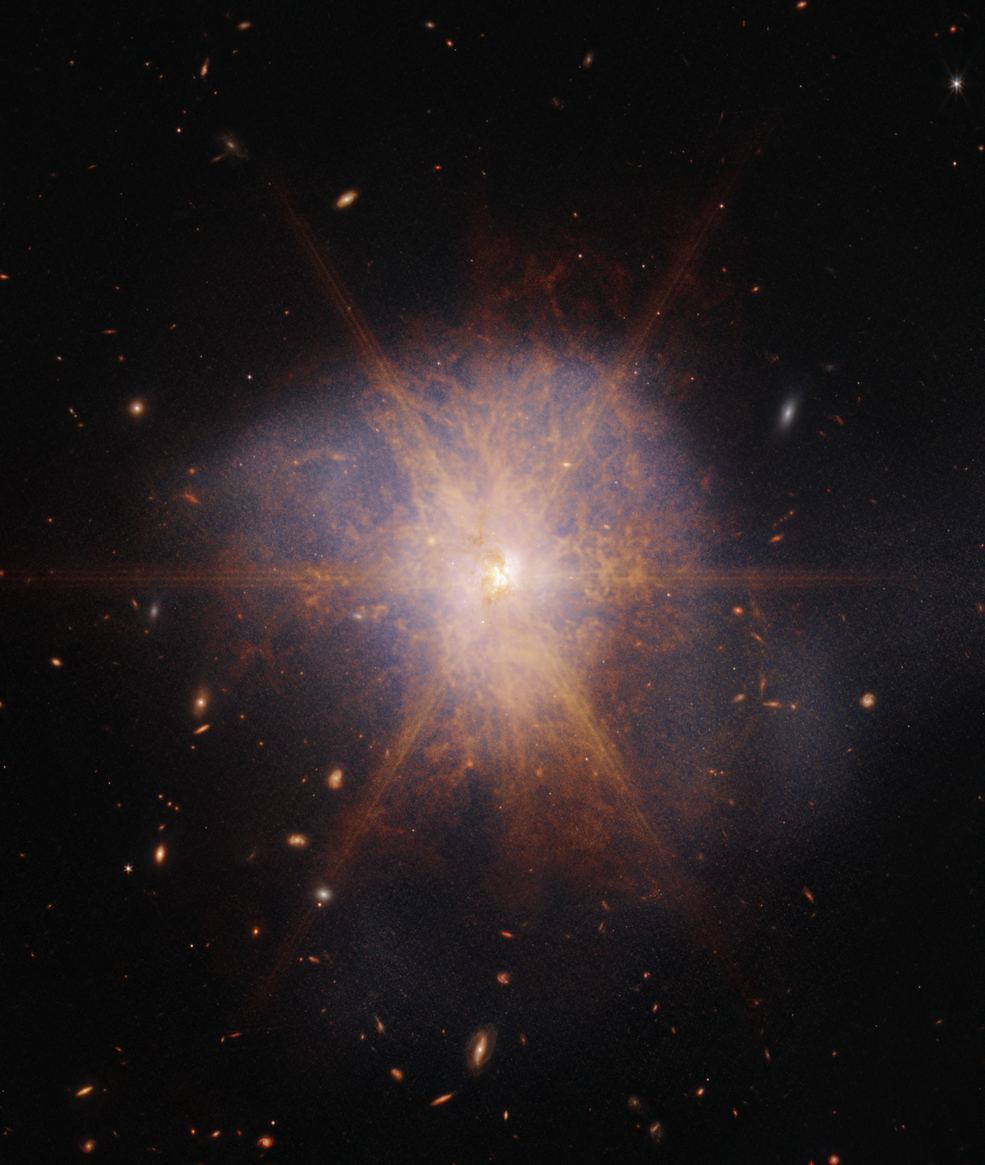
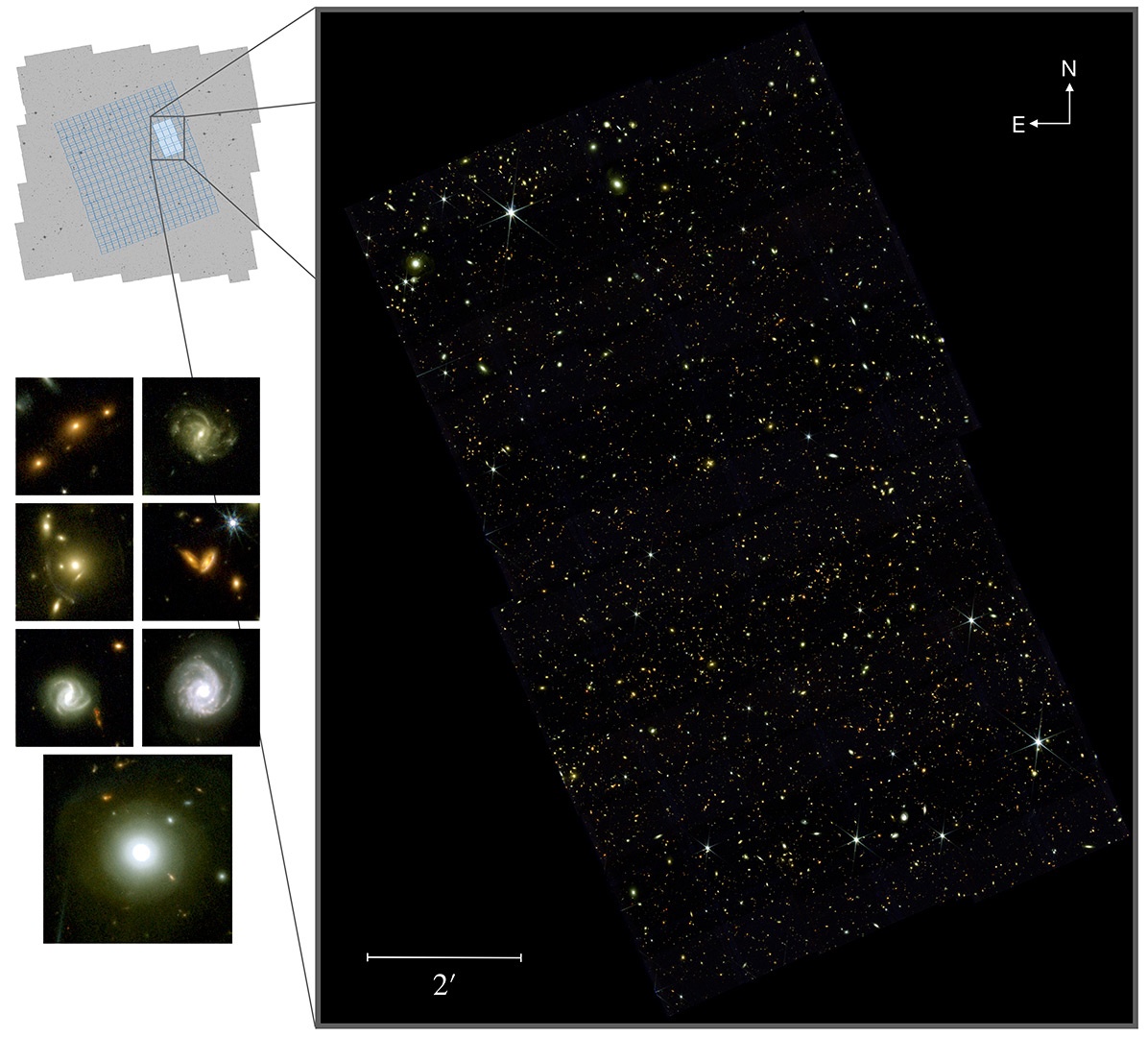
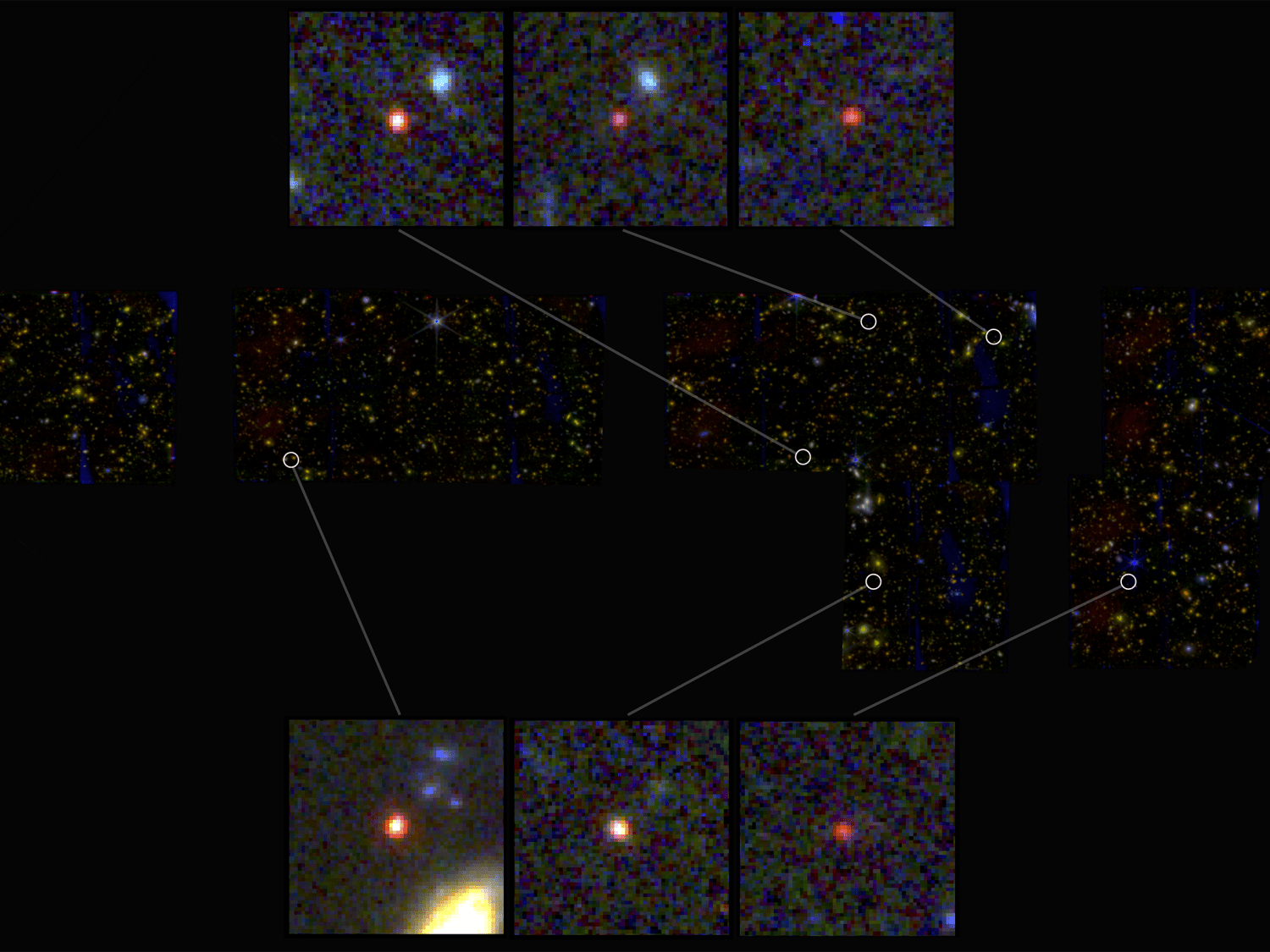
Over 13 billion years ago, the first galaxies in the Universe formed. They were elliptical, with intermediate black holes (IMBHs) at their centers surrounded by a halo of stars, gas, and dust. Over time, these galaxies evolved by flattening out into disks with a large bulge in the middle. They were then drawn together by mutual gravitational attraction to form galaxy clusters, massive collections that comprise the large-scale cosmic structure. This force of attraction also led to mergers, where galaxies and their central black holes came together to create larger spiral galaxies with central supermassive black holes (SMBHs).
This process of mergers and assimilation (and their role in galactic evolution) is still a mystery to astronomers today since much of it took place during the early Universe, which is still very difficult to observe with existing telescopes. Using data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the International Gemini Observatory, an international team of astronomers observed a lone distant galaxy that appears to have consumed all of its former companions. Their findings, which recently appeared in The Astrophysical Journal, suggest galaxies in the early Universe grew faster than previously thought.
Continue reading “A Distant Galaxy Ate All of its Friends. Now It’s All Alone”