Image caption: Context view of Curiosity working at ‘Rocknest’ Ripple. Curiosity’s maneuvers robotic arm for close- up examination of ‘Rocknest’ ripple site and inspects sandy material at “bootlike” wheel scuff mark with the APXS (Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer) and MAHLI (Mars Hand Lens Imager) instruments positioned on the rotatable turret at the arm’s terminus. Mosaic was stitched together from Sol 57 & 58 Navcam raw images and shows the arm extended to fine grained sand ripple in context with the surrounding terrain and eroded rim of Gale Crater rim on the horizon. Rocknest patch measures about 8 feet by 16 feet (2.5 meters by 5 meters).See NASA JPL test scooping video below. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
NASA’s Curiosity rover is set to scoop up her 1st sample of Martian soil this weekend at a soil patch nicknamed ‘Rocknest’ -see our context mosaic above – and will funtion as a sort of circulatory system cleanser for all the critical samples to follow. This marks a major milestone on the path to delivering Mars material to the sample acquisition and processing system for high powered analysis by the robots chemistry labs and looking for the ingredients of life, said the science and engineering team leading the mission at a media briefing on Thursday, Oct 4.
Since landing on the Red Planet two months ago on Aug. 5/6, Curiosity has trekked over 500 yards eastwards across Gale crater towards an intriguing area named “Glenelg” where three different types of geologic terrain intersect.
This week on Oct. 2 (Sol 56), the rover finally found a wind driven patch of dunes at ‘Rocknest’ with exactly the type of fine grained sand that the team was looking for and that’s best suited as the first soil to scoop and injest into the sample acquisition system.
See NASA JPL earthly test scooping video below to visualize how it works:
“We now have reached an important phase that will get the first solid samples into the analytical instruments in about two weeks,” said Mission Manager Michael Watkins of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
The rover used its wheels to purposely scuff the sand and expose fresh soil – and it sure looked like the first human “bootprint” left on the Moon by Apollo 11 astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin.
Curiosity will remain at the “Rocknest” location for the next two to three weeks as the team fully tests and cleans the walls of most of the sample collection, handling and analysis hardware – except for the drilling equipment – specifically to remove residual contaminants from Earth.
Image caption: ‘Rocknest’ From Sol 52 Location on Sept. 28, 2012, four sols before the rover arrived at Rocknest. The Rocknest patch is about 8 feet by 16 feet (1.5 meters by 5 meters). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
The purpose of this initial scoop is to use the sandy material to thoroughly clean out, rinse and scrub all the plumbing pipes, chambers, labyrinths and interfaces housed inside the complex CHIMRA sampling system and the SAM and CheMin chemistry labs of an accumulation of a very thin and fine oily layer that could cause spurious, interfering readings when the truly important samples of Martian soil and rocks are collected for analysis starting in the near future.
The scientists especially do not want any false signals of organic compounds or other inorganic materials and minerals stemming from Earthly contamination while the rover and its instruments were assembled together and processed for launch.
“Even though we make this hardware super squeaky clean when it’s delivered and assembled at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, by virtue of its just being on Earth you get a kind of residual oily film that is impossible to avoid,” said Daniel Limonadi of JPL, lead systems engineer for Curiosity’s surface sampling and science system. “And the Sample Analysis at Mars instrument is so sensitive we really have to scrub away this layer of oils that accumulates on Earth.”
The team plans to conduct three scoop and rinse trials – dubbed rinse and discard – of the sample acquisition systems. So it won’t be until the 3rd and 4th soil scooping at Rocknest that a Martian sample would actually be delivered for entry into the SAM and CheMin analytical chemistry instruments located on the rover deck.
“What we’re doing at the site is we take the sand sample, this fine-grained material and we effectively use it to rinse our mouth three times and then kind of spit out,” Limonadi said. “We will take a scoop, we will vibrate that sand on all the different surfaces inside CHIMRA to effectively sand-blast those surfaces, then we dump that material out and we rinse and repeat three times to finish cleaning everything out. Our Earth-based testing has found that to be super effective at cleaning.”
Limondi said the first scooping is likely to be run this Saturday (Oct 6) on Sol 61, if things proceed as planned. Scoop samples will be vibrated at 8 G’s to break them down to a very fine particle size that can be easily passed through a 150 micron sieve before entering the analytical instruments.
The team is being cautious, allowing plenty of margin time and will not proceed forward with undue haste.
“We’re being deliberately slow and incredibly careful,” said Watkins. “We’re taking a lot of extra steps here to make sure we understand exactly what’s going on, that we won’t have to do every time we do a scoop in the future.”
Curiosity’s motorized, clamshell-shaped scoop measures 1.8 inches (4.5 centimeters) wide, 2.8 inches (7 centimeters) long, and can sample to a depth of about 1.4 inches (3.5 centimeters). It is part of the CHIMRA collection and handling device located on the tool turret at the end of the rover’s arm.
“The scoop is about the size of an oversized table spoon,” said Limonadi.
Image caption: Curiosity extends 7 foot long arm to investigate ‘Bathurst Inlet’ rock outcrop with the MAHLI camera and APXS chemical element spectrometer in this mosaic of Navcam images assembled from Sols 53 & 54 (Sept. 29 & 30, 2012). Mount Sharp, the rover’s eventual destination is visible on the horizon. Thereafter the rover drove more than 77 feet (23 meters) eastwards to reach the ‘Rocknest’ sand ripple. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
During the lengthy stay at Rocknest, the rover will conduct extensive investigations of the surrounding rocks and terrain with the cameras, ChemCam laser, DAN, RAD as well as weather monitoring with the REMS instrument.
After finishing her work at Rocknest, Curiosity will resume driving eastward to Glenelg, some 100 meters (yards) away where the team will select the first targets and rock outcrops to drill, sample and analyze.
At Glenelg and elsewhere, researchers hope to find more evidence for the ancient Martian stream bed they discovered at rock outcrops at three different locations that Curiosity has already visited.
Curiosity is searching for organic molecules and evidence of potential habitable environments to determine whether Mars could have supported Martian microbial life forms, past or present.
Image caption: Curiosity’s Travels Through Sol 56 – Oct. 2, 2012




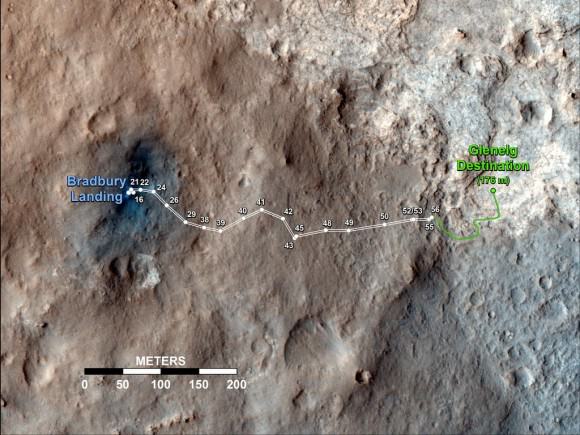
Ah, the first MER looking route maps. Curiosity is clearly joining the team!
Time to update my martian ground knowledge:
“The term Martian soil typically refers to the finer fraction of regolith, that which is composed of grains one centimeter in diameter or less. Some have argued that the term “soil” is not correct in reference to Mars because soil is defined as having organic content, whereas Mars is not known to have any. However, standard usage among planetary scientists is to ignore that distinction. Martian dust generally connotes even finer materials than Martian soil, the fraction which is less than 30 micrometres in diameter.
Disagreement over the significance of soil’s definition arises due to the lack of an integrated concept of soil in the literature. The pragmatic definition “medium for plant growth” has been commonly adopted in the planetary science community but a more complex definition describes soil as (bio)geochemically/physically altered material at the surface of a planetary body that encompasses surficial extraterrestrial telluric deposits. This definition emphasizes that soil is a body that retains information about its environmental history and that does not need the presence of life to form.”
Soil := weathered by gases or liquids, got it. Io would have sulfuric soils instead of mostly water chemistry soils of Mars or Titan.
Wonder if water chemistry of impact events count as soil forming? (Say, as on Vesta’s complex surface.)
By the way, what happened with the first atmospheric samples?
The very first round was soundly covered as it was a “fail” – looking at remaining Earth gases, since the SAM instrument itself was made to rinse and discard. The next, which was announced to be done at the start of last month and have tentative results a week after, hasn’t resulted in speculation even. Did they inhibit it? Or was the announcement mistaken?
Yeah, the term “soil” had been confusing for me too. I first encountered it in the context of asteroids and sample return missions.
I think when the term “soil” is used in the broadest form, it simply means “loose, small stuff on the surface of a Solar System body” – regardless what the process was by which it formed.
So in the broadest form, “material pulverized by impacts of small asteroids” is usually included.
Thanks! That makes even more sense, that is the most general interpretation of “altered” “surficial extraterrestrial telluric deposits”.
well that’s clearly windblown deposits. what’s the best guess at results?
silica and iron?
So after Curiosity cleansed itself, Rocknest will be the place where life on Mars started!
Sorry, I just couldn’t resist.
Hehehe right and hopefully shaking at 8Gs will not wreak havoc with the other instruments on the arm 🙂
Hope they can go more than an inch deep. Any plans to dig holes or
trenches to get at soil beneath the strong UV/etc rays? If the goal is
to detect organic molecules, then why just scrape off he surface.
The drill bit can go 2 inches, I believe. No digging equipment.
The plan is to look in impact craters to get to what was previously buried deeper.
I`m slightly disappointed that NASA doesn`t announce results of measurments thay have already made. Some of them have been taken 2-3 weeks ago – enough time to do all analysis.