Our understanding of galaxies is rooted in the fact that we can see so many of them. Some, such as the Andromeda and Pinwheel galaxies are fairly close, and others are more distant, but all of them give a unique view. Because of this, we can see how the various types of galaxies appear from different points of view, from face-on to edge-on and all angles in between. But there is one galaxy that’s a bit harder to map out, and that’s our own. Because we are in the galactic plane of the Milky Way, it can be difficult to create an accurate bird’s-eye view of our home galaxy. That’s where a recent study in Nature Astronomy comes in.
Continue reading “What Would the Milky Way Look Like From Afar?”JWST Glimpses the Cosmic Dawn of the Universe
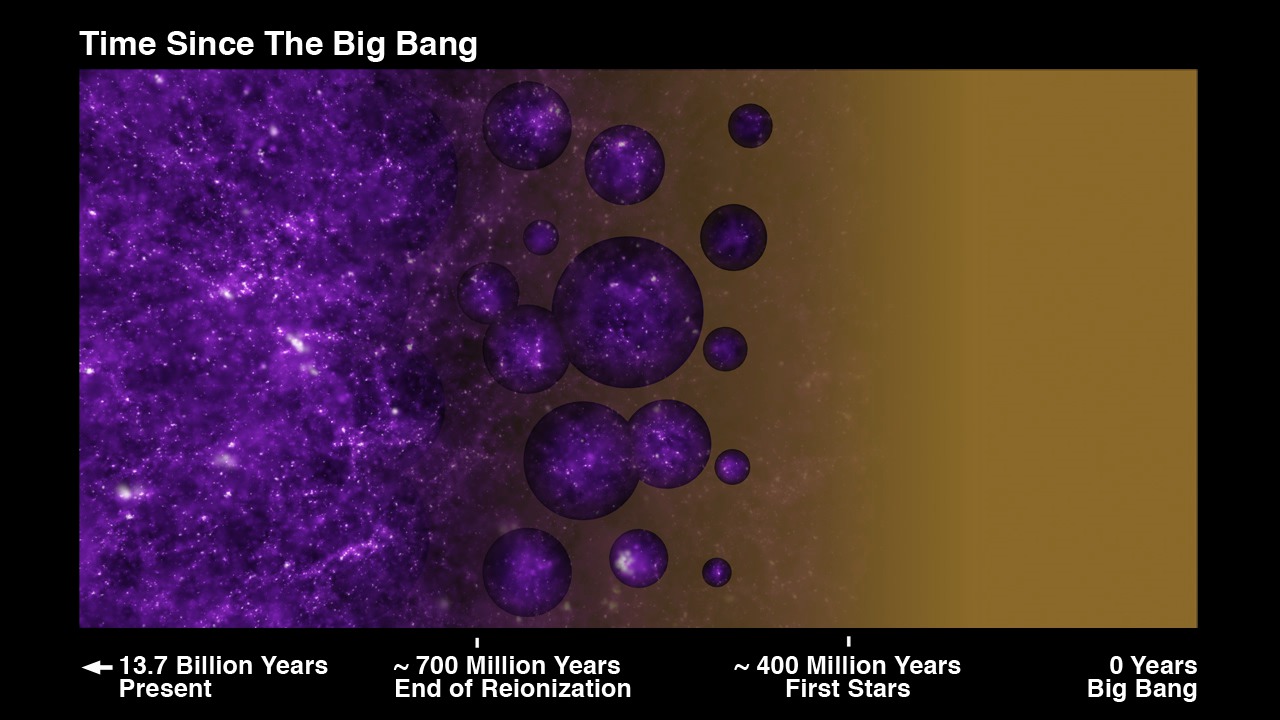
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) continues to push the boundaries of astronomy and cosmology, the very job it was created for. First conceived during the 1990s, and with development commencing about a decade later, the purpose of this next-generation telescope is to pick up where Spitzer and the venerable Hubble Space Telescope (HST) left off – examining the infrared Universe and looking farther back in time than ever before. One of the chief objectives of Webb is to observe high-redshift (high-Z) galaxies that formed during Cosmic Dawn.
This period refers to the Epoch of Reionization, where the first galaxies emitted large amounts of ultraviolet (UV) photons that ionized the neutral hydrogen that made up the intergalactic medium (IGM), causing the Universe to become transparent. The best way to measure the level of star formation is the H-alpha emission line, which is visible in the mid-infrared spectrum for galaxies with high redshifts. Using data from the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), an international team of researchers was able to resolve the H-alpha line and observe galaxies with redshift values higher than seven (z>7) for the first time.
Continue reading “JWST Glimpses the Cosmic Dawn of the Universe”JWST Shows How the Early Universe Was Furiously Forming Stars
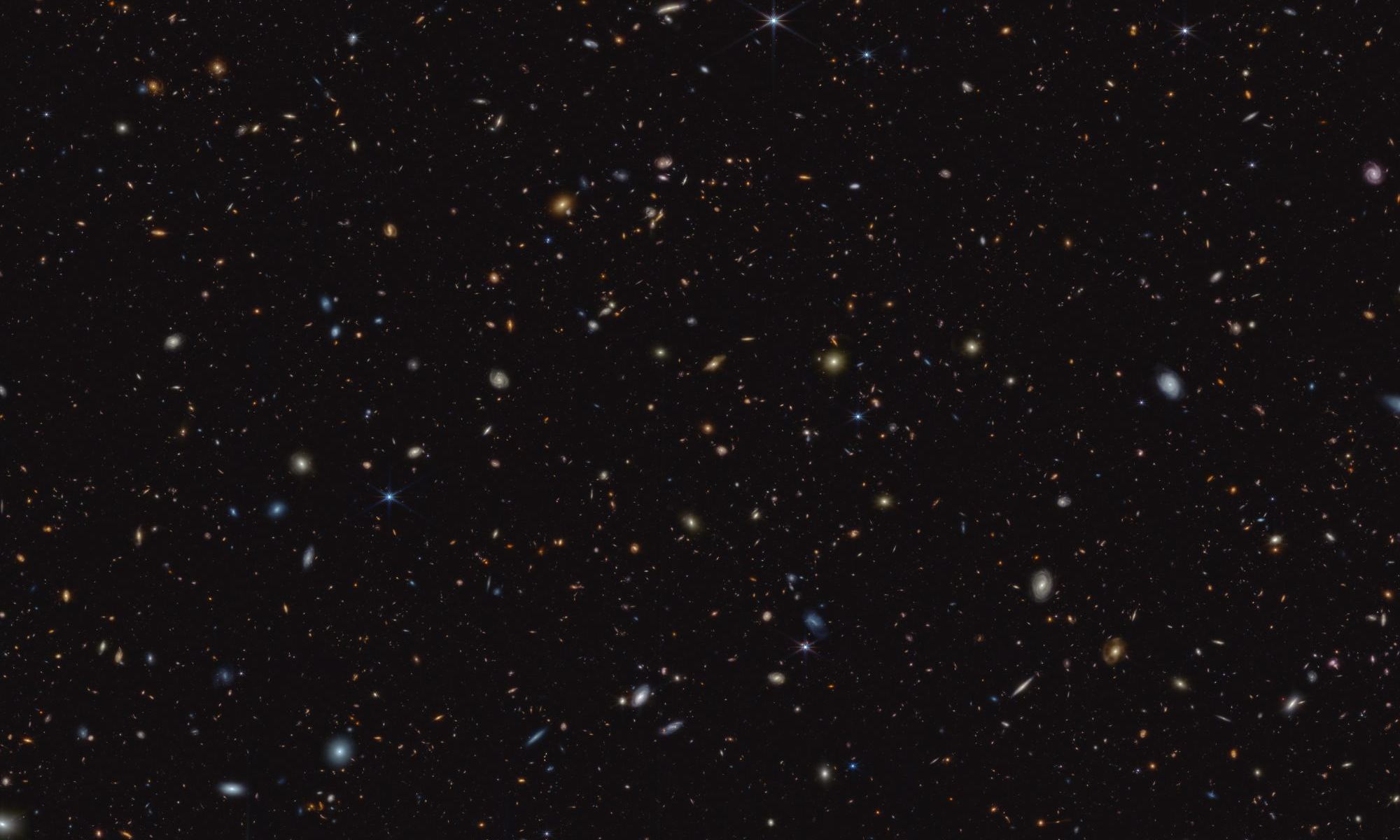

We can gaze out into regions in our neighbourhood of the Milky Way and find orgies of star birth. The closest region is in the Orion nebula, where astronomers have identified more than 700 young stars. They range from only 100,000 years—mere infancy for a star—to over a million years.
But we’re more than 13 billion years after the Big Bang now. What was star formation like way back when, when conditions in the Universe were so different?
Continue reading “JWST Shows How the Early Universe Was Furiously Forming Stars”JWST Sees Organic Molecules Ludicrously Far Away
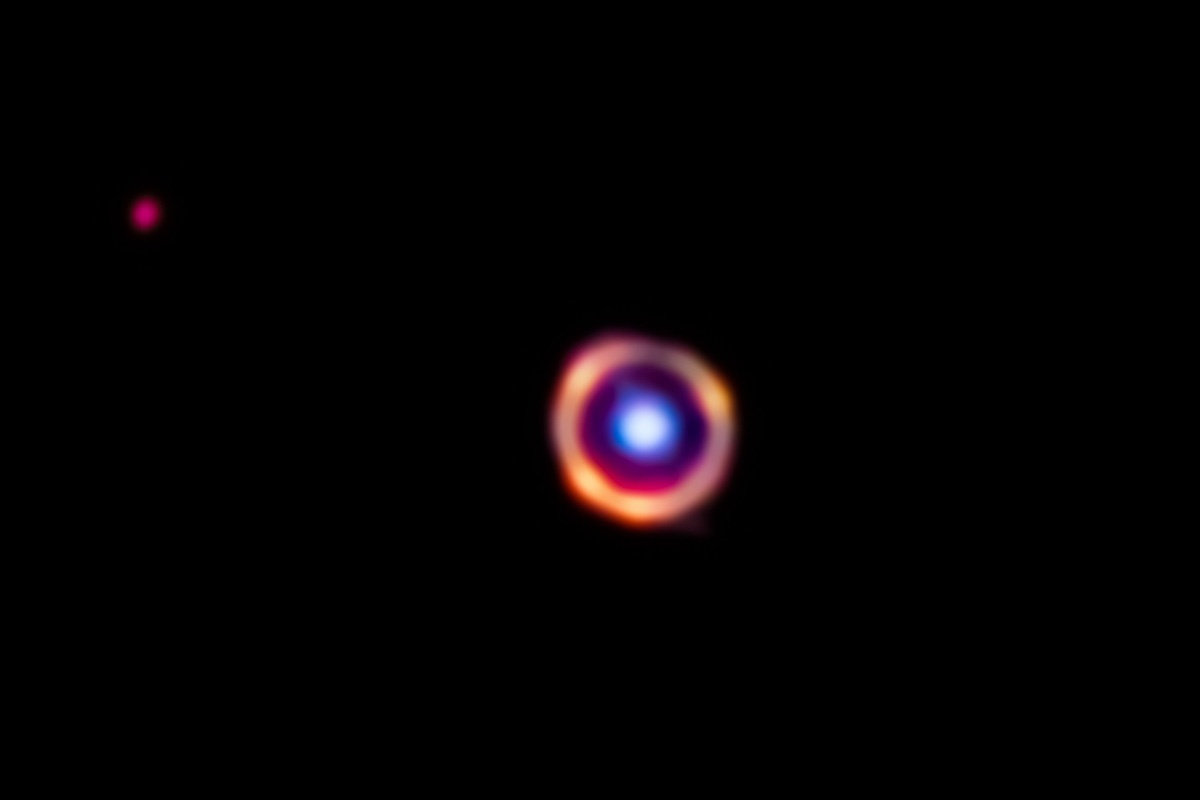

When astronomers used the JWST to look at a galaxy more than 12 billion light years away, they were also looking back in time. And when they found organic molecules in that distant galaxy, they found them in the early Universe.
The organic molecules are usually found where stars are forming, but in this case, they’re not.
Continue reading “JWST Sees Organic Molecules Ludicrously Far Away”The Latest JWST Image Pierces Through a Shrouded Star-Forming Galaxy

Sometimes an image is so engrossing that we can ignore what it’s telling us about its subject and just enjoy the splendour. That’s certainly true of this image of NGC 5068 released by the ESA. But Universe Today readers are curious, and after enjoying the galactic portrait for a while, they want to know more.
Continue reading “The Latest JWST Image Pierces Through a Shrouded Star-Forming Galaxy”Here's How You Could Get Impossibly Large Galaxies in the Early Universe
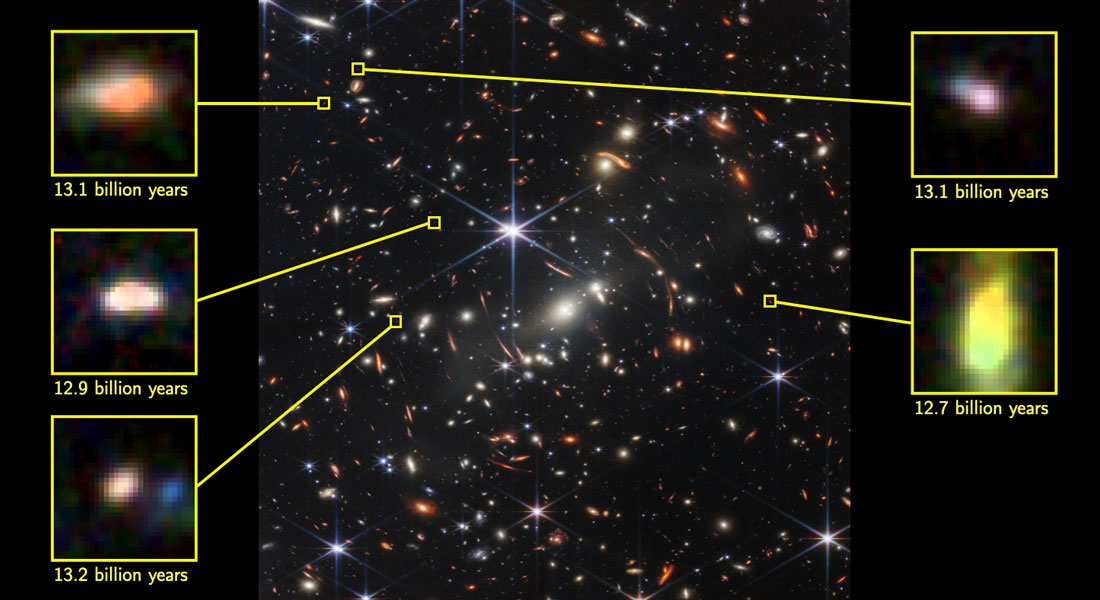

One of the most interesting (and confounding) discoveries made by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is the existence of “impossibly large galaxies.” As noted in a previous article, these galaxies existed during the “Cosmic Dawn,” the period that coincided with the end of the “Cosmic Dark Age” (roughly 1 billion years after the Big Bang). This period is believed to hold the answers to many cosmological mysteries, not the least of which is what the earliest galaxies in the Universe looked like. But after Webb obtained images of these primordial galaxies, astronomers noticed something perplexing.
The galaxies were much larger than what the most widely accepted cosmological model predicts! Since then, astronomers and astrophysicists have been racking their brains to explain how these galaxies could have formed. Recently, a team of astrophysicists from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Jerusalem published a theoretical model that addresses the mystery of these massive galaxies. According to their findings, the prevalence of special conditions in these galaxies (at the time) allowed highly-efficient rates of star formation without interference from other stars.
Continue reading “Here's How You Could Get Impossibly Large Galaxies in the Early Universe”Advanced Life Should Have Already Peaked Billions of Years Ago

Did humanity miss the party? Are SETI, the Drake Equation, and the Fermi Paradox all just artifacts of our ignorance about Advanced Life in the Universe? And if we are wrong, how would we know?
A new study focusing on black holes and their powerful effect on star formation suggests that we, as advanced life, might be relics from a bygone age in the Universe.
Continue reading “Advanced Life Should Have Already Peaked Billions of Years Ago”JWST Sees a Galaxy Cluster Coming Together in the Early Universe
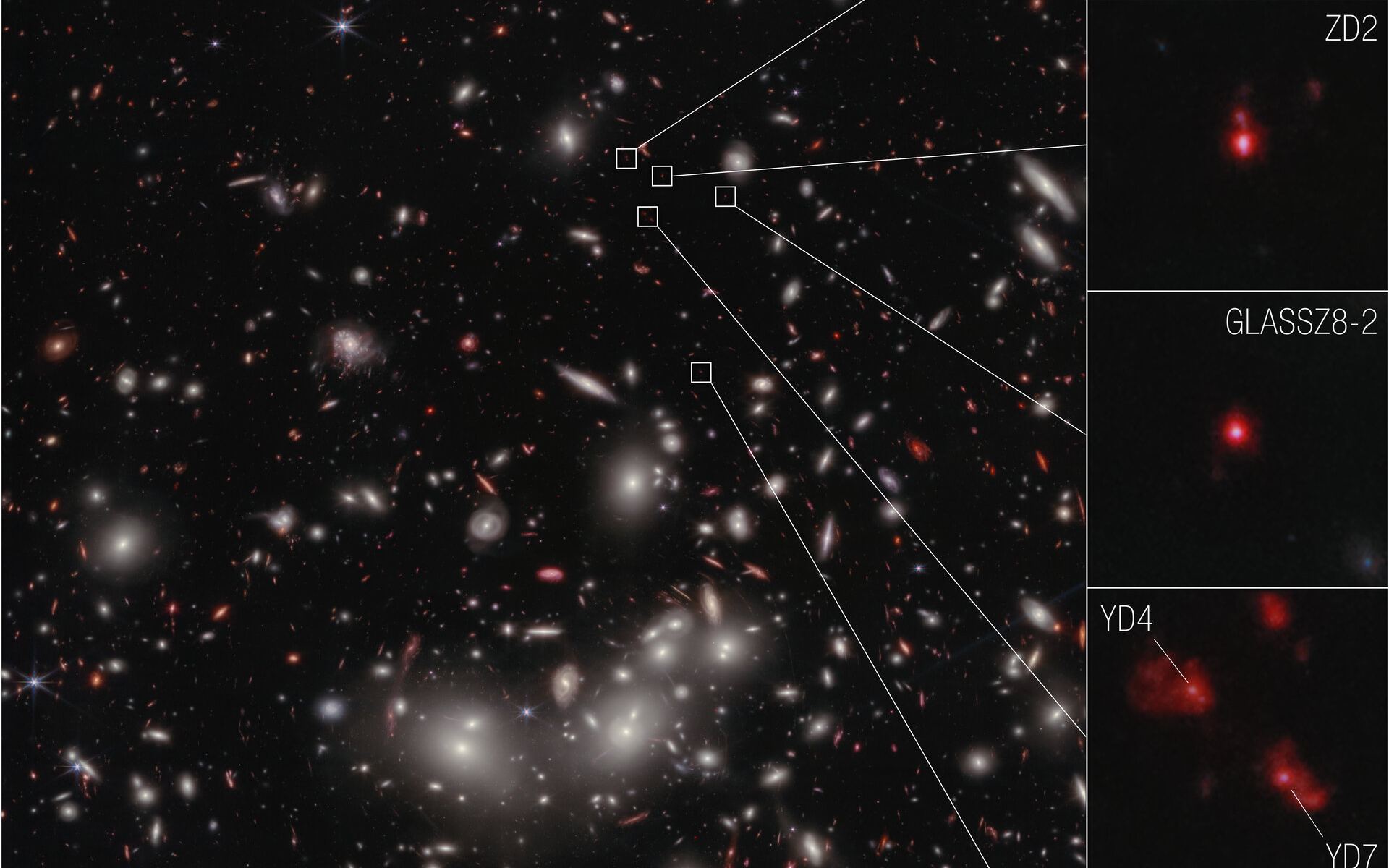

One of the James Webb Space Telescope’s science goals is to help cosmologists understand how the first galaxies and galaxy clusters formed in the early Universe. New images from the telescope show just that. Astronomers say the seven galaxies shown in this new JWST images are the earliest yet to be spectroscopically confirmed as part of a developing galaxy cluster. These galaxies are about 13 billion light-years away, meaning JWST is seeing them at about 95% of the age of the observable Universe.
Continue reading “JWST Sees a Galaxy Cluster Coming Together in the Early Universe”JWST Sees Merging Galaxies Releasing the Light of a Trillion Suns
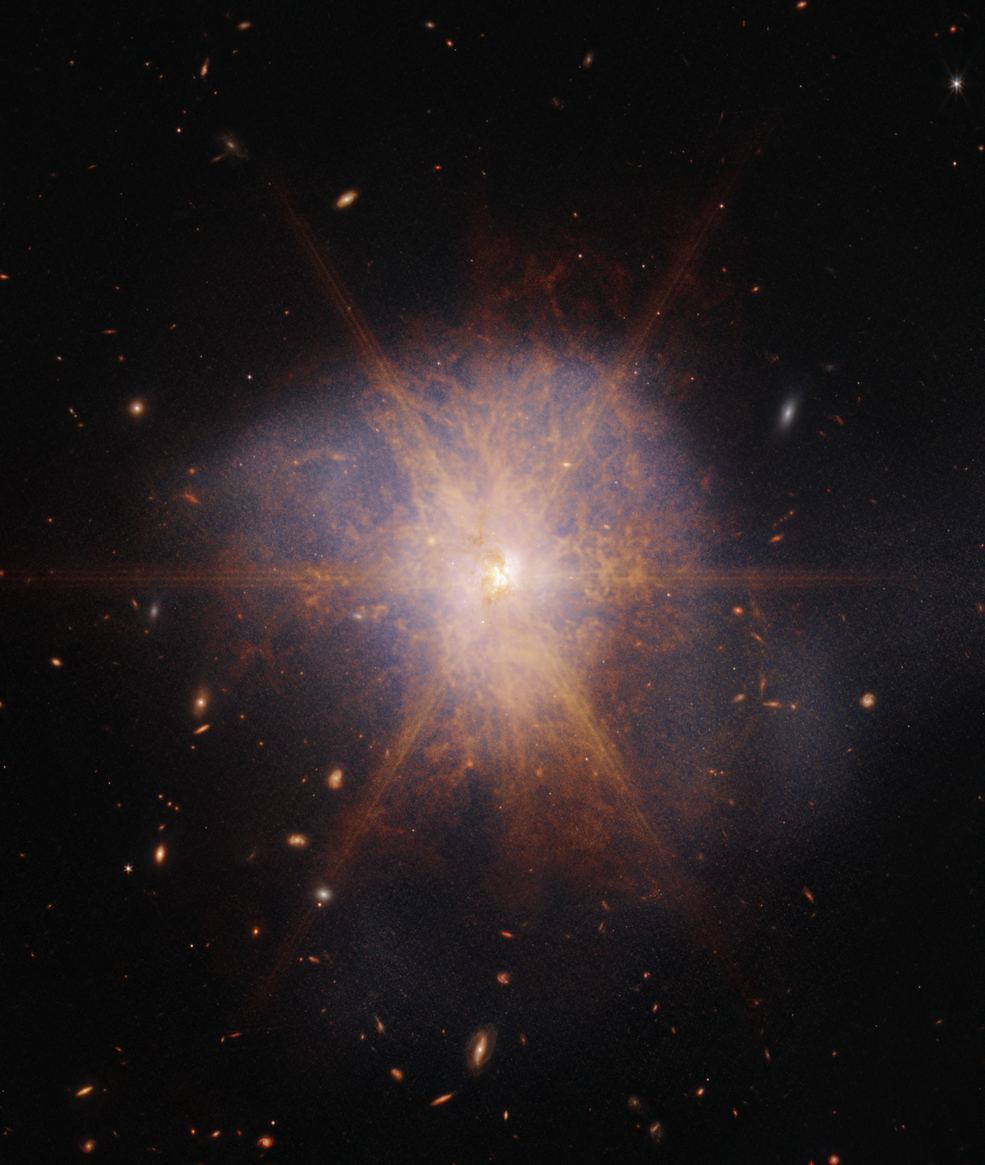

If we want to know what it’ll look like in about 4.5 billion years when our galaxy merges with Andromeda, we might take a look at ARP 220. ARP 220 is a pair of galaxies that are in the process of merging. The merging galaxies emit brilliant infrared light, and the James Webb Space Telescope captured that light in a vivid portrait.
Continue reading “JWST Sees Merging Galaxies Releasing the Light of a Trillion Suns”This JWST Image Shows Gravitational Lensing at its Finest
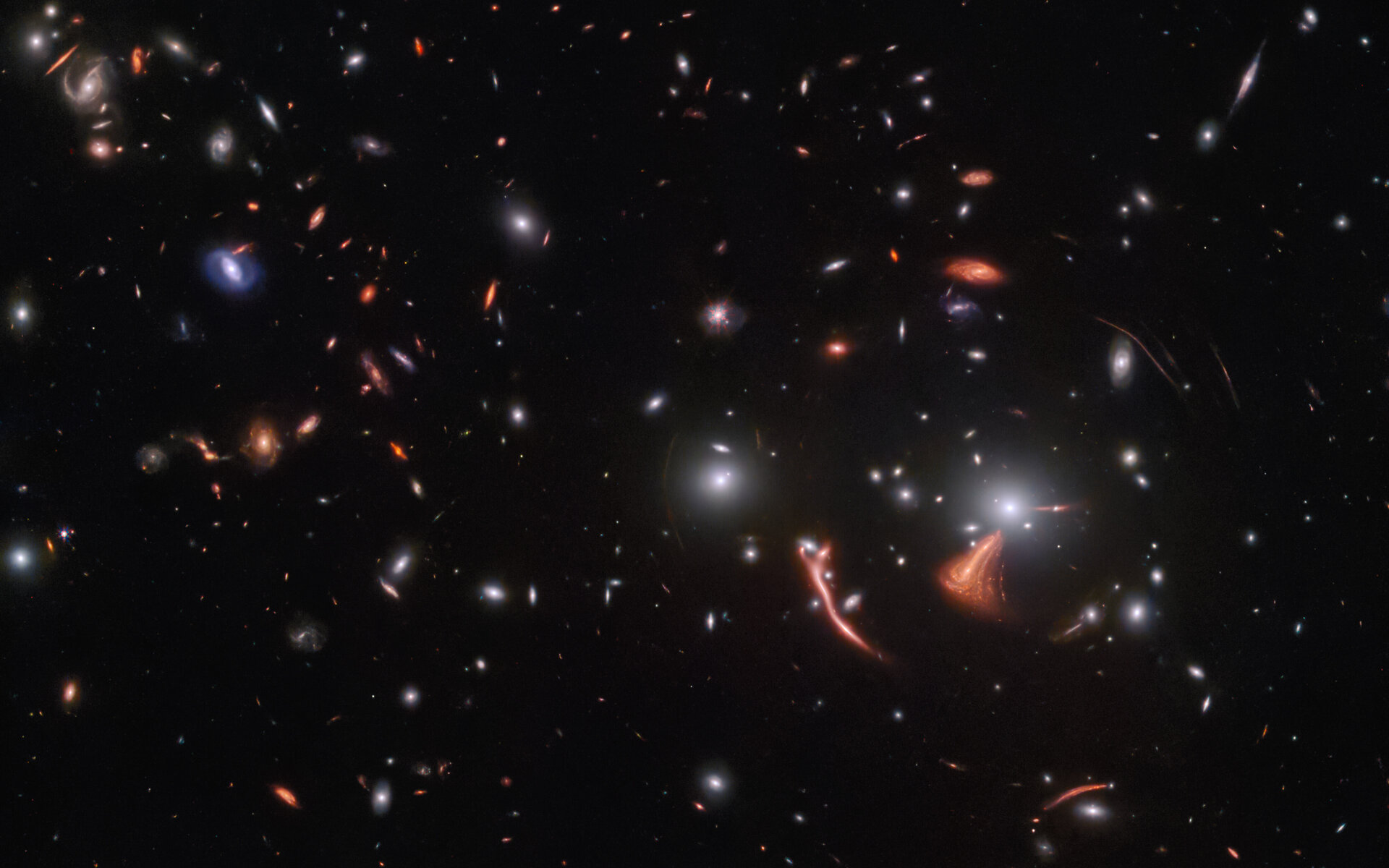
One of the more intriguing aspects of the cosmos, which the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has allowed astronomers to explore, is the phenomenon known as gravitational lenses. As Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity describes, the curvature of spacetime is altered by the presence of massive objects and their gravity. This effect leads to objects in space (like galaxies or galaxy clusters) altering the path light travels from more distant objects (and amplifying it as well). By taking advantage of this with a technique known as Gravitational Lensing, astronomers can study distant objects in greater detail.
Consider the image above, the ESA’s picture of the month acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The image shows a vast gravitational lens caused by SDSS J1226+2149, a galaxy cluster located roughly 6.3 billion light-years from Earth in the constellation Coma Berenices. The lens these galaxies created greatly amplified light from the more distant Cosmic Seahorse galaxy. Combined with Webb‘s incredible sensitivity, this technique allowed astronomers to study the Cosmic Seahorse in the hopes of learning more about star formation in early galaxies.
Continue reading “This JWST Image Shows Gravitational Lensing at its Finest”

