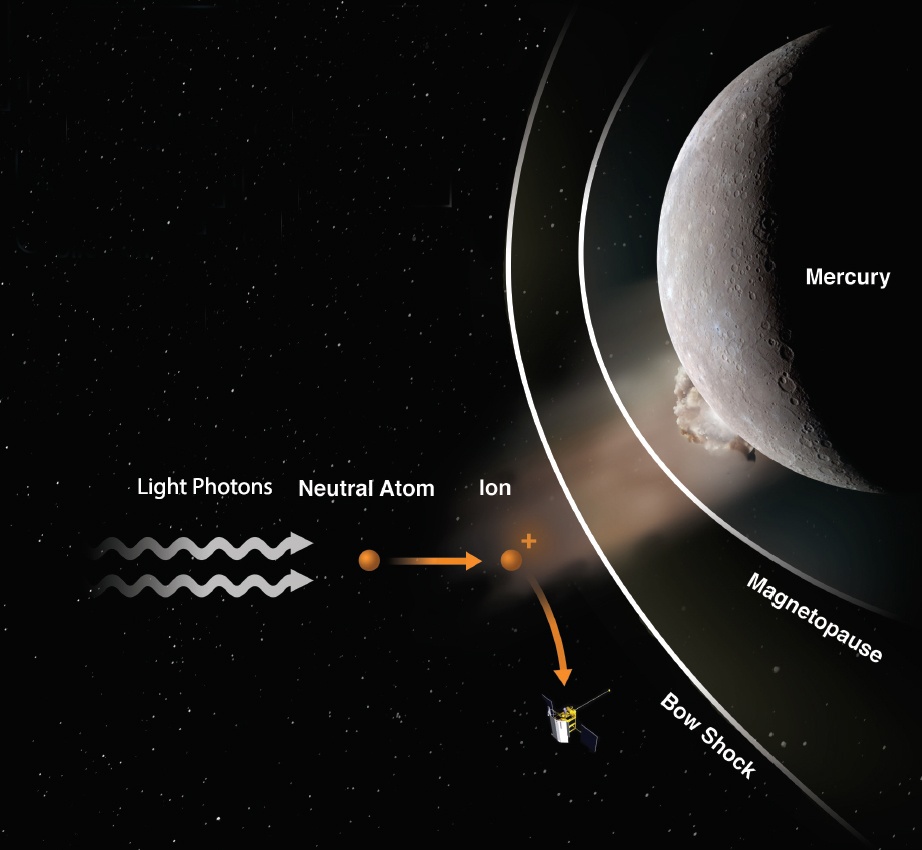
Can other planets have geomagnetic storms, even if their magnetosphere is weak and they don’t have an ionosphere like Earth? This question has now been answered, according to research done by a team of scientists in the United States, Canada, and China.
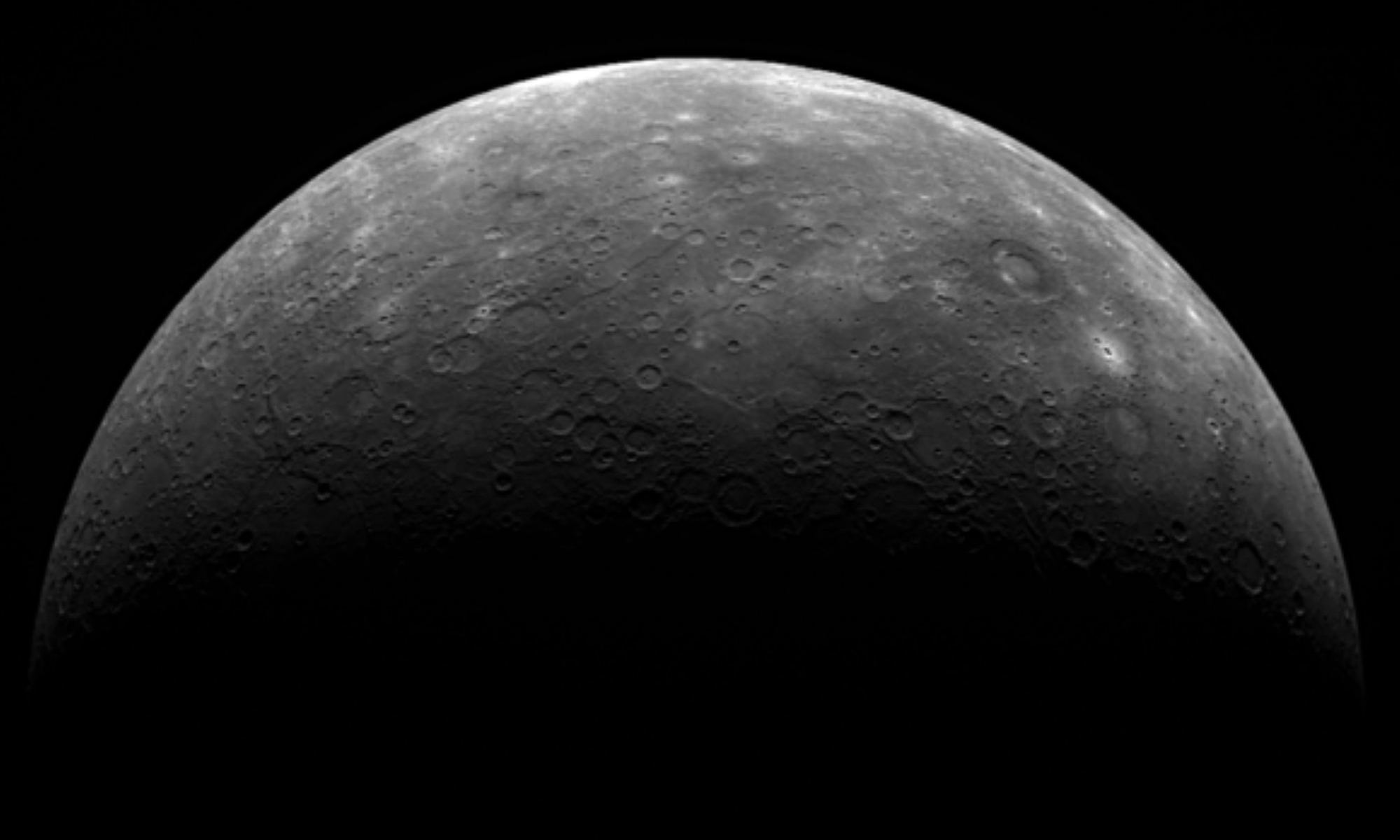
The research team found evidence that Mercury has a ring current, part of a magnetosphere, consisting of charged particles flowing laterally in a doughnut shape around the planet but that excludes the poles. This evidence came from data obtained from the Messenger space probe while it was dropping towards the planet at the end of its mission on April 14, 2015.
Continue reading “Even Mercury has Geomagnetic Storms”