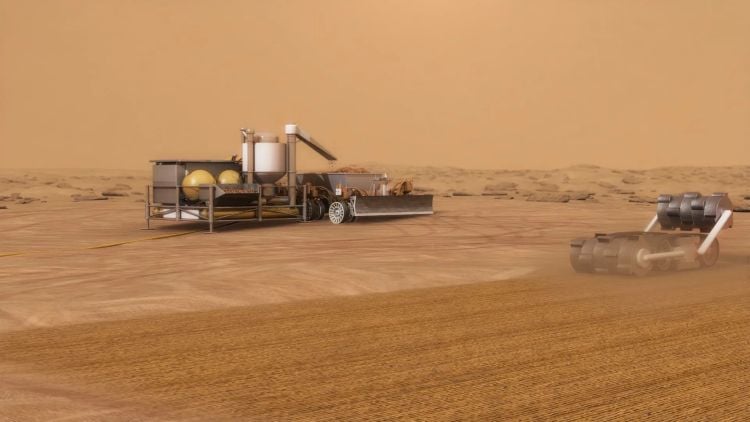

What steps can be taken to enhance in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) for future astronauts on Mars? This is what a recent study presented at the 56th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated the reasons, benefits, and challenges of conducting ISRU on Mars. This study has the potential to help astronauts, scientists, engineers, and mission planners develop new methods for enhancing the survivability of future Mars astronauts while also maximizing mission success.
Continue reading
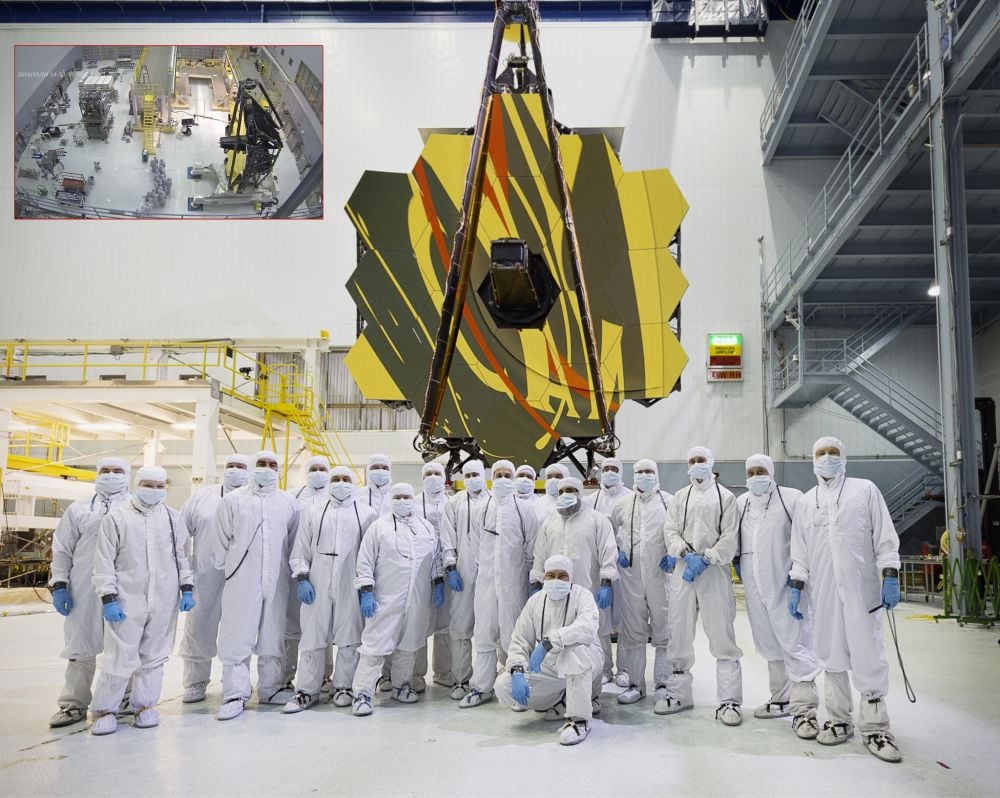

Spacecraft are expensive and intricately engineered machines designed to perform complex missions in harsh space environments. They're costly and require a long time to design and build. Due to their uniqueness and high value, and the need to keep them sterilized, they're assembled in cleanrooms that limit the amount of dust and microbes. New research shows that microbes are adapting to these clean rooms and learning how to thrive in them.
Continue reading
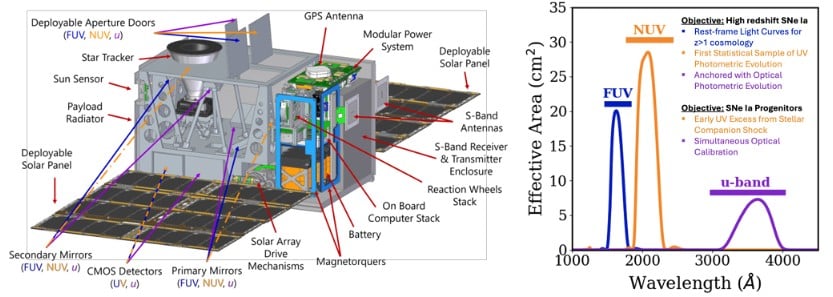
Technology Readiness Levels (or TRL levels, because repeating the last word of initialisms is common in English) is a metric commonly used by NASA to define how developed a technology for use on a mission is. These typically range from 1-9, with 1 being an idea in someone's head, and 9 having been successfully flown on a mission. One of the assessments of new projects that NASA does is a check of the TRL levels of its constituent components - those with a higher level get higher marks, since it is assumed that the technology necessary to get them ready will require less work. So, sometimes, NASA and other organizations will sponsor smaller missions to work on a specific technology needed for one of its big flagship programs. That seems to be the approach from a team led by Keri Hoadley of the University of Florida, who recently laid out a mission concept for the Ultraviolet Type Ia Supernova CubeSat (UVIa).
Continue reading
For a while now, there has been a problematic mystery at the heart of the standard cosmological model. Although all observations support the expanding Universe model, observations of the early period of the cosmos give a lower rate of acceleration than more local observations. We call it the Hubble tension problem, and we have no idea how to solve it. Naturally, there have been several proposed ideas: what if general relativity is wrong; what if dark matter doesn't exist; what if the rate of time isn't uniform; heck, what if the entire Universe rotates. So, let's add a new idea to the pile: what if dark matter evolves?
Continue reading
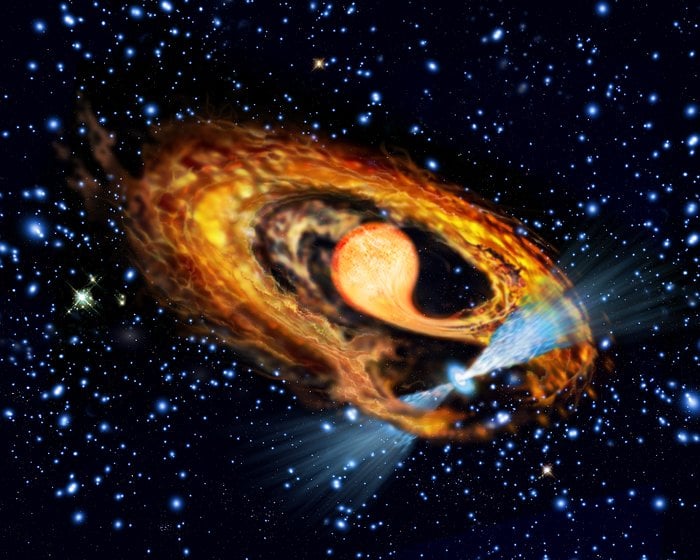

Tracking the sources of photons is a hobby of many astrophysicists. Some types of photons are tied so closely to particular phenomena that tracking their sources would help answer some larger questions in astrophysics itself. Photons on the "511 keV line" are one such type of photon, and they have been overrepresented near the galactic core, with no known source being prolific enough to create them. A new paper from Zachary Metzler and Zorawar Wadiasingh of the University of Maryland and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center suggests one potential source - millisecond pulsar (MSP) binaries.
Continue reading
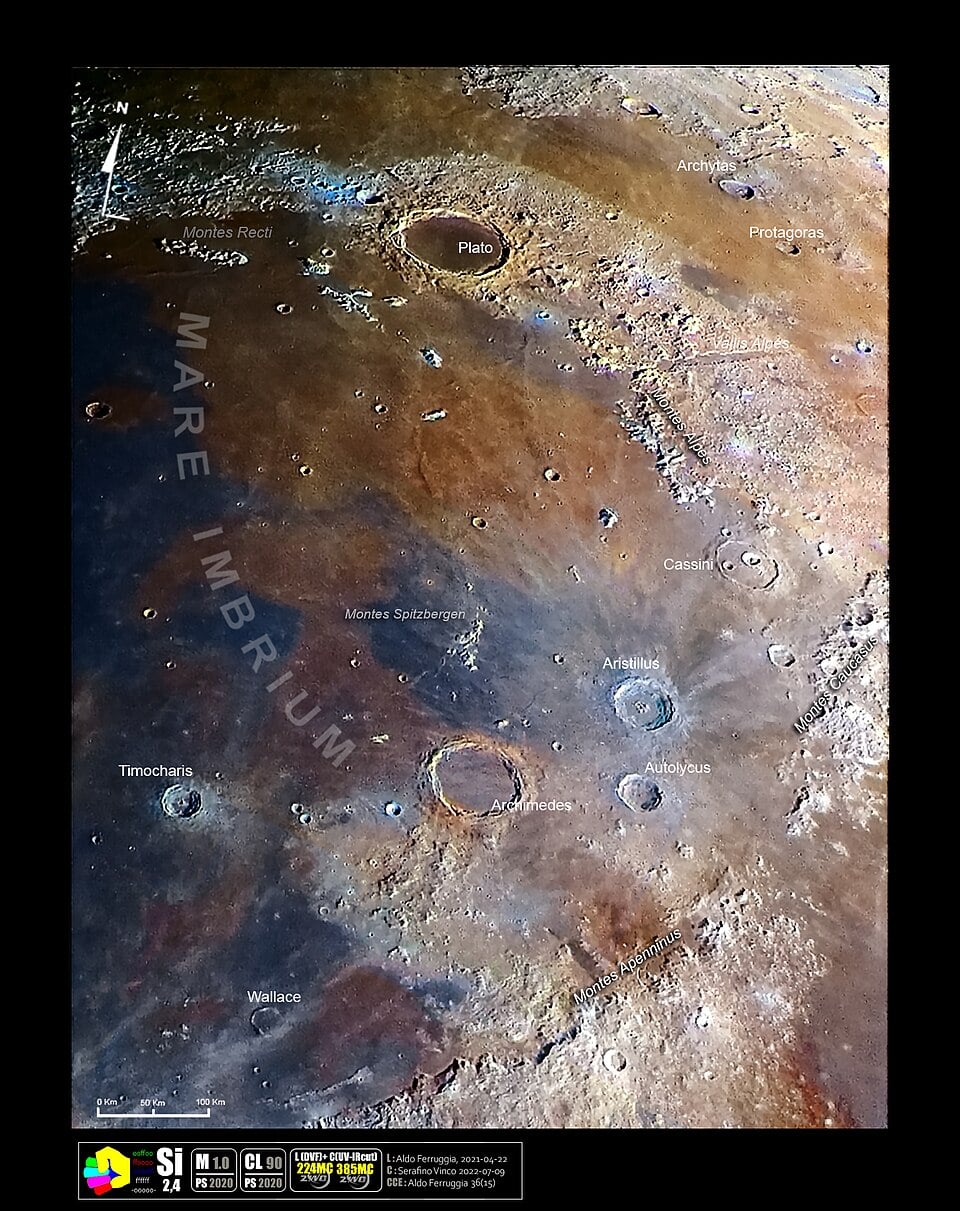

If we could peel back the Moon's cratered crust and examine its mantle, we might find answers to some foundational questions that date back to the Apollo moon landings. We lack the technological capability to excavate the Moon's mantle, but Nature has a way. A massive, ancient impact excavated material from deep beneath the Moon's crust and left it on the surface for us to study. It could help confirm the Moon's origins.
Continue reading

NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) has already uncovered hundreds of exoplanets of all sizes. Now, a team of astronomers is pushing the search even further—this time, looking for signs of planetary rings. Scanning 308 TESS planet candidates, they zeroed in on large, fast-orbiting worlds circling bright, nearby stars. Out of those, six showed subtle hints that rings might be present. But despite the tantalising clues, none offered definitive evidence of ring systems—at least not yet.
Continue reading
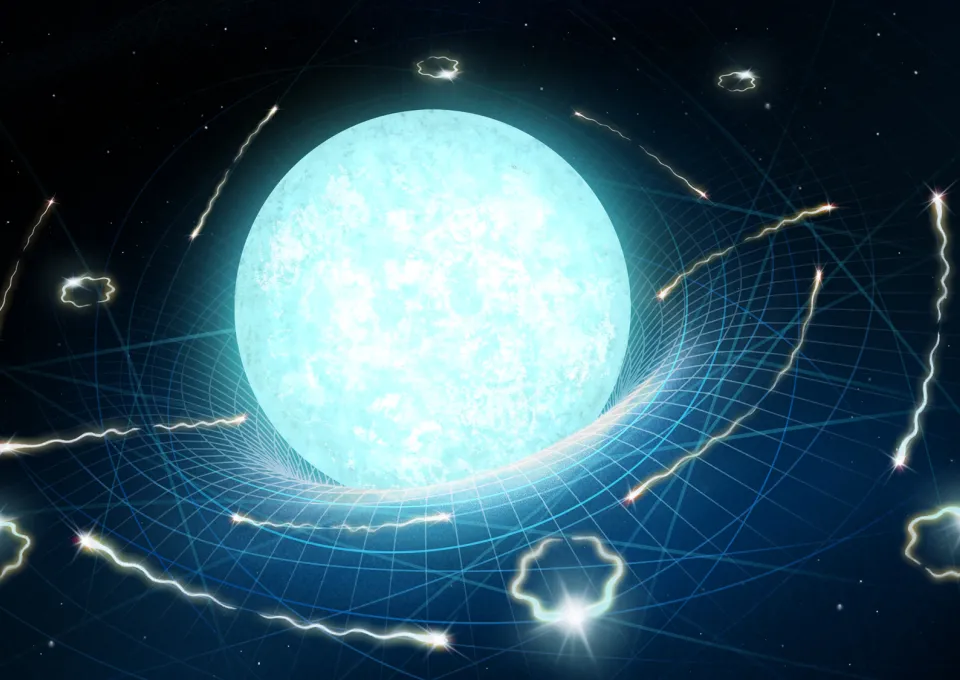

You've probably heard that black holes stick around for a long time—but even they are not eternal. Over unimaginable spans of time, they slowly evaporate into space through a process called Hawking radiation. And here's the kicker: this doesn't just apply to black holes. Anything with mass—stars, moons, even you—can, in theory, evaporate in this way. Black holes are a special case since they don't have a surface and can actually swallow some of their own radiation, making their demise painfully slow. The biggest ones might take up to 10^100 years to disappear. But smaller objects? Something like the Moon—or a human being—could fade into nothingness in "just" 10^90 years.
Continue reading
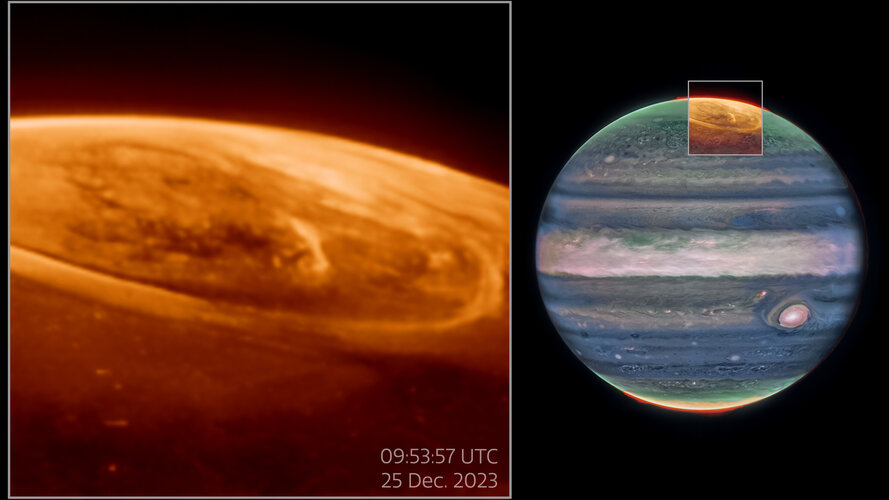
James Webb Space Telescope zoomed in on Jupiter's turbulent north pole in 2023 on the lookout for aurora. The results were amazing. Scientists have finally crunched through the data, revealing how the aurora rapidly change, fizzing and popping with light over the course of a few minutes. The team didn't stop there, training Hubble's ultraviolet eye on the same light show, they've created the most comprehensive view of Jupiter's auroral displays ever captured.
Continue reading
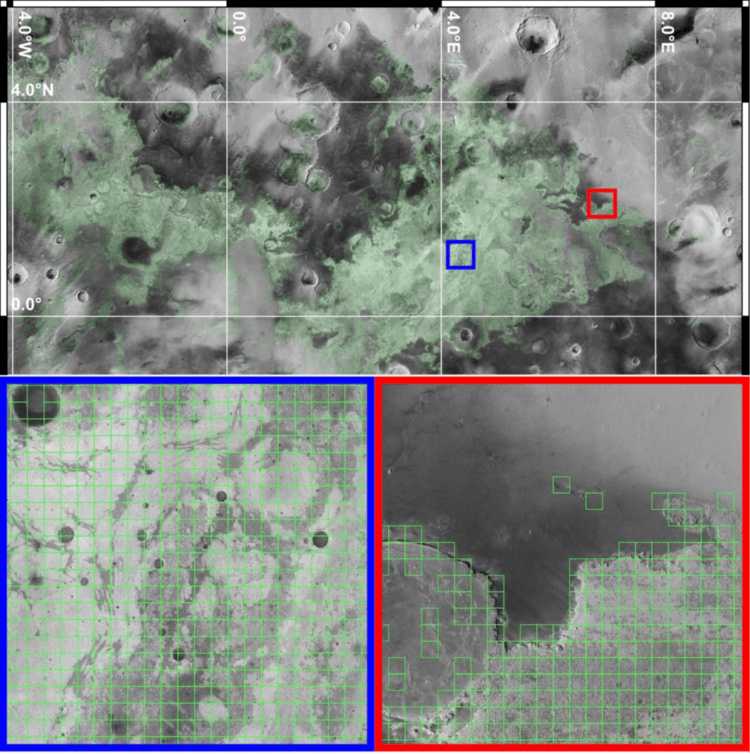
How can artificial intelligence (AI) be used to advance mapping and imaging methods on other planets? This is what a recent study presented at the 56th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference hopes to address as a lone researcher investigated using machine learning models to enhance mapping and imaging capabilities from orbital images obtained from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) Context Camera (CTX), which is currently orbiting Mars. This study has the potential to help scientists, engineers, and the public better understand the benefits of AI in conducting more advanced science, specifically regarding global images around Earth and other worlds.
Continue reading
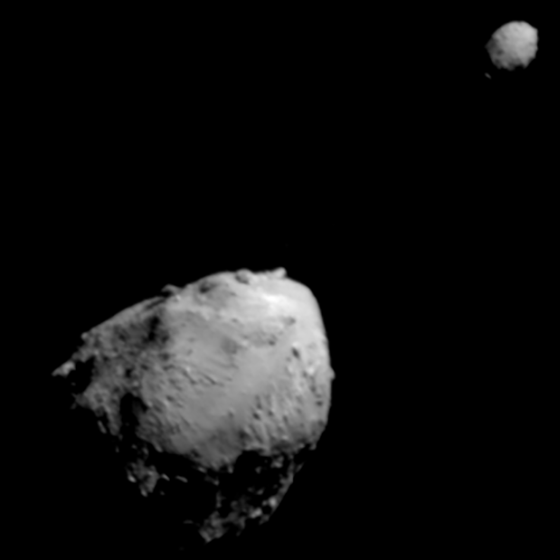
When NASA's Galileo spacecraft flew past asteroid Ida, it discovered a second, smaller asteroid in orbit: Dactyl. This was the first confirmed discovery of an asteroid with a moon, but now we know of many, including 13 asteroids larger than 100 km with satellites. Researchers have found that the mostly rapidly spinning asteroids are more likely to have moons; a large impact both spins up the asteroid and creates the debris that remains in orbit.
Continue reading
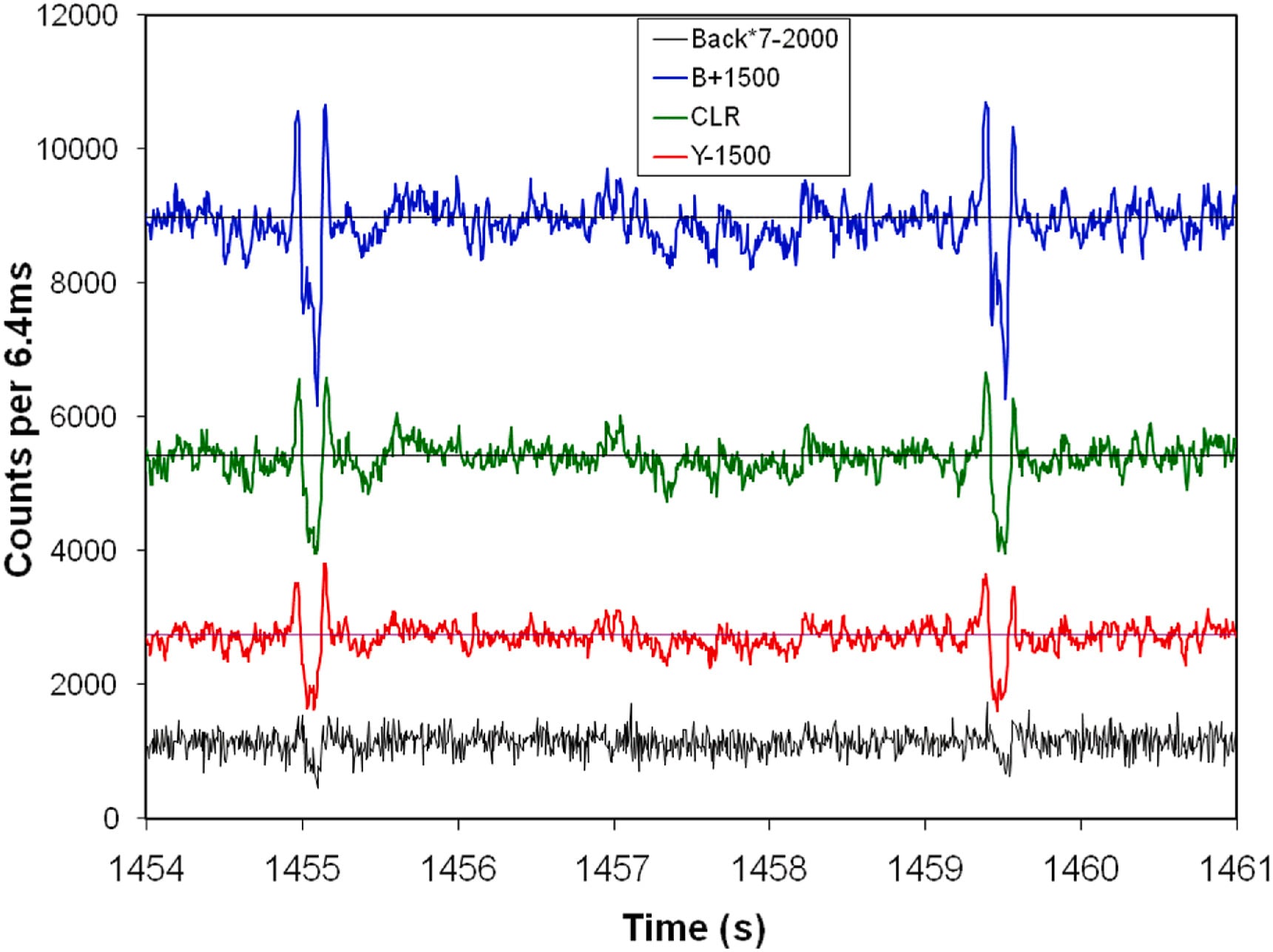
Veteran NASA scientist Richard H. Stanton describes the results of a multi-year survey of more than 1300 Sun-like stars for optical SETI signals. This survey revealed two fast identical pulses from a Sun-like star about 100 light-years from Earth, that match similar pulses from a different star observed four years ago.
Continue reading

The Cosmic Microwave Background is one of the bedrock pieces of evidence for the Big Bang. It's described as the cosmic afterglow from the Universe's birth. However, new research calls into question our understanding of the CMB and what it tells us about the evolution of the Universe.
Continue reading
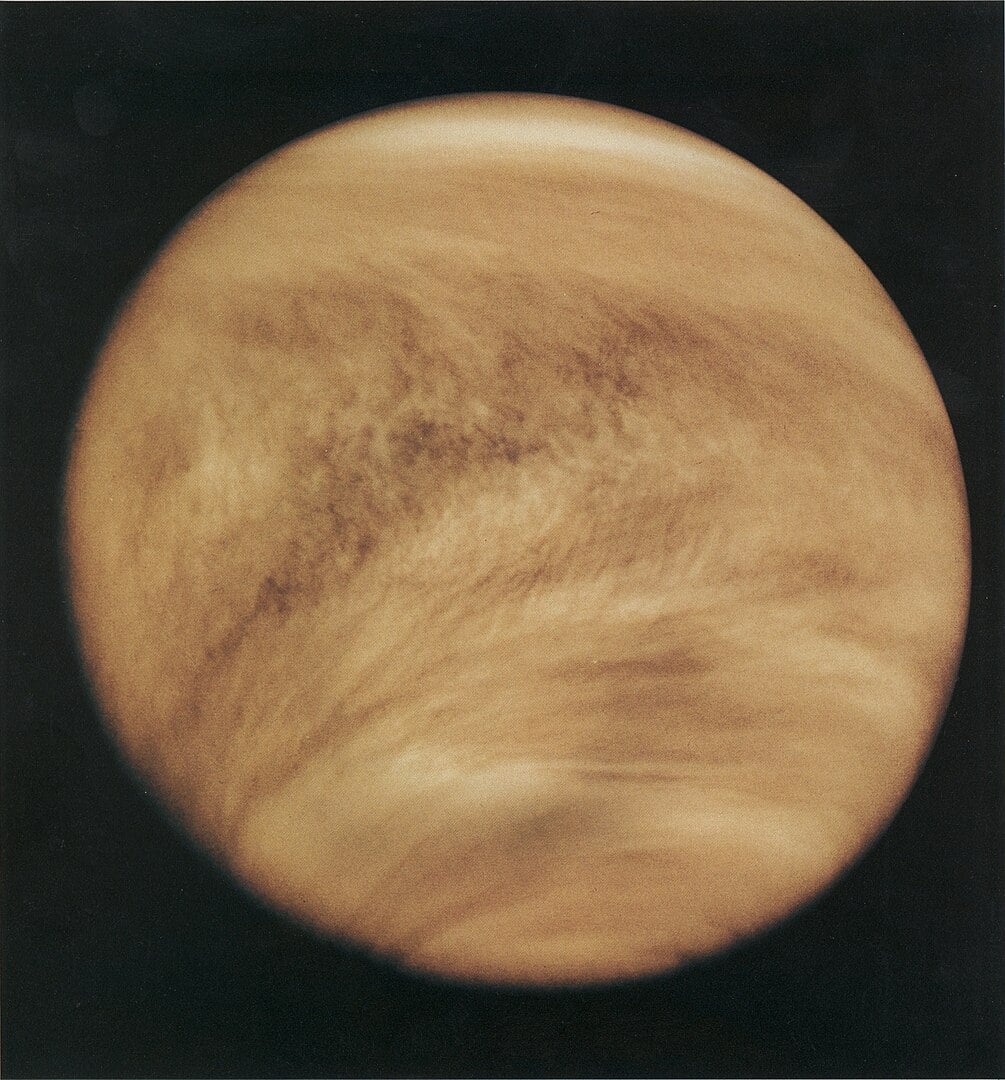

Could some type of life find refuge in Venus' clouds? The detection of phosphine and potentially ammonia in the planet's atmosphere is posing that question. If life could survive there, would it be like Earth life? Or would it have a different molecular basis?
Continue reading
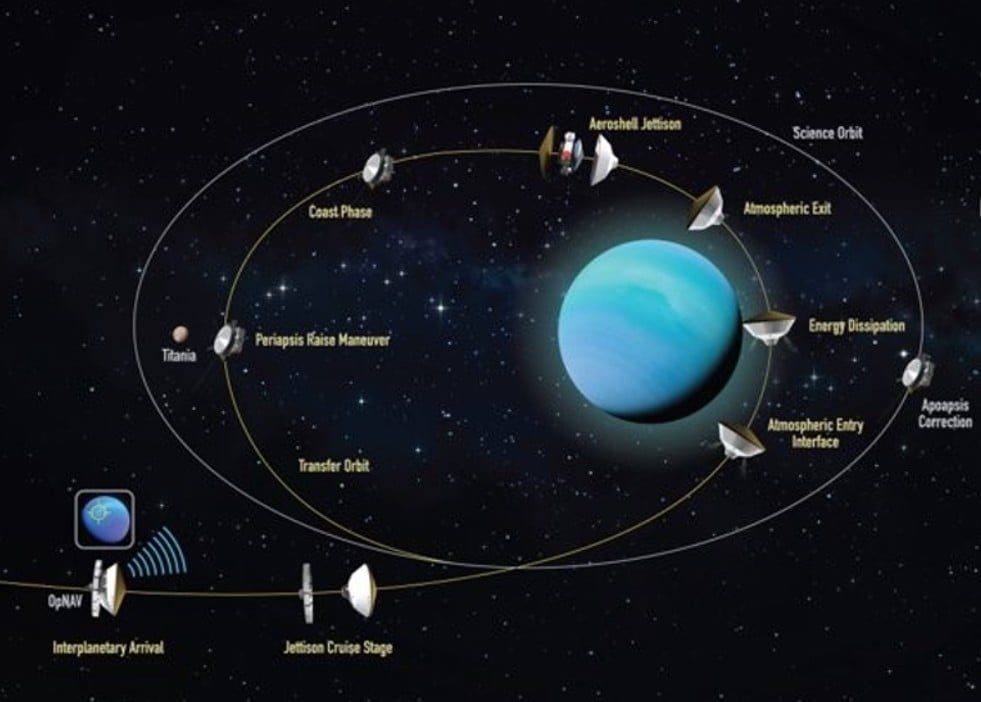
Getting a probe to the Icy Giant planets takes some time - a journey to Uranus could take as long as 13 years, even with a gravity assist from Jupiter. However, several ideas are in the works to speed up that process, especially given the increased interest in sending a probe their way. One of those ideas is to use an aerocapture system to slow a probe down once it reaches its intended target. A new paper from Andrew Gomez-Delrio and their co-authors at NASA's Langley Research Center describes how a proposed Uranus Orbiter and Probe (UOP) mission could utilize the same aerocapture technology that Curiosity used to dramatically improve both the speed and payload capacity of the mission.
Continue reading
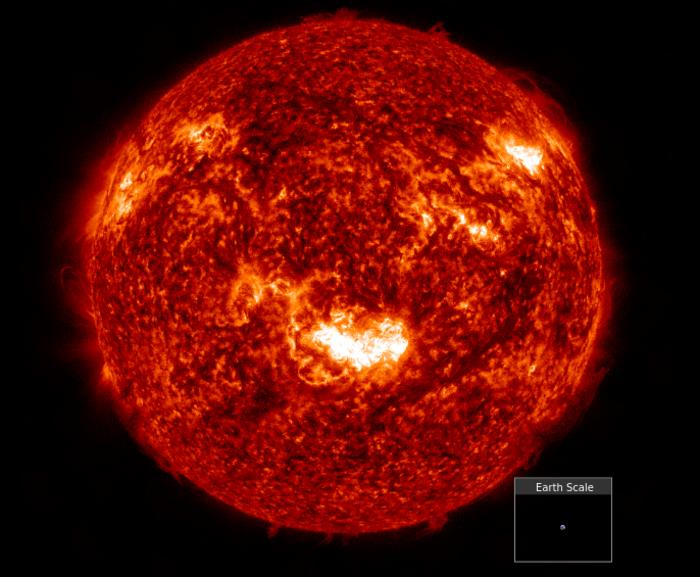

One year ago, our star erupted with almost apocalyptic force—unleashing the most violent solar assault in two decades. Dubbed the Gannon storm, it wasn't just another solar flare. Multiple coronal mass ejections collided and merged into a single devastating megastorm that slammed into Earth's protective shield. As our magnetosphere buckled the night skies exploded with spectacular auroral displays. The event even reached Mars with images from Curiosity sprinkled with streaks from charged particles.
Continue reading

Mars once flowed with water—then 3 billion years ago, it mysteriously disappeared. Where did these ancient Martian seas go? Did the Red Planet's collapsing magnetosphere allow solar winds to strip away its water into space or did the water sink into the Martian regolith, hiding from our view?NASA's InSight mission may have cracked the case. Seismic waves from meteorite impacts revealed water layer lurking 5.4-8 kilometres below the surface.
Continue reading
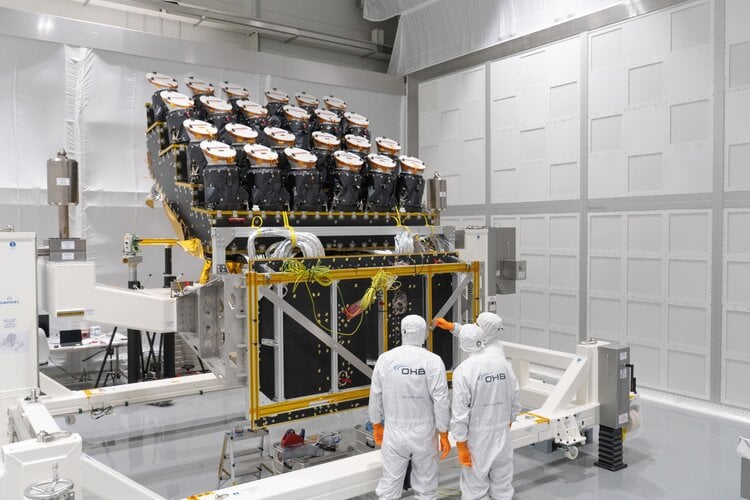

ESA's Plato Mission just hit a major milestone: 24 of 26 high-tech cameras have now been mounted and will soon be ready to hunt. This isn't your average telescope; it's a planet-spotting powerhouse designed to catch distant worlds passing in front of their stars. The clever camera arrangement creates a cosmic wide-angle lens, scanning a massive 5% of the entire sky in one go. No other planet-hunter comes close to this field of view.
Continue reading
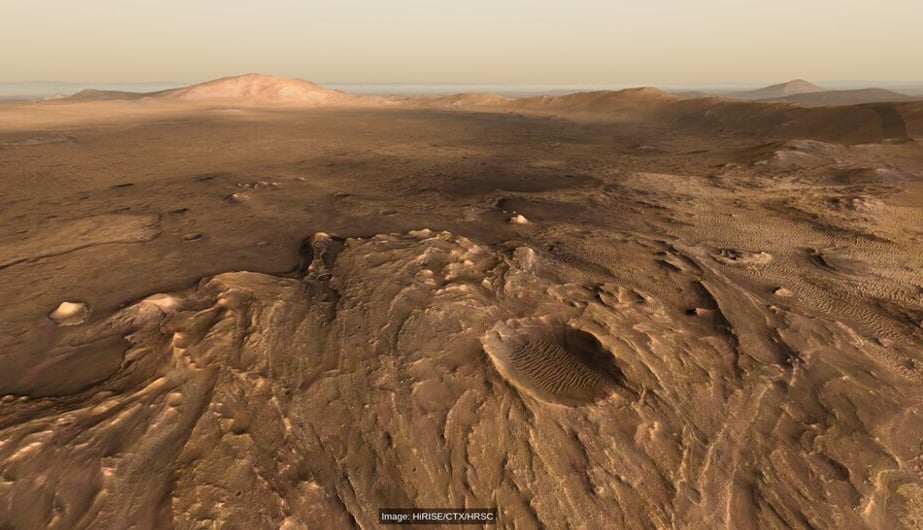

NASA's Perseverance Rover landed in Jezero Crater, an ancient impact crater that was probably filled with water for a long time. During its exploration, the rover has discovered volcanic rocks on the crater floor, but the original source hasn't been found. Now, a team of researchers thinks there's a composite volcano right on the edge of Jezero Crater. They identify a conical-shaped structure that rises about 2 km above the surrounding plains.
Continue reading
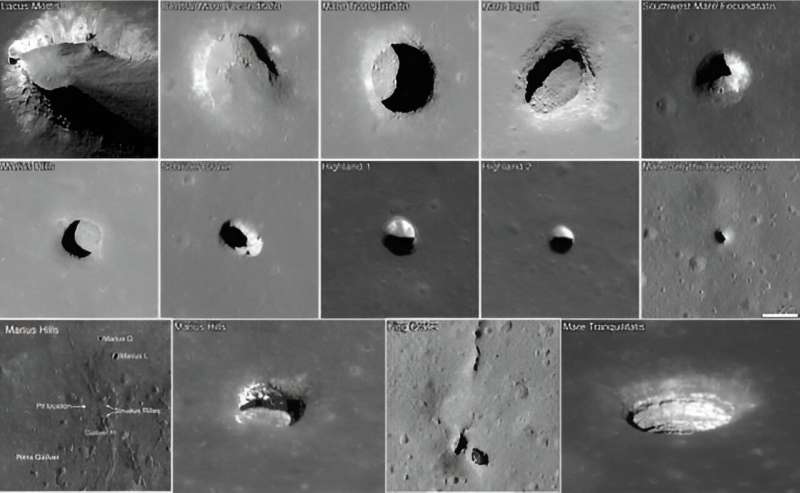
Some parts of the Moon are more interesting than others, especially when searching for future places for humans to land and work. There are also some parts of the Moon that we know less about than others, such as the Irregular Mare Patches (IMPs) that dot the landscape. We know very little about how they were formed, and what that might mean for the history of the Moon itself. A new mission, called the LUnar Geology Orbiter (LUGO), aims to collect more data on the IMPs and search for lava tubes that might serve as future homes to humanity.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today


















