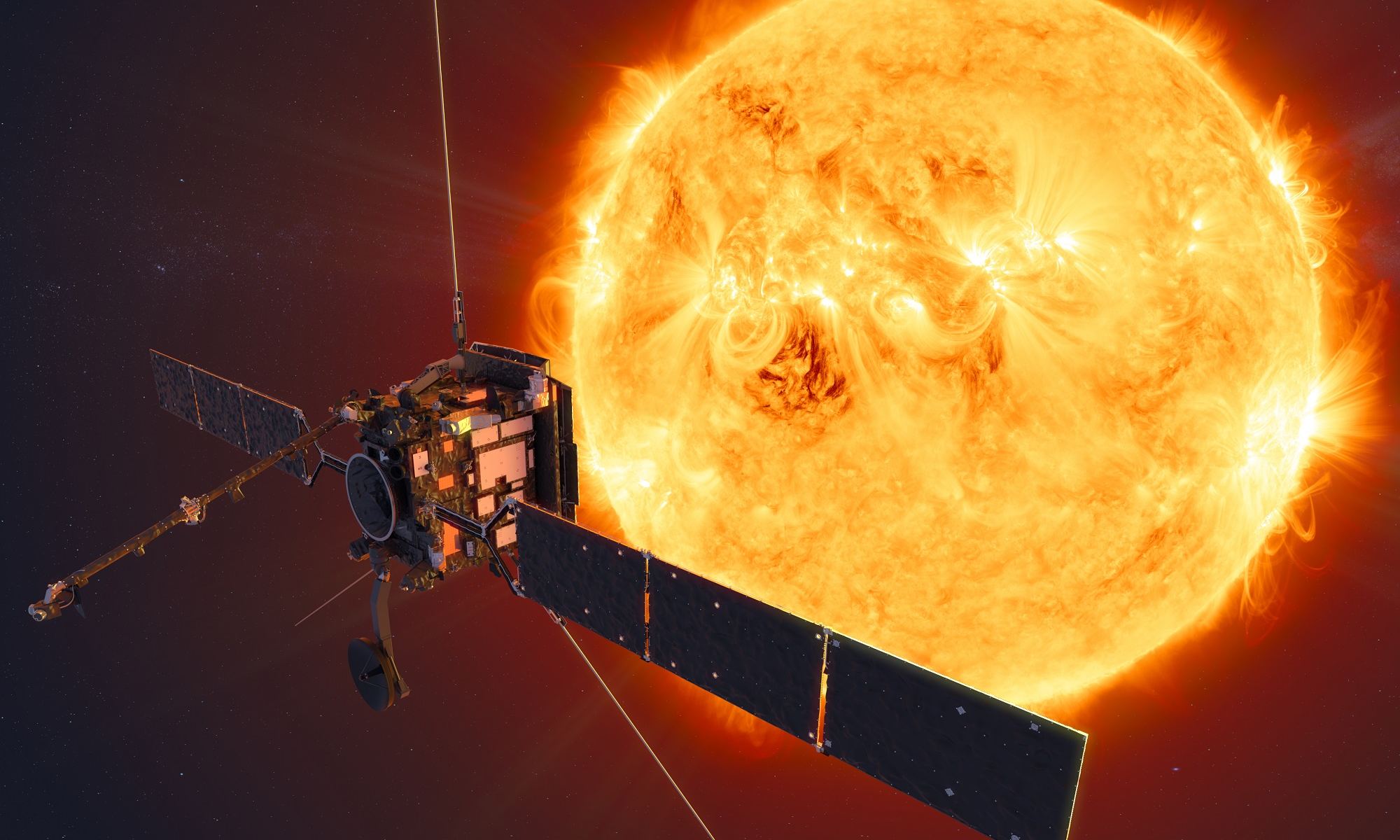
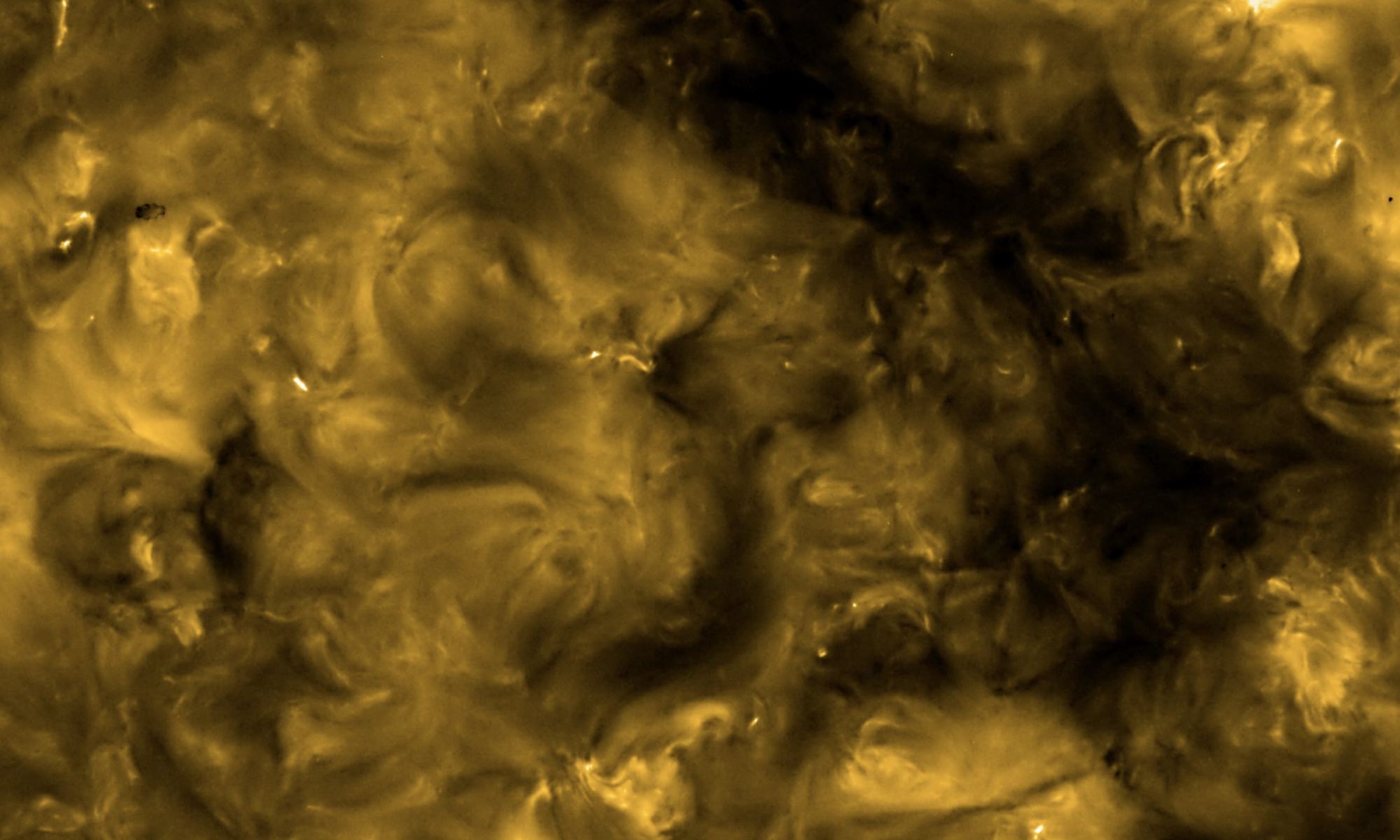
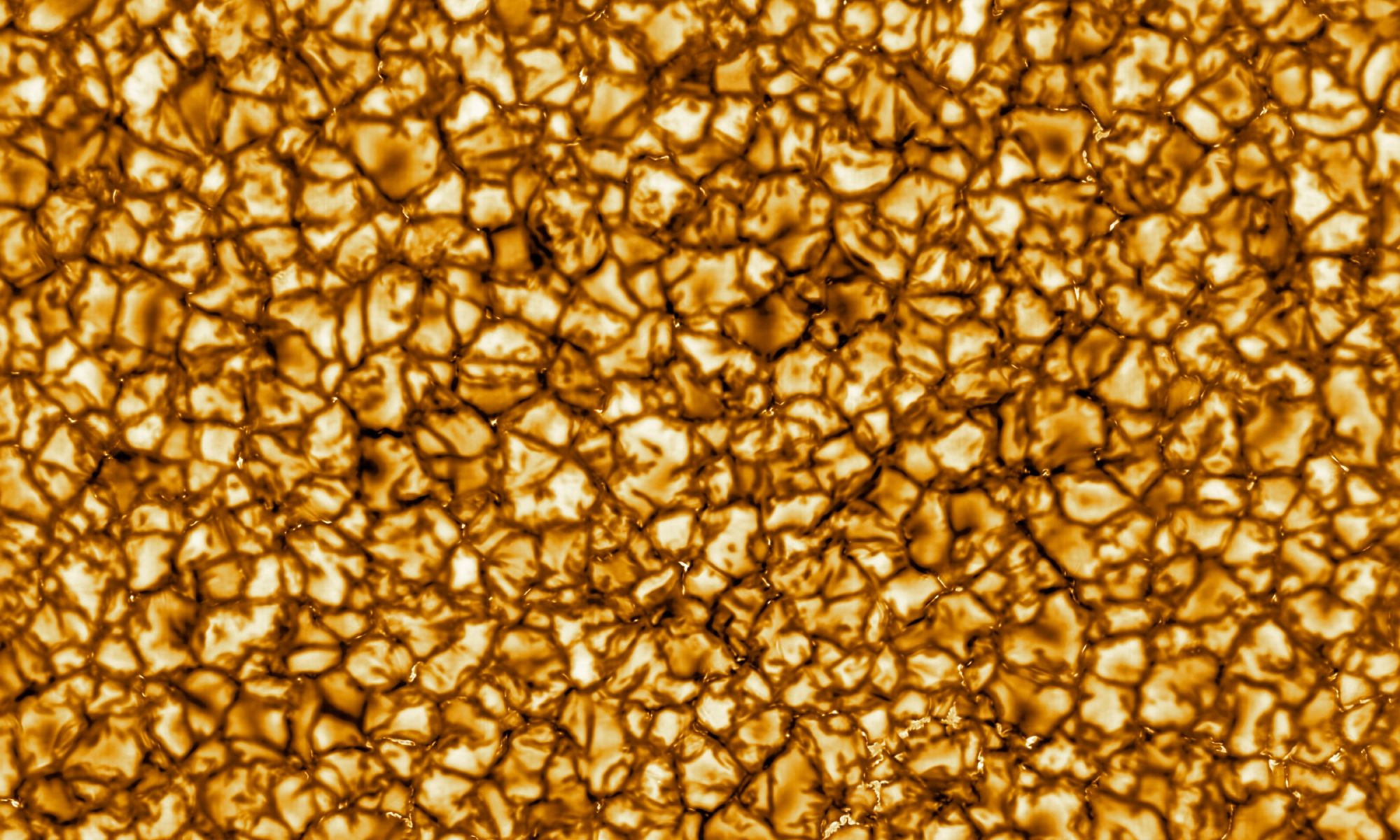
While actually walking on the sun is still just a dream of Smash Mouth fans, humanity has gotten a little bit closer to our nearest solar neighbor with the recent launch of the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter (SolO).
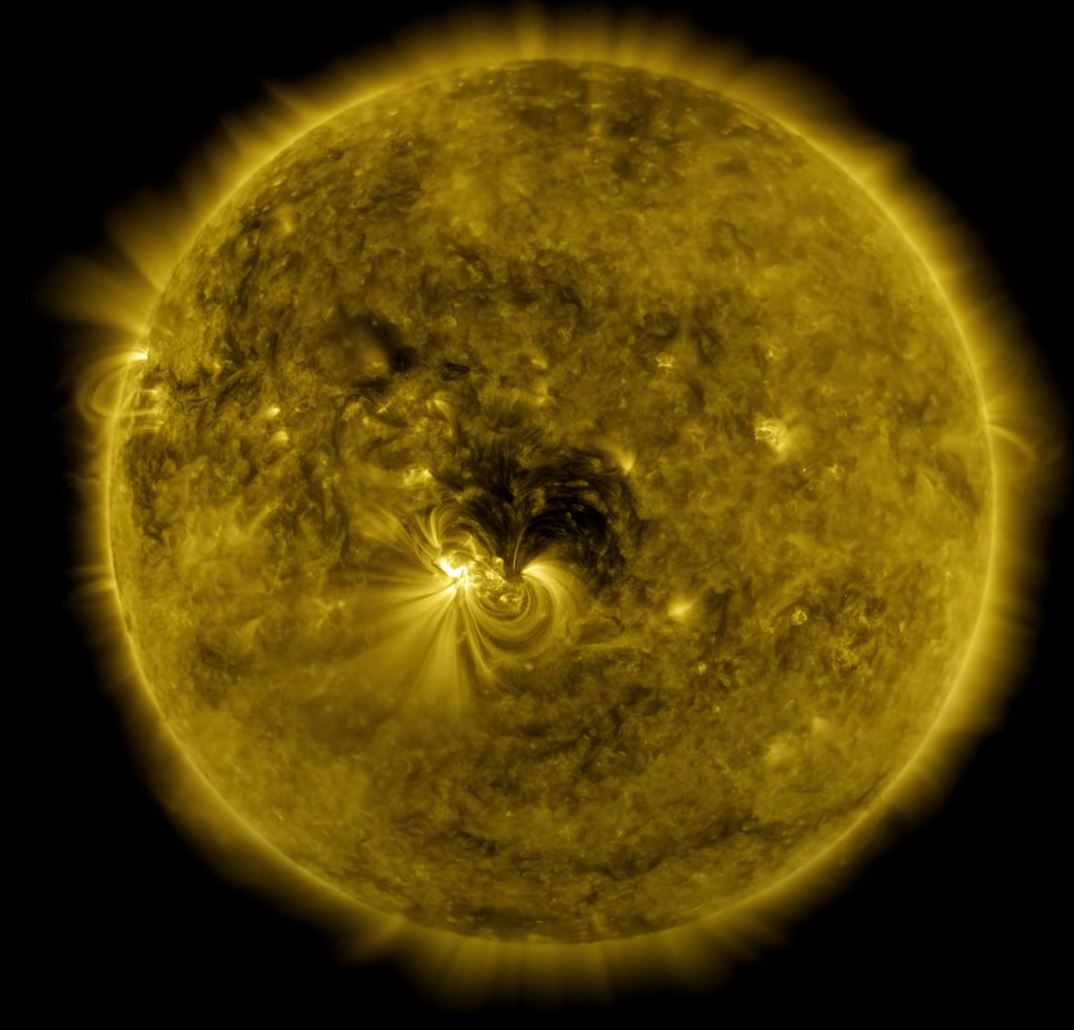
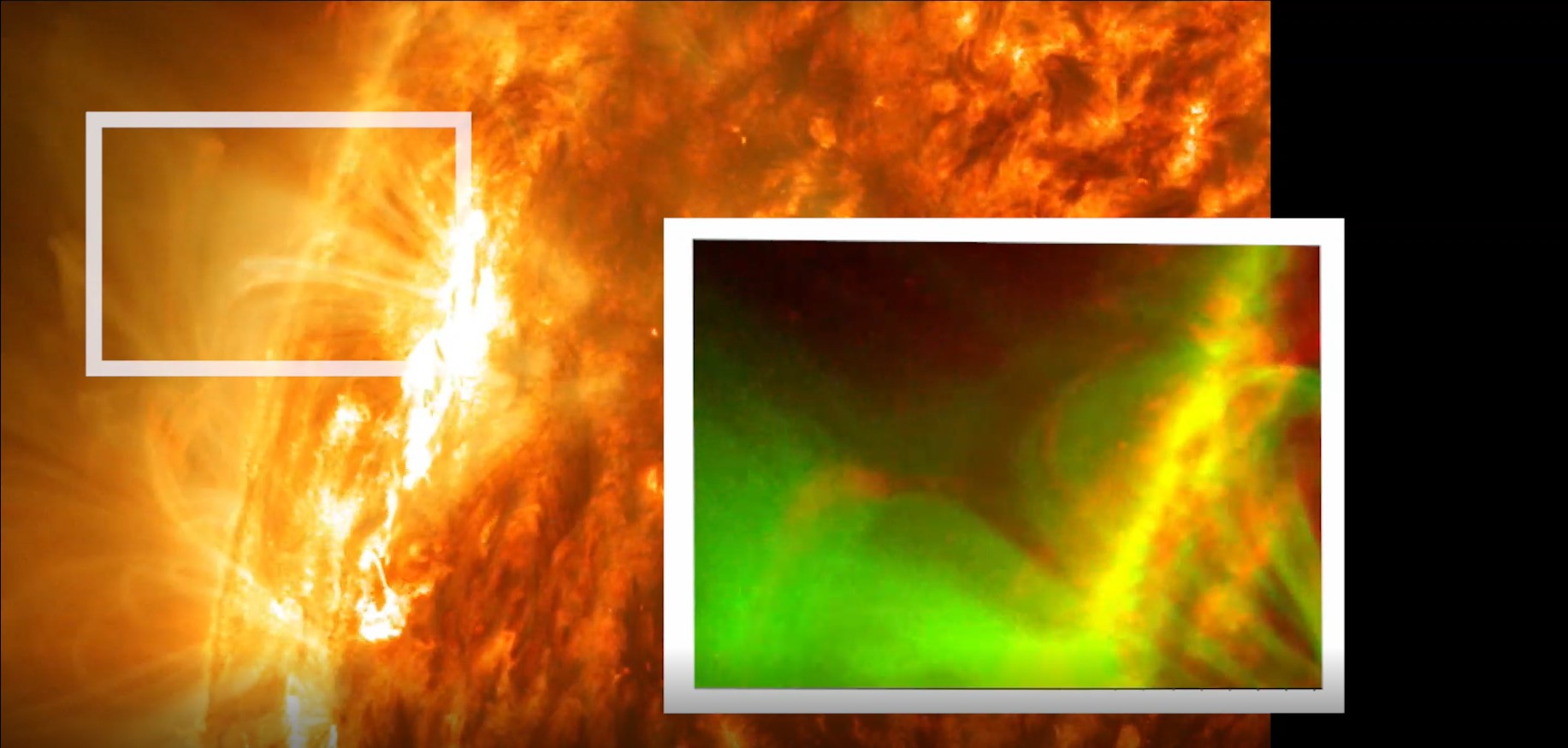
SolO has just produced its first round of photographs of the sun in action and they are already revealing some features that have been unseen until now. Those features might even hold the key to understanding one of the holy grails of heliophysics.
Continue reading “They’re In! The First Images From ESA’s Solar Orbiter”