
Rocky exoplanets orbiting red dwarfs are in a tough spot. Their stars are known for violent flaring that can destroy their atmospheres. But it's possible that asteroid impacts could later recreate their atmospheres.
Continue reading
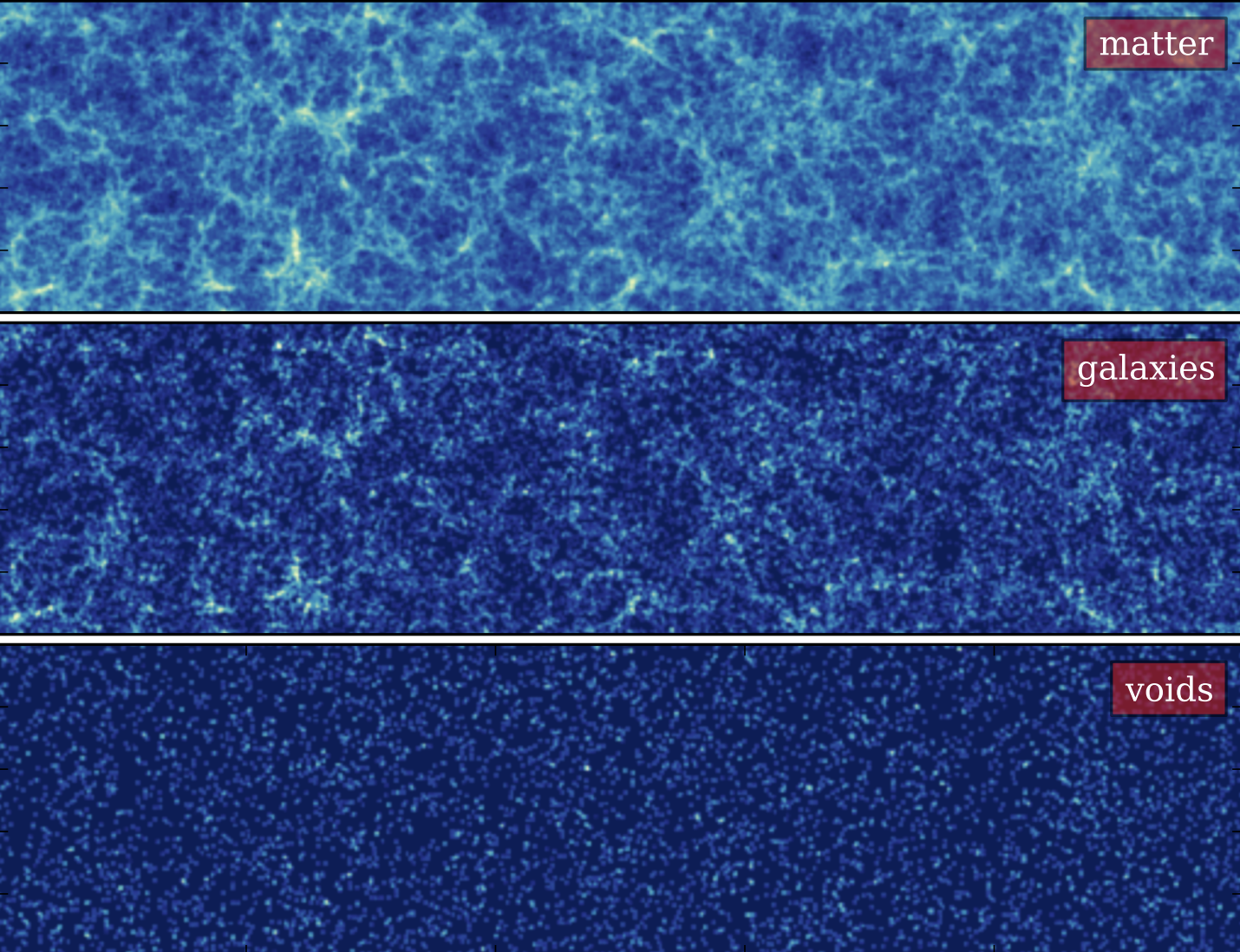
If we take out all the matter, neutrinos, dark matter, cosmic rays, and radiation from the deepest parts of the voids the only thing left is empty space.
Continue reading

Cosmic inflation helps black holes grow quickly, but it can't explain how supermassive black holes grew to billions of solar masses in less than 500 million years.
Continue reading
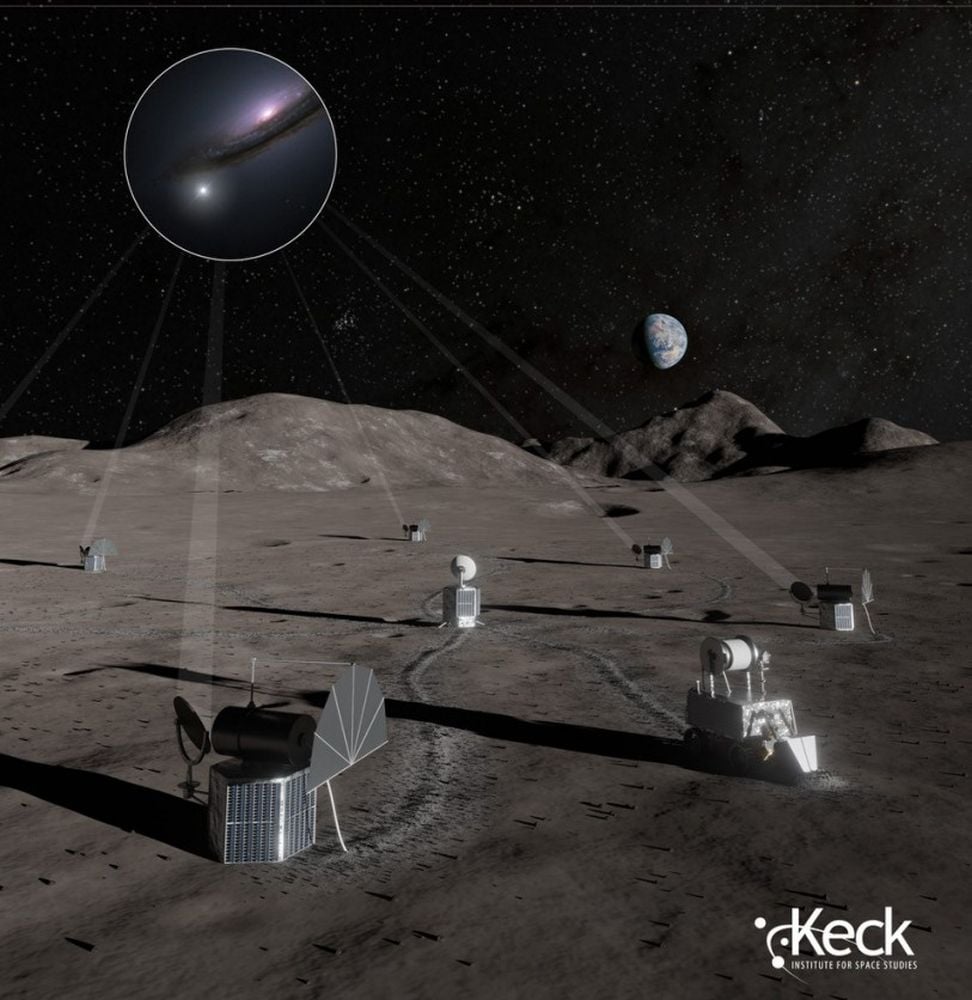

A new report outlines the benefits and obstacles to a lunar telescope. It comes from the Keck Institute for Space Studies, and presents an idea for a lunar optical interferometer. The authors say it could outperform powerful space telescopes.
Continue reading
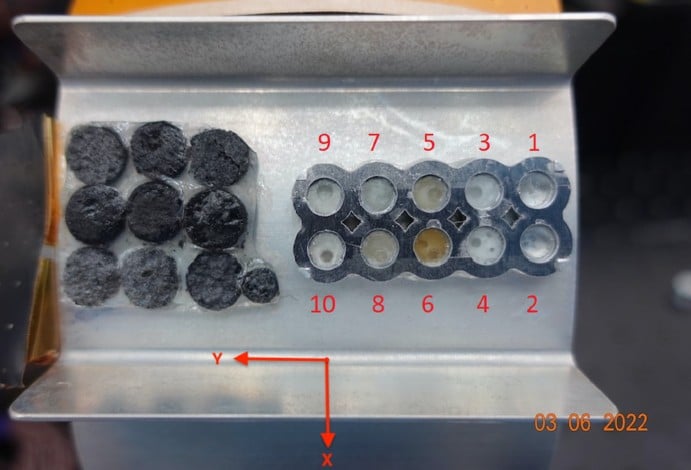

Sometimes space exploration doesn’t go as planned. But even in failure, engineers can learn, adapt, and try again. One of the best ways to do that is to share the learning, and allow others to reproduce the work that might not have succeeded, allowing them to try again. A group from MIT’s Space Enabled Research Group, part of its Media Lab, recently released a paper in Space Science Reviews that describes the design and testing results of a pair of passive sensors sent to the Moon on the ill-fated Rashid-1 rover.
Continue reading

With unprecedented detail, a team of astronomers led by MPE have imaged the youngest disks around new-born stars. Astronomers used to think that planet formation followed star formation. But these glowing, chaotic disks are hotter and heavier than expected, hinting that planets may start forming much earlier than previously thought.
Continue reading
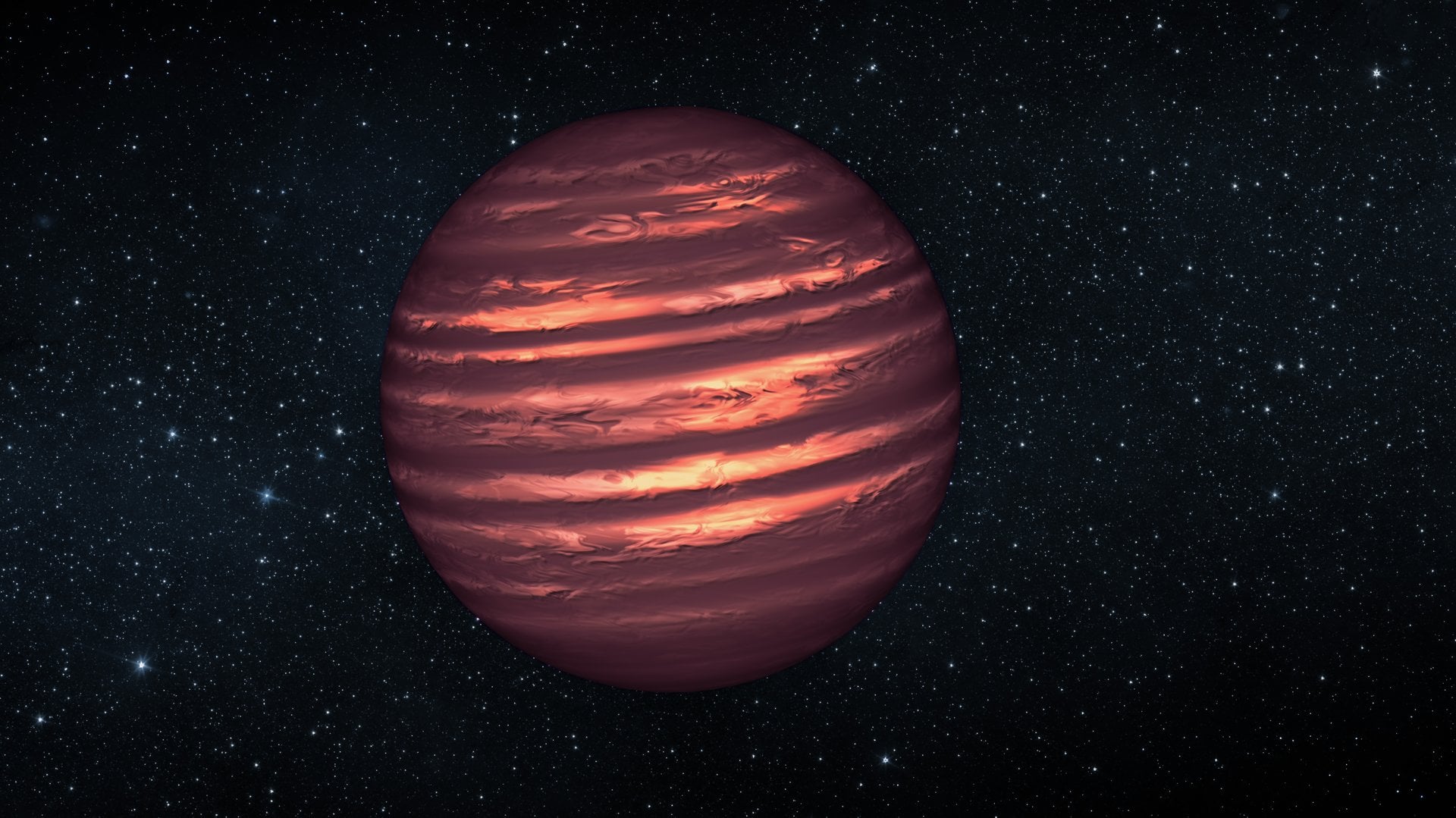
An international team of astronomers using the combined powers of space-based and ground-based observatories, including the W.M. Keck Observatory and Subaru Telescope on Maunakea, Hawaiʻi Island, have discovered a brown dwarf companion orbiting a nearby red dwarf star, providing key insight into how stars and planets form.
Continue reading
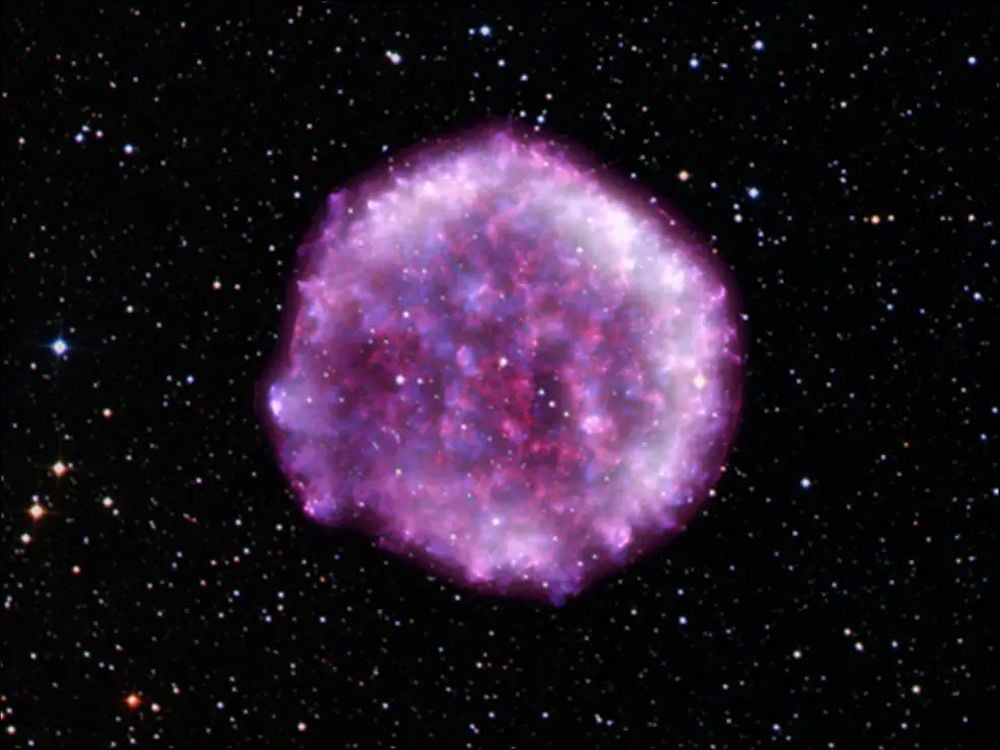

Before a supernova finally explodes, its progenitor ejects massive amounts of gas into its surroundings. When the doomed star finally explodes, its blast wave slams into this material. This is one of a supernova's signatures, and researchers have figured out how to detect it.
Continue reading
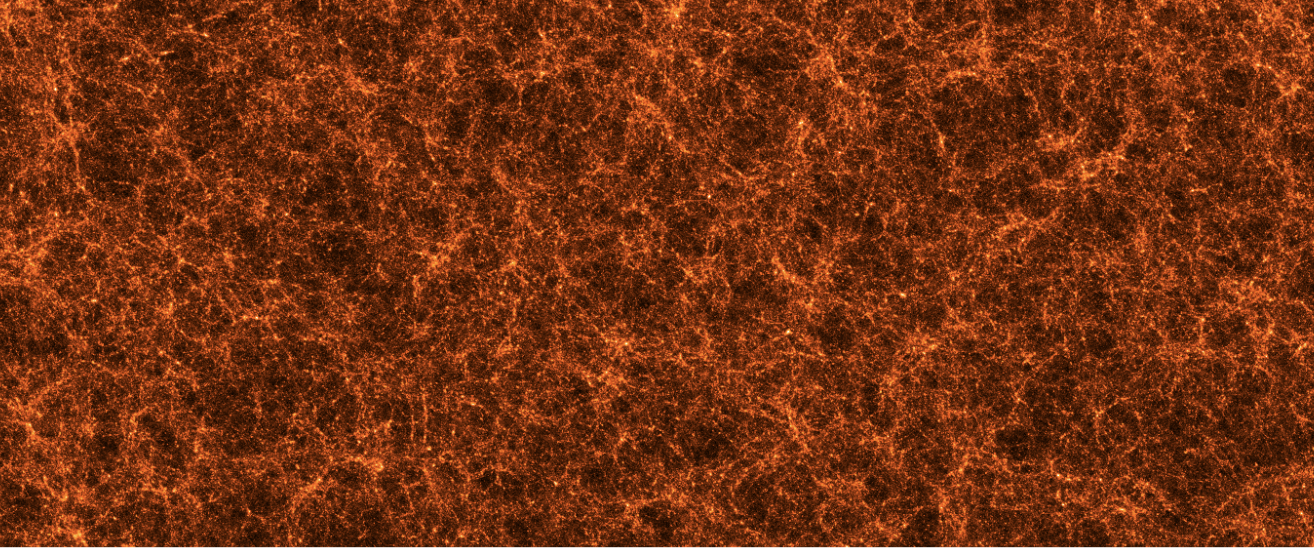
The cosmic voids of the universe are empty of matter. But we all know there’s more to the universe than just matter.
Continue reading
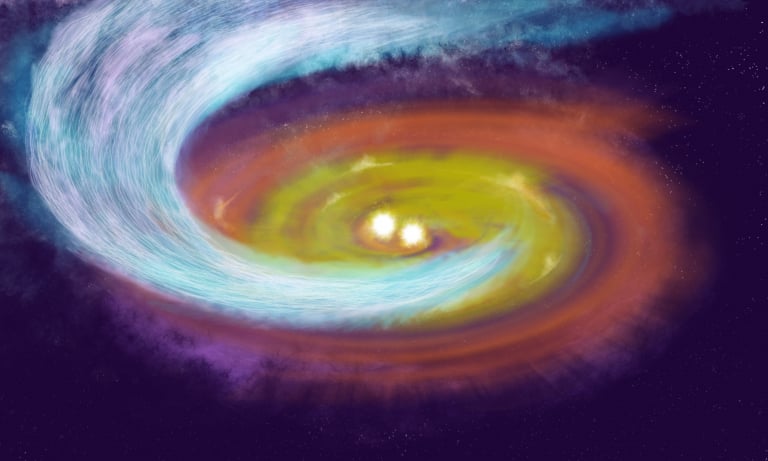

Star formation has a lot of complex physics that feed into it. Classical models used something equivalent to a “collapse” of a cloud of gas by gravity, with a star being birthed in the middle. More modern understandings show a feature called a “streamer”, which funnels gas and dust to proto-stars from the surrounding disc of material. But our understanding of those streamers is still in its early stages, like the stars they are forming. So a new paper published in Astrophysical Journal Letters by Pablo Cortes of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) and his co-authors is a welcome addition to the literature - and it shows a unique feature of the process for the first time.
Continue reading
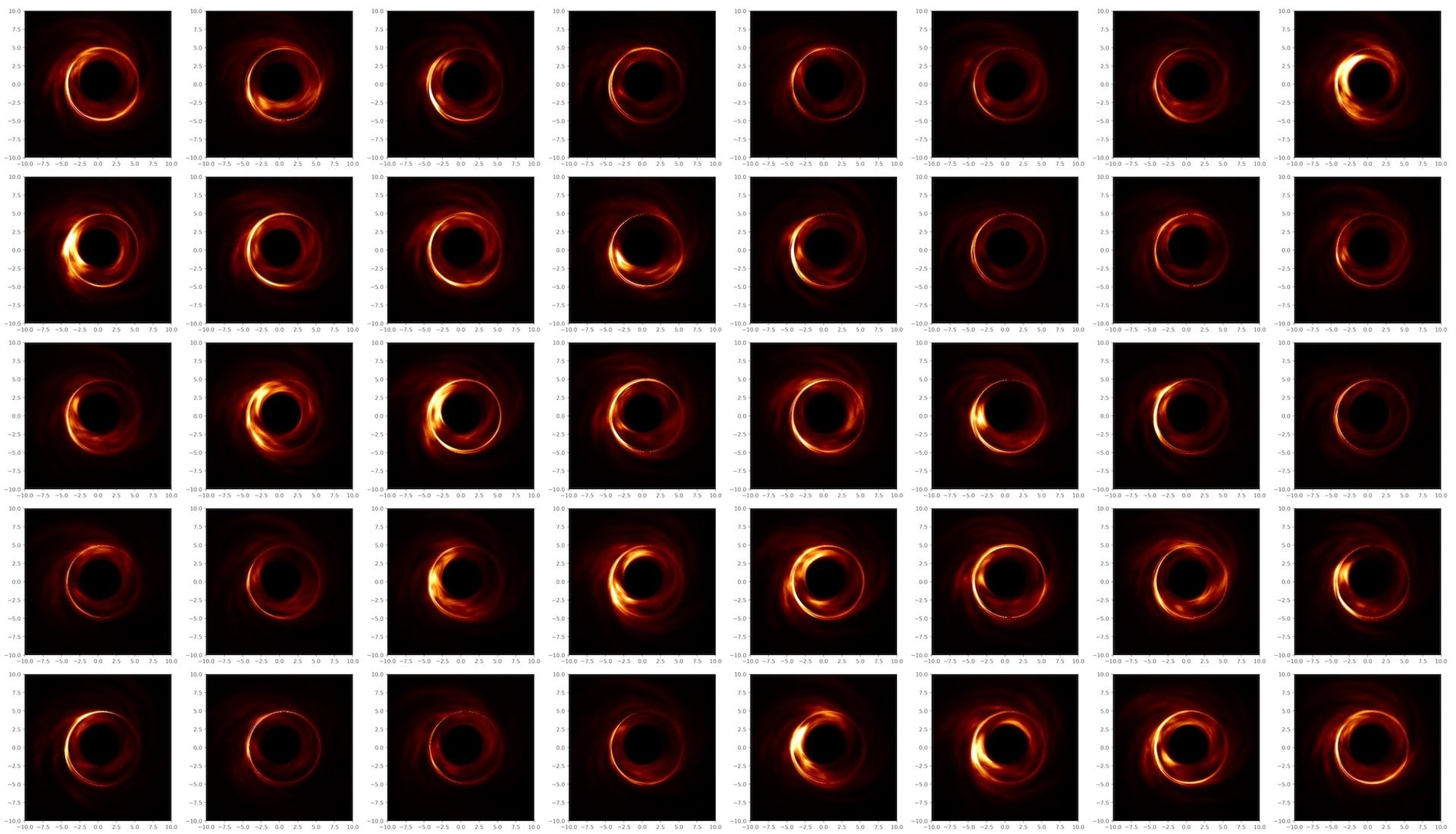
Modeling supermassive black holes is hard, but it's a bit easier if you use a non-singular model.
Continue reading

There is a limit to how big we can build particle colliders on Earth, whether that is because of limited space or limited economics. Since size is equivalent to energy output for particle colliders, that also means there’s a limit to how energetic we can make them. And again, since high energies are required to test theories that go Beyond the Standard Model (BSM) of particle physics, that means we will be limited in our ability to validate those theories until we build a collider big enough. But a team of scientists led by Yang Bai at the University of Wisconsin thinks they might have a better idea - use already existing neutrino detectors as a large scale particle collider that can reach energies way beyond what the LHC is capable of.
Continue reading

Now that we have tools to find vast numbers of voids in the universe, we can finally ask…well, if we crack em open, what do we find inside?
Continue reading

Astronomers found a 3 billion-year-old white dwarf actively accreting material from its former planetary system. This discovery challenges assumptions about the late stages of stellar remnant evolution.
Continue reading
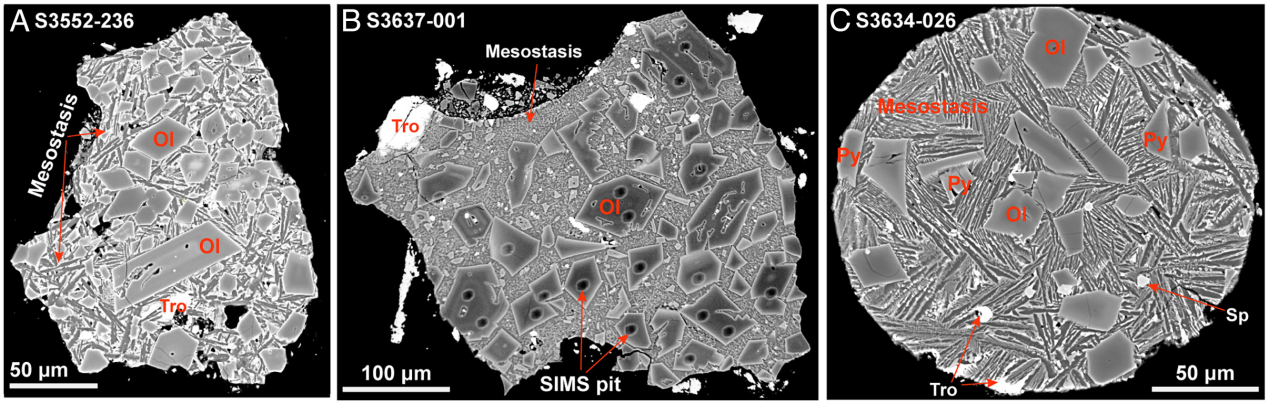
A research team with the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) examined samples returned by the Chang'e-6 mission from the far side of the Moon. They identified minerals that appear to be from a carbonaceous chondrite meteor, which are known to contain water and organic molecules. These findings support the theory that water and the ingredients for life were delivered by asteroids and comets to Earth billions of years ago.
Continue reading
To answer that question of what’s inside a void, we have to first decide what a void…is.
Continue reading
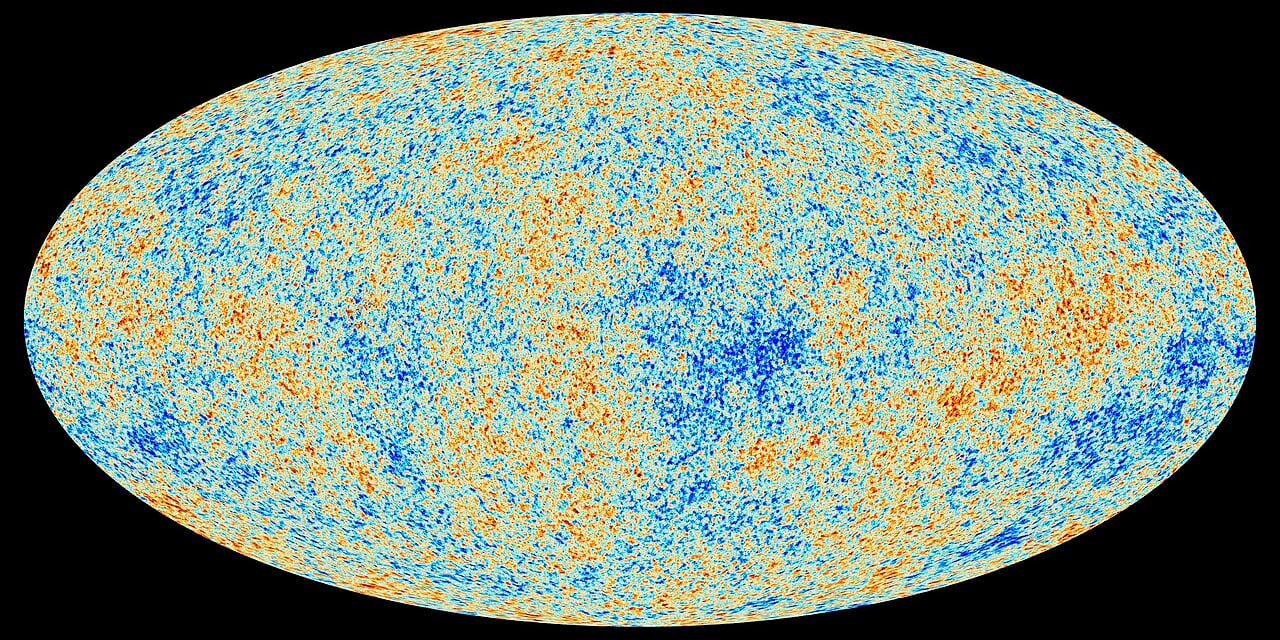
Researchers from Keio University have made the most precise measurement yet of the cosmic microwave background radiation's temperature from seven billion years ago, finding it was approximately 5.13 K, roughly twice today's temperature of 2.7 K. By analysing archived data from the ALMA telescope in Chile, the team confirmed a key prediction of Big Bang model, that the universe cools as it expands, meaning it was hotter in the past. This highly accurate measurement provides strong support for the standard cosmological model and helps scientists better understand the thermal history of our universe.
Continue reading
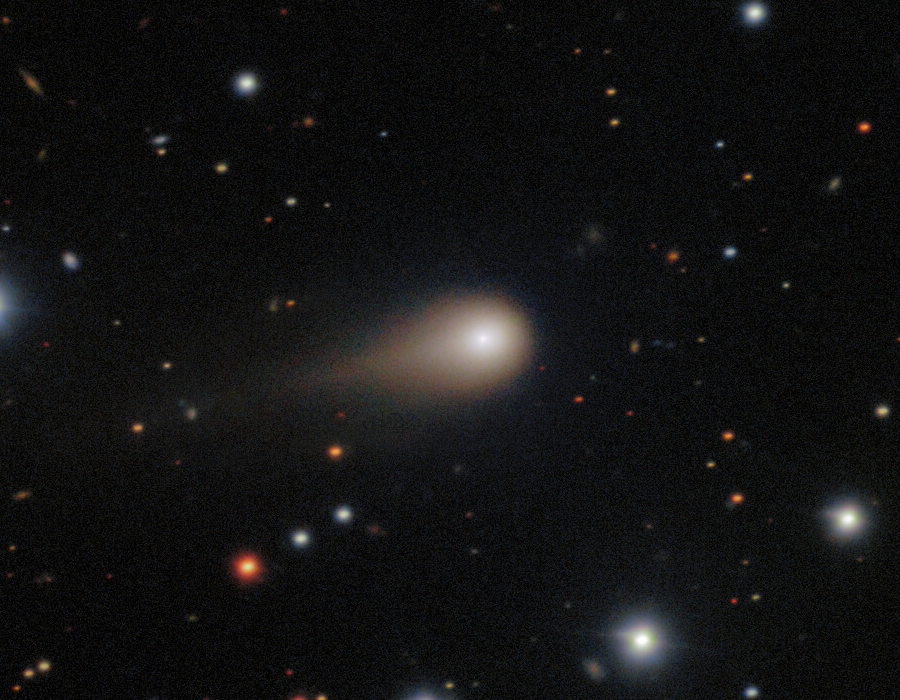

Interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS has undergone dramatic brightening as it approached its closest point to the Sun. Researchers have been using solar monitoring satellites to track it during a period when Earth based observations were impossible due to the comet's position behind the Sun. Analysis of data from STEREO-A, SOHO, and GOES-19 spacecraft revealed the comet brightened at an unexpectedly rapid rate between mid September and late October 2025, with its light showing a distinctly blue colour indicating significant gas emission rather than just reflected sunlight from dust. The comet's unusual behaviour and the cause of its steep brightening remain mysteries that ground based observers will now investigate as it emerges into dark skies.
Continue reading

Scientists at MIT have discovered over 100 different molecules in a stellar nursery called the Taurus Molecular Cloud-1, making it the most chemically diverse interstellar cloud ever observed. Using over 1,400 hours of telescope time, the team found mostly hydrocarbons and nitrogen rich compounds, along with 10 ring shaped aromatic molecules similar to those found in coffee, vanilla, and DNA. This discovery helps solve a decades old mystery about complex organic molecules in space and provides key insights into the chemical conditions that existed before our own Solar System formed.
Continue reading

For the first time, astronomers have mapped the three-dimensional atmosphere of a planet orbiting a distant star, revealing temperature variations and distinct atmospheric regions across an alien world 400 light years away. Using the James Webb Space Telescope to track minute changes in brightness as the scorching gas giant WASP-18b passed behind its star, scientists created a weather map of an exoplanet, transforming these distant worlds from featureless dots into environments we can actually study layer by layer. This new technique could soon map hundreds of other similar hot Jupiters, finally bringing alien atmospheres into focus as real places with their own geography and weather patterns.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today


















