve just returned from a theatre tour where my science show featured yeast in one of the experiments, so when research about yeast surviving Martian conditions crossed my desk, it immediately piqued my interest. These microscopic fungi that help our bread rise and our beer ferment might just have what it takes to endure one of the Solar System's harshest environments.
Continue reading
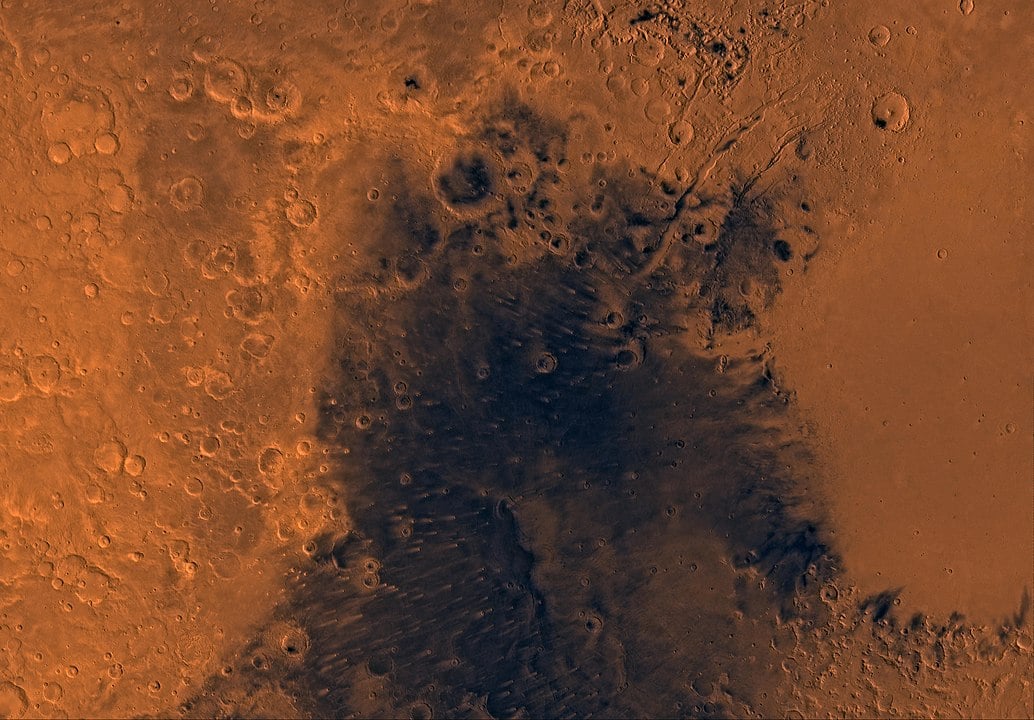

Mars is a planet of mystery! Its surface today is cold and dry, yet evidence suggests it was once home to flowing water. Most of the planet's remaining ice sits locked away at the poles, but recent observations have detected signals of hydrogen in equatorial regions that could indicate buried ice deposits where the environment should be too warm for ice to survive. How did frozen water end up at Mars's equator? It seems we might find the answer in Martian volcanoes.
Continue reading

White dwarfs are stellar corpses, the slowly cooling remnants of stars that ran out of fuel billions of years ago. Our Sun will eventually share this fate, collapsing into a compact object so dense that the heavier it becomes, the smaller it shrinks. This rather strange property is just one of the aspects of white dwarfs that makes them utterly fascinating and occasionally, utterly baffling. Sometimes we find white dwarfs as part of binary systems and they are usually cool and gently radiating their energy out into space. A team of astronomers have recently discovered a peculiar class of these binary systems that defies expectations. The pair of white dwarfs are orbiting each other faster than once per hour and exhibiting temperatures between 10,000 and 30,000 degrees Kelvin, significantly hotter than expected and twice their usual size.
Continue reading

It rains on the Sun! Although not in any way we'd recognise from Earth. In the Sun's corona, the superheated atmosphere that extends millions of kilometres above its visible surface, cooler blobs of plasma occasionally form and fall back downward in what astronomers are calling coronal rain. Until now, the mechanism behind the rain has remained a mystery especially during solar flares where it seems to accelerate but researchers at the University of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy have finally cracked the puzzle.
Continue reading

Scientists have begun to piece together the origin story of a cataclysmic collision between two black holes that met their fate on an unusual orbital path. The merger, designated GW200208_222617 (that really rolls of the tongue,) stands out among gravitational wave detections as one of the rare events showing clear signs of orbital eccentricity, meaning the black holes followed a squashed, oval shaped orbit rather than a circular one as they spiralled toward their final encounter.
Continue reading
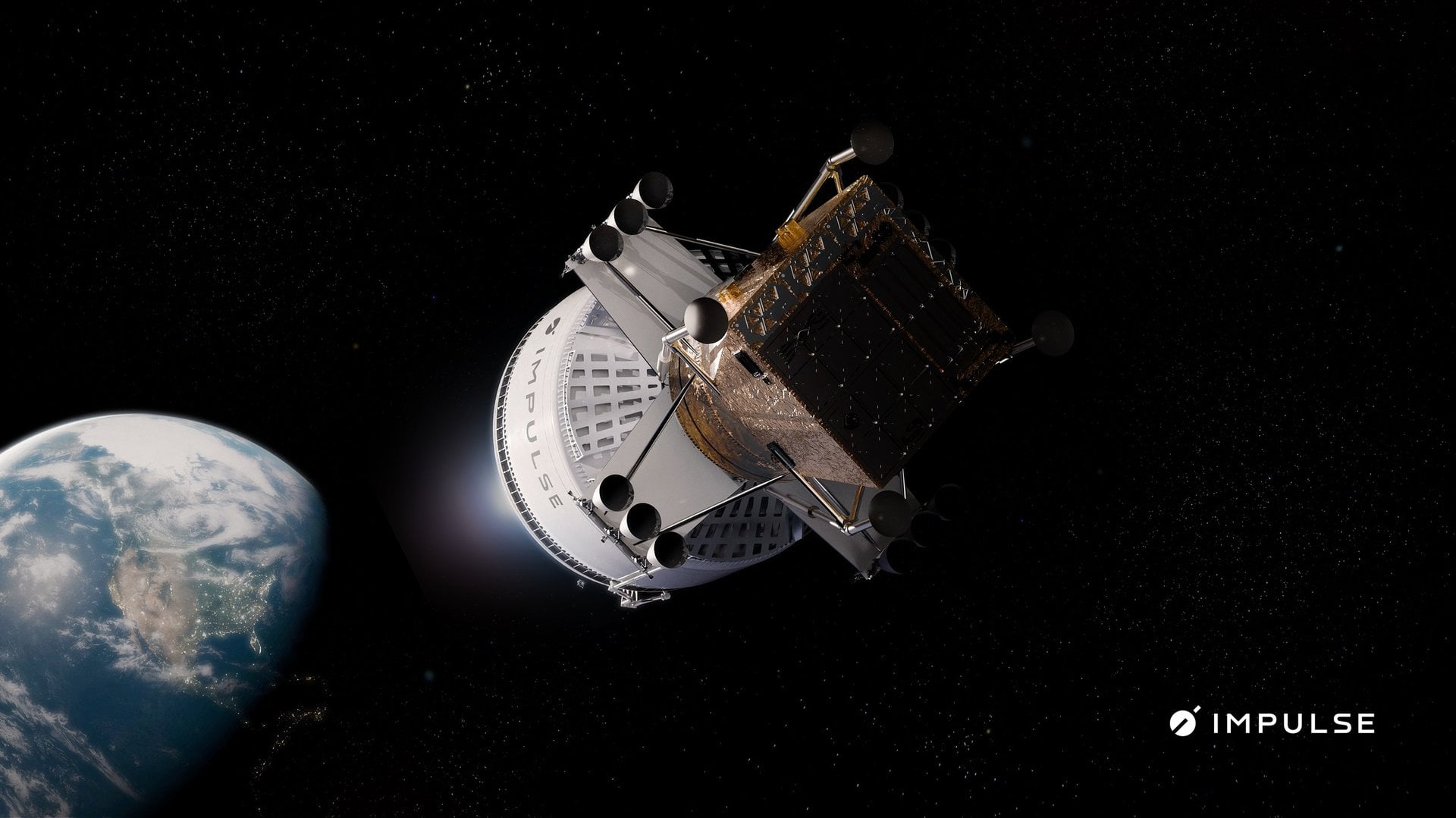

Impulse Space, the California-based venture founded by veteran SpaceX engineer Tom Mueller, has unveiled its proposed architecture for delivering medium-sized payloads to the moon, starting as early as 2028.
Continue reading
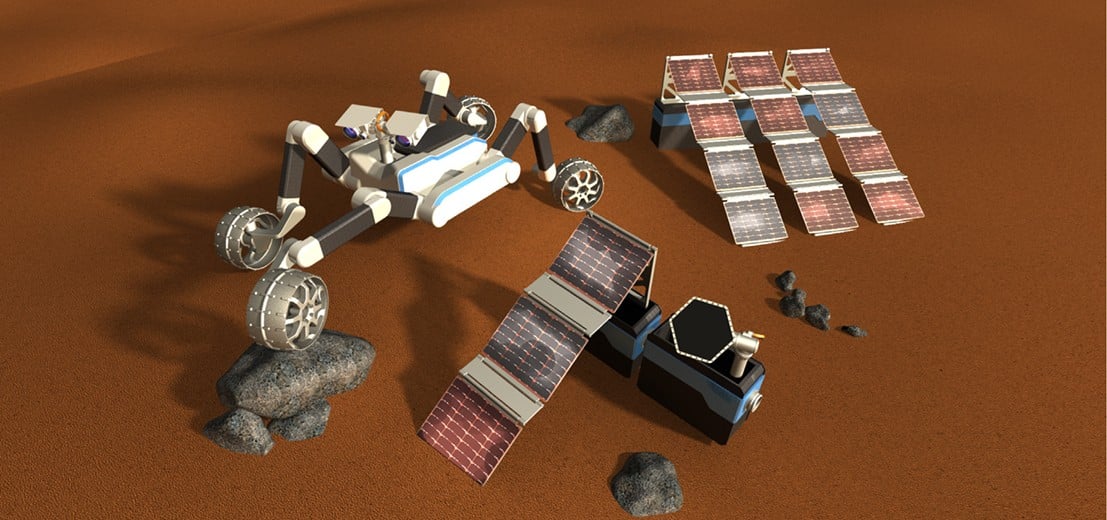

Modularity is taking off in more ways than one in space exploration. The design of the upcoming “Lunar Gateway” space station is supposed to be modular, with different modules being supplied by different organizations. In an effort to extend that thinking down to rovers on the ground, a new paper from researchers at Germany’s space agency (DLR), developed an architecture where a single, modular rover could be responsible for both exploration and carrying payloads around the Moon or Mars.
Continue reading
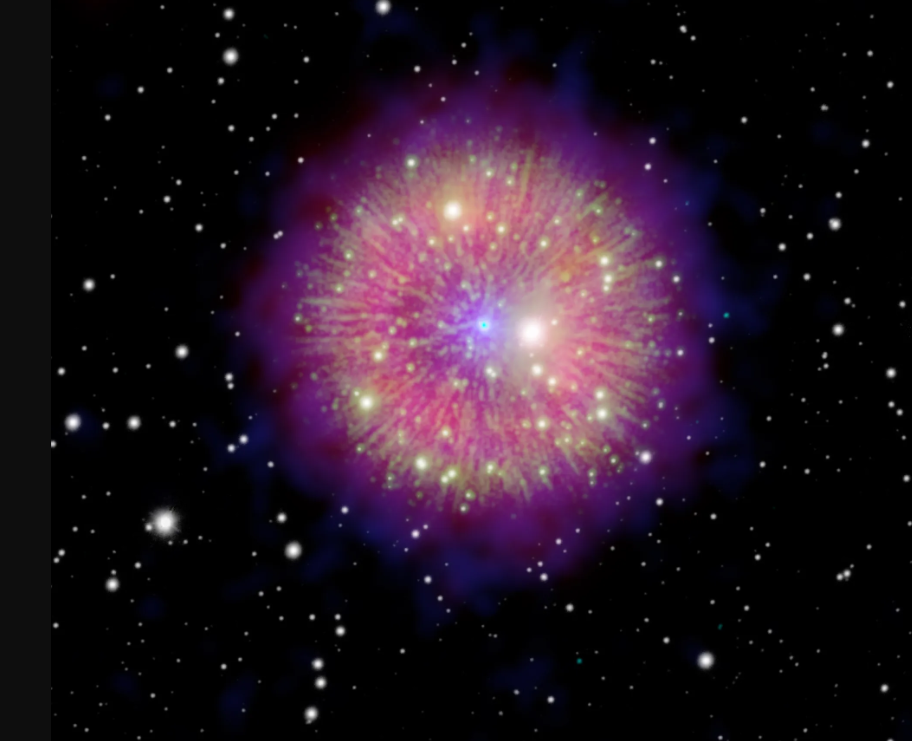

It’s great to see old astronomical observations come to light. Not only can these confirm or refute what’s known about historic astronomical events, but they can describe what early observers actually saw. A recent study cites two Arabic texts that may refer to accounts of two well-known supernovae seen in our galaxy: one in 1006 AD and another in 1181 AD.
Continue reading
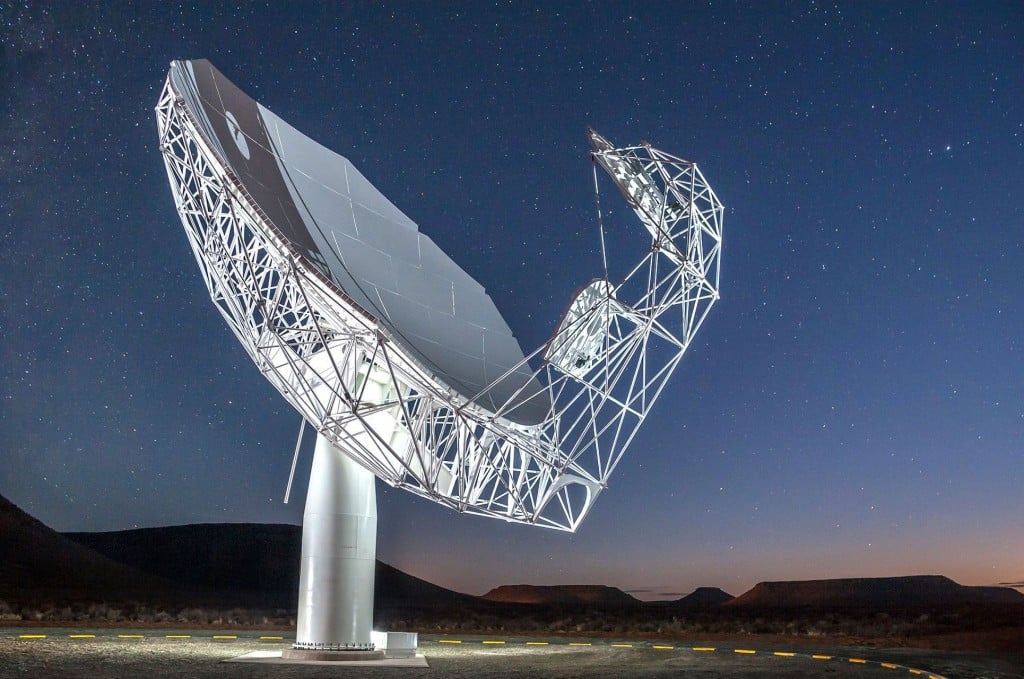

We know lots about our Galaxy yet still, some regions still hold countless secrets. Recently, a team of astronomers using South Africa's MeerKAT radio telescope uncovered 164 of them, compact radio rings. Each one smaller than an arcminute across, were hiding along the plane of the Milky Way, and were just waiting for a telescope powerful enough to reveal them.
Continue reading
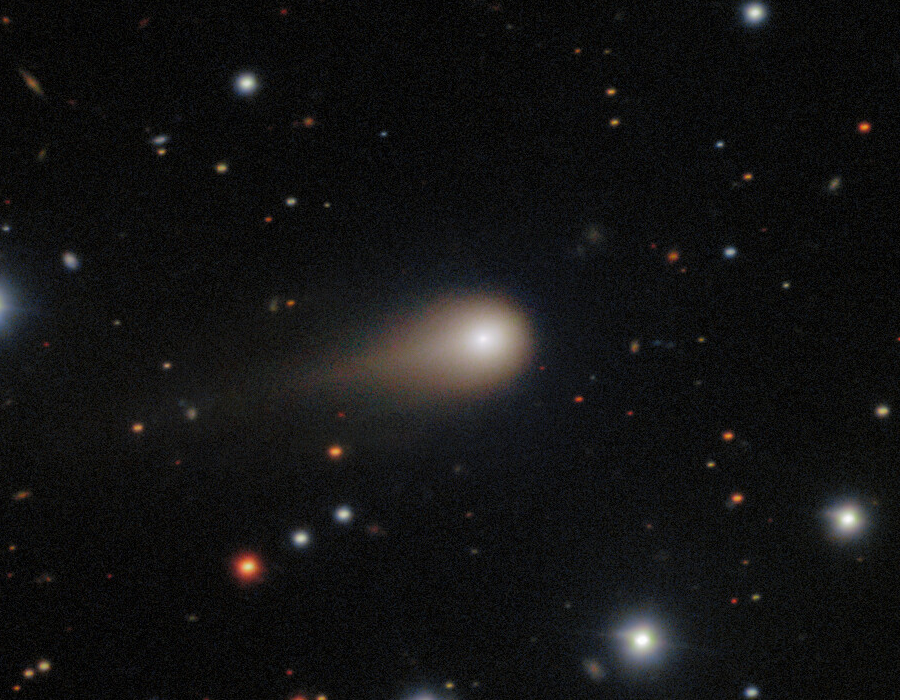

For millions of years, a fragment of ice and dust drifted through interstellar space, its origin, a distant planetary system. This summer, that fragment finally entered our Solar System, becoming only the third confirmed interstellar visitor and earning the designation 3I/ATLAS. When astronomers at Auburn University pointed NASA's Swift Observatory toward this icy chunk, they detected water vapour streaming from its surface. It was revealed through the faint ultraviolet glow of hydroxyl molecules and was completely unexpected.
Continue reading

SpaceX closed out a dramatic chapter in the development of its super-heavy-lift Starship launch system with a successful flight test that mostly followed the script for the previous flight test.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today

















