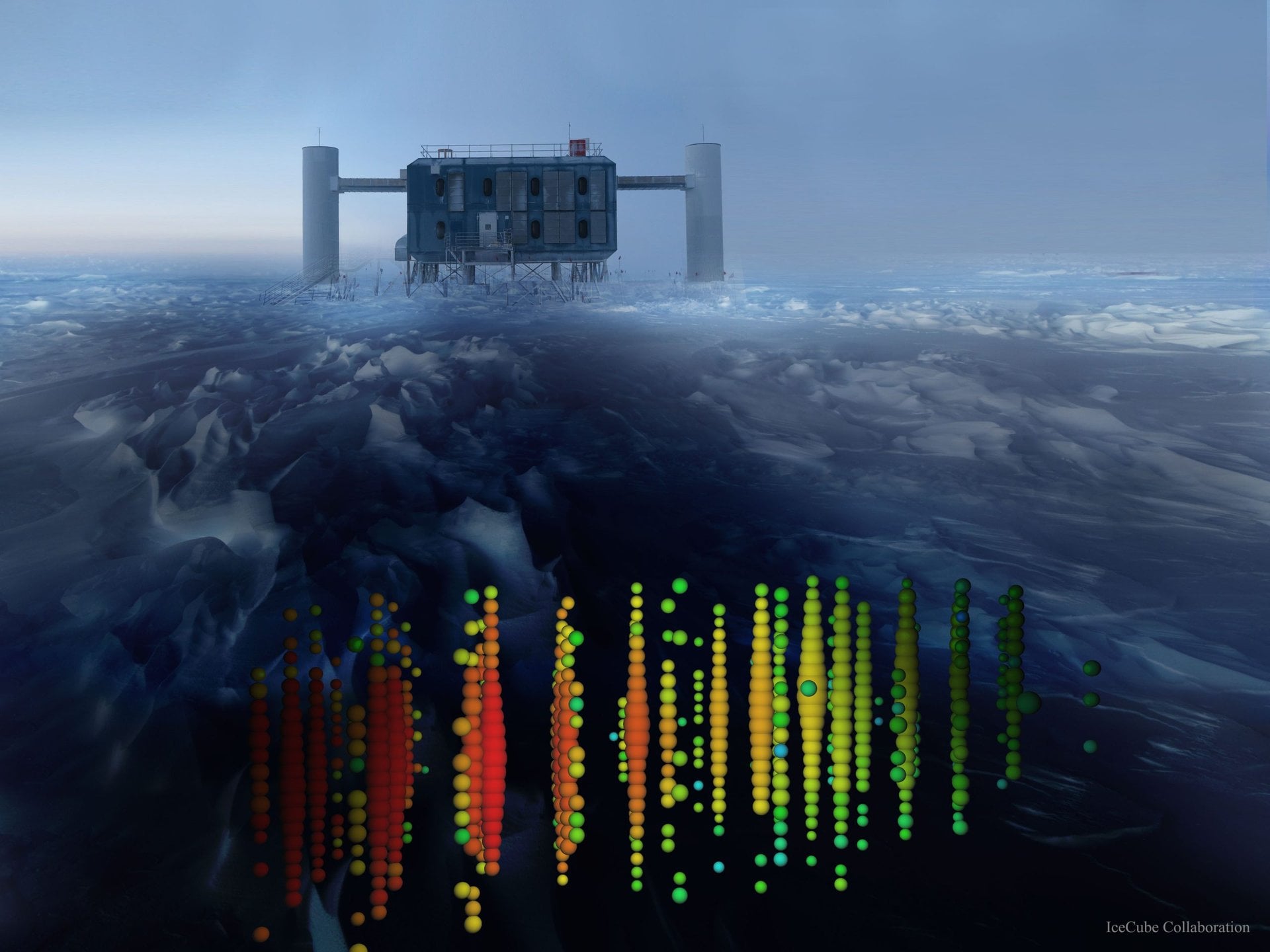
A research team has conducted the first systematic search for optical counterparts to a neutrino "multiplet," a rare event in which multiple high-energy neutrinos are detected from the same direction within a short period. The event was observed by the IceCube Neutrino Observatory, a massive detector buried deep within the Antarctic ice.
Continue reading
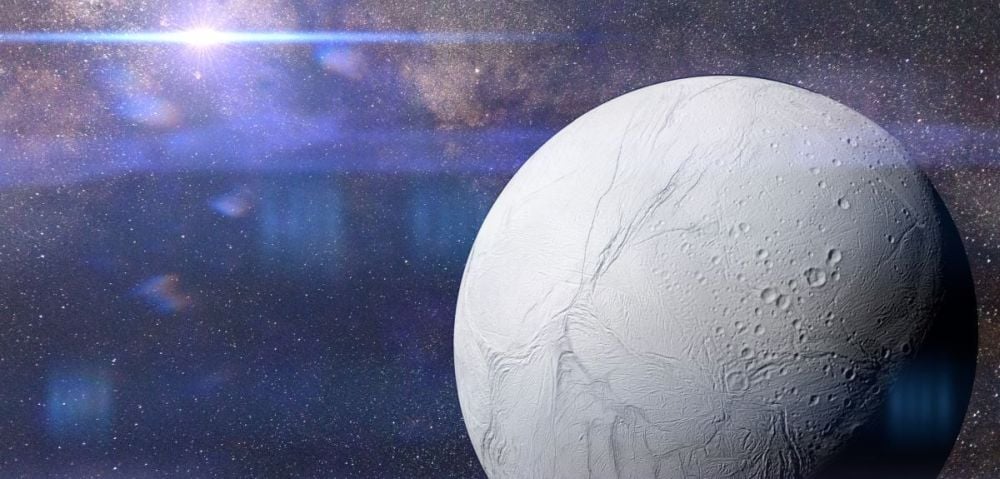

Is Saturn's moon Enceladus habitable? There's ample evidence that the moon holds a warm ocean underneath its frozen surface, and that the building blocks of life are present in that ocean. But for life to arise and persist, the ocean needs to sustain itself for a long time, and new research shows that's exactly what's happening.
Continue reading
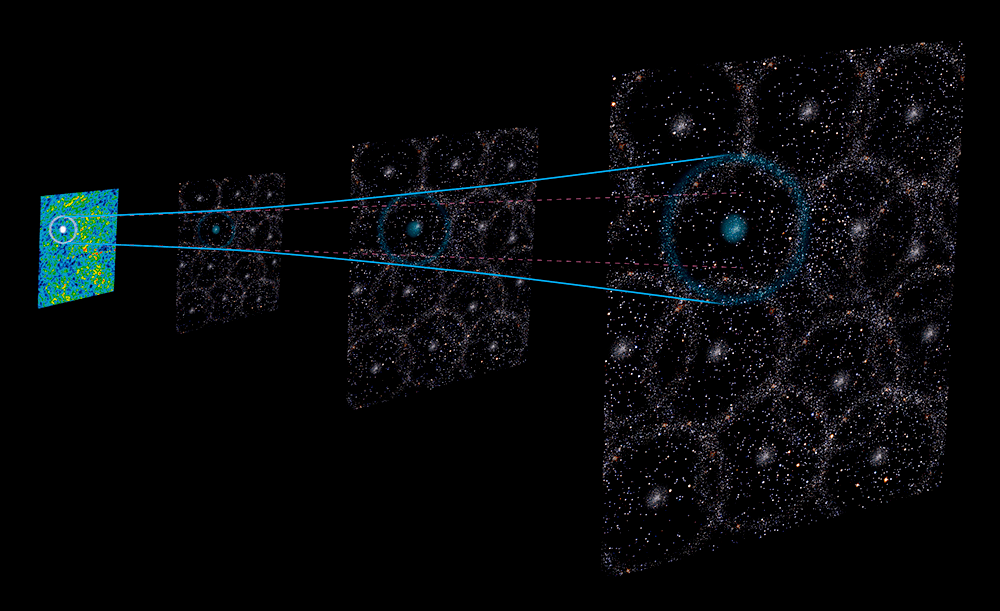
New evidence suggests the standard model of cosmology is wrong, but the results could resolve the long-standing Hubble Tension problem in modern cosmology.
Continue reading
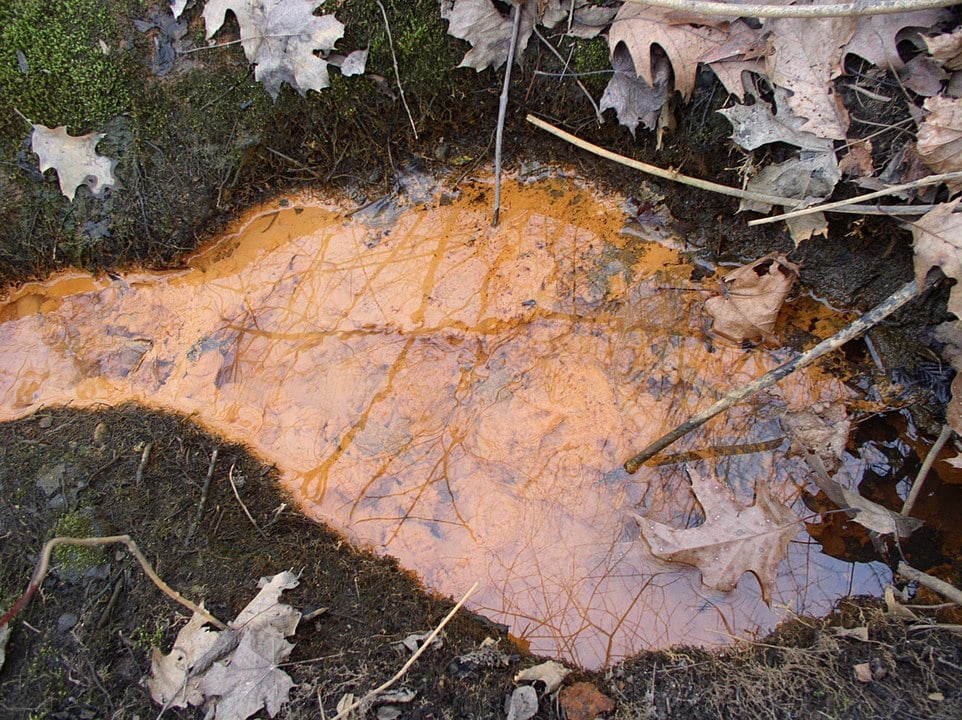

Iron rusts. On Earth, this common chemical reaction often signals the presence of something far more interesting than just corroding metal for example, living microorganisms that make their living by manipulating iron atoms. Now researchers argue these microbial rust makers could provide some of the most promising biosignatures for detecting life on Mars and the icy moons of the outer Solar System.
Continue reading

Astronomers have deployed a survey with the most memorable and tasty acronym in astrophysics - SPAM, The Search for Protoplanets with Aperture Masking - to catch planets in the act of being born. Using Keck Observatory's most powerful instruments, researchers have just captured the closest ever view of a protoplanetary disk 400 light years away, revealing a telltale gap and clumpy structures that hint at a world coalescing from interstellar dust.
Continue reading
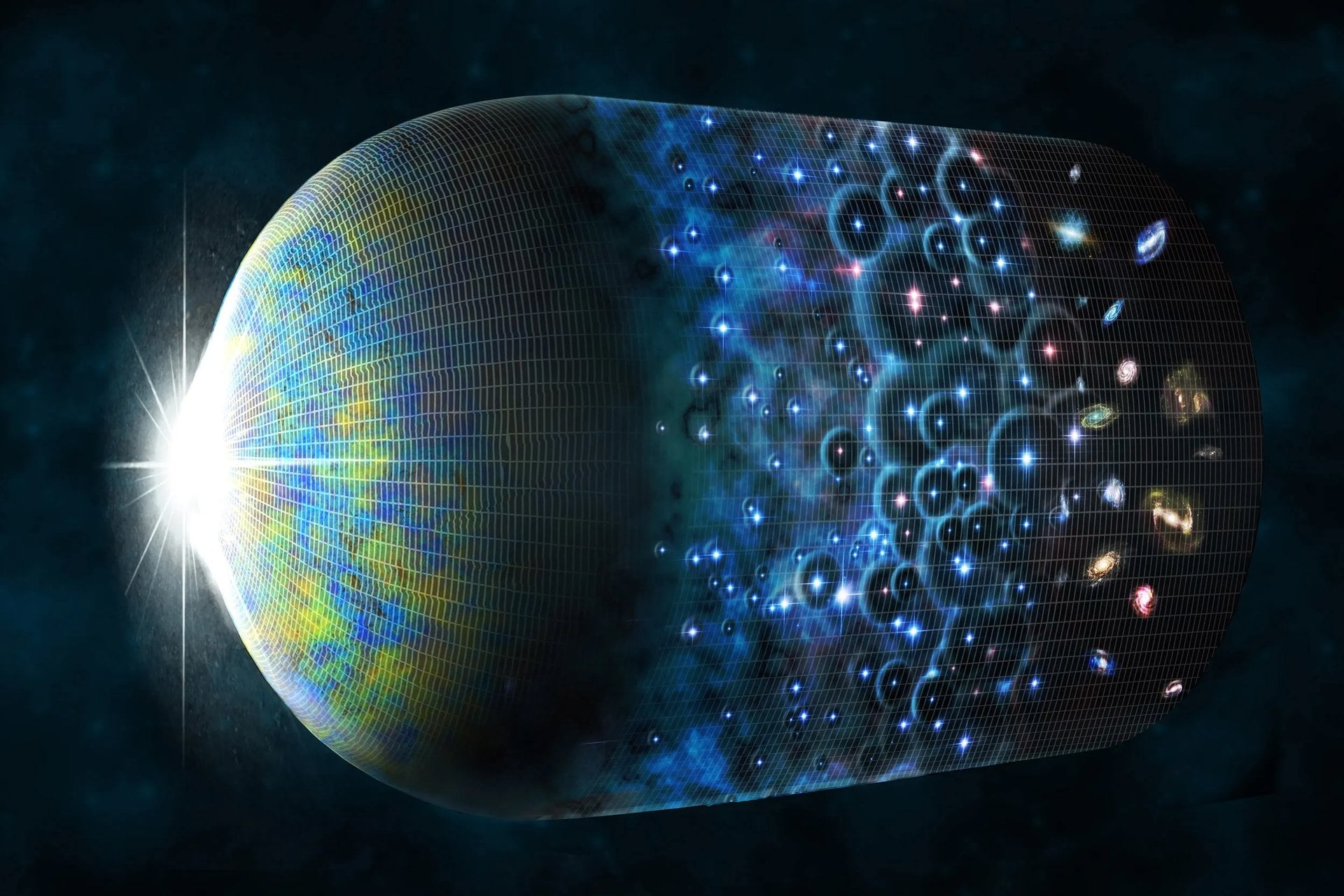
A new study argues that the Universe is decelerating, based on a correlation between the brightness of Type-Ia supernovae and the age of their host galaxies.
Continue reading

Tracking time is one of those things that seems easy, until you really start to get into the details of what time actually is. We define a second as 9,192,631,770 oscillations of a cesium atom. However, according to Einstein’s theory of general relativity, mass slows down these oscillations, making time appear to move more slowly for objects in large gravity wells. This distinction becomes critical as we start considering how to keep track of time between two separate gravity wells of varying strengths, such as on the Earth and the Moon. A new paper by Pascale Defraigne at the Royal Observatory of Belgium and her co-authors discusses some potential frameworks for solving that problem and settles on using the new Lunar Coordinate Time (TCL) suggested by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
Continue reading

ESA’s Euclid space telescope is revealing the patterns of galaxy evolution of millions of galaxies across cosmic time. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE) are using this data to trace how galaxies grow, merge, and transform.
Continue reading
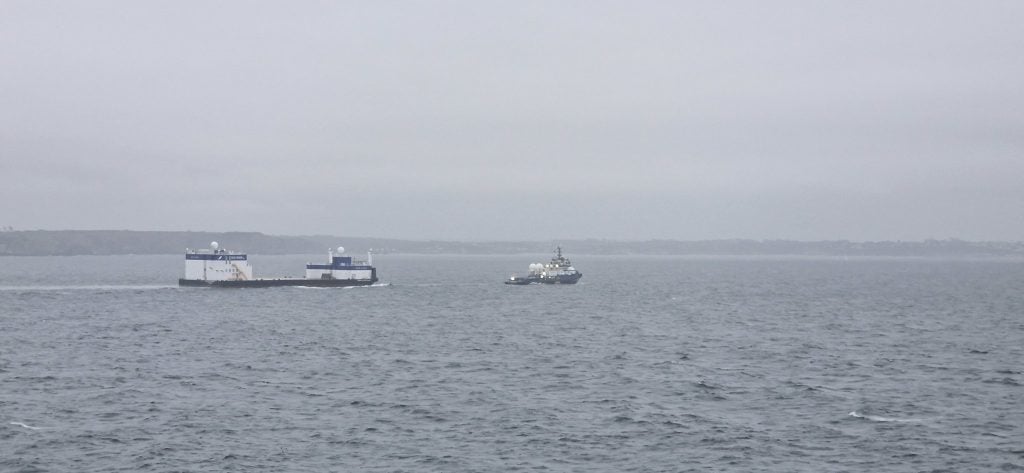

After spending four years converting a massive cargo ferry into a rocket catching ship, Blue Origin scrapped the entire vessel and started from scratch. The story of Jacklyn, named after Jeff Bezos's mother, reveals how even a company founded by one of the world's richest people had to learn hard lessons about what actually works when trying to catch 57 metre rocket boosters descending from space at hypersonic speeds. The barge that ultimately took its name represents a dramatic shift in strategy, from elegant complexity to purpose built simplicity.
Continue reading

Billions of years ago, a rogue planet eight times more massive than Jupiter tore through our Solar System, passing closer to the Sun than Mars orbits today. That single violent encounter may explain why our giant planets don't orbit in perfect circles like formation theories predict and new simulations suggest there was roughly a one in 9,000 chance it happened at all. The discovery reveals that near misses with interstellar wanderers might be more important in shaping planetary systems than anyone realised.
Continue reading
When a chunk of SpaceX rocket debris crashed into a Polish warehouse this year, it exposed a troubling reality, that the international laws governing space accidents were written for a world where only governments launched rockets. Now, as private companies deploy thousands of satellites and debris rains down with increasing frequency, victims have no direct legal recourse and must rely on their governments to pursue claims on their behalf, that’s if those governments choose to act at all. A new analysis reveals how a Cold War era treaty struggles to protect ordinary people in the age of commercial spaceflight, and why some nations are now taking matters into their own hands.
Continue reading
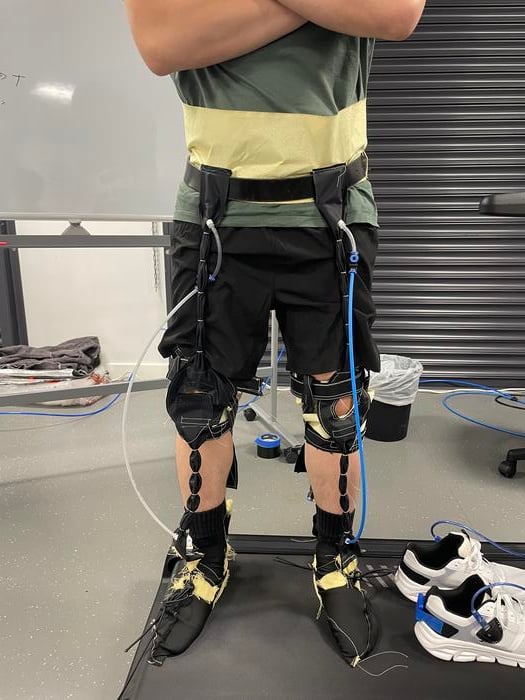

Astronauts lose significant amounts of muscle mass during any prolonged stay in space. Despite spending 2-3 hours a day exercising in an attempt to keep the atrophy at bay, many still struggle with health problems caused by low gravity. A new paper and some further work done by Emanuele Pulvirenti of the University of Bristol’s Soft Robotics Lab and his colleagues, describe a new type of fabric-based exoskeleton that could potentially solve at least some of the musculoskeletal problems astronauts suffer from without dramatically affecting their movement.
Continue reading

In 2023, gravitational wave detectors caught two black holes colliding 7 billion light years away, both spinning at nearly the speed of light and both existing in a mass range where black holes simply cannot form. The mystery baffled astronomers until researchers discovered what everyone else had missed, magnetic fields in the chaotic aftermath of a supernova can eject half a star's mass into space, creating black holes that defy the rules of physics.
Continue reading

When astronomers detected potential biosignatures in the atmosphere of exoplanet K2-18 b, it raised a critical question, ‘could this world's atmosphere even survive its host star's radiation?’ A new study using the Very Large Array searched for radio emissions from the K2-18 system and found something surprising, it was absolutely silent. That absence of radio signals reveals K2-18 is an unusually quiet star, suggesting the planet's atmosphere faces minimal erosion from stellar activity.
Continue reading

NASA's plans for a permanent lunar base face the threat of up to 23,000 micrometeoroid impacts per year travelling at speeds of 70 kilometres per second. A new study quantifies this relentless bombardment for the first time, revealing that even microscopic particles carry enough energy to puncture equipment and even threaten astronaut safety. The research shows impact rates vary dramatically by location with the lunar south pole, NASA's chosen site for the first Artemis base, fortunately experiencing the lowest bombardment.
Continue reading
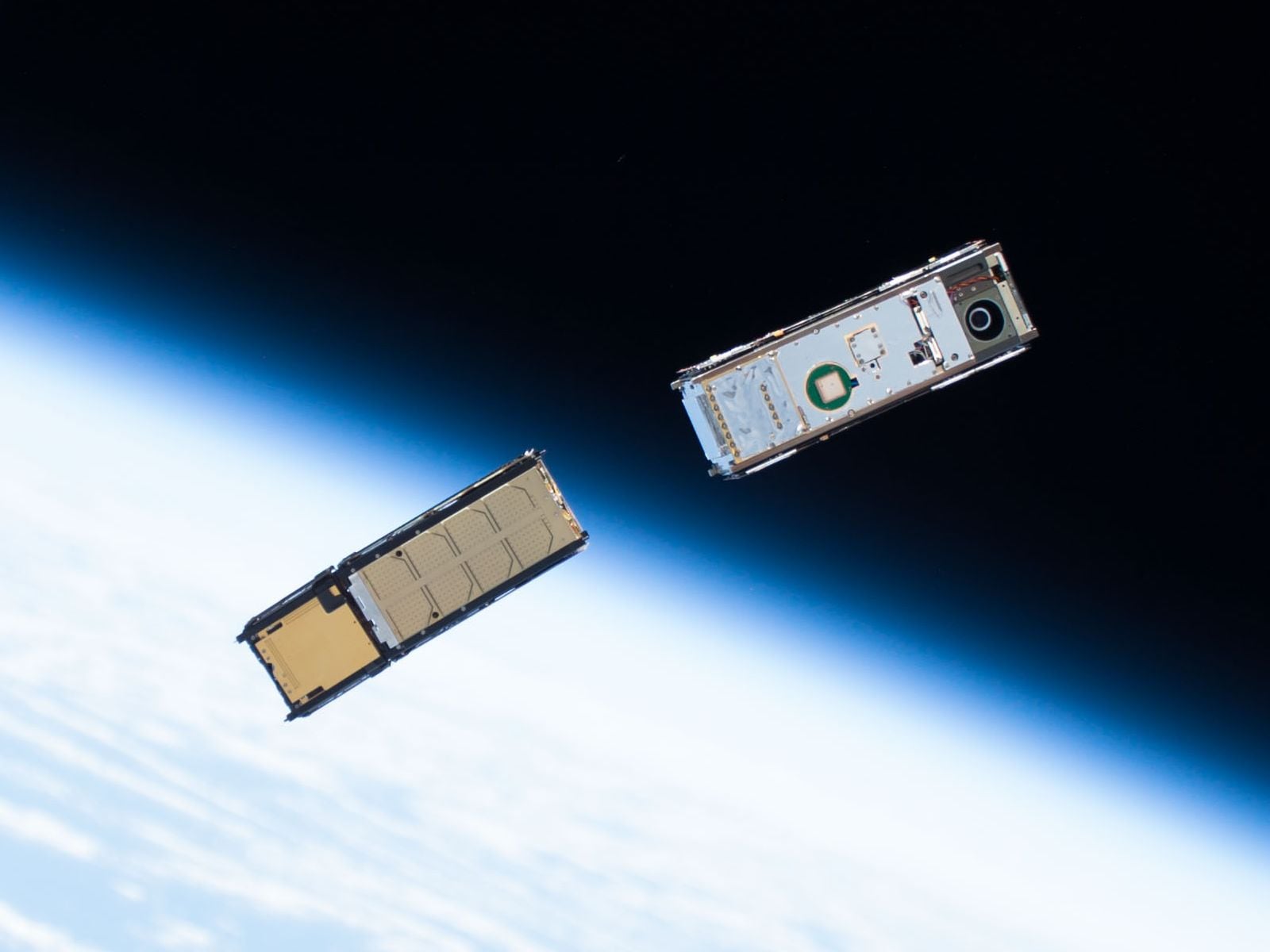

Google's Project Suncatcher is fascinating solution to AI's massive energy demands…. building data centres in space powered directly by the solar power. The company's new research explores the possibility of constellations of satellites equipped with processors flying in tight formation just hundreds of meters apart, connected by terabit per second laser links to distribute information. Early testing shows their chips are surprisingly radiation resistant, while falling launch costs could make space based computing economically viable by the mid 2030s. With a prototype mission planned for 2027, this could fundamentally change where our most powerful computing infrastructure is located.
Continue reading

Weather forecasting is notoriously wonky - climate modeling even more so. But their slowing increasing ability to predict what the natural world will throw at us humans is largely thanks to two things - better models and increased computing power. Now, a new paper from researchers led by Daniel Klocke of the Max Planck Institute in Germany, and available in pre-print form on arXiv, describes what some in the climate modeling community have described as the “holy grail” of their field - an almost kilometer-scale resolution model that combines weather forecasting with climate modeling.
Continue reading
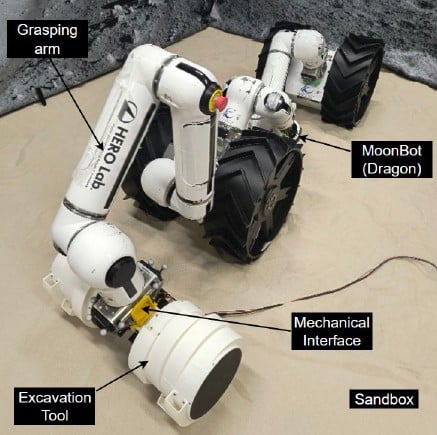
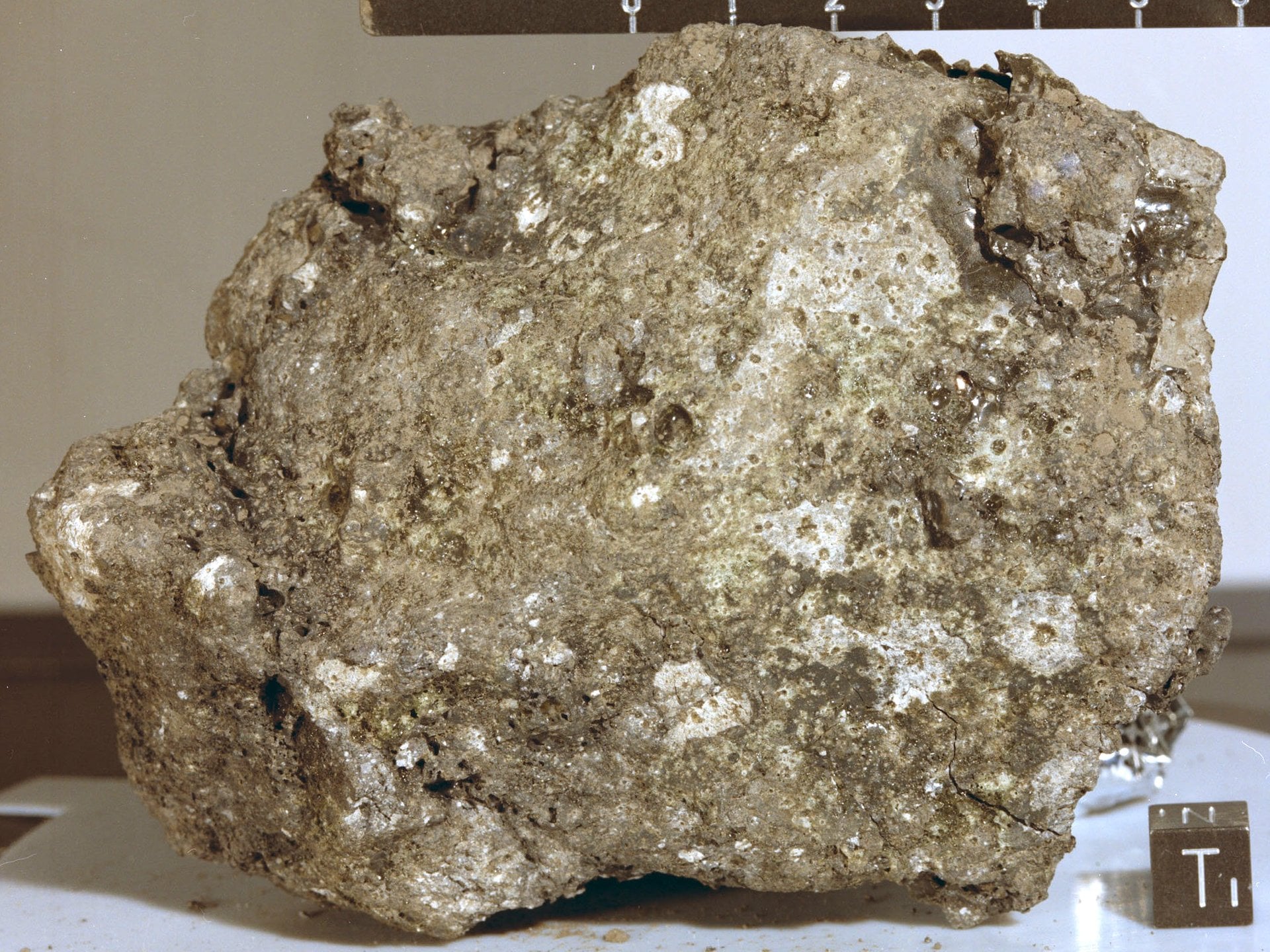
Work continues on designs for robots that can help assist the first human explorers on the Moon in over half a century. One of the most important aspects of that future trip will be utilizing the resources available on the Moon’s surface, known as in-situ resource utilization (ISRU). This would give the explorers access to materials like water, structural metals, and propellant, but only if they can recover it from the rock and regolith that make up the Moon’s surface. A new paper from researchers mainly affiliated with Tohoku University describes the design and testing of a type of robot excavator that could one day assist lunar explorers in unlocking the world’s potential.
Continue reading

Aboard China's space station, astronauts have begun using a new hot air oven delivered by Shenzhou XXI to prepare freshly baked dishes, including chicken wings and steaks, as shown in a recent video from orbit.
Continue reading
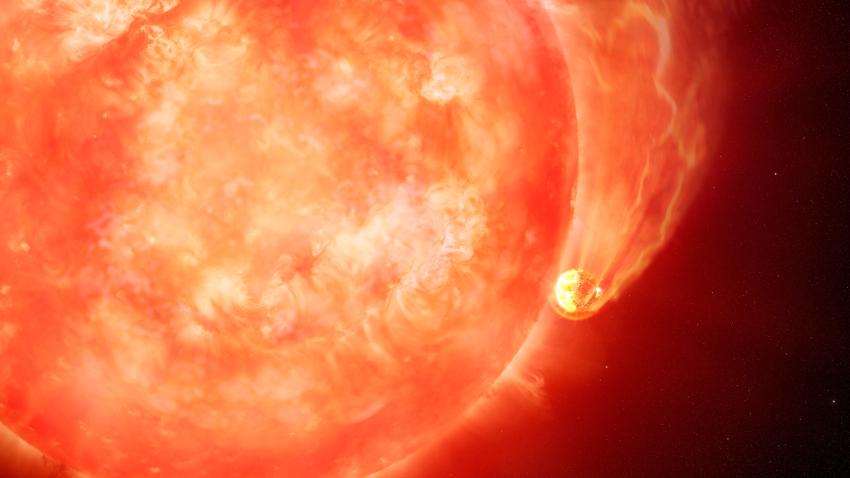

As stars age, they expand. That’s bad news for planets orbiting close to their stars, according to a new study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society this month. The study suggests that planets closest to their stars, especially those that orbit their stars in just 12 days or less, are at a higher risk of being sent to their doom by their aging suns.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today

















