Andy Tomaswick
Andy has been interested in space exploration ever since reading Pale Blue Dot in middle school. An engineer by training, he likes to focus on the practical challenges of space exploration, whether that's getting rid of perchlorates on Mars or making ultra-smooth mirrors to capture ever clearer data. When not writing or engineering things he can be found entertaining his wife, four children, six cats, and two dogs, or running in circles to stay in shape.
Recent Articles
-

-

Turning Forgotten Telescope Data into New Discoveries
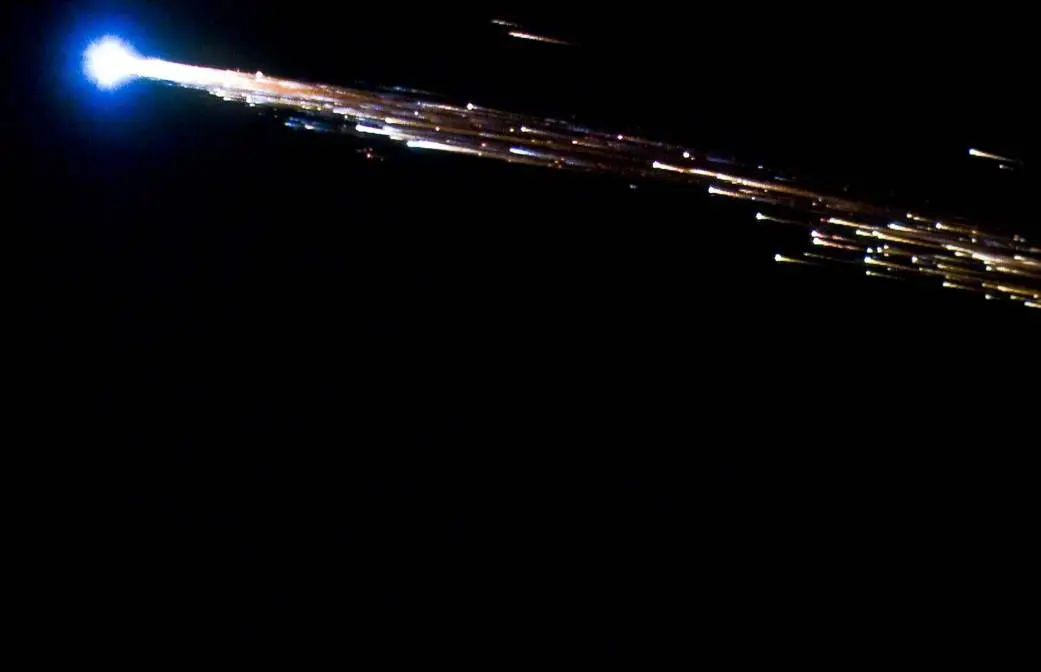
February 05, 2026Astronomers have been collecting data for generations, and the sad fact is that not all of it has yet been fully analyzed. There are still discoveries hiding in the dark recesses of data archives strewn throughout the astronomical world. Some of them are harder to access than others, such as actual physical plates containing star positions from more than a hundred years ago. But as more and more of this data is archived, astronomers also keep coming up with ever more impressive tools to analyze it. A recent paper from Cyril Tasse of the Paris Observatory and his co-authors, published recently in Nature Astronomy describes an algorithm that analyzes hundreds of thousands of previously unknown data points in radio telescope archives - and they found some interesting features in it.
-
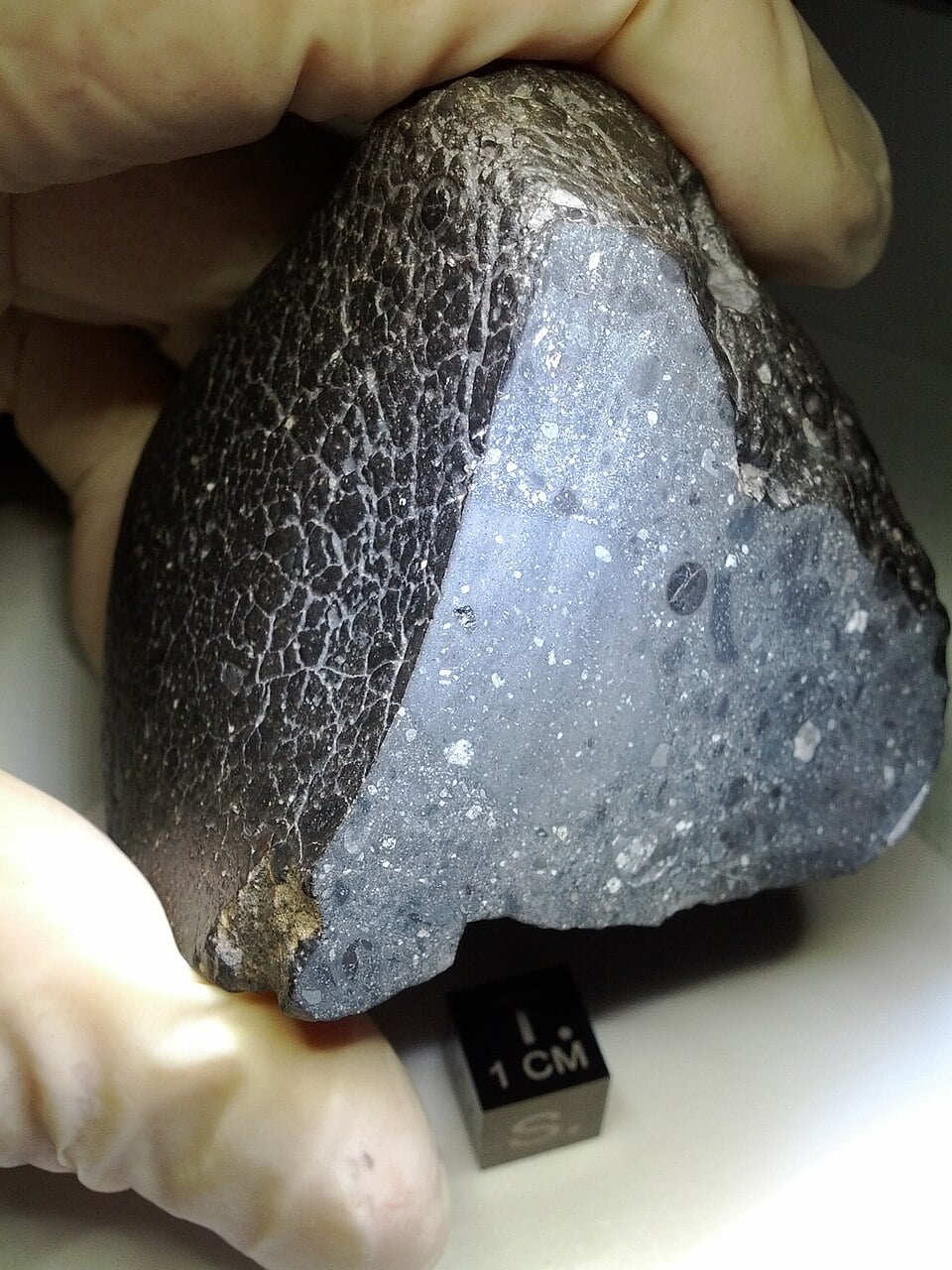

Neutron Scans Reveal Hidden Water in Famous Martian Meteorite
February 04, 2026New tools unlock new discoveries in science. So when a new type of non-destructive technology becomes widely available, it's inevitable that planetary scientists will get their hands on it to test it on some meteorites. A new paper, available in pre-print on arXiv, by Estrid Naver of the Technical University of Denmark and her co-authors, describes the use of two of those (relatively) new tools to one of the most famous meteorites in the world - NWA 7034 - also known as Black Beauty.
-
Reading the Moon’s Diary, One Speck of Dust at a Time
February 03, 2026Magnetism on the Moon has always been a bit confusing. Remote sensing probes have noted there is some magnetic signature, but far from the strong cocoon that surrounds Earth itself. Previous attempts to detect it in returned regolith samples blended together all of the rocks in those samples, leading to confusion about the source - whether they were caused by a strong inner dynamo in ages past, or by powerful asteroid impacts that magnetized the rocks they hit. A new study from Yibo Yang of Zhejiang University and Lin Xing of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, published recently in the journal Fundamental Research, shows that the right answer seems to be - a little of both.
-
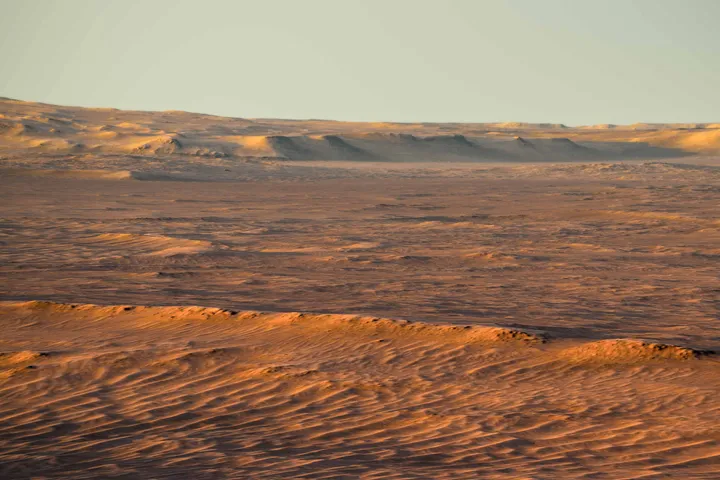

Perseverance Rover Discovers an Ancient Martian Beach, Complete with Waves
January 30, 2026When the rover now named Perseverance landed in Jezero crater in early 2021, scientists already knew they had picked an interesting place to scope out. From space, they could see what looked like a bathtub ring around the crater, indicating there could once have been water there. But there was some debate about what exactly that meant, and it’s taken almost five years to settle it. A new paper from PhD student Alex Jones at Imperial College London and his co-authors has definitively settled the debate on the source of that feature - part of it was once a beach.
-
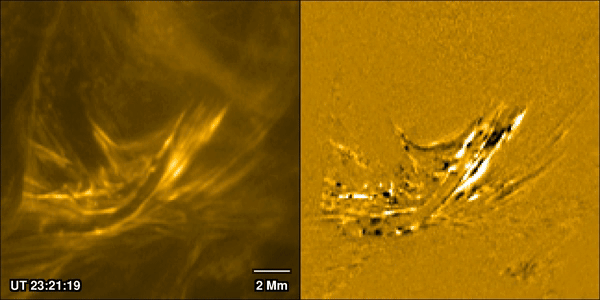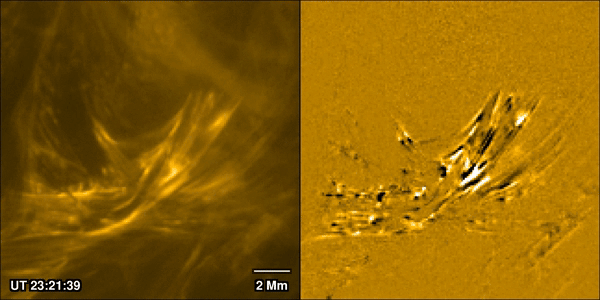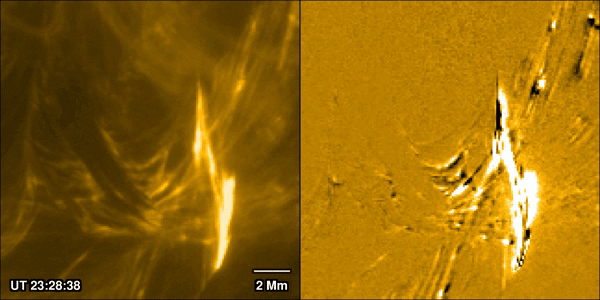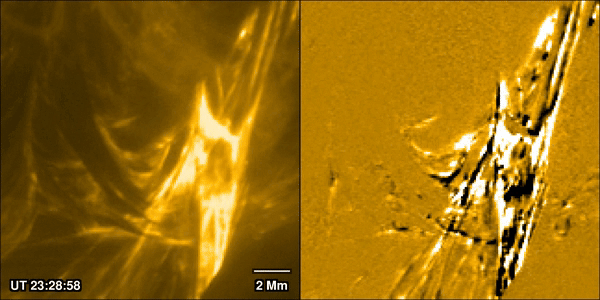
A New Theory for What Really Powers a Flare
January 30, 2026Solar flares are one of the most closely watched processes in solar physics. Partly that’s because they can prove hazardous both to life and equipment around Earth, and in extreme cases even on it. But also, it’s because of how interestingly complex they are. A new paper from Pradeep Chitta of the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research and his co-authors, available in the latest edition of Astronomy & Astrophysics, uses data collected by ESA’s Solar Orbiter spacecraft to watch the formation process of a massive solar flare. They discovered the traditional model used to describe how solar flares form isn’t accurate, and they are better thought of as being caused by miniaturized “magnetic avalanches.”
-
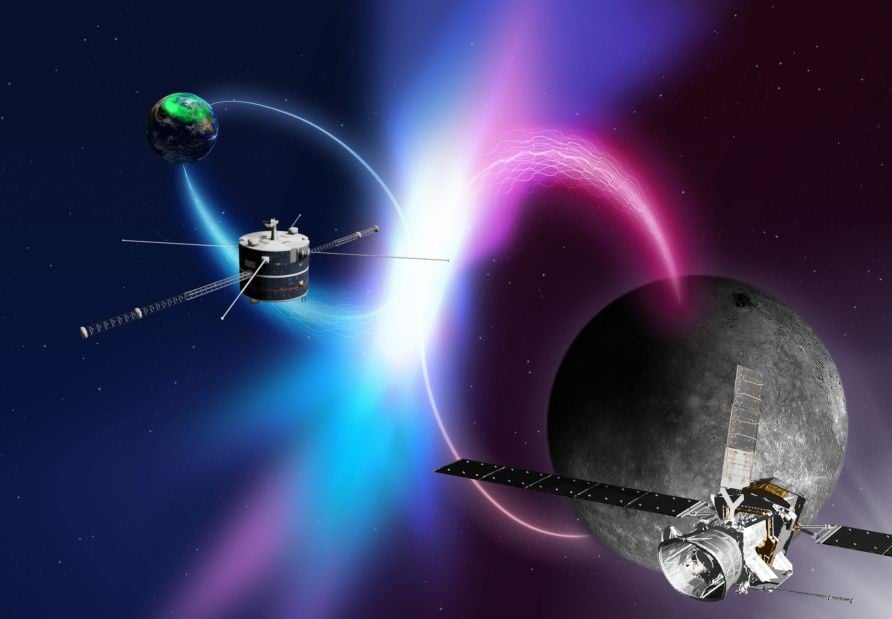

The Magnetic "Birdsong" of the Smallest Planet
January 28, 2026BepiColombo is slowly uncovering more and more fun facts about Mercury as it continues its preliminary mission. One of the more interesting things found so far is a magnetic “chorus” that appears similar to a phenomenon found in Earth’s much larger magnetic field. A new paper in Nature Communications from the researchers responsible for the probe’s Mio instrument that is studying Mercury’s magnetic field describes what could be thought of as a form of magnetic birdsong.
-

The HWO Must Be Picometer Perfect To Observe Earth 2.0
January 27, 2026Lately we’ve been reporting about a series of studies on the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO), NASA’s flagship telescope mission for the 2040s. These studies have looked at the type of data they need to collect, and what the types of worlds they would expect to find would look like. Another one has been released in pre-print form on arXiv from the newly formed HWO Technology Maturation Project Office, which details the technology maturation needed for this powerful observatory and the “trade space” it will need to explore to be able to complete its stated mission.
-
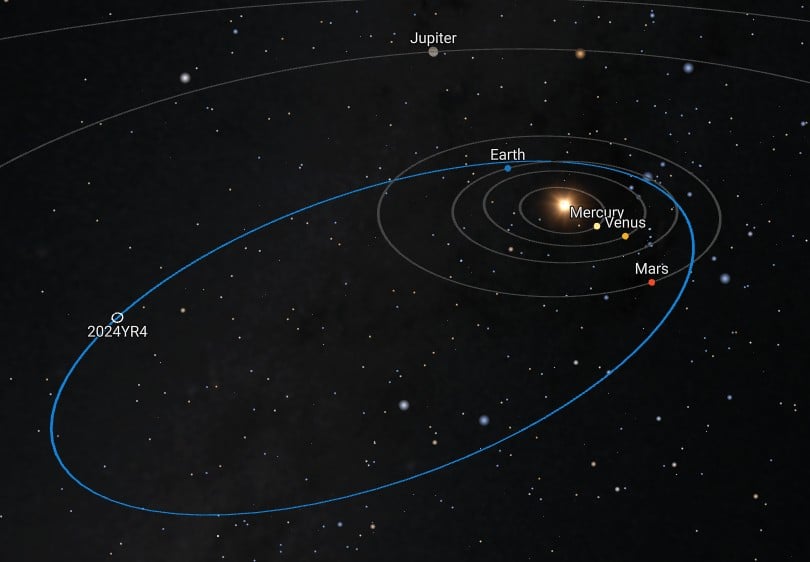
Asteroid 2024 YR4 Has a 4% Chance of Hitting the Moon. Here’s Why That’s a Scientific Goldmine.
January 27, 2026There’s a bright side to every situation. In 2032, the Moon itself might have a particularly bright side if it is blasted by a 60-meter-wide asteroid. The chances of such an event are still relatively small (only around 4%), but non-negligible. And scientists are starting to prepare both for the bad (massive risks to satellites and huge meteors raining down on a large portion of the planet) and the good (a once in a lifetime chance to study the geology, seismology, and chemical makeup of our nearest neighbor). A new paper from Yifan He of Tsinghua University and co-authors, released in pre-print form on arXiv, looks at the bright side of all of the potential interesting science we can do if a collision does, indeed, happen.
-

Investigating the Star That Almost Vanished for Eight Months
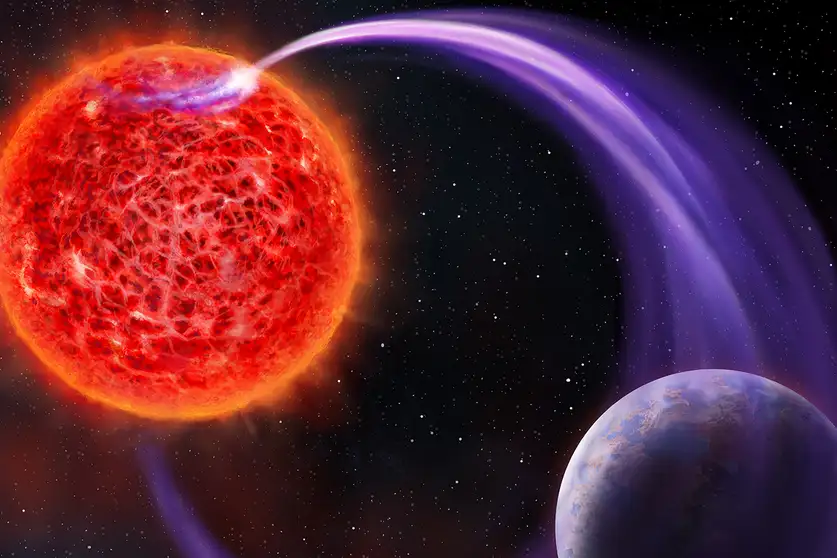
January 26, 2026Stars change in brightness for all kinds of reasons, but all of them are interesting to astronomers at some level. So imagine their excitement when a star known as J0705+0612 (or, perhaps more politically incorrectly, ASASSN-24fw) dropped to around 2.5% of its original brightness for 8.5 months. Two new papers - one from Nadia Zakamska and her team at the Gemini Telescope South and one from Raquel Forés-Toribio at Ohio State and her co-authors - examine this star and have come to the same conclusion - it’s likely being caused by a circumsecondary disk.
-
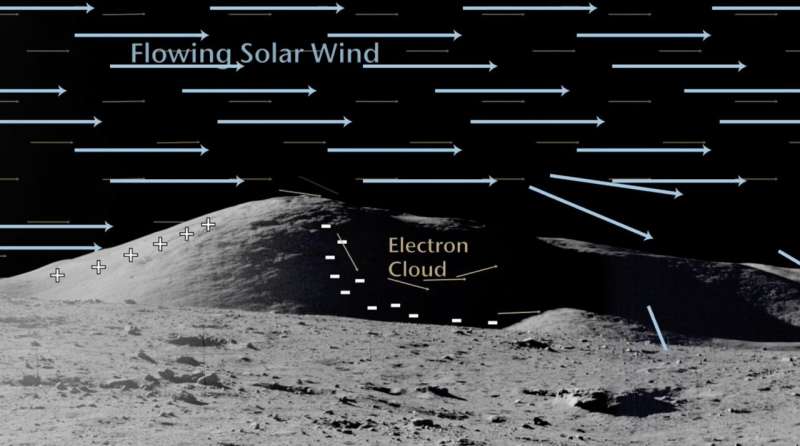

Electric Shocks Could Enforce a Lunar Speed Limit
January 23, 2026As they roll across shadowed regions of the moon's surface, future lunar rovers could develop hazardous buildups of electric charge on their wheels. Through new analysis published in Advances in Space Research, Bill Farrell at the Space Science Institute in Colorado, together with Mike Zimmerman at Johns Hopkins University, outline realistic precautions for mitigating this risk—offering valuable guidance for engineers designing future lunar missions.
-
Mutations from Space Might Solve an Antibiotic Crisis
January 22, 2026If humans are ever going to expand into space itself, it will have to be for a reason. Optimists think that reason is simply due to our love of exploration itself. But in history, it is more often a profit motive that has led humans to seek out new lands. So, it stands to reason that, in order for us to truly begin space colonization, we will have to have a business-related reason to do so. A new paper from the lab of Srivatsan Raman at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and recently published in PLOS Biology, describes one potential such business case - genetically modifying bacteriophages to attack antibiotic resistant bacteria.
-
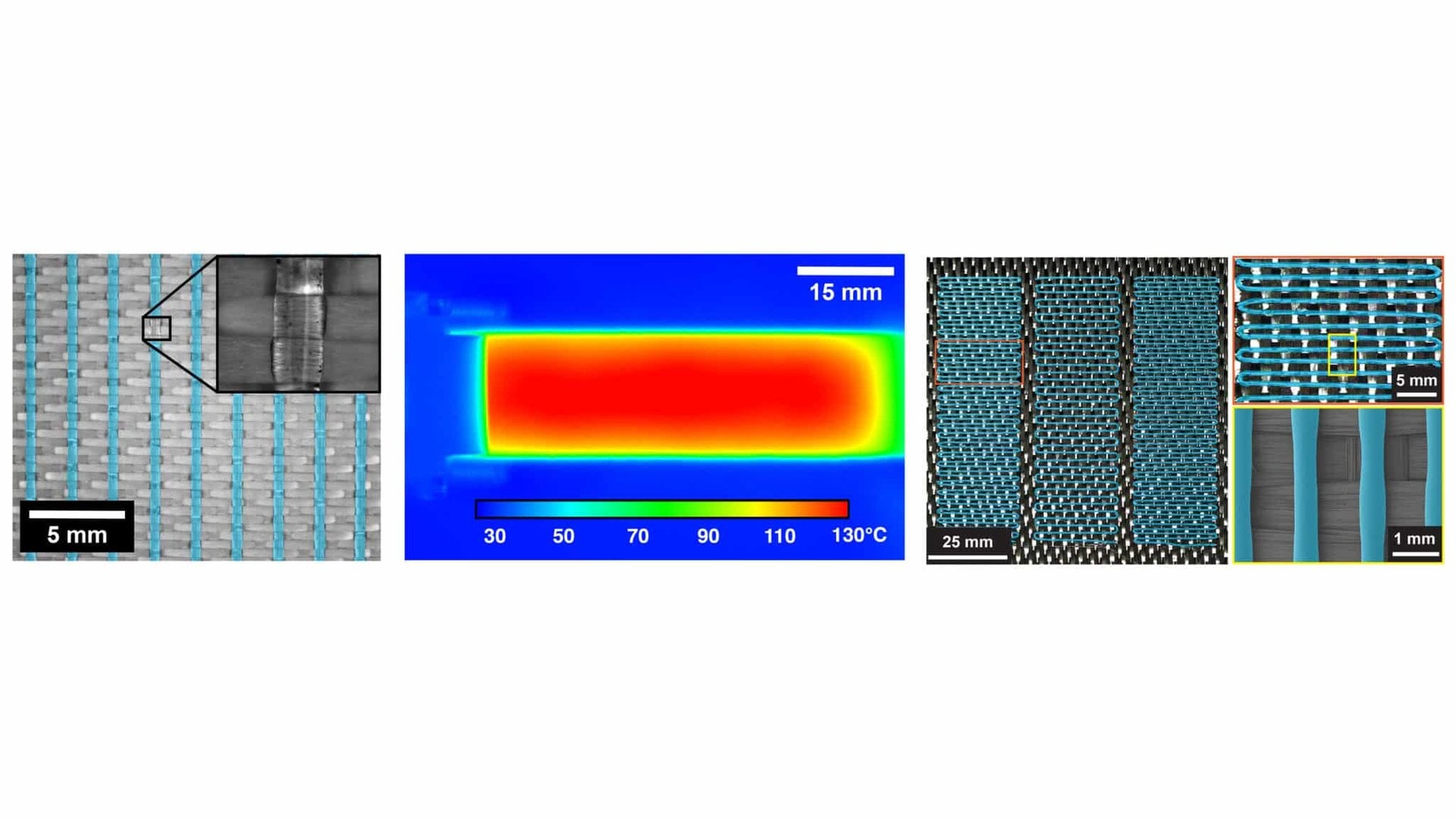
The New Composite That Heals Itself 1,000 Times
January 21, 2026Material science plays an absolutely critical role in space exploration. So when a new type of self-healing composite is announced, it’s worth a look–especially when the press release specifically calls out its ability to repair microtears associated with micrometeoroid impacts on satellites. It sounds like just such a composite material was recently invented at North Carolina State University - and it’s even already been spun out into a start-up company.
-
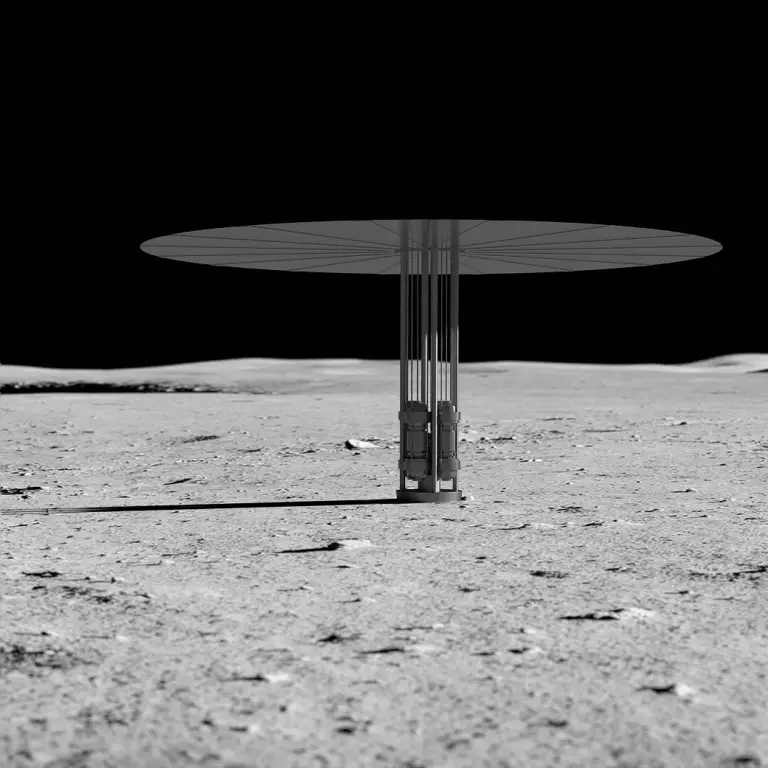

The 2030 Race for a Moon Reactor
January 20, 2026The US’s federally funded space program has been struggling of late. With the recent cancellation of the Mars Sample Return mission, and mass layoffs / resignations taking place at NASA, the general sense of a lack of morale at the agency is palpable, even from a distance. Jared Isaacman, the billionaire software entrepreneur and rocket enthusiast who was recently confirmed as NASA administrator during his second confirmation hearing, hopes to change that, and one of his priorities is pushing the Artemis missions for a permanent human presence on the Moon. However, at least one big technical hurdle remains before being able to do so - how to power a base during the two week long lunar night. A recent press release describes how NASA, and another branch of the federal government (the Department of Energy - DoE) hope to solve that problem - with a lunar-ready nuclear fission reactor
-
The Alien Hunter's Shopping List
January 20, 2026We recently discussed the different types of worlds that the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO) is expected to find that might have noticeable biosignatures. However, no matter how good the instrumentation on board the observatory is, the data it collects will be useless if scientists don’t know how to interpret it. A paper explaining what data they need to collect before analyzing HWO data was authored by Niki Parenteau, a research biologist at NASA, and her co-authors, which is now available in pre-print on arXiv.
-
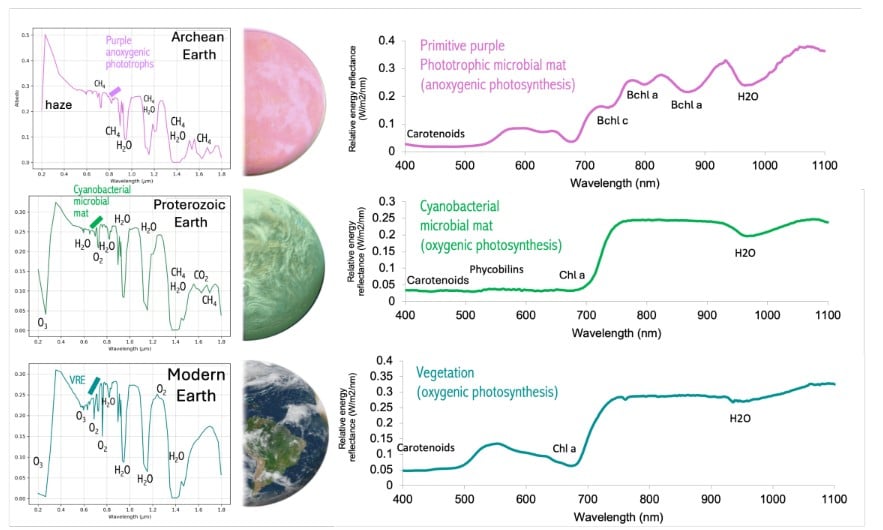
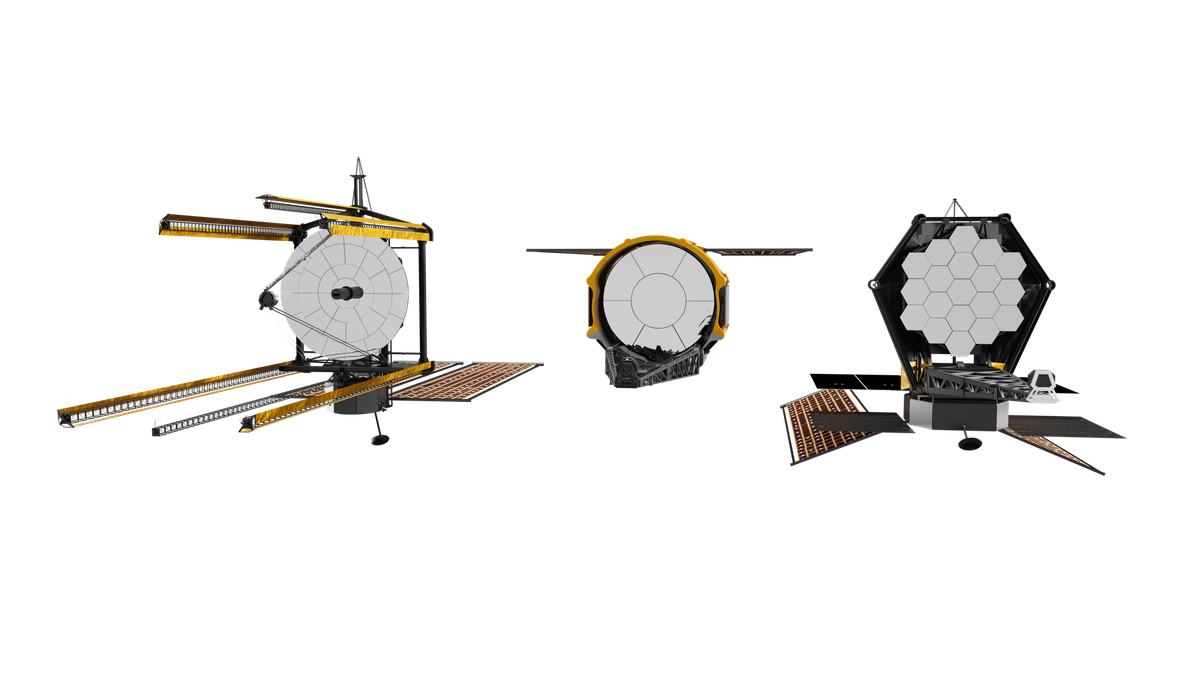
Searching for 'Green Oceans' and 'Purple Earths'
January 19, 2026The early stage of giant telescope development involves a lot of horse-trading to try to appease all the different stakeholders that are hoping to get what they want out of the project, but also to try to appease the financial managers that want to minimize its cost. Typically this horse-trading takes the form of a series of white papers that describe what would be needed to meet the stated objectives of the mission and suggest the type of instrumentation and systems that would be needed to achieve them. One such white paper was recently released by the Living Worlds Working Group, which is tasked with speccing out the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO), one of the world’s premiere exoplanet hunting telescopes that is currently in the early development stage. Their argument in the paper, which is available in pre-print on arXiv, shows that, in order to meet the objectives laid out in the recent Decadal survey that called for the telescope, it must have extremely high signal-to-noise ratio, but also be able to capture a very wide spectrum of light.
-
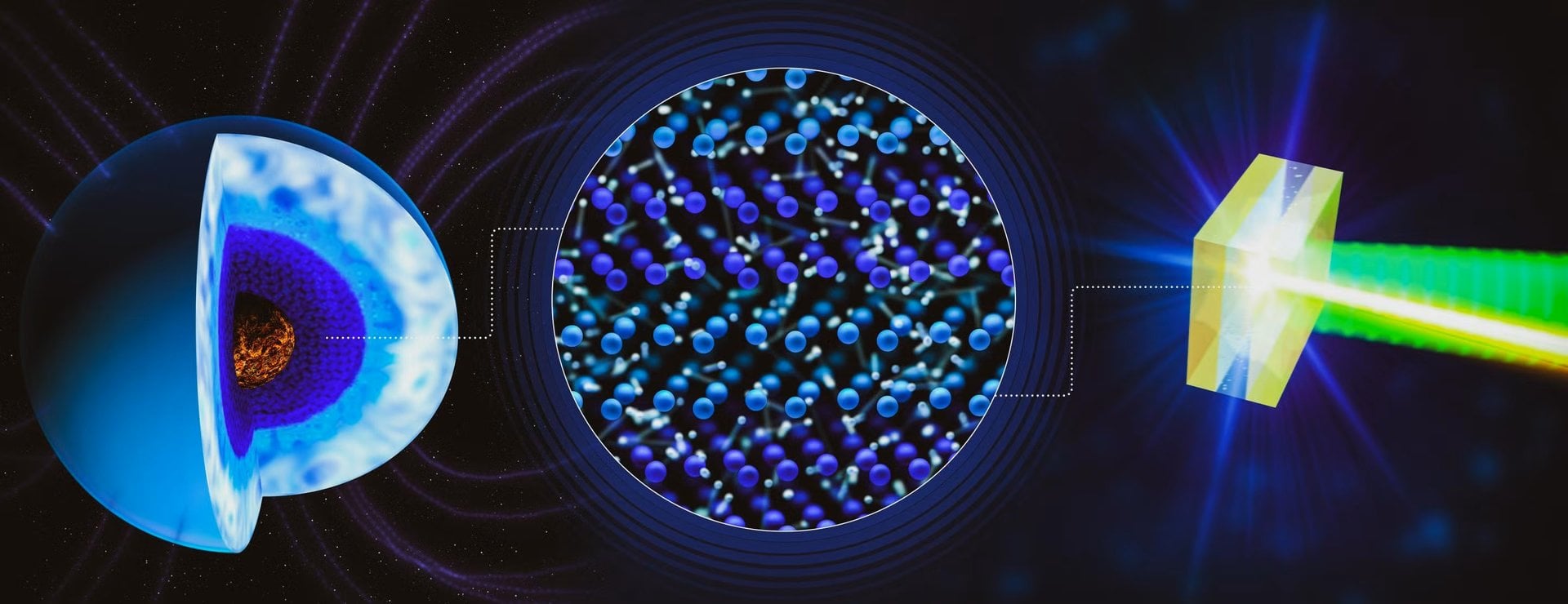
The Universe's Most Common Water is a Hot Mess
January 19, 2026Inside the cores of ice giant planets, the pressure and temperature are so extreme that the water residing there transitions into a phase completely unfamiliar under the normal conditions of Earth. Known as “superionic water”, this form of water is a type of ice. However, unlike regular ice it’s actually hot, and also black. For decades, scientists thought that the superionic water in the core of Neptune and Uranus is responsible for the wild, unaligned magnetic fields that the Voyager 2 spacecraft saw when passing them. A series of experiments described in a paper published in Nature Communications by Leon Andriambariarijaona and his co-authors at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and the Sorbonne provides experimental evidence of why exactly the ice causes these weird magnetic fields - because it is far messier than anyone expected.
-
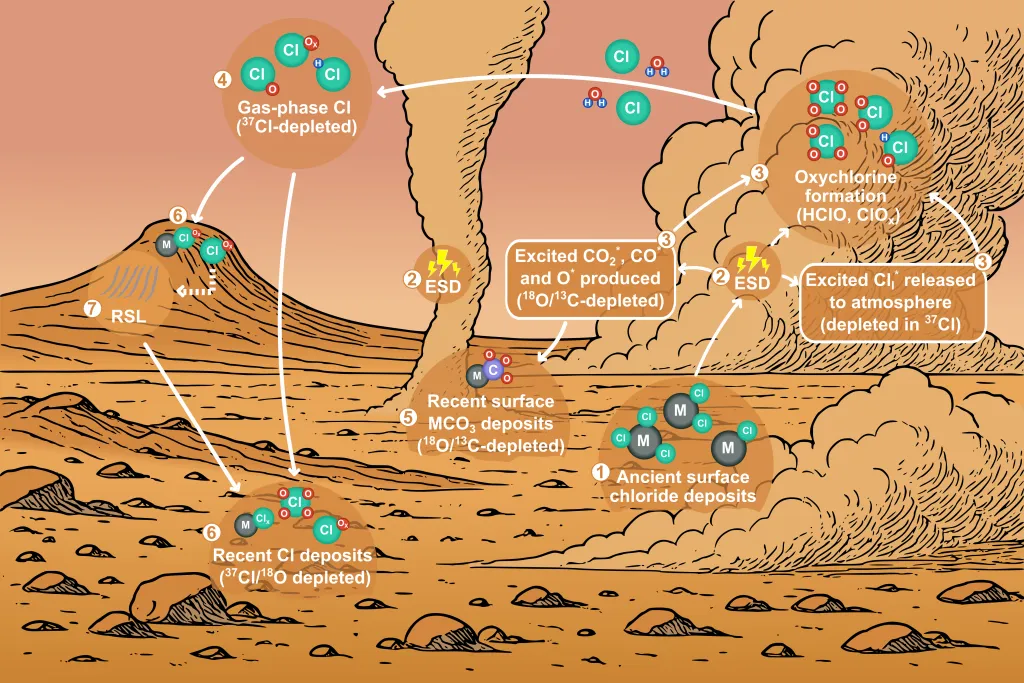
Why Mars is Actively Manufacturing Poison
January 16, 2026Chemistry on other worlds varies widely from that on Earth. Much of Earth’s chemistry is driven by well-understood processes, which typically involve water and heat in some form. Mars lacks both of those features, which makes how some of its chemicals formed a point of ongoing debate in the scientific community. A new paper led by Alian Wang and Neil Sturchio of Washington University of St. Louis and the University of Delaware, respectively, and published recently in Earth and Planetary Science Letters offers a new framework for understanding chemical reaction processes on Mars. Despite the differences, Earthlings will still be familiar with the driving force behind Martian chemistry - electricity.
-

How Astronauts Will Fix Their Gear Using Thin Air
January 16, 2026Additive Manufacturing, more commonly known as 3D printing, will be an absolutely critical technology for any long-term settlement on another world. Its ability to take a generic input, such as plastic strips or metal powder, and turn it into any shape of tool an astronaut will need is an absolute game changer. But the chemistry behind these technologies is complicated, and their applications are extremely varied, ranging from creating bricks for settlements to plastics for everything from cups to toothbrush holders. A new paper available in pre-print on arXiv from Zane Mebruer and Wan Shou of the University of Arkansas, explores one specific aspect of a particularly important type of 3D printing, and realized that they could save millions of dollars on Mars missions by simply using the planet’s atmosphere to help print metal parts.
-
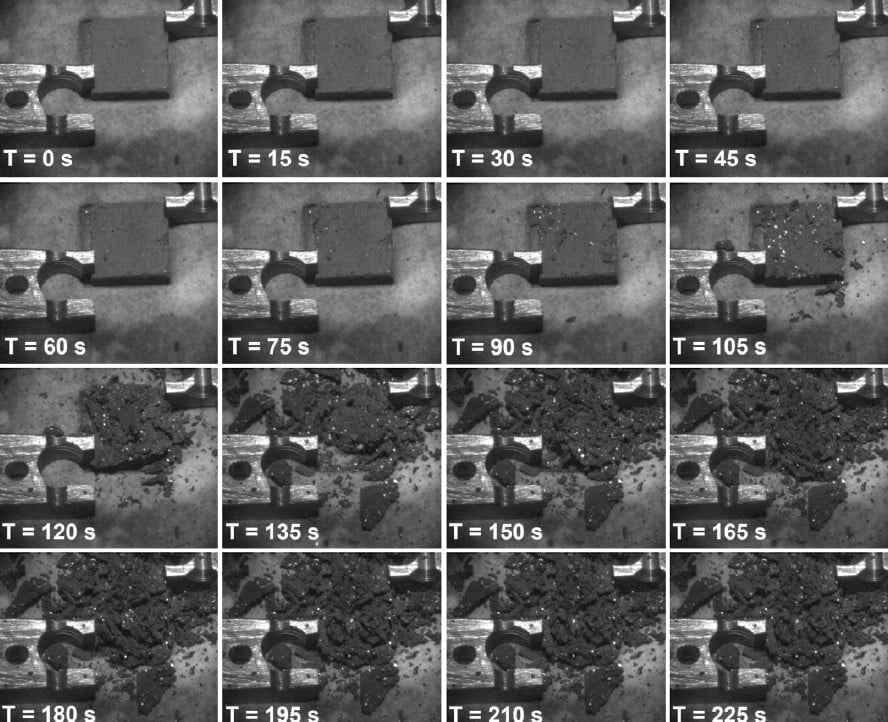
How Dark Asteroids Die
January 15, 2026Back in the earlier days of the internet, there was a viral video from a creator called Bill Wurtz called “the history of the entire world, i guess” which spawned a number of memorable memes, some of which are still in use to this day. One of those was a clip from the video where Wurtz states “The Sun is a deadly laser.” Apparently, that was more true than even he knew, as a new paper from Georgios Tsirvouils of the Luleå University of Technology in Sweden and his co-authors have shown experimental evidence that the Sun’s laser-like radiation is likely responsible for the death of a vast majority of closely-orbiting asteroids.
 Universe Today
Universe Today