
Astronomers have seen exoplanetary systems at almost every stage, from extremely young to older than the Solar System. But now, they've spotted the exact moment when planet formation is initiated around a young star. Meteorites store a history of when the first minerals formed in the Solar System, and the ALMA telescope has seen the signal of these minerals forming in a protostellar system, about 1,300 light-years from Earth.
Continue reading

NASA has discovered that 7 out of 10 astronauts returning from the International Space Station have been unable to see clearly, with vision problems that can last for years! As we prepare for multi year Mars missions, scientists are racing to solve this mysterious "space blindness" before it derails humanity's greatest journey. It seems the cause could be as simple as the effects of weightlessness and the distribution of fluids around the body. Thankfully, it seems there are some possible solutions to what could become one of our greatest health challenges as we reach out further among the planets.
Continue reading
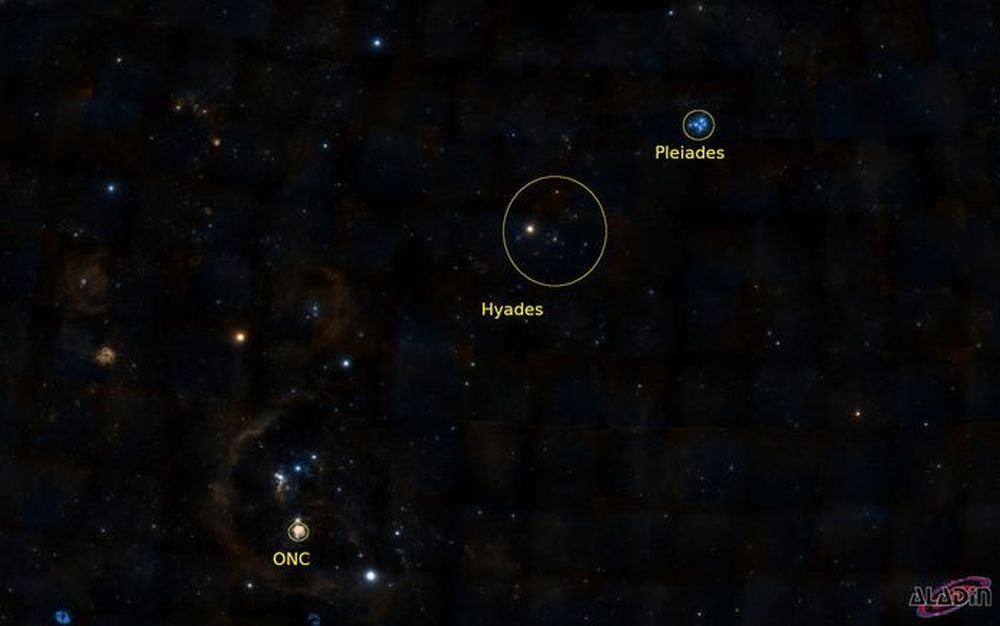
Astronomers found evolutionary links that connect three well-known star clusters. The Orion Nebular Cluster, the Pleiades, and the Hyades are located roughly in the same region in space, but have different ages. New research shows that they're connected and have similar origins.
Continue reading

Lunar regolith is the crushed up volcanic rock that buries the surface of the Moon. Remote observations and sample analysis have shown there are trace amounts of water ice mixed in with the regolith, which can be extracted. By mixing this water with CO2 exhaled by astronauts, scientists have demonstrated this can be turned into hydrogen gas and carbon monoxide. This can then be turned into fuels and oxygen to support the astronauts. Everything we need is there on the Moon. We just need to learn how to use it.
Continue reading

A Chinese team presents a new model for accurately predicting the performance of Sterling engines, which are being investigated as a possible means of powering
Continue reading
Continue reading

If astronomers can find ancient, pristine galaxies with no metals, they will confirm our understanding of the Big Bang. Those galaxies have proven elusive, but a team of astronomers think they've found one. It may be the first Population 3 galaxy.
Continue reading
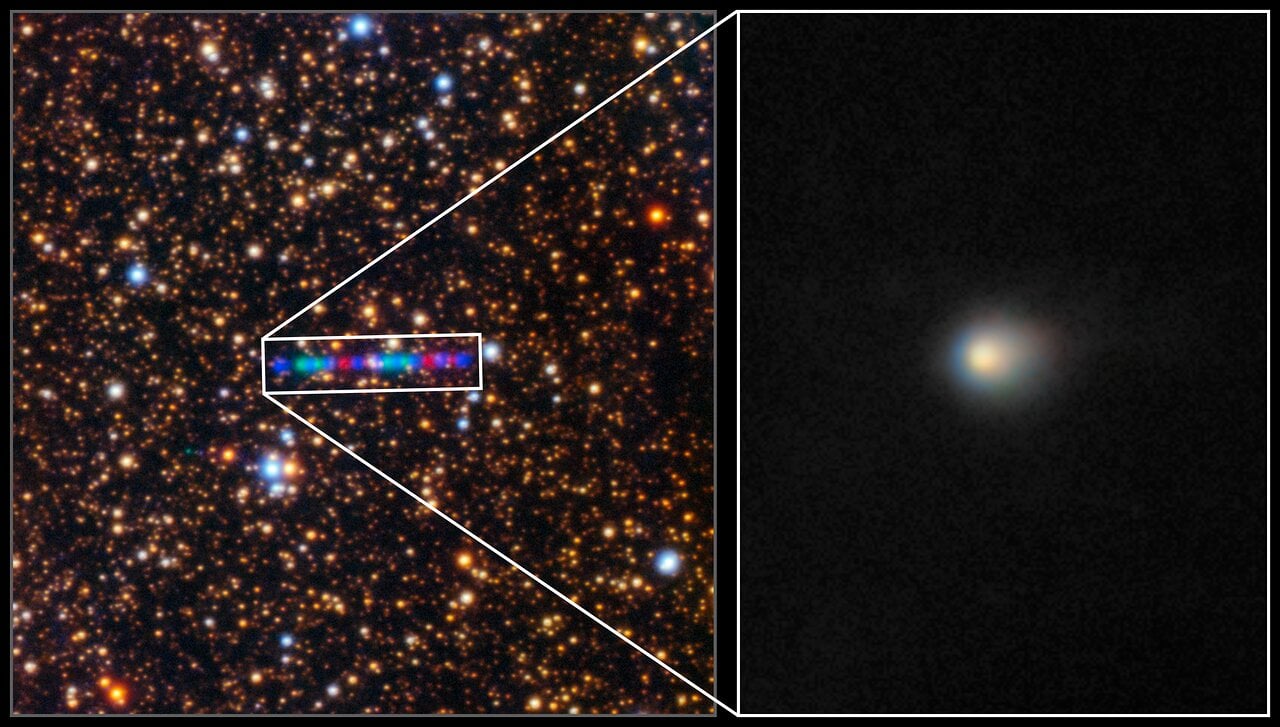
We’re getting better views of interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS, as it makes its speedy passage through the inner solar system. This week, astronomers at the Gemini North observatory located on Mauna Kea in Hawai’i turned the facility’s enormous 8.1-meter telescope on the object, with amazing results.
Continue reading
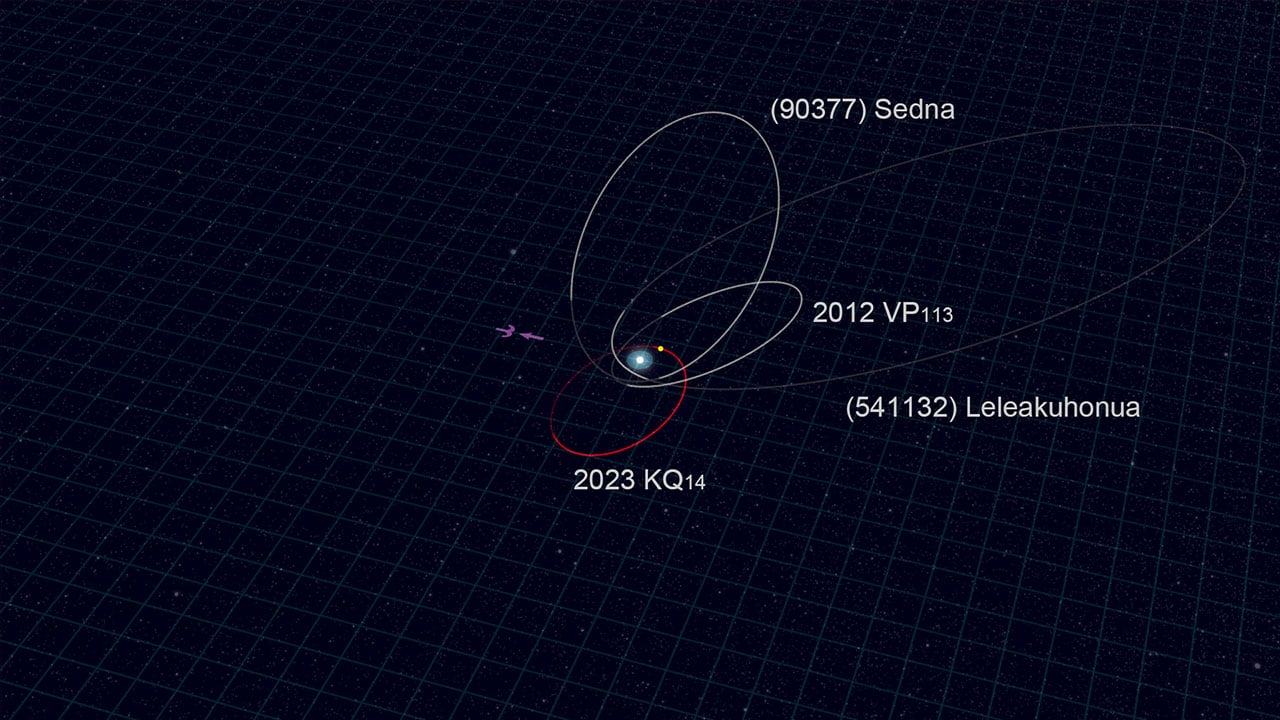
Astronomers using the Subaru Telescope have discovered a new object in the Kuiper Belt, beyond the orbit of Pluto. Designated 2023 KQ14, it's categorized as a "sednoid," with an extremely eccentric orbit - only the 4th ever discovered. Its orbit is much different from other sednoids, which challenges the hypothesis that Planet Nine could be aligning their orbits. It was found at 72 AU, but its path takes it all the way out to 438 AU, taking almost 4,000 years to complete one orbit.
Continue reading
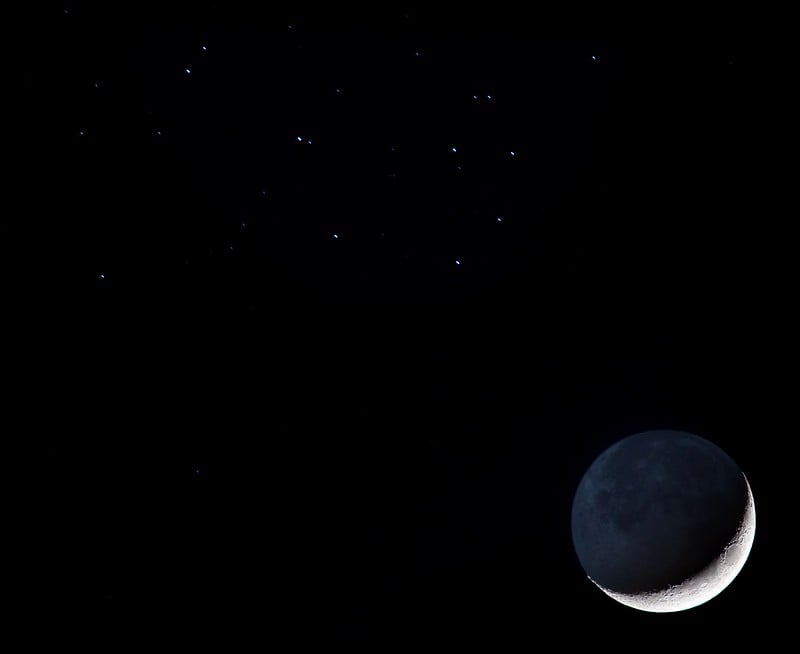

There’s a good reason for sky watchers to set their alarms this coming Sunday morning. If skies are clear, viewers across most of North America will have a rare chance to see the waning crescent Moon occult (pass in front of) the Pleiades open star cluster.
Continue reading
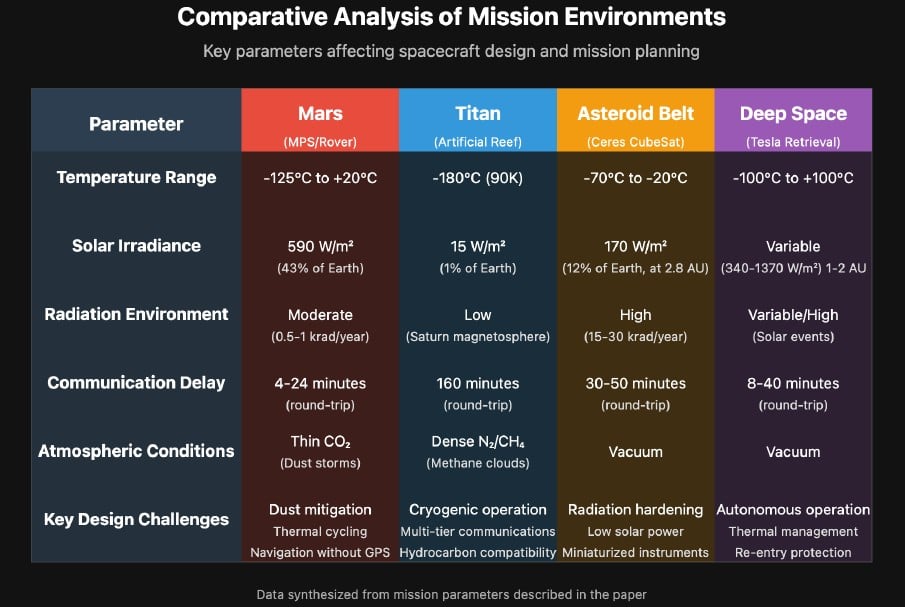
There are plenty of engineering challenges facing space exploration missions, most of which are specific to their missions objectives. However, there are some that are more universal, especially regarding electronics. A new paper primarily written by a group of American students temporarily studying at Escuela Tecnica Superior de Ingenieria in Madrid, attempts to lay out plans to tackle several of those challenges for a variety of mission architectures.
Continue reading
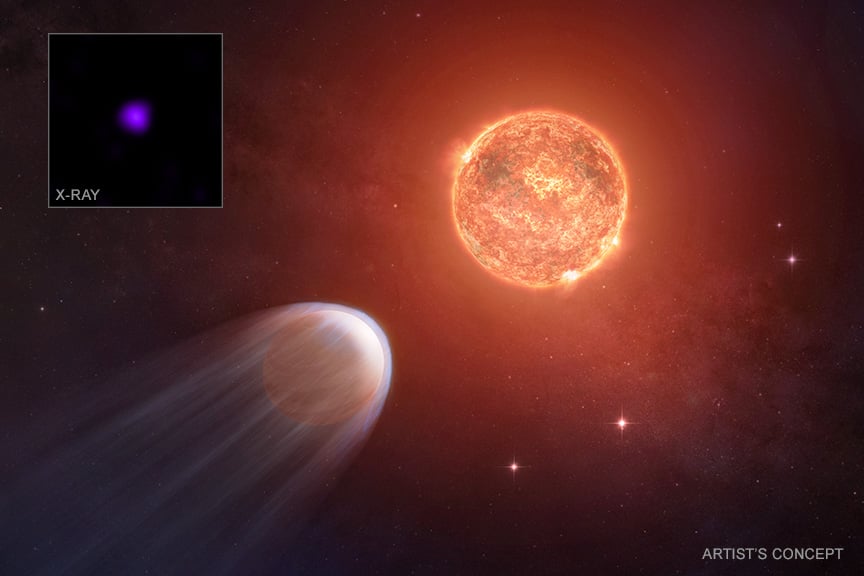

Astronomers have found a young star bathing a planet in intense X-ray radiation, wearing it away at a rapid rate. The planet is Jupiter-sized and orbits its red dwarf star at a fifth the distance from Mercury to the Sun. It's only 8 million years old, and researchers estimate that within a billion years, it will lose its entire atmosphere, going from 17 Earth masses down to just 2 Earth masses. They estimate that it's losing an Earth's atmosphere worth of mass every 200 years.
Continue reading
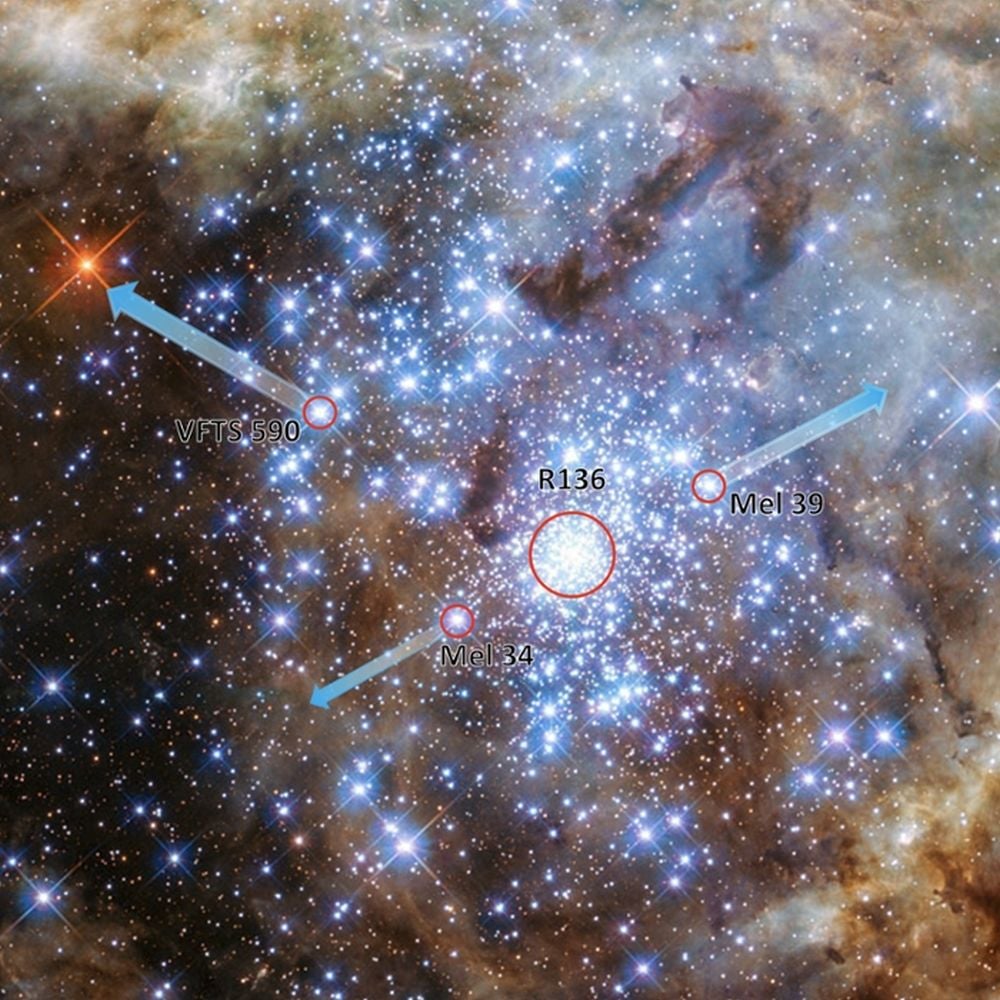

Mysteries abound in space. In the Tarantula Nebula, which lies in the Large Magellanic Cloud, astronomers used simulations to reconstruct how three stars were ejected from the star cluster R136, about 60,000 years ago. The analysis, published in Physical Review Letters, reveals that five stars were involved, an unexpected result.
Continue reading

Astronomers using the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA gravitational wave detectors announced the most massive black hole merger ever seen. Two black holes crashed together, producing a final black hole with approximately 225 times the mass of the Sun. Designated GW231123, it was detected during the 2023 observing run, and appears to be from the collision of 100- and 140-stellar-mass black holes. Black holes this massive are hard to get through standard stellar evolution, but could be the results of previous mergers.
Continue reading

The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope isn't due to launch until May 2027, but astronomers are preparing for its science operations by running simulated operations. One of those involves supernovae, massive stars the end their lives in gargantuan explosions. Research shows that the Roman could find 100,000 supernovae in one of its surveys.
Continue reading
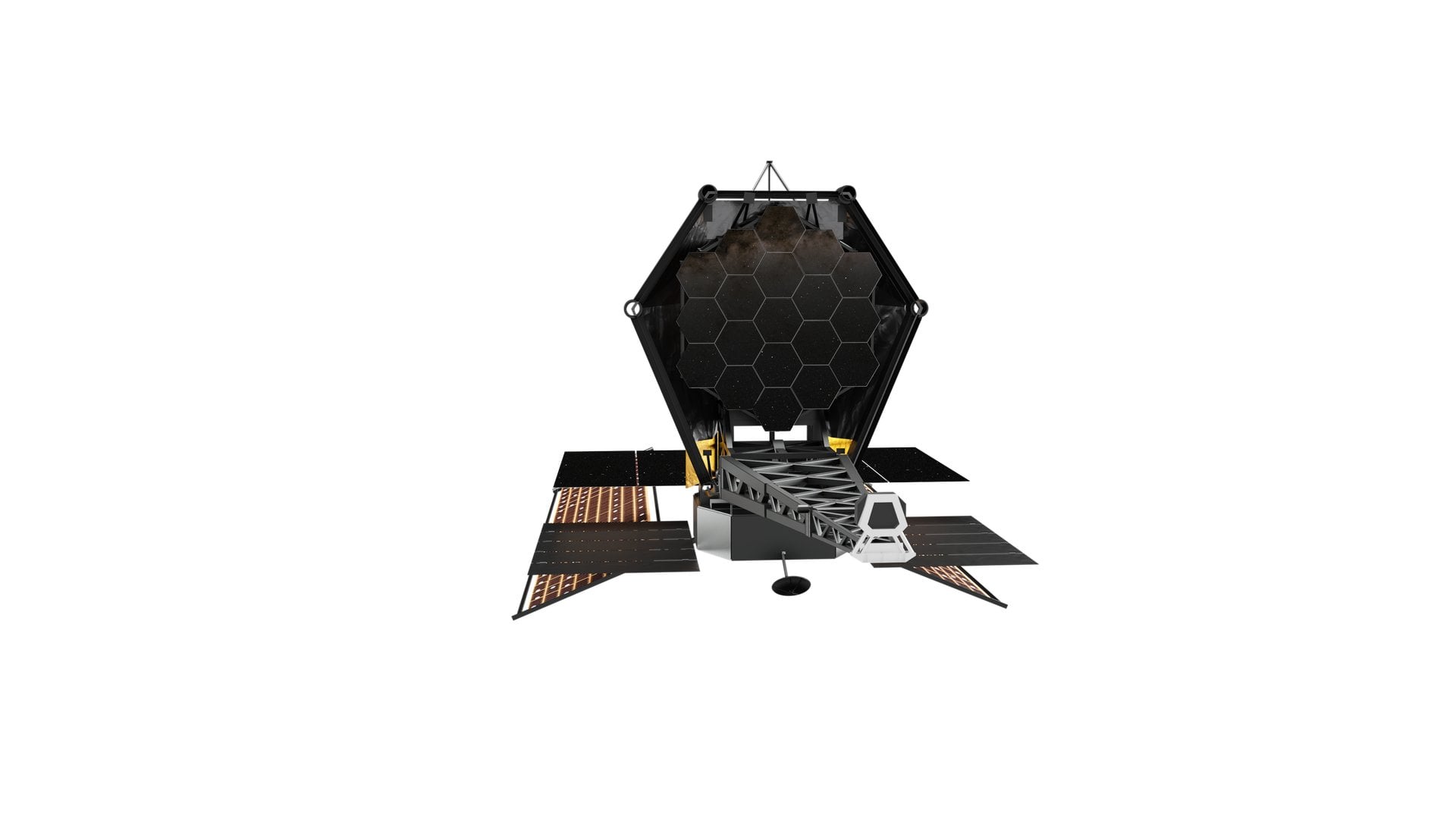

Searching for habitable exoplanets will require decades of work, new technologies, and new ideas. A lot of that effort seems to coalescing around the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO), a proposed mission expected to launch in the early 2040s that would be capable of directly imaging potentially habitable worlds, and, importantly, detecting features about them that could prove whether or not they host life as we know it. A new paper by exobiology specialists in Europe and the US, led by Svetlana Berdyugina of ISROL in Locarno, Switzerland, details an observational plan with HWO that could definitely prove that life exists on another planet - if they’re able to find one where it does anyway.
Continue reading
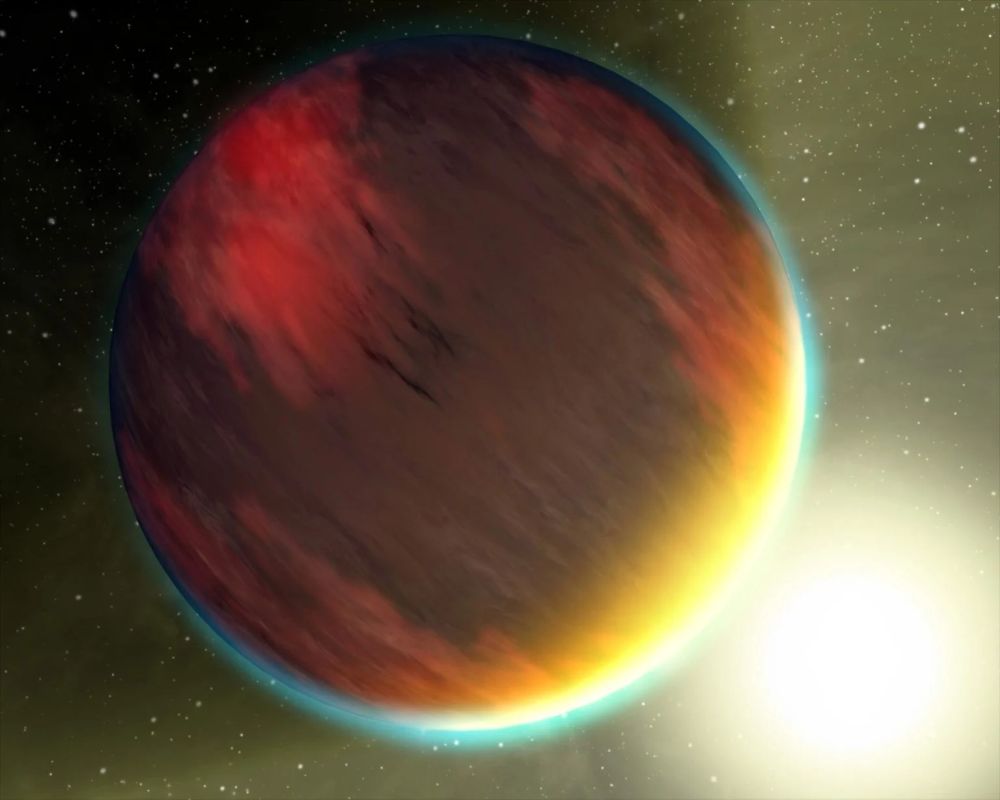

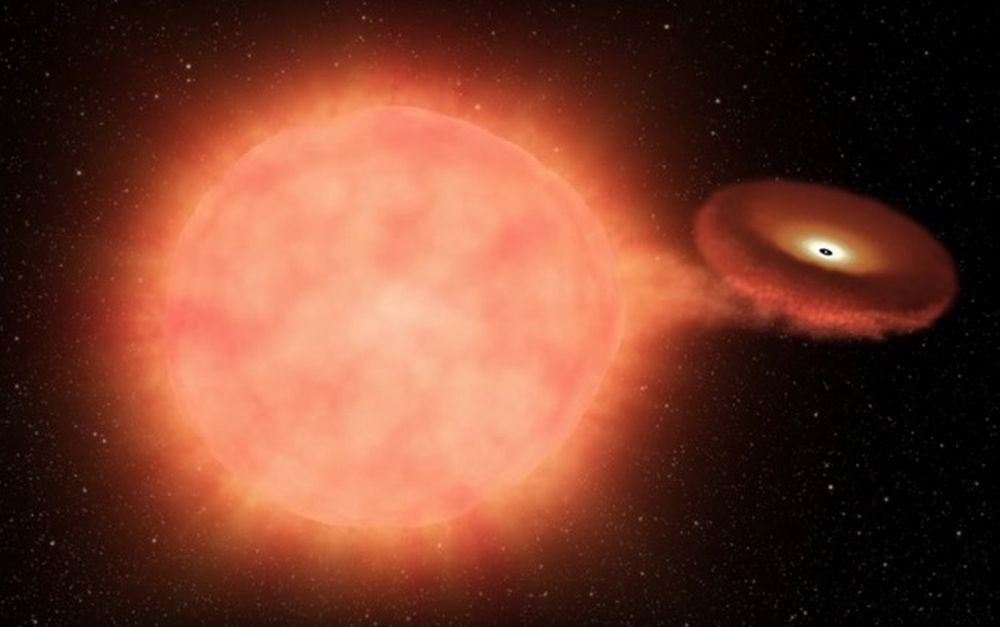
Macquarie University astronomers have tracked an extreme planet's orbital decay, confirming it is spiraling toward its star in a cosmic death dance that could end in three possible ways. It could cross the Roche line and be torn apart, it could plunge to destruction in its star, or it could be stripped all the way down to a rocky core.
Continue reading
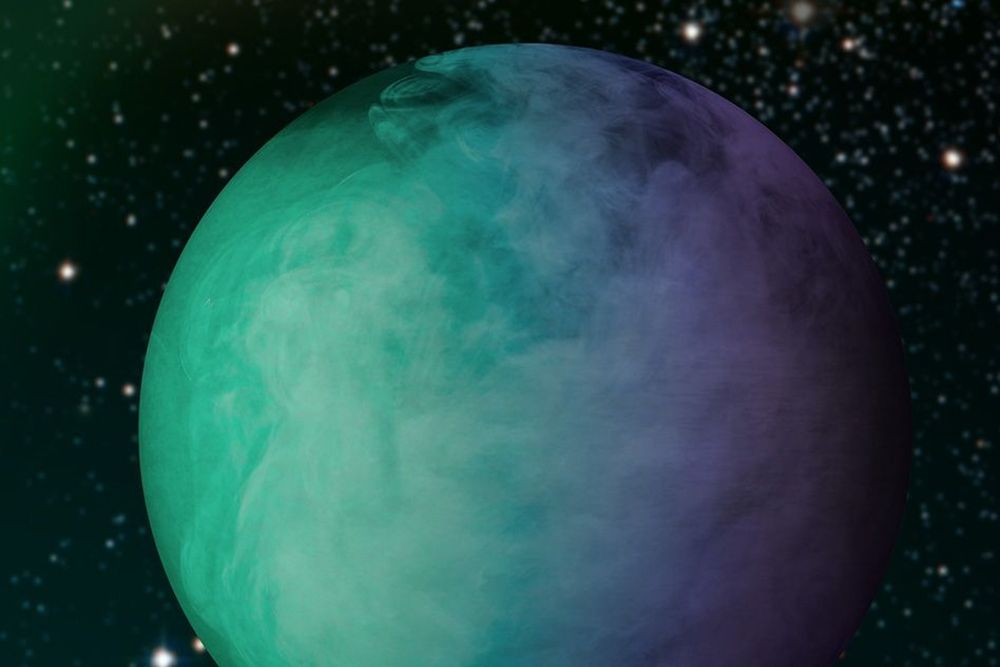

Atmospheric escape shapes an exoplanet's future. Earth's exosphere is extended and detectable due to ocean-related atmospheric escape. If we can detect the same features on an exoplanet, it could suggest oceans and habitability. But we need to build the Habitable Worlds Observatory first.
Continue reading
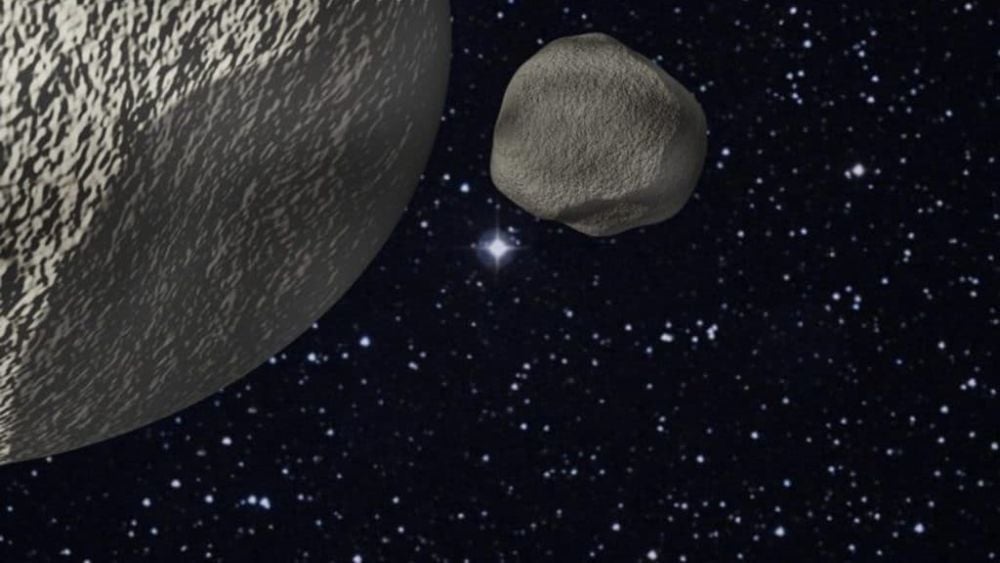

Trans-Neptunian Objects reside in the distant Solar System as remnants of the System's early days. They follow unusual orbits and range in colour from reds to greys. New research uses their colours and orbits to show how a stellar flyby can account for their modern-day orbits.
Continue reading

All eyes are on the newly discovered interstellar object 3I/ATLAS, currently inbound to the inner solar system. Initial observations have revealed that it's rich in water ice, and it's believed that it originated from the Milky Way's thick disk, ancient stars that orbit above and below the galactic plane. This could mean that 3I/ATLAS is billions of years older than the Solar System, the oldest comet ever discovered. It should reveal more as it heats up and outgasses as it gets closer to the Sun.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today


















