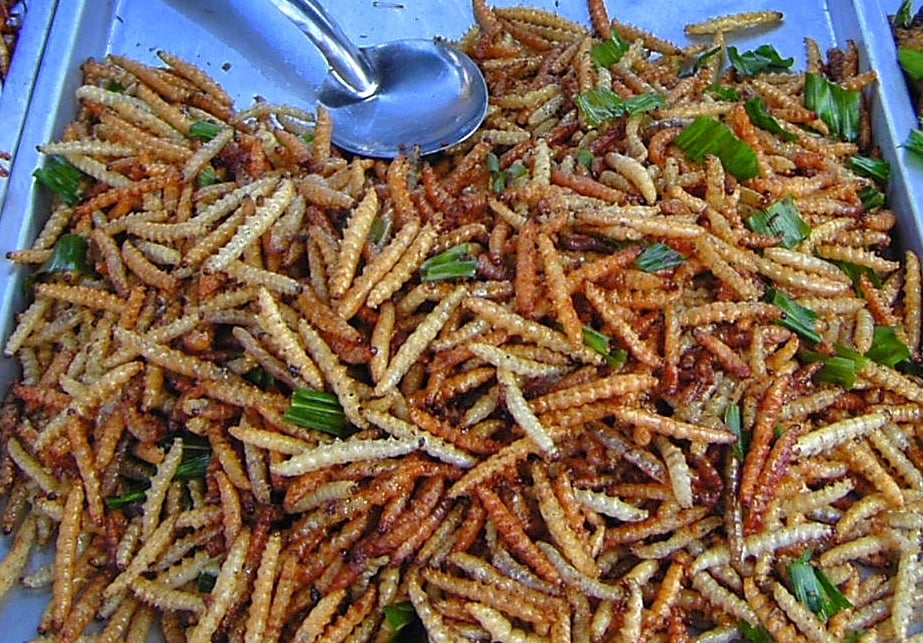

Insects have been travelling to space since 1947, but now they might become dinner for astronauts on missions to the Moon and Mars. A new European Space Agency study explores whether crickets and mealworms could provide sustainable protein for future space explorers, with research showing many species handle microgravity surprisingly well, even completing entire life cycles in orbit. Is it possible that these tiny creatures could become essential for humanity's expansion beyond Earth.
Continue reading
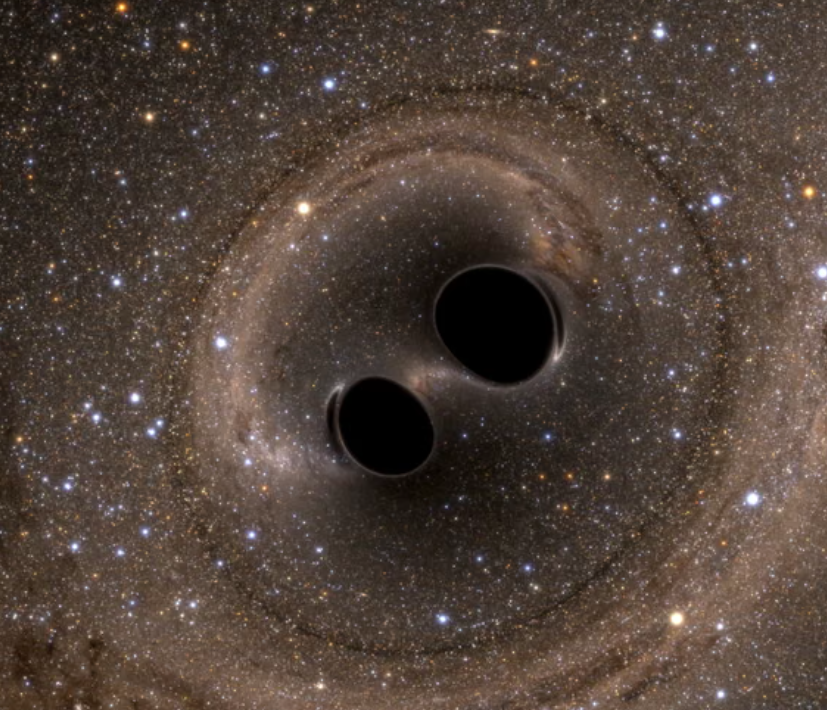

Two black hole collisions detected just a month apart last autumn are challenging our understanding of how they form. One merger features a black hole spinning backwards against its orbit while the other involves one of the fastest rotating black holes ever detected. These unusual properties suggest both are “second generation" black holes, products of earlier collisions formed in violent stellar environments. The precision measurements have also tested Einstein's general relativity changing not only our understanding of black holes but also our understanding of the cosmos.
Continue reading

When massive stars explode as supernovae, the powerful blast can send planets off into space where they drift as rogue or free-floating planets. But what happens to their moons? Can their natural satellites stay bound to these planets, and could tidal heating be a viable source of energy to fuel life on these moons?
Continue reading

Models help scientists understand everything from the particles that make up the universe to massive superstructures of galaxies at the beginning of time. But sometimes they model more mundane, though perhaps even more complex, features - including the course of human civilization. A new paper by Thomas Leppard of the International Archaeological Research Institute and his co-authors, all of whom are also archeologists, propose applying a model of how humans expanded to the different islands across the Pacific Ocean during their early migration to what glean insights into how humanity should manage our colonization of space.
Continue reading
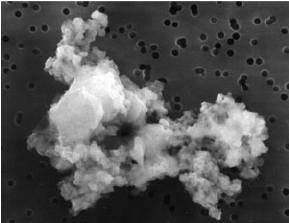
Space dust provides more than just awe-inspiring pictures like the Pillars of Creation. It can provide the necessary materials to build everything from planets to asteroids. But what it actually looks like, especially in terms of its “porosity” (i.e. how many holes it has) has been an area of debate for astrochemists for decades. A new paper from Alexey Potapov of Friedrich Schiller University Jena and his co-authors suggest that the dust that makes up so much of the universe might be “spongier” than originally thought.
Continue reading
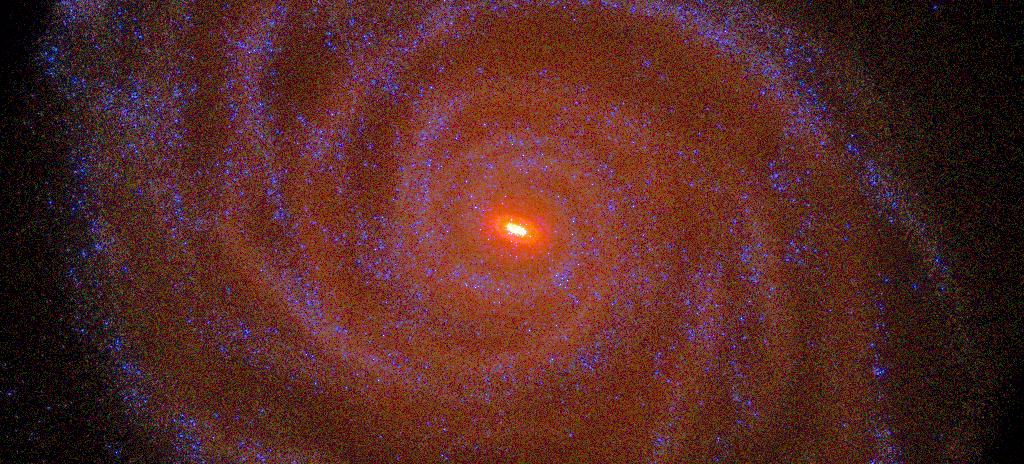

Back in 2009, astronomers using the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope noticed that there was a lot more gamma-ray light coming from the center of the Milky Way than might otherwise be expected given the objects there. Since then, two theories have appeared to explain this Galactic Center Excess (GCE) as it’s become known. One theory posits that the extra gamma rays are created by thousands of unseen milli-second pulsars (MSPs) in the Galactic center, while the other suggests that dark matter annihilating itself could also be the source. A new paper from Moortis Muru and hisco-authors at the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP) hasn’t necessarily solved the conundrum, but does level the playing field between the two theories again.
Continue reading
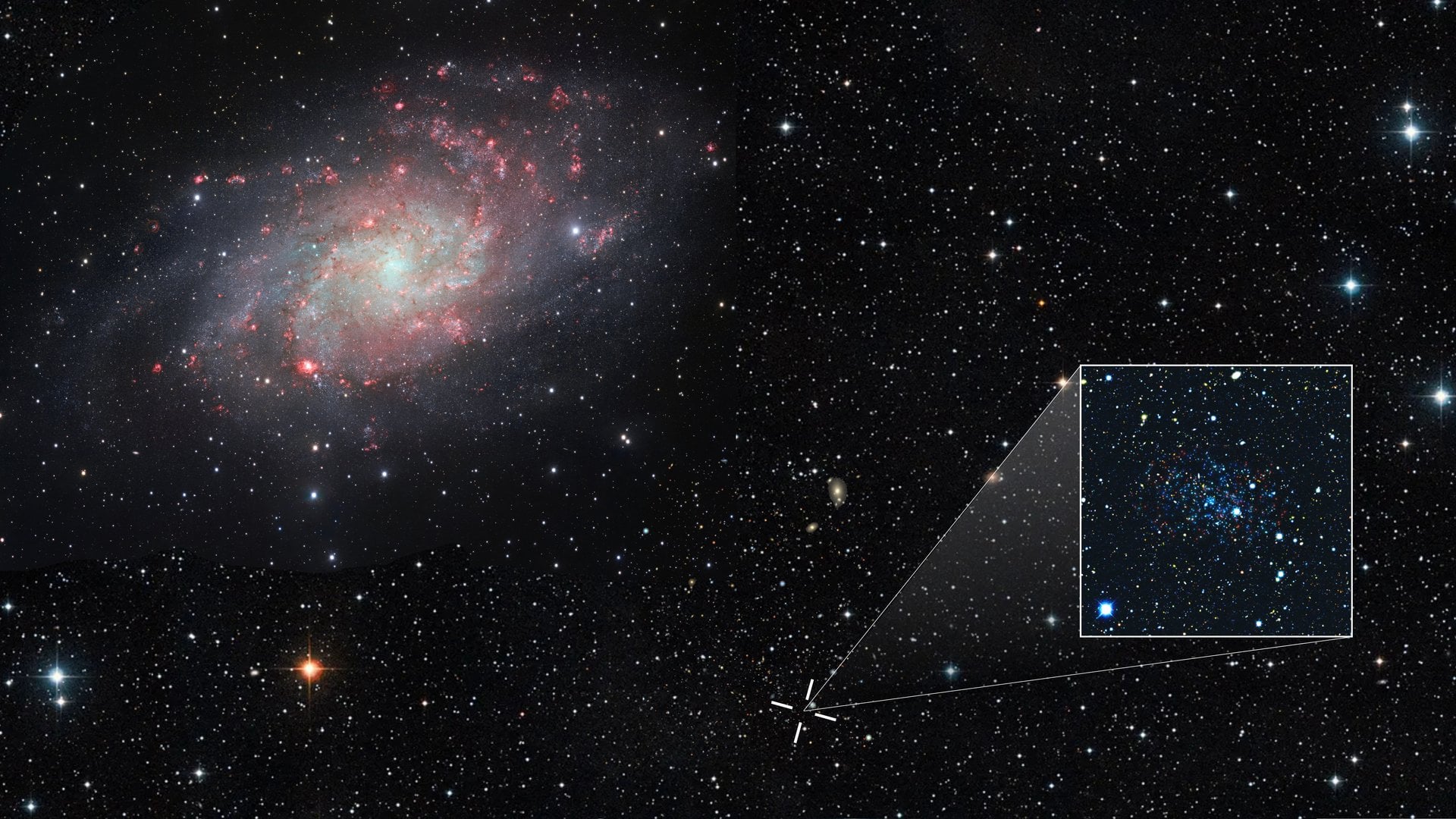

An international team of researchers, led by the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP), has shed light on a decades-long debate about why galaxies rotate faster than expected, and whether this behaviour is caused by unseen dark matter or a breakdown of gravity on cosmic scales.
Continue reading
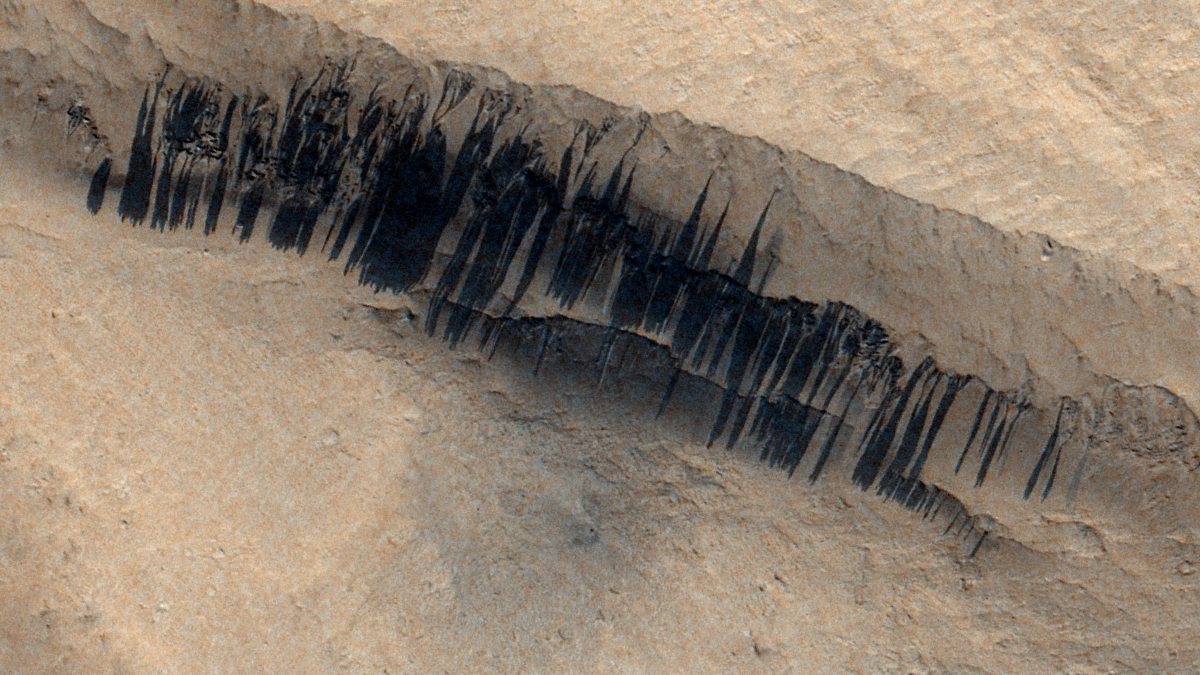

The ESA's ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) recently captured images of streaks formed from a dust avalanche on the slopes of Apollinaris Mons the night before Christmas in 2023. A new study reveals that these types streaks are largely the result of seasonal factors, rather than meteoroid impacts.
Continue reading

It’s almost become expected that many space telescopes and probes can have “extended missions”. Both Voyagers are still sending data back 40+ years after their 5-year primary mission ended. But figuring out what to do with those spacecraft after their primary mission takes some negotiation. One such craft that will reach its end-of-mission in 2030 is Euclid, which is currently on a mission to map the “dark universe” of dark energy and dark matter. According to a new paper from Luigi “Rolly” Bedin of the Astronomical Institute of Padova, which is available in pre-print form on arXiv, for its second act we could turn Euclid into the most powerful astrometric telescope ever made.
Continue reading
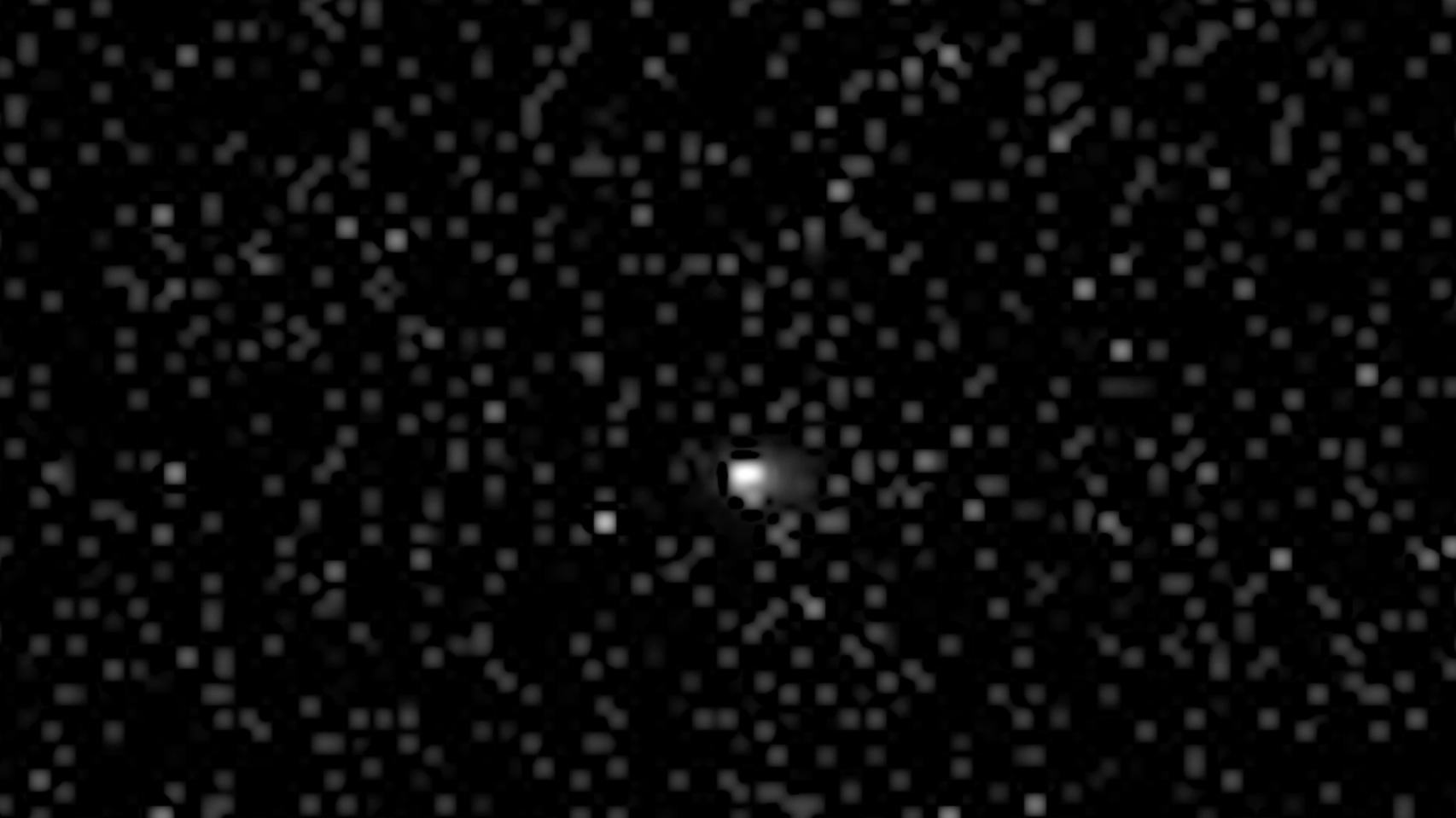

Using its high-resolution camera, China's Tianwen-1 orbiter has successfully observed the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS at a distance of about 30 million kilometers, according to the China National Space Administration (CNSA).
Continue reading
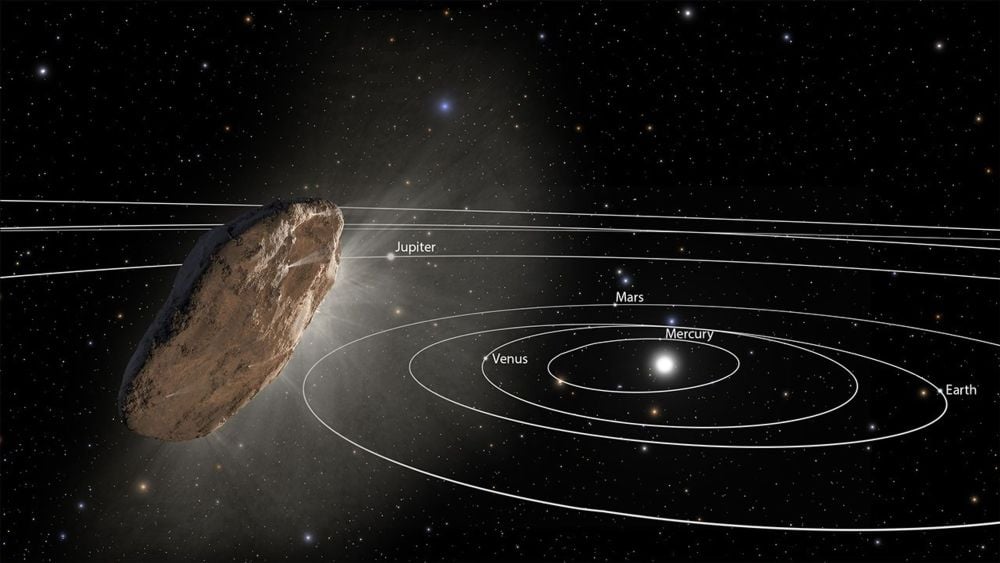
We're only starting to awaken to the passage of interstellar objects through our inner Solar System. So far we know of three, but there are bound to be many more. Do they pose an impact threat to Earth?
Continue reading
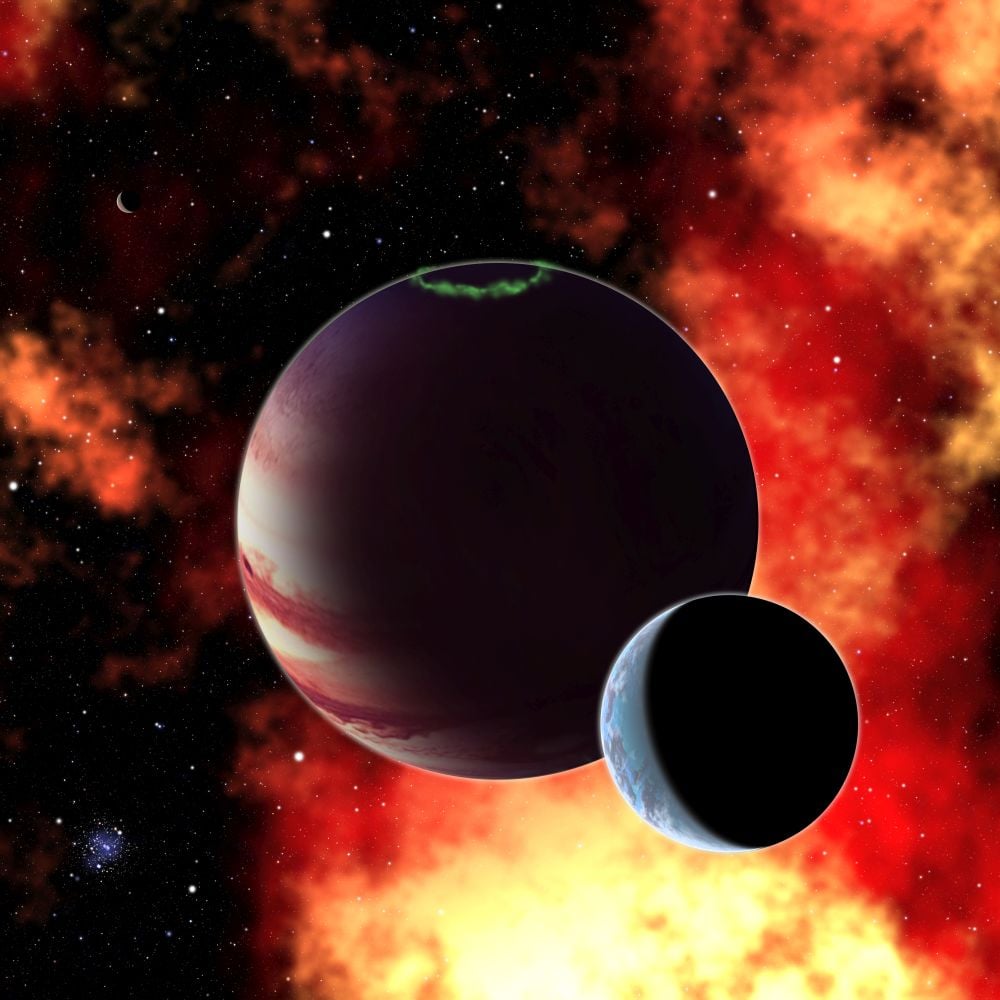

The planets in our Solar System host hundreds of moons, so it seems likely that planets in other solar systems do, too. New research examines the likelihood of rocky planets around M dwarfs having exomoons, and it doesn't look good. They don't last long enough for them to give life a helping hand like Earth's moon has.
Continue reading
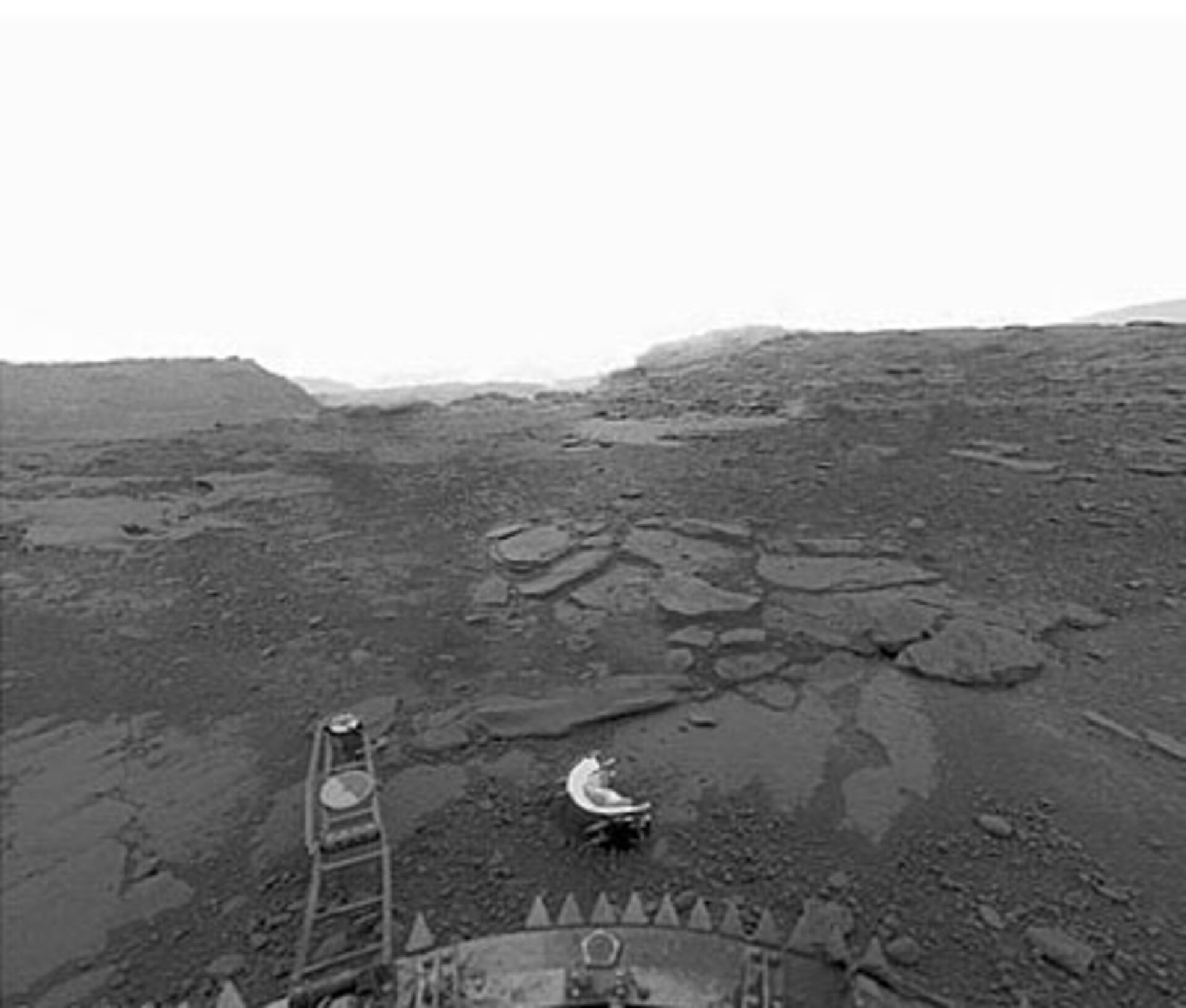

Conditions on Venus’ surface have largely remained a mystery for decades. Carl Sagan famously pointed out that people were quick to jump to conclusions, such as that there are dinosaurs living there, from scant little evidence collected from the planet. But just because we have little actual data doesn’t mean we can’t draw conclusions, and better yet models, from the data we do have. A new paper from Maxence Lefèvre of the Sorbonne and his colleagues takes what little data has been collected from Venus’ surface and uses it to valid a model of what the wind and dust conditions down there would be like - all for the sake of making the work of the next round of Venusian explorer easier.
Continue reading
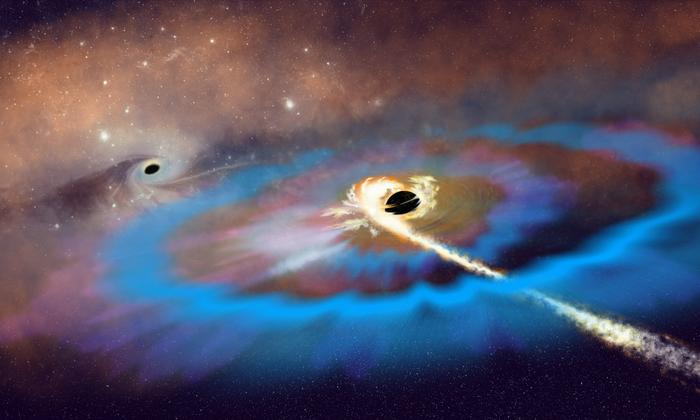

New study reveals, for the first time, a tidal disruption event (TDE), where a black hole tears apart a star, occurring outside the center of a galaxy that produced exceptionally strong and rapidly evolving radio signals. This rare discovery shows that supermassive black holes can exist and remain active far from galactic cores, challenging current understanding of where such black holes reside and how they behave. The event’s delayed and powerful radio outbursts also suggest previously unknown processes in how black holes eject material over time.
Continue reading
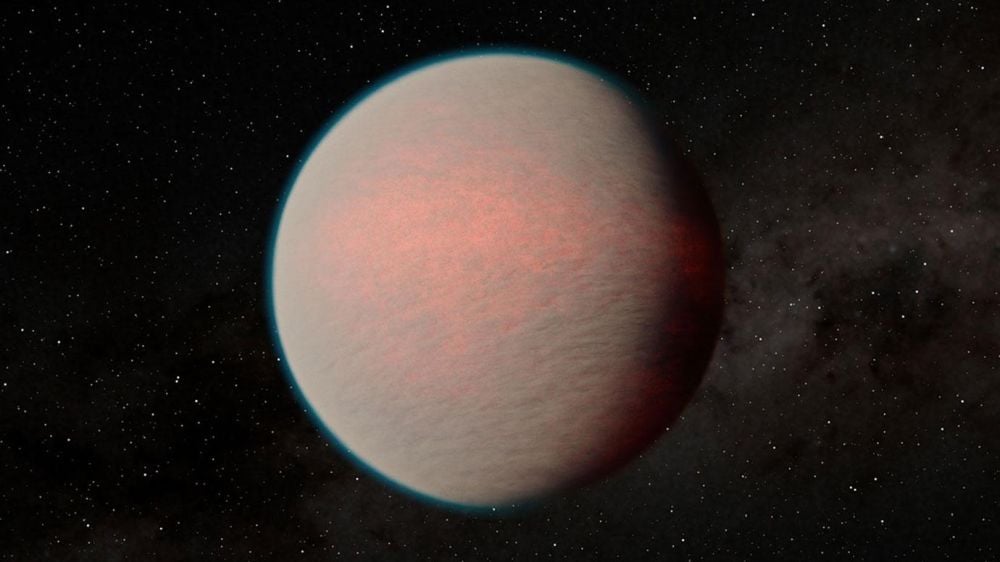

There are no mini-Neptunes in our Solar System, yet they seem to be one of the most common types of exoplanets out there. Previous research shows that these planets are magma oceans. But new research based on JWST data shows that many of them may actually have solid surfaces.
Continue reading
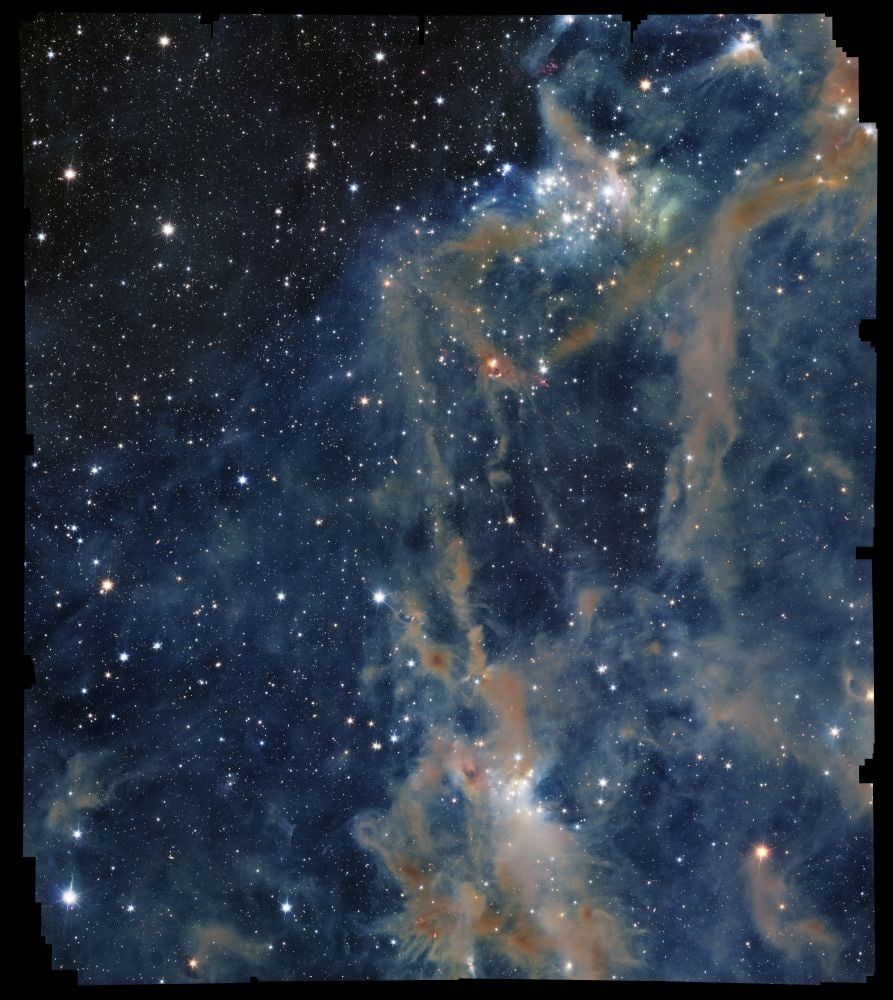

The Euclid Space Telescope found some stars hiding in thick gas and dust in the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. They're inside a so-called dark cloud named LDN 1641.
Continue reading
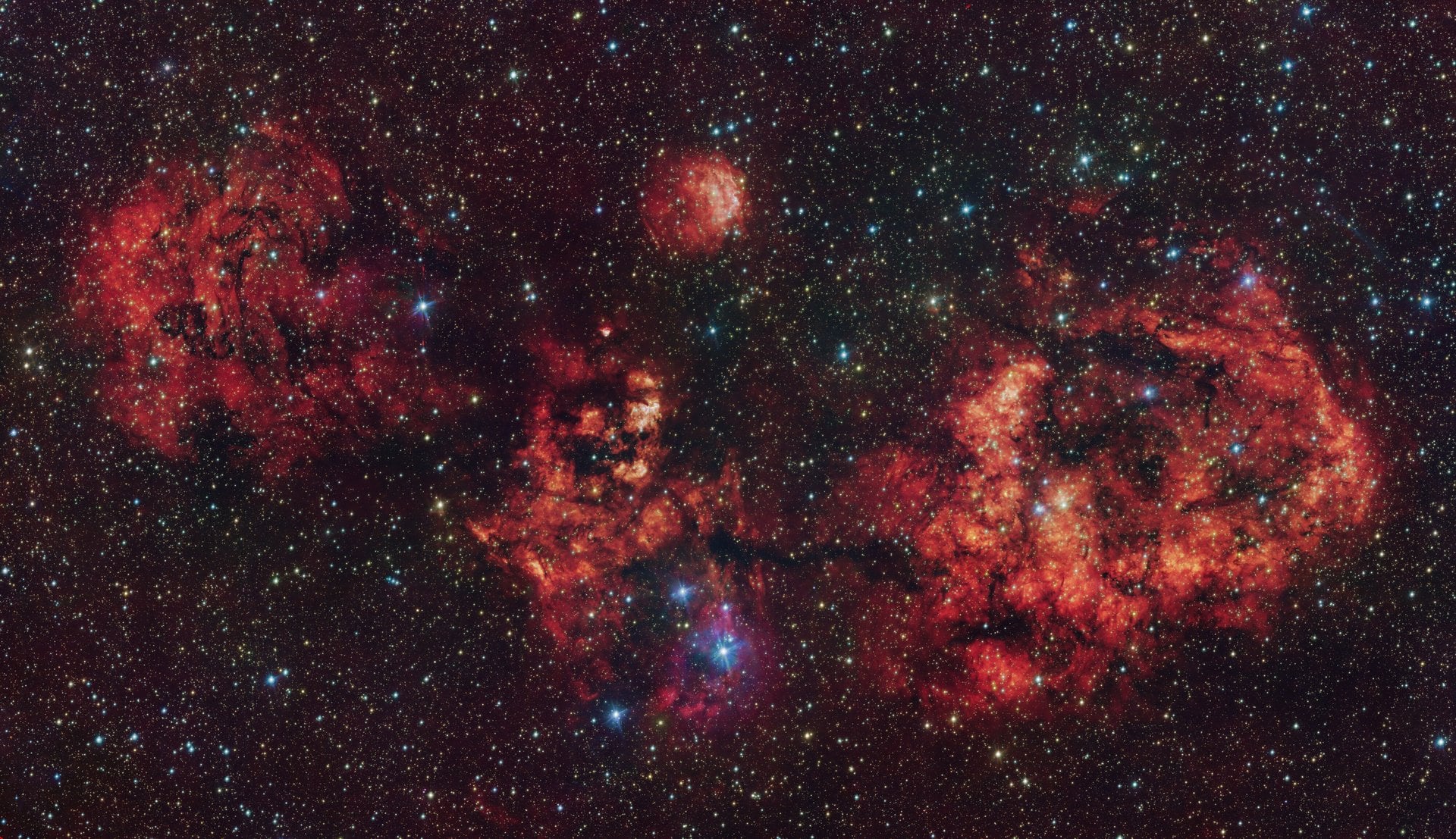

A spooky bat has been spotted flying over the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO’s) Paranal site in Chile, right in time for Halloween. Thanks to its wide field of view, the VLT Survey Telescope (VST) was able to capture this large cloud of cosmic gas and dust, whose mesmerising appearance resembles the silhouette of a bat.
Continue reading
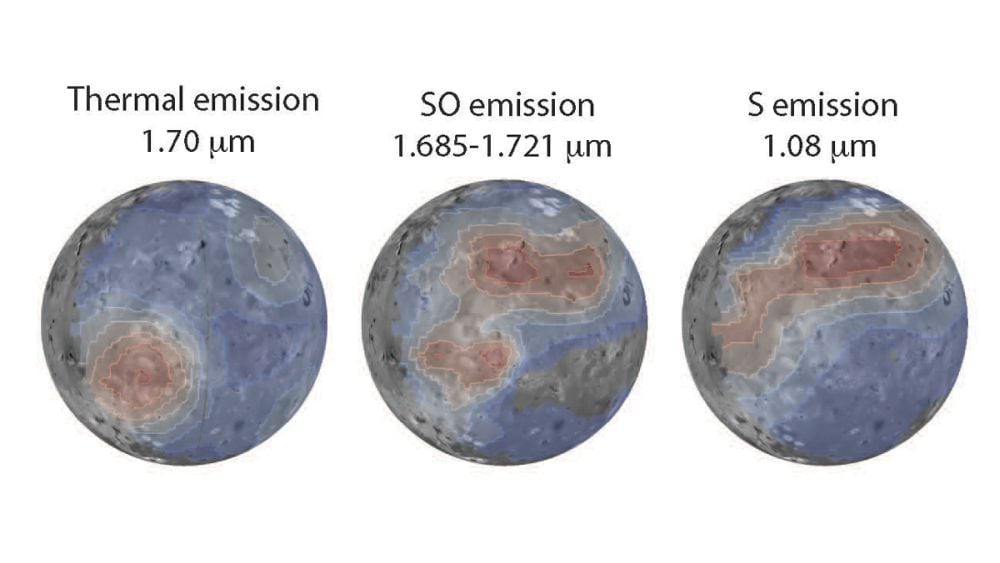
Trapped in a gravitational push and pull between Jupiter and other Jovian moons, Io is constantly being stretched and compressed. Heat generated by these contortions has melted pockets of the moon's interior so much that Io is our solar system's most volcanically active body. New research shows how its atmosphere is shaped both by volcanoes and by Jupiter's overpowering magnetosphere.
Continue reading

When neutron stars collide, neutrinos can play a significant role in the outcome. Even more so when you take flavor mixing into account.
Continue reading
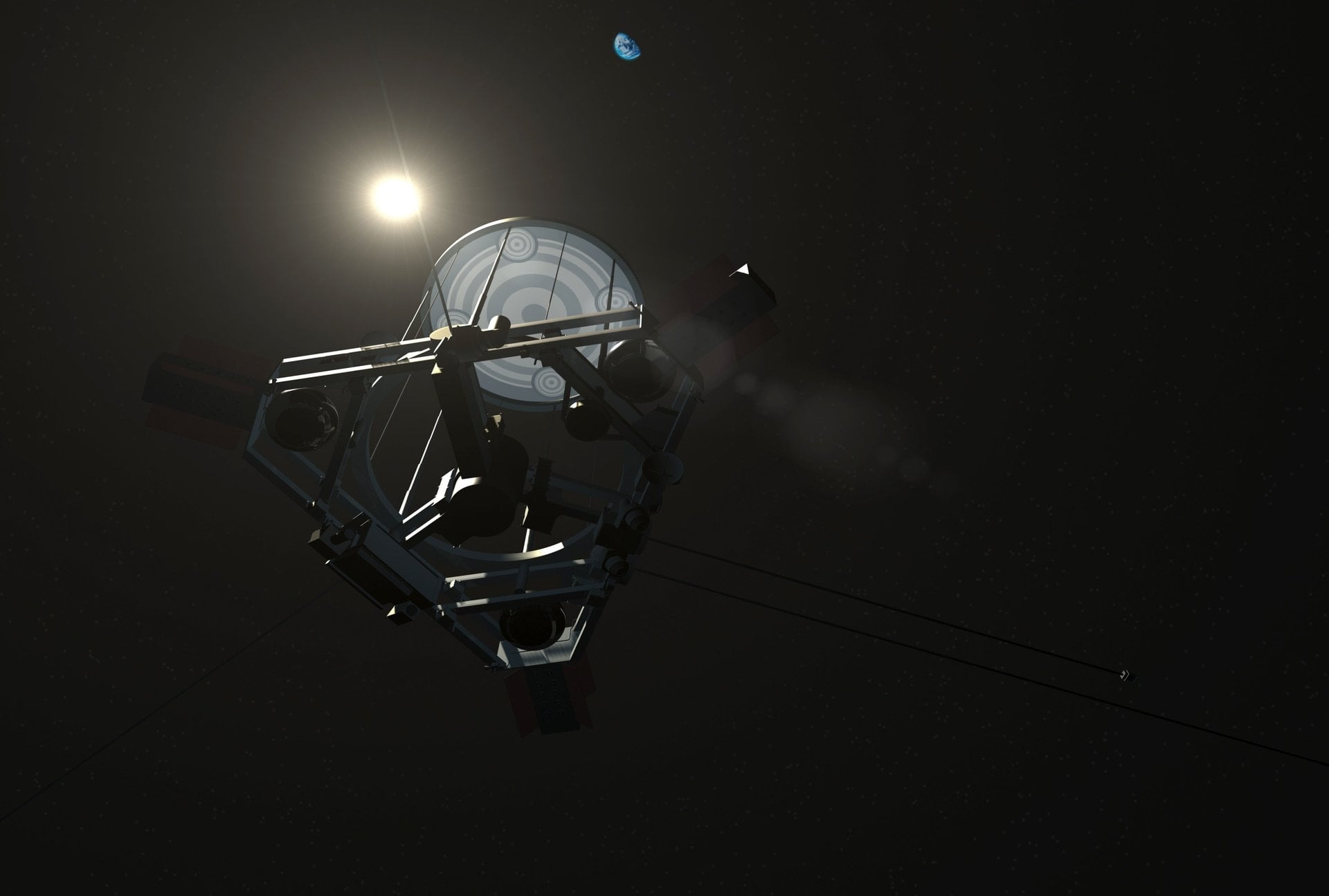

A new study proposes how we could look for signs of self-replicating (Von Neumann) probes that would prove that the Solar System has been explored by an advanced extraterrestrial intelligence (ETI).
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today


















