A new generation of space rockets ready to lift new and exciting payloads spaceward is coming to a sky near you.
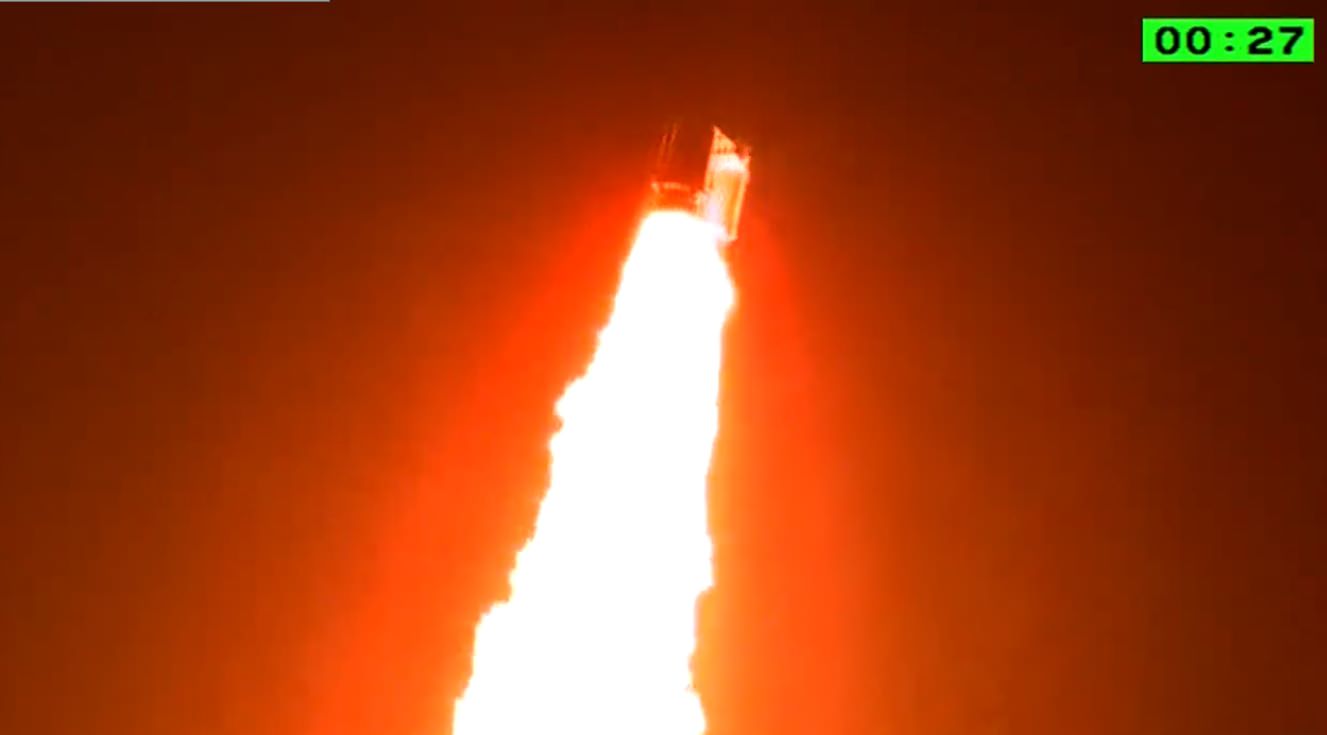
Tomorrow, a Delta IV Heavy rocket will boost the Orion space capsule on a two orbit journey around the Earth that will test key systems. And though tomorrow’s launch is uncrewed, the Orion Command Module will one day form the core of NASA’s Orion MPCV Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle and is slated to care out humanity’s first mission to an asteroid and beyond in the next decade.
But a second, lesser known launch also leaves Earth tomorrow as well, atop a rocket that will soon give way to a new generation of lift boosters as launch services vie for new customers. Just over eight hours after the launch of EFT-1, an Ariane 5 rocket lifts off from French Guiana with GSAT-16.

Is the ‘battle of the boosters’ heating up?
This comes after the December 2nd announcement earlier this week by participating members of the European Space Agency to proceed with the development of the next generation Ariane 6 rocket. Also included in the 5.9 billion Euro (7.3 billion USD) budget proposal is funding for the 2018 ExoMars mission, along with further support of ESA’s International Space Station commitments.
To date, ESA has fielded five of its Automated Transfer cargo Vehicles (ATVs) on missions to the International Space Station. ESA will also design the Service Module segment of the Orion MPCV.
“I can summarize this ministerial council by say it was a success… I’d even go so far as to say that it is a great success,” said Jean-Jacques Dordain, the director-general of the European Space Agency.
The Ariane 6 is expected to be on the launch pad by 2020, and will feature two variants capable of placing 5 to 11 tonnes in a geostationary transfer orbit. The solid fuel booster to be incorporated will be based on the Vega rocket design, while the upper stage Vinci engine is already currently in development.
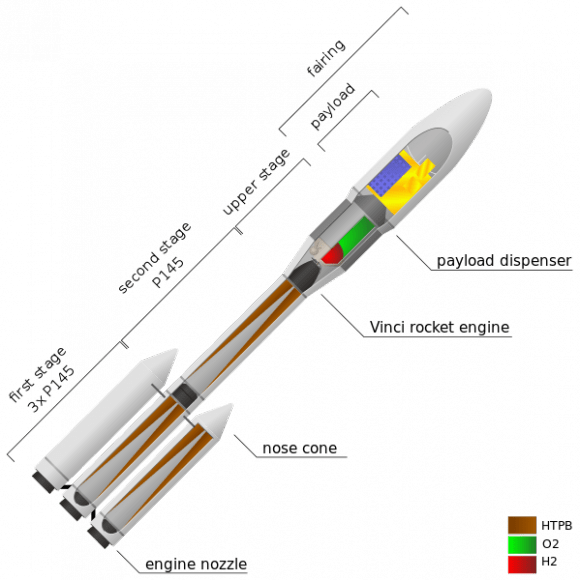
The design has been hotly contested among European Space Agency members, many of whom are in favor of other variants based on the upgraded Ariane 5. Some of the largest rockets of all time included those developed by NPO Energia, capable of lofting 100,000 kilograms into low Earth orbit. An Energia N1 Moon rocket exploded on the pad on July 3rd 1969, effectively ending the Soviet Union’s bid to put a man on the Moon. In comparison, the massive Saturn V rocket — thus far, the largest and most powerful ever fielded by the United States — could deploy the equivalent of 118,000 kg to low Earth orbit and 47,000 kg to a Trans-Lunar Insertion orbit around the Moon.
But that’s just the beginning. Though the Orion capsule will ride atop a United Launch Services Delta IV Heavy tomorrow — a system usually employed for launching clandestine spy satellites — NASA hopes to have its own Space Launch System (SLS) rocket sitting on the pad by the end of 2018. Boeing was awarded the contract for SLS earlier this year, and the system largely rose re-imagined from the ashes of the cancelled Constellation program. The SLS Block 1 is expected to have a lift capacity of 70,000 kg to LEO, while Boeing’s proposed SLS Block 2 variant would, if fielded, have the largest lift capacity of all time at 130,000 kg to LEO. Only the Long March 9 proposed by China approaches that lofty goal.
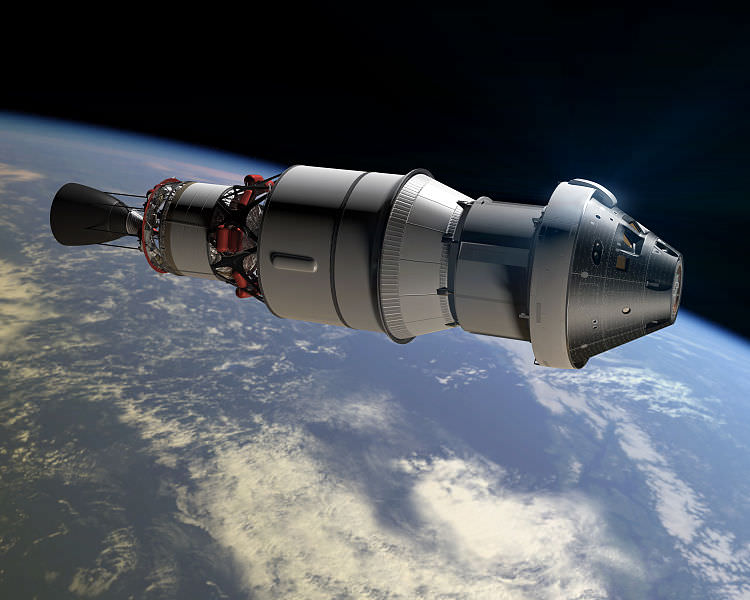

And the wild card is Elon Musk’s SpaceX. Already in the game of sending cargo via its Dragon spacecraft to the ISS, SpaceX is developing a reputation for dependability when it comes to getting satellites into orbit at relatively low cost. SpaceX hopes to field its Falcon 9 Heavy with a lift capacity of 53,000 kg to LEO sometime in 2015, and many proposed missions are banking on the the Falcon 9 Heavy as a future service provider for solar system exploration. Certainly, with the recent failure of the Antares rocket on October 28th, SpaceX may look like the more attractive option to many, and the development of the Ariane 6 is expected to face stiff competition in the brave new world of high tech rocketry.
Ever wonder what all of these launch vehicles and spacecraft past and present look like stacked up against each other? There’s a graphic for that, recently featured on Io9:
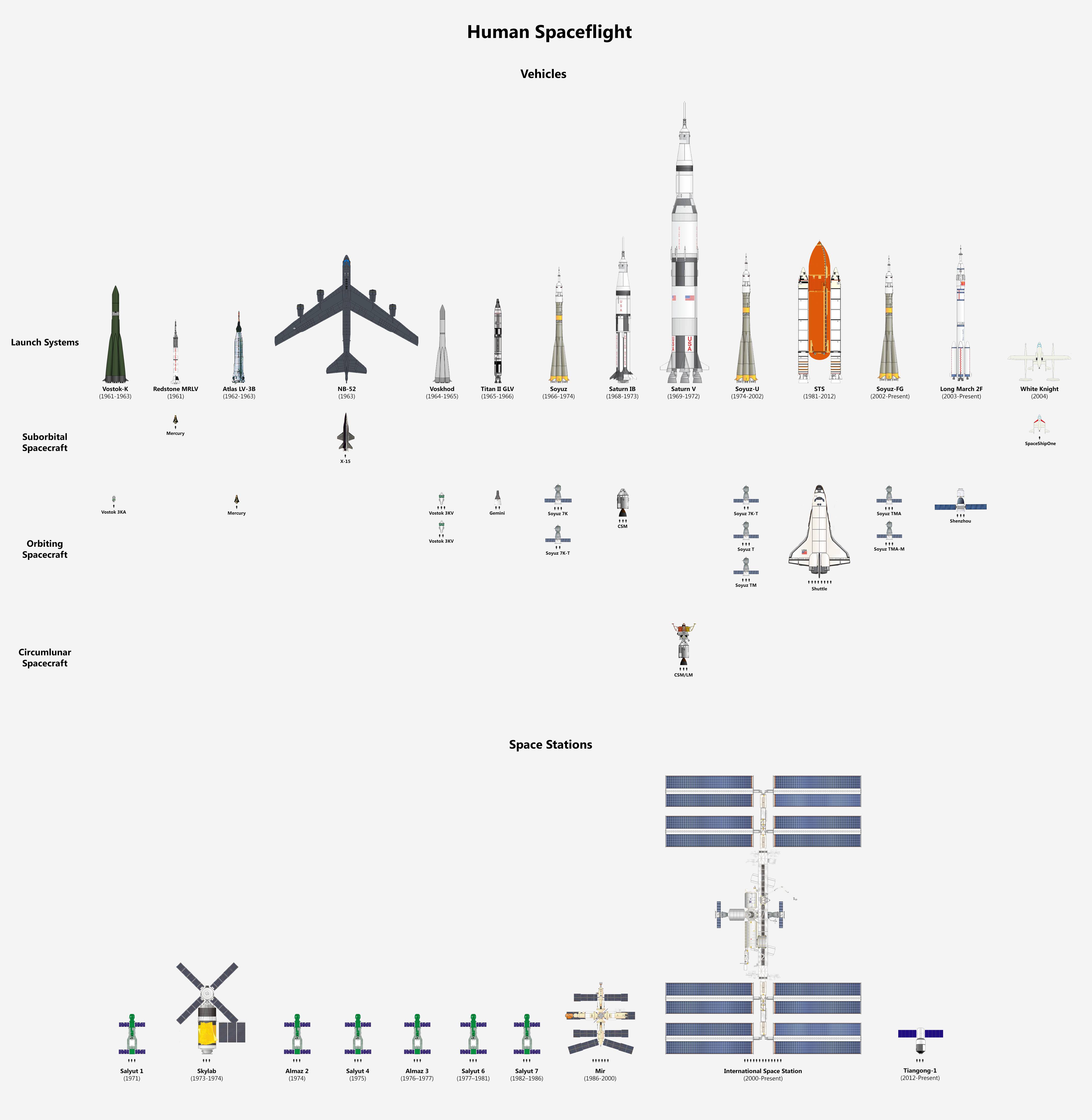
From Almaz to Zarya, this is a fascinating study in scale comparison. Be sure to zoom in and check out the tiny ant-like crew compliment of each, also to scale. Of course, the backyard satellite-tracker in us can’t help be notice the brightness-versus size comparison for many of these. For example, the International Space Station on a good pass can appear as bright as Venus at -4th magnitude — and even look “TIE Fighter shaped” in binoculars — while the smaller Shenzhou and Soyuz modules are often barely visible as they pass overhead. And how we miss watching the Shuttle paired with the International Space Station as they both glided silently by:
But such orbital drama can still be caught if you know when and where to look for it. And speaking of which, viewers in western Australia and the southwestern United States may be able to see Orion and EFT-1 on its first lap around the Earth tomorrow before it fires its engines over the Atlantic headed for a 5,800 km apogee over southern Africa. Assuming EFT-1 lifts off at the beginning of its 159 minute launch window at 7:05 AM EST/12:05 UT, expect it to see it crossing dusk skies over western Australia at 55 minutes after liftoff, and dawn skies for the southwestern U.S. at 95 minutes post-launch respectively.
An awesome sight to behold indeed, marking the start of a brave new era of space exploration.
So what do you, the astute and space-minded reader of Universe Today think? Are the SLS and its kin the lift vehicle(s) of the future, or ‘rockets to nowhere?’ Will they survive the political winds that are bound to blow over the coming decade? Will the Ariane 6 best the Falcon 9 as the lift platform of choice?
One thing is for sure, expect coverage of space exploration drama and more to continue here at Universe Today!


There was much rejoicing hereabouts (Europe) over the A6 announcement, but no word of reusability. There might be harsh reality checks ahead.
General thoughts about the rocket to nowhere questions. Yes many of us in the enthusiast community have been saying for years that more money should go to private enterprise (in Particular Space X) who have demonstrated they are worthy to compete for funding. I am willing to put aside differences to support NASA in its efforts – To put things in perspective, in the 2014 Federal Budget, NASA received 0.1% (That’s 1/10th of one percent) of the overall budget. In contrast, in 1966, Nasa peaked at 4.41% of the Federal Budget – and we see what a great revolution in science and industry was born from the Apollo era…
I wish to still ask NASA to reconsider its use of solid boosters as aluminum perchlorate being the active constituent of the oxidiser is quite long lived (there are always uncombusted leftovers) and proven detrimental to developing human fetuses, humans generally and the ecosystem. Existing liquid propulsion while providing less specific impulse thrust is much friendlier on the environment and powered the Saturn V rockets (along with a jet grade diesel fuel which is still less detrimental)…
I also would love to see more R&D on new types of propulsion such as paraffin powered rockets JPL has developed…
Quoting:
http://www.spg-corp.com/hybrid-rocket-propulsion.html
Based on the measured efficiencies, SPG’s LOX/paraffin-based hybrid motor would deliver a vacuum Isp performance of 340 seconds (for an nozzle expansion ratio of 70:1), which is approximately 30 seconds higher than modern solid rockets and better than most liquid LOX/RP systems.
Yeah, why not waste all of the space budget on inventing a rocket which is smaller and more expensive and does less than already existing rockets? Why doesn’t ESA try to invent a new version of the Internet, which is slower and worse than the existing internet, but much more expensive and not compatible with the existing internet? That’d “create jobs”.
Hurray hurray hurray! (brainlessly dancing around like a fooled space cadet who doesn’t care to understand anything about what is actually happening…)