In the standard model of cosmology, dark energy fills the universe. It causes the universe to expand at an ever-increasing rate, and it makes up more than 70% of the cosmos. But there’s a problem. When we measure the rate of cosmic expansion in different ways, we get results that disagree with each other.
Continue reading “A New Test Confirms Dark Energy and the Expansion of the Universe”There’s a new method to measure the expansion rate of the Universe, but it doesn’t resolve the Crisis in Cosmology

In a recent post I wrote about a study that argued dark energy isn’t needed to explain the redshifts of distant supernovae. I also mentioned we shouldn’t rule out dark energy quite yet, because there are several independent measures of cosmic expansion that don’t require supernovae. Sure enough, a new study has measured cosmic expansion without all that mucking about with supernovae. The study confirms dark energy, but it also raises a few questions.
Continue reading “There’s a new method to measure the expansion rate of the Universe, but it doesn’t resolve the Crisis in Cosmology”Quasars with a Double-Image Gravitational Lens Could Help Finally Figure out how Fast the Universe is Expanding

How fast is the Universe expanding? That’s a question that astronomers haven’t been able to answer accurately. They have a name for the expansion rate of the Universe: The Hubble Constant, or Hubble’s Law. But measurements keep coming up with different values, and astronomers have been debating back and forth on this issue for decades.
The basic idea behind measuring the Hubble Constant is to look at distant light sources, usually a type of supernovae or variable stars referred to as ‘standard candles,’ and to measure the red-shift of their light. But no matter how astronomers do it, they can’t come up with an agreed upon value, only a range of values. A new study involving quasars and gravitational lensing might help settle the issue.
Continue reading “Quasars with a Double-Image Gravitational Lens Could Help Finally Figure out how Fast the Universe is Expanding”Gravitational waves were only recently observed, and now astronomers are already thinking of ways to use them: like accurately measuring the expansion rate of the Universe
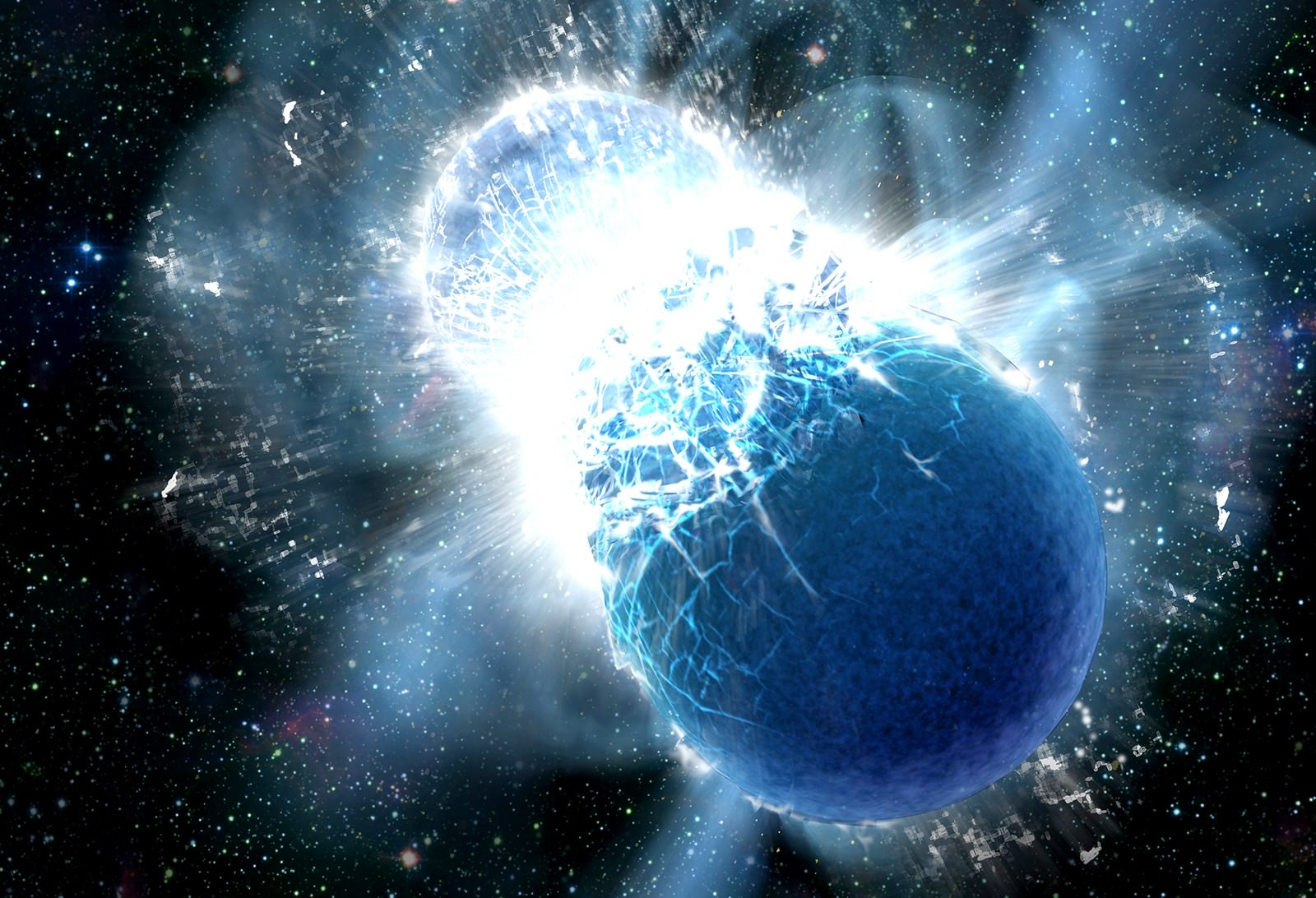

Neutron stars scream in waves of spacetime when they die, and astronomers have outlined a plan to use their gravitational agony to trace the history of the universe. Join us as we explore how to turn their pain into our cosmological profit.
How Fast is the Universe Expanding? Hubble and Gaia Team Up to Conduct the Most Accurate Measurements to Date

In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble made the groundbreaking discovery that the Universe was in a state of expansion. Originally predicted as a consequence of Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity, measurements of this expansion came to be known as Hubble’s Constant. Today, and with the help of next-generation telescopes – like the aptly-named Hubble Space Telescope (HST) – astronomers have remeasured and revised this law many times.
These measurements confirmed that the rate of expansion has increased over time, though scientists are still unsure why. The latest measurements were conducted by an international team using Hubble, who then compared their results with data obtained by the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Gaia observatory. This has led to the most precise measurements of the Hubble Constant to date, though questions about cosmic acceleration remain.
The study which describes their findings appeared in the July 12th issue of the Astrophysical Journal, titled “Milky Way Cepheid Standards for Measuring Cosmic Distances and Application to Gaia DR2: Implications for the Hubble Constant.” The team behind the study included members from the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI), the Johns Hopkins University, the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), UC Berkeley, Texas A&M University, and the European Southern Observatory (ESO).
Since 2005, Adam Riess – a Nobel Laureate Professor with the Space Telescope Science Institute and the Johns Hopkins University – has been working to refine the Hubble Constant value by streamlining and strengthening the “cosmic distance ladder”. Along with his team, known as Supernova H0 for the Equation of State (SH0ES), they have successfully reduced the uncertainty associated with the rate of cosmic expansion to just 2.2%
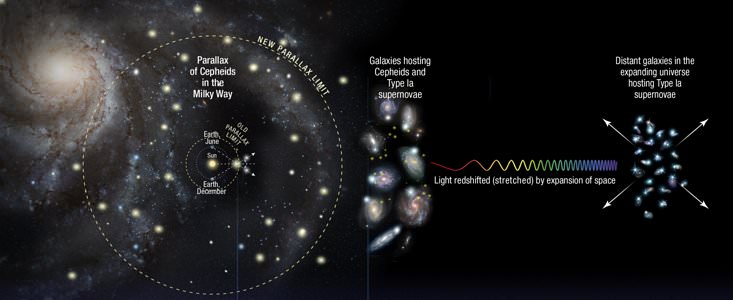
To break it down, astronomers have traditionally used the “cosmic distance ladder” to measure distances in the Universe. This consists of relying on distance markers like Cepheid variables in distant galaxies – pulsating stars whose distances can be inferred by comparing their intrinsic brightness with their apparent brightness. These measurements are then compared to the way light from distant galaxies is redshifted to determine how fast the space between galaxies is expanding.
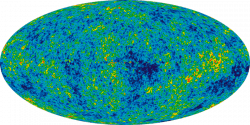
From this, the Hubble Constant is derived. Another method that is used is to observe the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) to trace the expansion of the cosmos during the early Universe – circa. 378,000 years after the Big Bang – and then using physics to extrapolate that to the present expansion rate. Together, the measurements should provide an end-to-end measurement of how the Universe has expanded over time.
However, astronomers have known for some time that the two measurements don’t match up. In a previous study, Riess and his team conducted measurements using Hubble to obtain a Hubble Constant value of 73 km/s (45.36 mps) per megaparsec (3.3 million light-years). Meanwhile, results based on the ESA’ Planck observatory (which observed the CMB between 2009 and 2013) predicted that the Hubble constant value should now be 67 km/s (41.63 mps) per megaparsec and no higher than 69 km/s (42.87 mps) – which represents a discrepancy of 9%.

As Riess indicated in a recent NASA press release:
“The tension seems to have grown into a full-blown incompatibility between our views of the early and late time universe. At this point, clearly it’s not simply some gross error in any one measurement. It’s as though you predicted how tall a child would become from a growth chart and then found the adult he or she became greatly exceeded the prediction. We are very perplexed.”
In this case, Riess and his colleagues used Hubble to gauge the brightness of distant Cepheid variables while Gaia provided the parallax information – the apparent change in an objects position based on different points of view – needed to determine the distance. Gaia also added to the study by measuring the distance to 50 Cepheid variables in the Milky Way, which were combined with brightness measurements from Hubble.
This allowed the astronomers to more accurately calibrate the Cepheids and then use those seen outside the Milky Way as milepost markers. Using both the Hubble measurements and newly released data from Gaia, Riess and his colleagues were able to refine their measurements on the present rate of expansion to 73.5 kilometers (45.6 miles) per second per megaparsec.

As Stefano Casertano, of the Space Telescope Science Institute and a member of the SHOES team, added:
“Hubble is really amazing as a general-purpose observatory, but Gaia is the new gold standard for calibrating distance. It is purpose-built for measuring parallax—this is what it was designed to do. Gaia brings a new ability to recalibrate all past distance measures, and it seems to confirm our previous work. We get the same answer for the Hubble constant if we replace all previous calibrations of the distance ladder with just the Gaia parallaxes. It’s a crosscheck between two very powerful and precise observatories.”
Looking to the future, Riess and his team hope to continue to work with Gaia so they can reduce the uncertainty associated with the value of the Hubble Constant to just 1% by the early 2020s. In the meantime, the discrepancy between modern rates of expansion and those based on the CMB will continue to be a puzzle to astronomers.
In the end, this may be an indication that other physics are at work in our Universe, that dark matter interacts with normal matter in a way that is different than what scientists suspect, or that dark energy could be even more exotic than previously thought. Whatever the cause, it is clear the Universe still has some surprises in store for us!
Further Reading: NASA
Precise New Measurements From Hubble Confirm the Accelerating Expansion of the Universe. Still no Idea Why it’s Happening
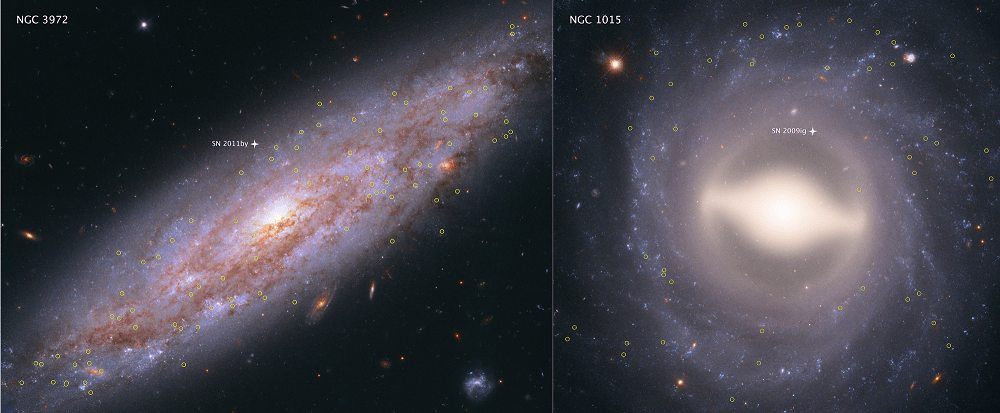
In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble made the groundbreaking revelation that the Universe was in a state of expansion. Originally predicted as a consequence of Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity, this confirmation led to what came to be known as Hubble’s Constant. In the ensuring decades, and thanks to the deployment of next-generation telescopes – like the aptly-named Hubble Space Telescope (HST) – scientists have been forced to revise this law.
In short, in the past few decades, the ability to see farther into space (and deeper into time) has allowed astronomers to make more accurate measurements about how rapidly the early Universe expanded. And thanks to a new survey performed using Hubble, an international team of astronomers has been able to conduct the most precise measurements of the expansion rate of the Universe to date.
This survey was conducted by the Supernova H0 for the Equation of State (SH0ES) team, an international group of astronomers that has been on a quest to refine the accuracy of the Hubble Constant since 2005. The group is led by Adam Reiss of the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) and Johns Hopkins University, and includes members from the American Museum of Natural History, the Neils Bohr Institute, the National Optical Astronomy Observatory, and many prestigious universities and research institutions.
The study which describes their findings recently appeared in The Astrophysical Journal under the title “Type Ia Supernova Distances at Redshift >1.5 from the Hubble Space Telescope Multi-cycle Treasury Programs: The Early Expansion Rate“. For the sake of their study, and consistent with their long term goals, the team sought to construct a new and more accurate “distance ladder”.
This tool is how astronomers have traditionally measured distances in the Universe, which consists of relying on distance markers like Cepheid variables – pulsating stars whose distances can be inferred by comparing their intrinsic brightness with their apparent brightness. These measurements are then compared to the way light from distance galaxies is redshifted to determine how fast the space between galaxies is expanding.
From this, the Hubble Constant is derived. To build their distant ladder, Riess and his team conducted parallax measurements using Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) of eight newly-analyzed Cepheid variable stars in the Milky Way. These stars are about 10 times farther away than any studied previously – between 6,000 and 12,000 light-year from Earth – and pulsate at longer intervals.
To ensure accuracy that would account for the wobbles of these stars, the team also developed a new method where Hubble would measure a star’s position a thousand times a minute every six months for four years. The team then compared the brightness of these eight stars with more distant Cepheids to ensure that they could calculate the distances to other galaxies with more precision.

Using the new technique, Hubble was able to capture the change in position of these stars relative to others, which simplified things immensely. As Riess explained in a NASA press release:
“This method allows for repeated opportunities to measure the extremely tiny displacements due to parallax. You’re measuring the separation between two stars, not just in one place on the camera, but over and over thousands of times, reducing the errors in measurement.”
Compared to previous surveys, the team was able to extend the number of stars analyzed to distances up to 10 times farther. However, their results also contradicted those obtained by the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Planck satellite, which has been measuring the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) – the leftover radiation created by the Big Bang – since it was deployed in 2009.
By mapping the CMB, Planck has been able to trace the expansion of the cosmos during the early Universe – circa. 378,000 years after the Big Bang. Planck’s result predicted that the Hubble constant value should now be 67 kilometers per second per megaparsec (3.3 million light-years), and could be no higher than 69 kilometers per second per megaparsec.
Based on their sruvey, Riess’s team obtained a value of 73 kilometers per second per megaparsec, a discrepancy of 9%. Essentially, their results indicate that galaxies are moving at a faster rate than that implied by observations of the early Universe. Because the Hubble data was so precise, astronomers cannot dismiss the gap between the two results as errors in any single measurement or method. As Reiss explained:
“The community is really grappling with understanding the meaning of this discrepancy… Both results have been tested multiple ways, so barring a series of unrelated mistakes. it is increasingly likely that this is not a bug but a feature of the universe.”
These latest results therefore suggest that some previously unknown force or some new physics might be at work in the Universe. In terms of explanations, Reiss and his team have offered three possibilities, all of which have to do with the 95% of the Universe that we cannot see (i.e. dark matter and dark energy). In 2011, Reiss and two other scientists were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their 1998 discovery that the Universe was in an accelerated rate of expansion.
Consistent with that, they suggest that Dark Energy could be pushing galaxies apart with increasing strength. Another possibility is that there is an undiscovered subatomic particle out there that is similar to a neutrino, but interacts with normal matter by gravity instead of subatomic forces. These “sterile neutrinos” would travel at close to the speed of light and could collectively be known as “dark radiation”.

Any of these possibilities would mean that the contents of the early Universe were different, thus forcing a rethink of our cosmological models. At present, Riess and colleagues don’t have any answers, but plan to continue fine-tuning their measurements. So far, the SHoES team has decreased the uncertainty of the Hubble Constant to 2.3%.
This is in keeping with one of the central goals of the Hubble Space Telescope, which was to help reduce the uncertainty value in Hubble’s Constant, for which estimates once varied by a factor of 2.
So while this discrepancy opens the door to new and challenging questions, it also reduces our uncertainty substantially when it comes to measuring the Universe. Ultimately, this will improve our understanding of how the Universe evolved after it was created in a fiery cataclysm 13.8 billion years ago.
Further Reading: NASA, The Astrophysical Journal
At the Largest Scales, Our Milky Way Galaxy is in the Middle of Nowhere

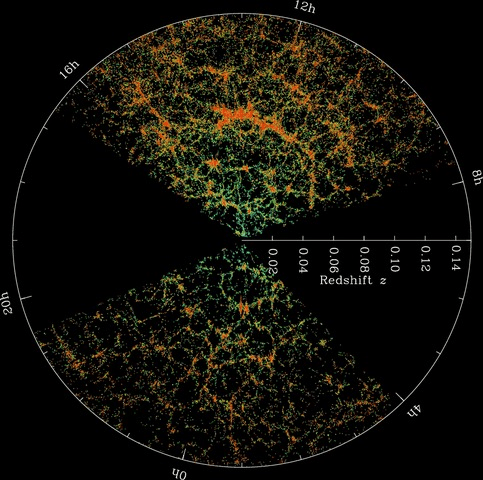
Ever since Galileo pointed his telescope at Jupiter and saw moons in orbit around that planet, we began to realize we don’t occupy a central, important place in the Universe. In 2013, a study showed that we may be further out in the boondocks than we imagined. Now, a new study confirms it: we live in a void in the filamental structure of the Universe, a void that is bigger than we thought.
In 2013, a study by University of Wisconsin–Madison astronomer Amy Barger and her student Ryan Keenan showed that our Milky Way galaxy is situated in a large void in the cosmic structure. The void contains far fewer galaxies, stars, and planets than we thought. Now, a new study from University of Wisconsin student Ben Hoscheit confirms it, and at the same time eases some of the tension between different measurements of the Hubble Constant.
The void has a name; it’s called the KBC void for Keenan, Barger and the University of Hawaii’s Lennox Cowie. With a radius of about 1 billion light years, the KBC void is seven times larger than the average void, and it is the largest void we know of.
The large-scale structure of the Universe consists of filaments and clusters of normal matter separated by voids, where there is very little matter. It’s been described as “Swiss cheese-like.” The filaments themselves are made up of galaxy clusters and super-clusters, which are themselves made up of stars, gas, dust and planets. Finding out that we live in a void is interesting on its own, but its the implications it has for Hubble’s Constant that are even more interesting.
Hubble’s Constant is the rate at which objects move away from each other due to the expansion of the Universe. Dr. Brian Cox explains it in this short video.
The problem with Hubble’s Constant, is that you get a different result depending on how you measure it. Obviously, this is a problem. “No matter what technique you use, you should get the same value for the expansion rate of the universe today,” explains Ben Hoscheit, the Wisconsin student who presented his analysis of the KBC void on June 6th at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society. “Fortunately, living in a void helps resolve this tension.”
There are a couple ways of measuring the expansion rate of the Universe, known as Hubble’s Constant. One way is to use what are known as “standard candles.” Supernovae are used as standard candles because their luminosity is so well-understood. By measuring their luminosity, we can determine how far away the galaxy they reside in is.
Another way is by measuring the CMB, the Cosmic Microwave Background. The CMB is the left over energy imprint from the Big Bang, and studying it tells us the state of expansion in the Universe.
The two methods can be compared. The standard candle approach measures more local distances, while the CMB approach measures large-scale distances. So how does living in a void help resolve the two?
Measurements from inside a void will be affected by the much larger amount of matter outside the void. The gravitational pull of all that matter will affect the measurements taken with the standard candle method. But that same matter, and its gravitational pull, will have no effect on the CMB method of measurement.
“One always wants to find consistency, or else there is a problem somewhere that needs to be resolved.” – Amy Barger, University of Hawaii, Dept. of Physics and Astronomy
Hoscheit’s new analysis, according to Barger, the author of the 2013 study, shows that Keenan’s first estimations of the KBC void, which is shaped like a sphere with a shell of increasing thickness made up of galaxies, stars and other matter, are not ruled out by other observational constraints.
“It is often really hard to find consistent solutions between many different observations,” says Barger, an observational cosmologist who also holds an affiliate graduate appointment at the University of Hawaii’s Department of Physics and Astronomy. “What Ben has shown is that the density profile that Keenan measured is consistent with cosmological observables. One always wants to find consistency, or else there is a problem somewhere that needs to be resolved.”
What are Cepheid Variables?
The Universe is a really, really big place. We’re talking… imperceptibly big! In fact, based on decades worth of observations, astronomers now believe that the observable Universe measures about 46 billion light years across. The key word there is observable, because when you take into account that which we cannot see, scientists think it’s actually more like 92 billion light years across.
The hardest part in all of this is making accurate measurements of the distances involved. But since the birth of modern astronomy, increasingly accurate methods have evolved. Aside from redshift and examining the light coming from distant stars and galaxies, astronomers also rely on a class of stars known as Cepheid Variables (CVs) to determine the distance of objects within and beyond our Galaxy.
Definition:
Variable stars are essentially stars that experience fluctuations in their brightness (aka. absolute luminosity). Cepheids Variables are special type of variable star in that they are hot and massive – five to twenty times as much mass as our Sun – and are known for their tendency to pulsate radially and vary in both diameter and temperature.
What’s more, these pulsations are directly related to their absolute luminosity, which occurs within well-defined and predictable time periods (ranging from 1 to 100 days). When plotted as a magnitude vs. period relationship, the shape of the Cephiad luminosity curve resembles that of a “shark fin” – do its sudden rise and peak, followed by a steadier decline.
The name is derived from Delta Cephei, a variable star in the Cepheus constellation that was the first CV to be identified. Analysis of this star’s spectrum suggests that CVs also undergo changes in terms of temperature (between 5500 – 66oo K) and diameter (~15%) during a pulsation period.
Use in Astronomy:
The relationship between the period of variability and the luminosity of CV stars makes them very useful in determining the distance of objects in our Universe. Once the period is measured, the luminosity can be determined, thus yielding accurate estimates of the star’s distance using distance modulus equation.
This equation states that: m – M = 5 log d – 5 – where m is the apparent magnitude of the object, M is the absolute magnitude of the object, and d is the distance to the object in parsecs. Cepheid variables can be seen and measured to a distance of about 20 million light years, compared to a maximum distance of about 65 light years for Earth-based parallax measurements and just over 326 light years for the ESA’s Hipparcos mission.

Because they are bright, and can be clearly seen million of light years away, they can be easily distinguished from other bright stars in their vicinity. Combined with the relationship between their variability and luminosity, this makes them highly useful tools in deducing the size and scale of our Universe.
Classes:
Cepheid variables are divided into two subclasses – Classical Cepheids and Type II Cepheids – based on differences in their masses, ages, and evolutionary histories. Classical Cepheids are Population I (metal-rich) variable stars that are 4-20 times more massive than the Sun and up to 100,000 times more luminous. They undergo pulsations with very regular periods on the order of days to months.
These Cepheids are typically yellow bright giants and supergiants (spectral class F6 – K2) and they experience radius changes in the millions of kilometers during a pulsation cycle. Classical Cepheids are used to determine distances to galaxies within the Local Group and beyond, and are a means by which the Hubble Constant can be established (see below).
Type II Cepheids are Population II (metal-poor) variable stars which pulsate with periods of typically between 1 and 50 days. Type II Cepheids are also older stars (~10 billion years) that have around half the mass of our Sun.
Type II Cepheids are also subdivided based on their period into the BL Her, W Virginis, and RV Tauri subclasses (named after specific examples) – which have periods of 1-4 days, 10-20 days, and more than 20 days, respectively. Type II Cepheids are used to establish the distance to the Galactic Center, globular clusters, and neighboring galaxies.
There are also those that do not fit into either category, which are known as Anomalous Cepheids. These variables have periods of less than 2 days (similar to RR Lyrae) but have higher luminosities. They also have higher masses than Type II Cepheids, and have unknown ages.
A small proportion of Cepheid variables have also been observed which pulsate in two modes at the same time, hence the name Double-mode Cepheids. A very small number pulsate in three modes, or an unusual combination of modes.
History of Observation:
The first Cepheid variable to be discovered was Eta Aquilae, which was observed on September 10th, 1784, by English astronomer Edward Pigott. Delta Cephei, for which this class of star is named, was discovered a few months later by amateur English astronomer John Goodricke.
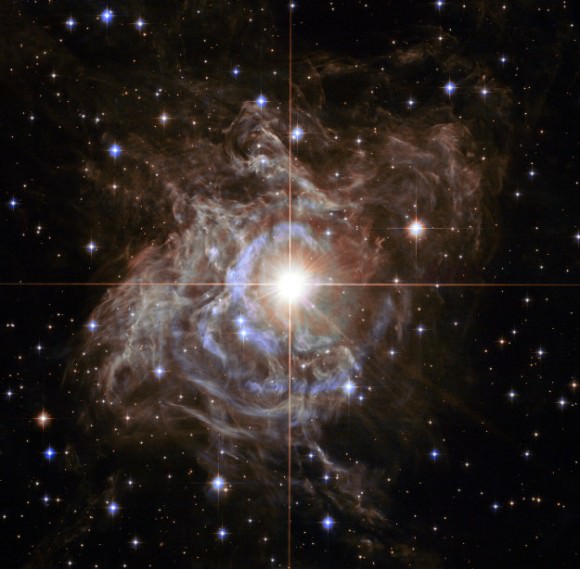

In 1908, during an investigation of variable stars in the Magellanic Clouds, American astronomer Henrietta Swan Leavitt discovered the relationship between the period and luminosity of Classical Cepheids. After recording the periods of 25 different variables stars, she published her findings in 1912.
In the following years, several more astronomers would conduct research on Cepheids. By 1925, Edwin Hubble was able to establish the distance between the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy based on Cepheid variables within the latter. These findings were pivotal, in that they settled the Great Debate, where astronomers sought to established whether or not the Milky Way was unique, or one of many galaxies in the Universe.
By gauging the distance between the Milky Way and several other galaxies, and combining it with Vesto Slipher’s measurements of their redshift, Hubble and Milton L. Humason were able to formulate Hubble’s Law. In short, they were able to prove that the Universe is in a state of expansion, something that had been suggested years prior.
Further developments during the 20th century included dividing Cepheids into different classes, which helped resolve issues in determining astronomical distances. This was done largely by Walter Baade, who in the 1940s recognized the difference between Classical and Type II Cepheids based on their size, age and luminosities.
Limitations:
Despite their value in determining astronomical distances, there are some limitations with this method. Chief among them is the fact that with Type II Cepheids, the relationship between period and luminosity can be effected by their lower metallicity, photometric contamination, and the changing and unknown effect that gas and dust have on the light they emit (stellar extinction).
These unresolved issues have resulted in different values being cited for Hubble’s Constant – which range between 60 km/s per 1 million parsecs (Mpc) and 80 km/s/Mpc. Resolving this discrepancy is one of the largest problems in modern cosmology, since the true size and rate of expansion of the Universe are linked.
However, improvements in instrumentation and methodology are increasing the accuracy with which Cepheid Variables are observed. In time, it is hoped that observations of these curious and unique stars will yield truly accurate values, thus removing a key source of doubt about our understanding of the Universe.
We have written many interesting articles about Cepheid Variables here at Universe Today. Here’s Astronomers Find New Way to Measure Cosmic Distances, Astronomers Use Light Echo to Measure the Distance to a Star, and Astronomers Closing in on Dark Energy with Refined Hubble Constant.
Astronomy Cast has an interesting episode that explains the differences between Population I and II stars – Episode 75: Stellar Populations.
Sources:
The Hubble Constant Just Got Constantier
Just when we think we understand the Universe pretty well, along come some astronomers to upend everything. In this case, something essential to everything we know and see has been turned on its head: the expansion rate of the Universe itself, aka the Hubble Constant.
A team of astronomers using the Hubble telescope has determined that the rate of expansion is between five and nine percent faster than previously measured. The Hubble Constant is not some curiousity that can be shelved until the next advances in measurement. It is part and parcel of the very nature of everything in existence.
“This surprising finding may be an important clue to understanding those mysterious parts of the universe that make up 95 percent of everything and don’t emit light, such as dark energy, dark matter, and dark radiation,” said study leader and Nobel Laureate Adam Riess of the Space Telescope Science Institute and The Johns Hopkins University, both in Baltimore, Maryland.
But before we get into the consequences of this study, let’s back up a bit and look at how the Hubble Constant is measured.
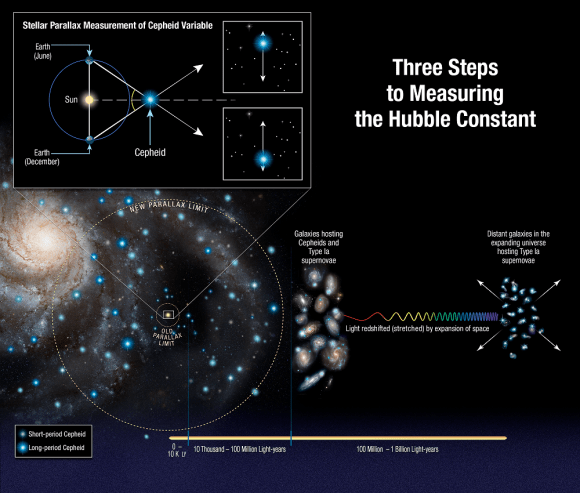
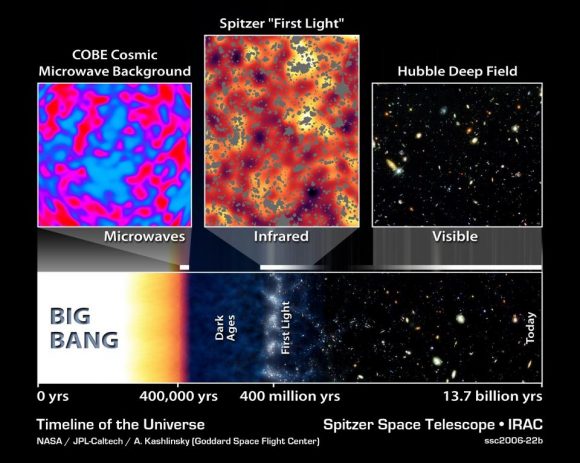
Measuring the expansion rate of the Universe is a tricky business. Using the image at the top, it works like this:
- Within the Milky Way, the Hubble telescope is used to measure the distance to Cepheid variables, a type of pulsating star. Parallax is used to do this, and parallax is a basic tool of geometry, which is also used in surveying. Astronomers know what the true brightness of Cepheids are, so comparing that to their apparent brightness from Earth gives an accurate measurement of the distance between the star and us. Their rate of pulsation also fine tunes the distance calculation. Cepheid variables are sometimes called “cosmic yardsticks” for this reason.
- Then astronomers turn their sights on other nearby galaxies which contain not only Cepheid variables, but also Type 1a supernova, another well-understood type of star. These supernovae, which are of course exploding stars, are another reliable yardstick for astronomers. The distance to these galaxies is obtained by using the Cepheids to measure the true brightness of the supernovae.
- Next, astronomers point the Hubble at galaxies that are even further away. These ones are so distant, that any Cepheids in those galaxies cannot be seen. But Type 1a supernovae are so bright that they can be seen, even at these enormous distances. Then, astronomers compare the true and apparent brightnesses of the supernovae to measure out to the distance where the expansion of the Universe can be seen. The light from the distant supernovae is “red-shifted”, or stretched, by the expansion of space. When the measured distance is compared with the red-shift of the light, it yields a measurement of the rate of the expansion of the Universe.
- Take a deep breath and read all that again.
The great part of all of this is that we have an even more accurate measurement of the rate of expansion of the Universe. The uncertainty in the measurement is down to 2.4%. The challenging part is that this rate of expansion of the modern Universe doesn’t jive with the measurement from the early Universe.
The rate of expansion of the early Universe is obtained from the left over radiation from the Big Bang. When that cosmic afterglow is measured by NASA’s Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) and the ESA’s Planck satellite, it yields a smaller rate of expansion. So the two don’t line up. It’s like building a bridge, where construction starts at both ends and should line up by the time you get to the middle. (Caveat: I have no idea if bridges are built like that.)

“You start at two ends, and you expect to meet in the middle if all of your drawings are right and your measurements are right,” Riess said. “But now the ends are not quite meeting in the middle and we want to know why.”
“If we know the initial amounts of stuff in the universe, such as dark energy and dark matter, and we have the physics correct, then you can go from a measurement at the time shortly after the big bang and use that understanding to predict how fast the universe should be expanding today,” said Riess. “However, if this discrepancy holds up, it appears we may not have the right understanding, and it changes how big the Hubble constant should be today.”
Why it doesn’t all add up is the fun, and maybe maddening, part of this.
What we call Dark Energy is the force that drives the expansion of the Universe. Is Dark Energy growing stronger? Or how about Dark Matter, which comprises most of the mass in the Universe. We know we don’t know much about it. Maybe we know even less than that, and its nature is changing over time.
“We know so little about the dark parts of the universe, it’s important to measure how they push and pull on space over cosmic history,” said Lucas Macri of Texas A&M University in College Station, a key collaborator on the study.
The team is still working with the Hubble to reduce the uncertainty in measurements of the rate of expansion. Instruments like the James Webb Space Telescope and the European Extremely Large Telescope might help to refine the measurement even more, and help address this compelling issue.
How Are Galaxies Moving Away Faster Than Light?
So, how can galaxies be traveling faster than the speed of light when nothing can travel faster than light?
I’m a little world of contradictions. “Not even light itself can escape a black hole”, and then, “black holes and they are the brightest objects in the Universe”. I’ve also said “nothing can travel faster than the speed of light”. And then I’ll say something like, “ galaxies are moving away from us faster than the speed of light.” There’s more than a few items on this list, and it’s confusing at best. Thanks Universe!
So, how can galaxies be traveling faster than the speed of light when nothing can travel faster than light? Warp speed galaxies come up when I talk about the expansion of the Universe. Perhaps it’s dark energy acceleration, or the earliest inflationary period of the Universe when EVERYTHING expanded faster than the speed of light.
Imagine our expanding Universe. It’s not an explosion from a specific place, with galaxies hurtling out like cosmic jetsam. It’s an expansion of space. There’s no center, and the Universe isn’t expanding into anything.
I’d suggested that this is a terribly oversimplified model for our Universe expanding. Unfortunately, it’s also terribly convenient. I can steal it from my children whenever I want.
Imagine you’re this node here, and as the toy expands, you see all these other nodes moving away from you. And if you were to move to any other node, you’d see all the other nodes moving away from you.
Here’s the interesting part, these nodes over here, twice as far away as the closer ones, appear to move more quickly away from you. The further out the node is, the faster it appears to be moving away from you.
This is our freaky friend, the Hubble Constant, the idea that for every megaparsec of distance between us and a distant galaxy, the speed separating them increases by about 71 kilometers per second.
Galaxies separated by 2 parsecs will increase their speed by 142 kilometers every second. If you run the mathatron, once you get out to 4,200 megaparsecs away, two galaxies will see each other traveling away faster than the speed of light. How big Is that, is it larger than the Universe?
The first light ever, the cosmic microwave background radiation, is 46 billion light-years away from us in all directions. I did the math and 4,200 megaparsecs is a little over 13.7 billion light-years.There’s mountains of room for objects to be more than 4,200 megaparsecs away from each other. Thanks Universe?!?
Most of the Universe we can see is already racing away at faster than the speed of light. So how it’s possible to see the light from any galaxies moving faster than the speed of light. How can we even see the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation? Thanks Universe.
Light emitted by the galaxies is moving towards us, while the galaxy itself is traveling away from us, so the photons emitted by all the stars can still reach us. These wavelengths of light get all stretched out, and duckslide further into the red end of the spectrum, off to infrared, microwave, and even radio waves. Given time, the photons will be stretched so far that we won’t be able to detect the galaxy at all.
In the distant future, all galaxies and radiation we see today will have faded away to be completely undetectable. Future astronomers will have no idea that there was ever a Big Bang, or that there are other galaxies outside the Milky Way. Thanks Universe.
I stand with Einstein when I say that nothing can move faster than light through space, but objects embedded in space can appear to expand faster than the speed of light depending on your perspective.
What aspects about cosmology still give you headaches? Give us some ideas for topics in the comments below.