October 2025 may provide a memorable sky scene, as Comet C/2025 A6 Lemmon puts on an encore appearance at dusk. The comet joins Comet R2 SWAN, which slides 0.26 Astronomical Units (AU) past Earth on October 20th. Both are currently fine objects for binoculars or a small telescope, vying for top spot at magnitude +6.
Continue reading

Peering back into the early years of the universe requires scientists to make a lot of assumptions. But sometimes, we get better instruments that then allow them to either confirm or replace those assumptions. That happened recently when it came to our study of J0529, a supermassive black hole that is currently the brightest known quasar in the universe. A new paper from a massive team of researchers used the GRAVITY+ instrument on the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO’s) Very Large Telescope (VLT) Interferometer to map this unique object’s Broad Line Region (BLR), and thereby calculated a new, updated mass that is 10 times smaller than previous estimates.
Continue reading

This ESA/Webb Picture of the Month shows eight stunning examples of gravitational lensing. Gravitational lensing, which was first predicted by Einstein, occurs because massive objects like galaxies and clusters of galaxies dramatically warp the fabric of spacetime. When a massive foreground object lines up just so with a background galaxy, the light from the background galaxy bends as it navigates the warped spacetime on its way to our telescopes.
Continue reading
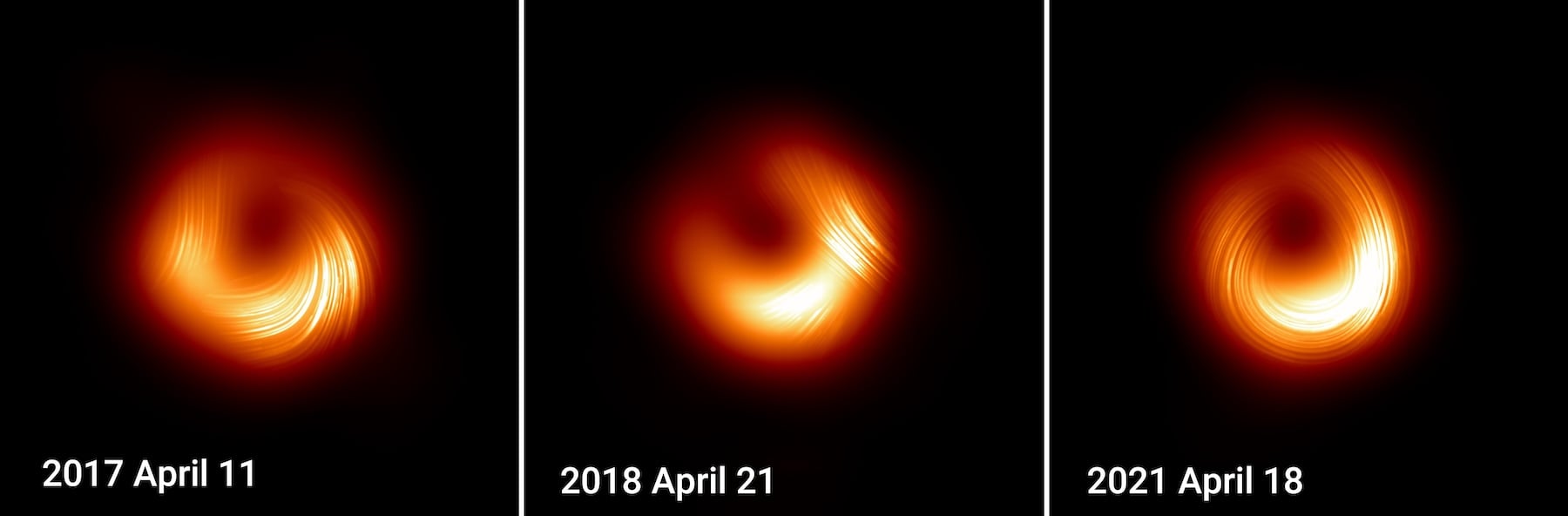

Black have no hair, but the material surrounding them does, and the two can interact in unusual ways. As observations from the Event Horizon Telescope show, the magnetic fields surrounding a black hole can change extremely fast.
Continue reading
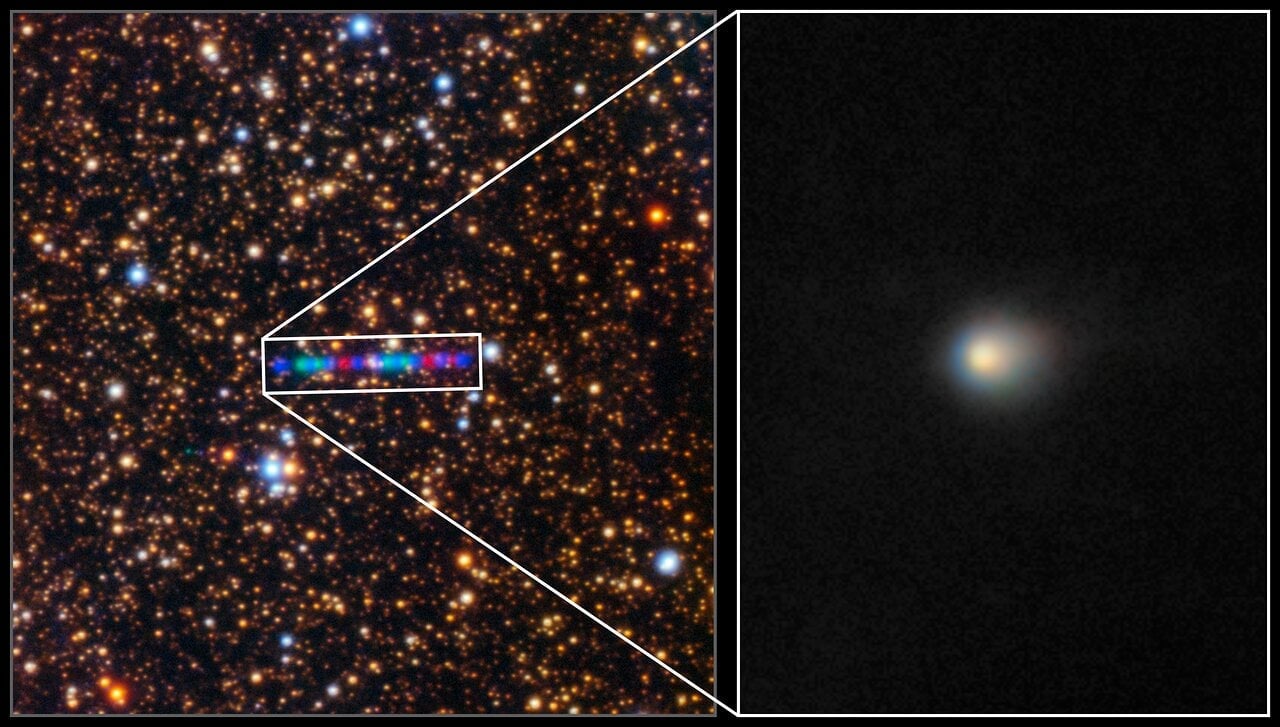
Interstellar visitor 3I/ATLAS has been constantly changing as it makes its way through our solar system. That’s to be expected, as, for the first time in potentially billions of years, it's getting close to the energy put out by a star. Scientists have been keeping a close watch on those changes, both to ensure there’s nothing unexplainable by our current understanding, but also to compare 3I/ATLAS to both previous interstellar visitors as well as comets in our own solar system. A recent paper from European researchers describes how the changes in a particular material ratio in 3I/ATLAS’ coma fit with our current understanding of cometary geology.
Continue reading
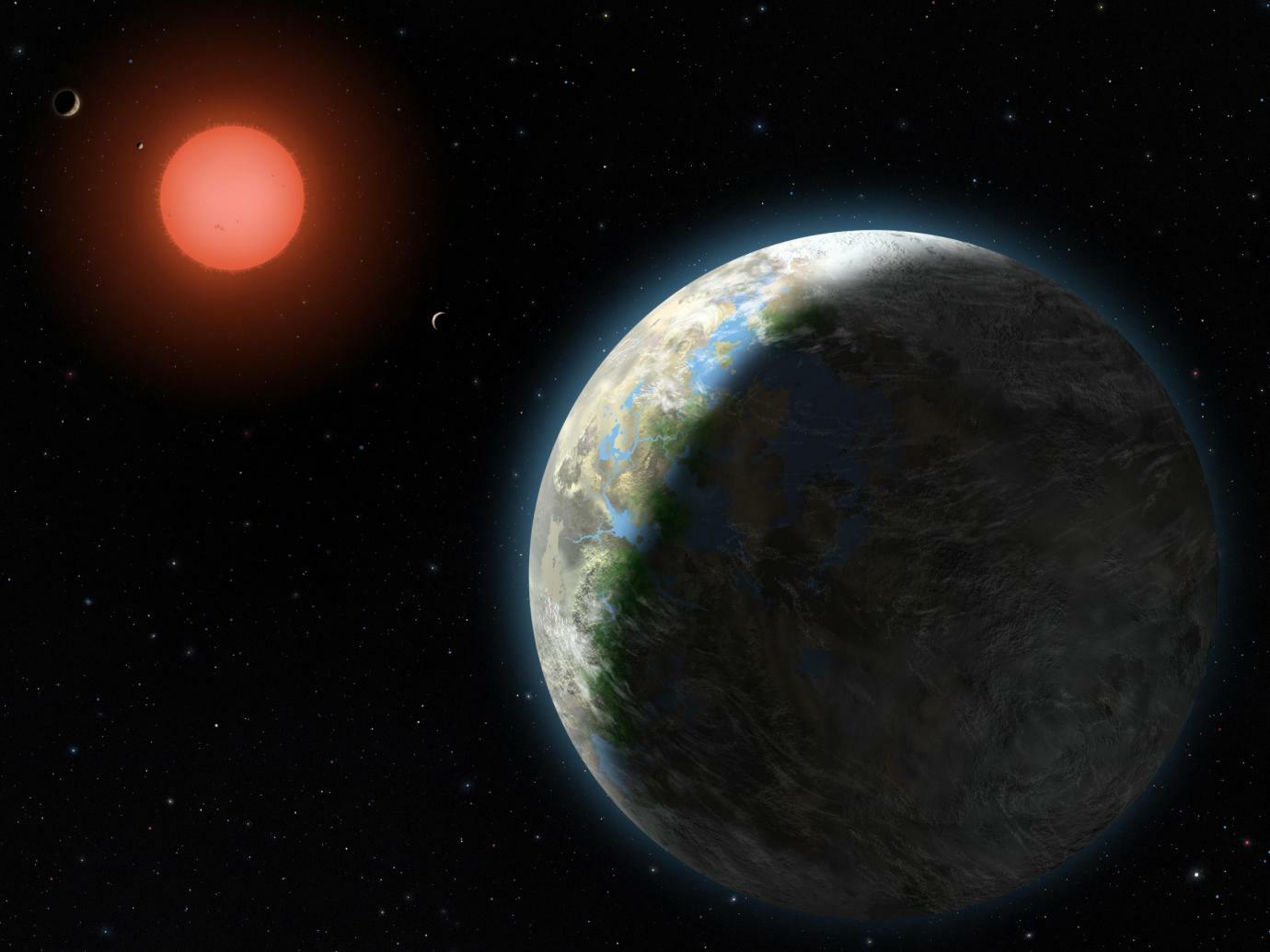

While no evidence of life beyond Earth has been found (yet), it is assumed that life and habitable planets are the norm (per the Copernican Principle). Meanwhile, exoplanet studies have revealed several rocky planets orbiting within the habitable zones of nearby dwarf suns. But as Columbia University Professor David Kipping argues in a recent paper, there is evidence that Earth could be an outlier, while rocky planets orbiting red dwarfs may not be capable of supporting advanced life.
Continue reading
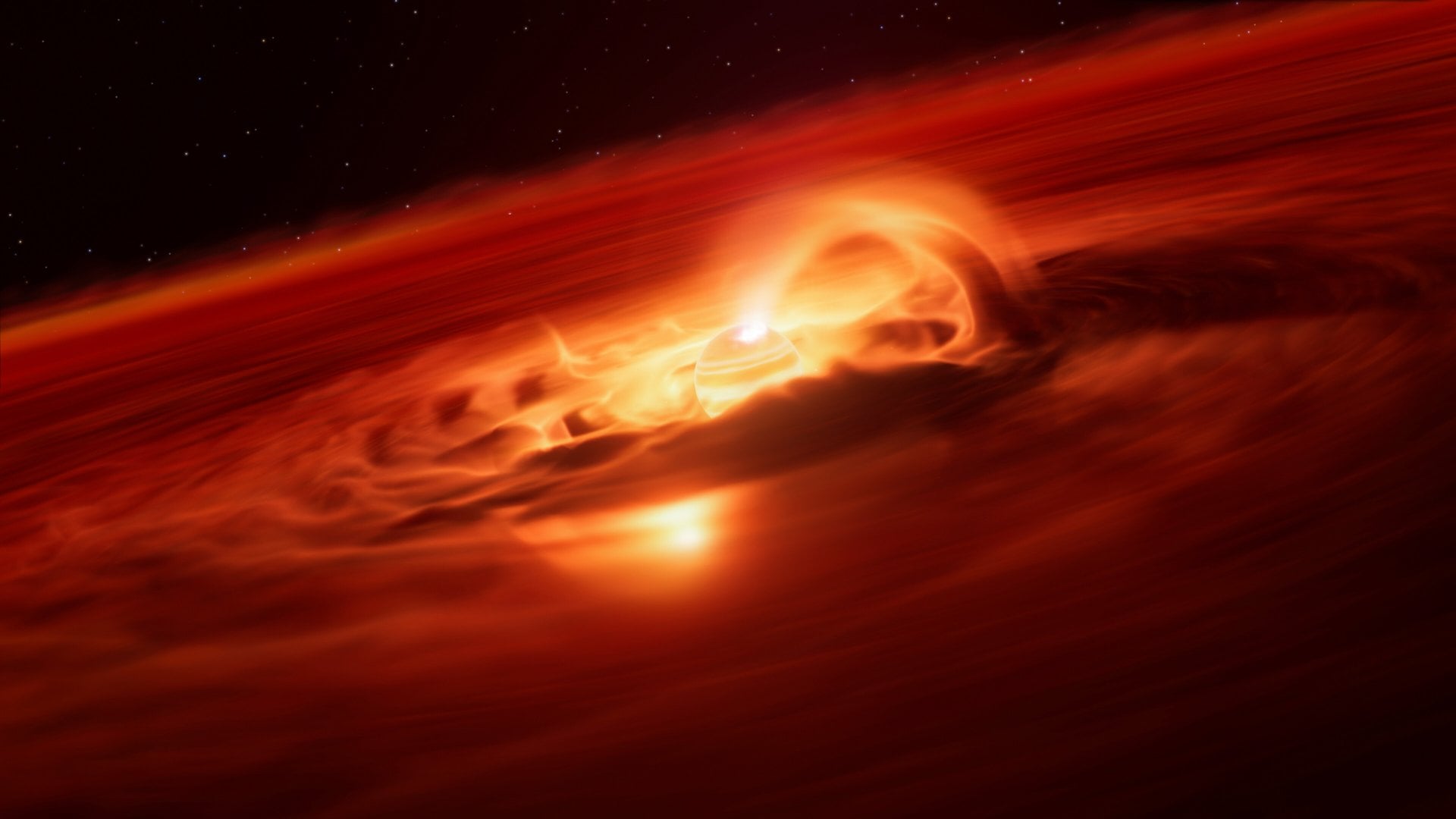

New observations made with the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) identified an enormous a rogue planet with the strongest growth rate ever recorded. These observations reveal that this free-floating planet is eating up gas and dust from its surroundings at a rate of six billion tonnes a second.
Continue reading

By modeling the limb darkening of a star, astronomers can get a better measure of the transit depth of an exoplanet. This will allow us to get better measurements of the size of exoplanets.
Continue reading

ESA’s Mars Express takes us on another mesmerizing flight over the highlands of Xanthe Terra to the smoother lowlands of Chryse Planitia. Billions of years ago, water surged through this region, creating many of the features we see today.
Continue reading
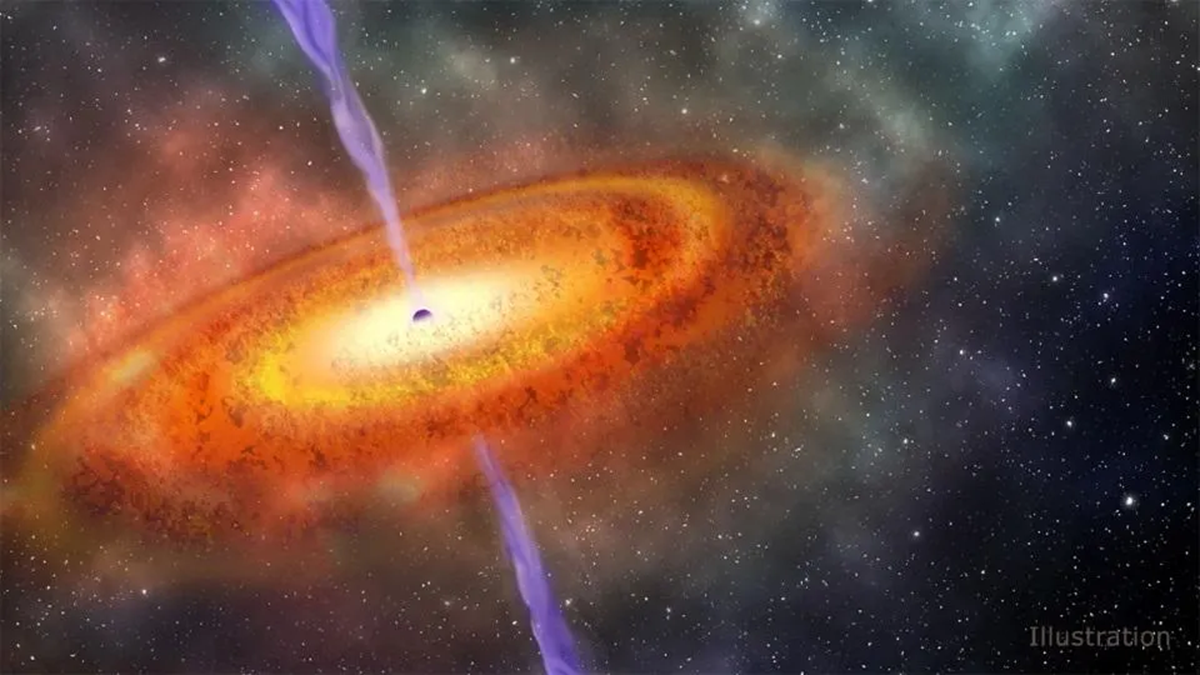

An international of researchers, including the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU, WPI) have used the James Webb Space Telescope to uncover 12 black holes from 12.9 billion years ago, shedding light on how black holes and galaxies evolved in the early Universe.
Continue reading
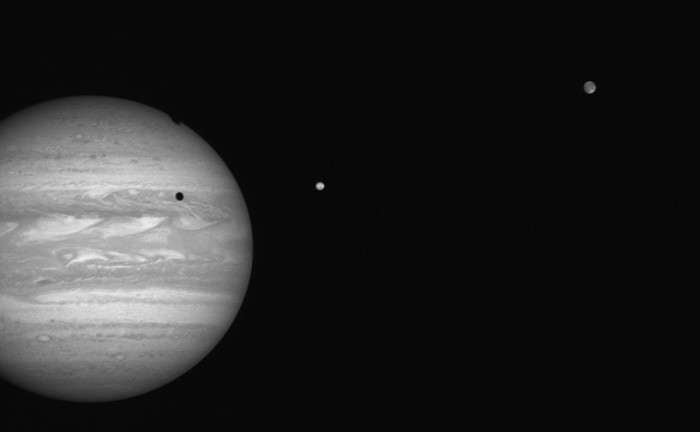

Jupiter and its moons are busy in October. If skies are clear, be sure to set your alarm and follow the largest planet in our solar system this month. While massive Jupiter always warrants a view through even a small telescope, its four major Galilean moons warrant special interest, as we’re in the midst of a season of rare double shadow transits.
Continue reading
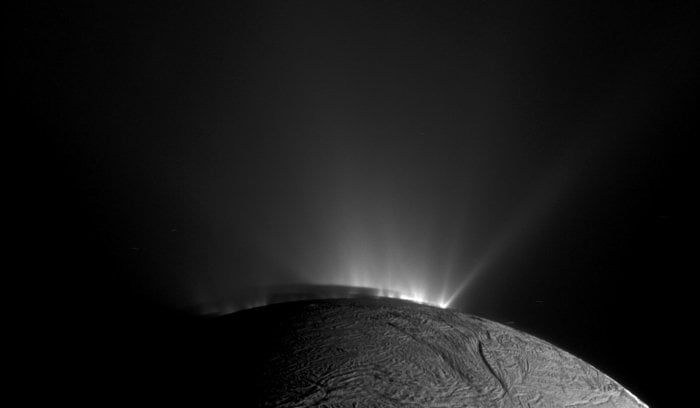

Enceladus’ ice continues to get more and more intriguing as researchers continue to unlock more secrets taken from a probe over ten years ago. When Cassini crashed into Saturn in 2017, it ended a 13 year sojourn that is still producing new research papers today. A recent one in Nature Astronomy from the researchers at the Freie Universität Berlin and the University of Stuttgart found hints of organic molecules discovered for the first time on the icy moon, some of which could serve as precursors to even more advanced biomolecules.
Continue reading

Modeling something like geysers on a far-away moon seems like it should be easy. How much complexity could there possibly be when a geyser is simply a hole in some ice shooting superheated water through it? The answer is pretty complex, to be honest - enough that accurate models require a supercomputer to run on. Luckily, the supercomputing cluster at the University of Texas, known as the Texas Advanced Computing Center, gave some time to researcher modeling Enceladus’ ice plumes, and their recent paper in JGR Planets discusses the results, which show there might not be as much water and ice getting blown into orbit as originally thought.
Continue reading
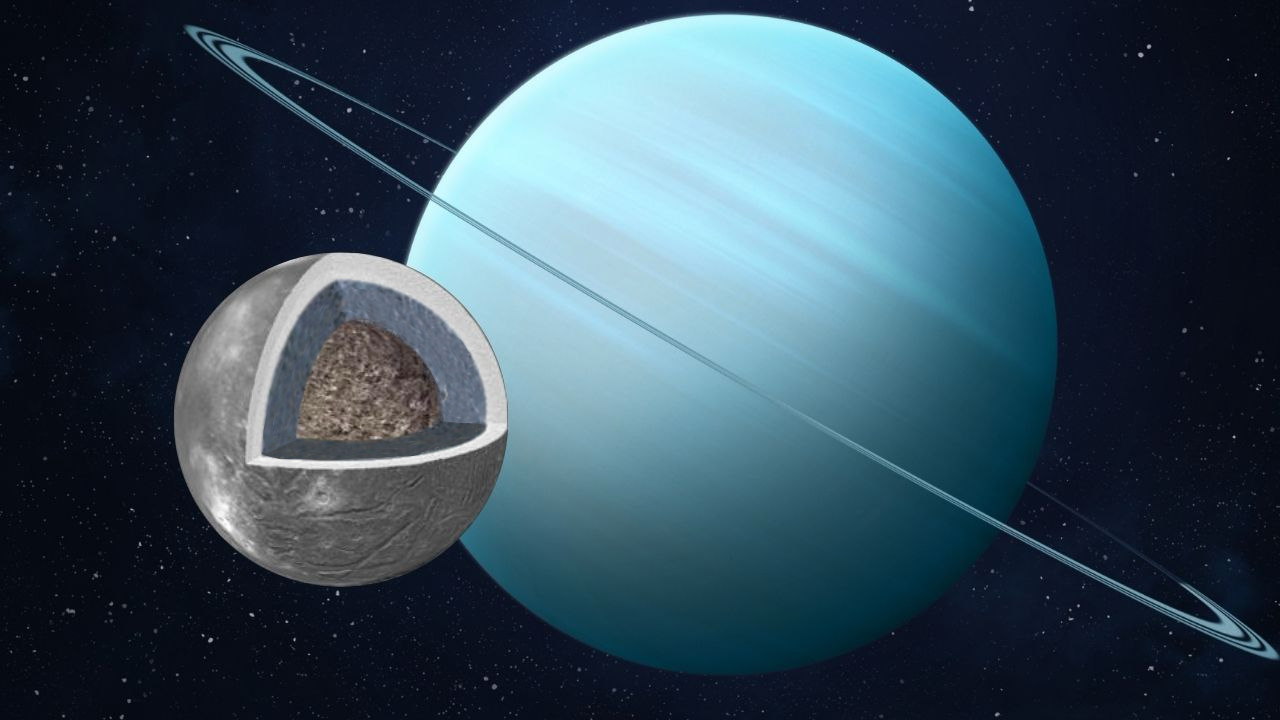

Interest in icy moons has been growing steadily as they become more and more interesting to astrobiologists. Some take the majority of the attention, like Enceladus with its spectacular geysers. But there are interesting ones that might be hiding amongst even thicker ice shells in the Uranian system. A new paper published in Icarus from researchers at the Planetary Science Institute, Johns Hopkins University, and the University of North Dakota, looks at what Ariel, the fourth biggest moon in the Uranian system, might look like under its icy surface.
Continue reading
Reanalyzing old data with our modern understanding seems to be in vogue lately. However, the implications of that reanalysis for some topics are more impactful than others. One of the most hotly debated topics of late in the astrobiological community has been whether or not life can exist on Venus - specifically in its cloud layers, some of which have some of the most Earth-like conditions anywhere in the solar system, at least in terms of pressure and temperature. A new paper from a team of American researchers have just added fuel to that debate by reanalyzing data from the Pioneer mission to Venus NASA launched in the 70s - and finding that the Venus’ clouds are primarily made out of water.
Continue reading
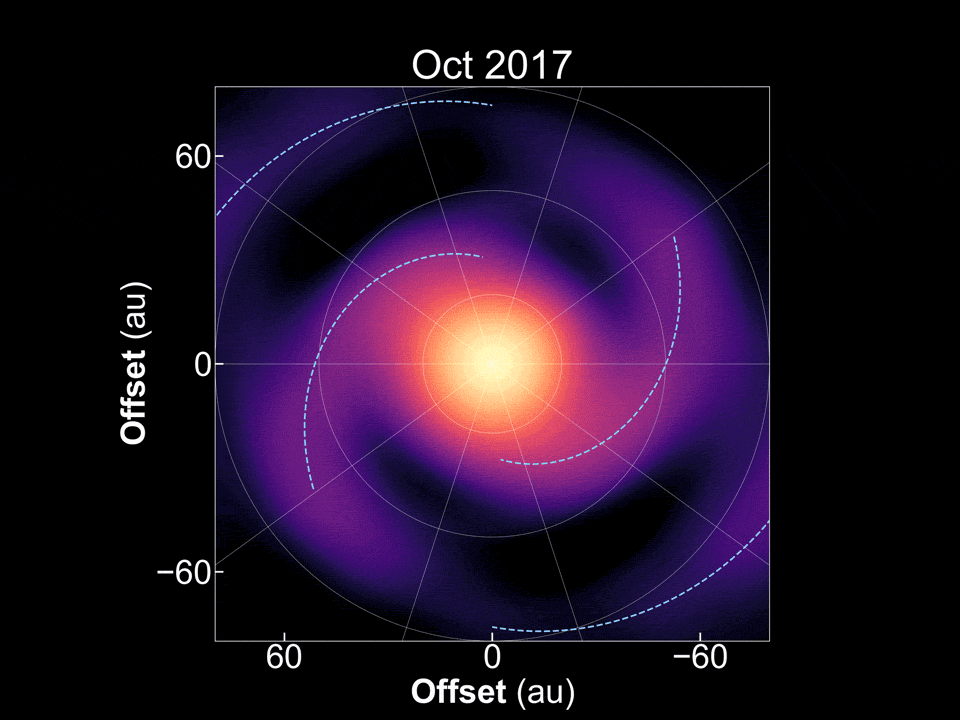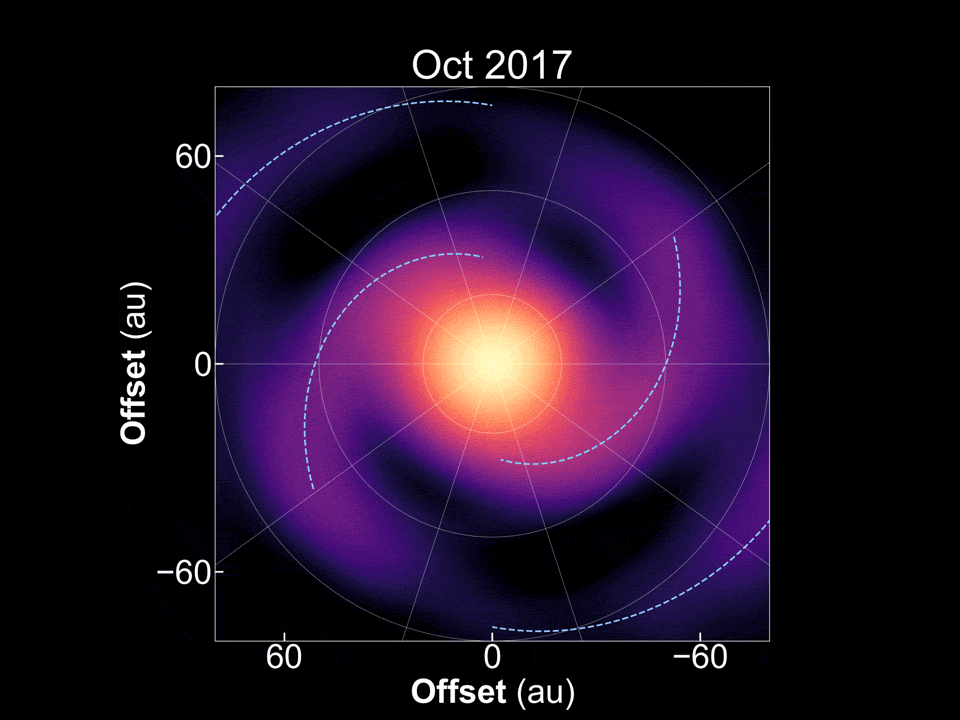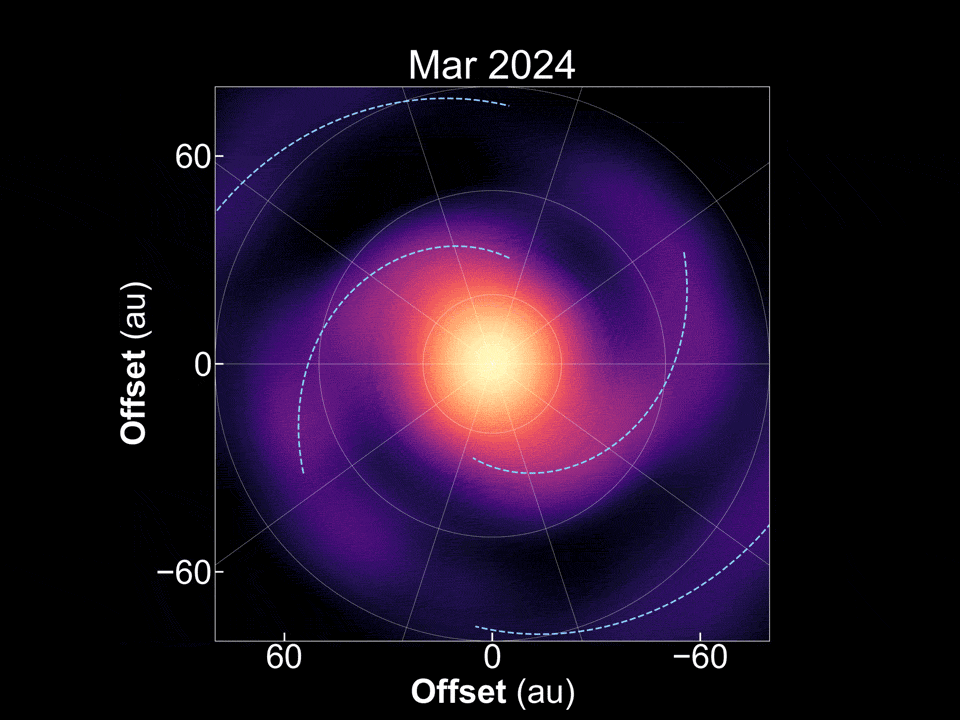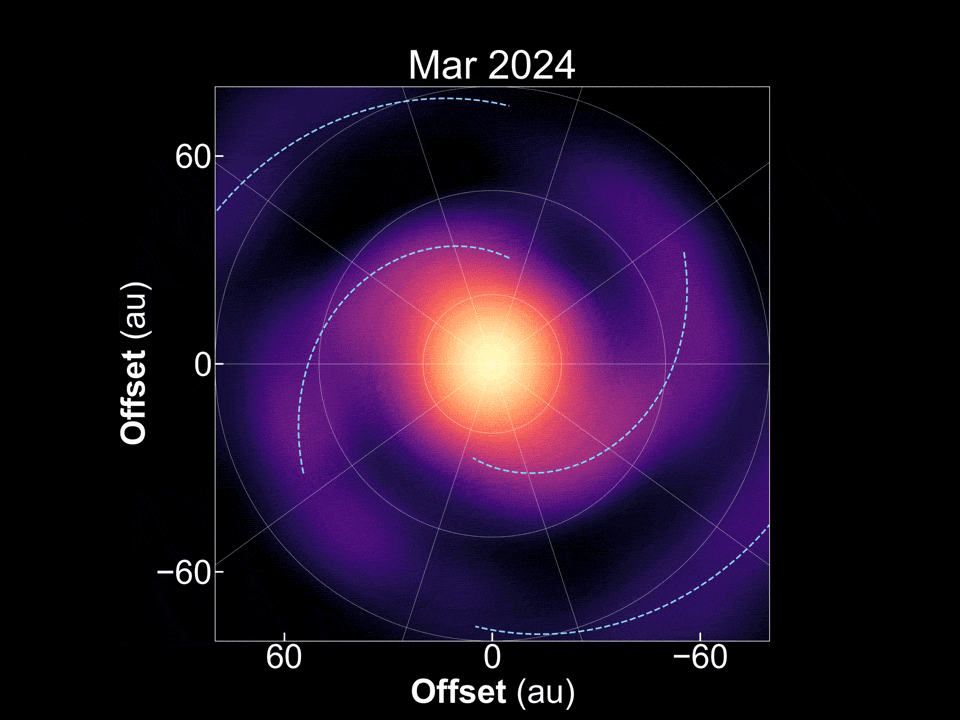
There are plenty of exoplanets scattered throughout the galaxy, so it would stand to reason there are also plenty of stars that are in the process of forming new exoplanets. Tracking down stars that are in different stages of that process can shed light on the exoplanet formation process, and potentially even on how planets in our own solar system developed. But determining what star systems are going through that process, let alone where they are in the process itself, can be tricky. A new paper in Nature Astronomy from Tomohiro Yoshida and his co-authors at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan and several other Japanese and American research institutions, seems to have found one that finally answers a mystery that has stood in planetary formation theory for decades - how do gas giant exoplanets form so far away from their stars?
Continue reading

Astronomy is increasingly becoming an online affair. Recent discoveries of interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS and R2 SWAN highlighted this fact, when both were first discussed on message boards and verified via remote telescopes before confirmation. Another recent find also shows what’s possible, as devoted amateur astronomer Filipp Romanov accomplished an amazing feat, and discovered a supernova in a remote galaxy.
Continue reading

The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) has a data scale problem. There are just too many places to look for an interstellar signal, and even if you’re looking in the right place you could be looking at the wrong frequency or at the wrong time. Several strategies have come up to deal narrow the search given this overabundance of data, and a new paper from Naoki Seto of the Kyoto University falls nicely into that category - by using the Brightest Of All TIme (BOAT) Gamma Ray Burst, with some help from our own galaxy.
Continue reading
Dark matter, as its name suggests, is really dark, so dark in fact that it doesn’t interact in any way with light or any other part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Even thought it makes up about 80 percent of all matter in the universe and plays a vital role in galaxy formation we still don’t really know what it is. Of all the methods and techniques used to try and unravel this mystery, never would I think I would be writing about the Moon and how it could help us. However, a new piece of research suggests that future missions to the far side of the Moon could help us determine the mass of individual dark matter particles.
Continue reading

Gamma ray bursts are among the most luminous explosions in the universe, briefly outshining entire galaxies in a violent flash of energy. For decades, scientists have debated what powers these incredibly powerful detonations and, to date, the leading candidates have been black holes or highly magnetised neutron stars called magnetars. Distinguishing between the two has proven frustratingly difficult though but a new study has just provided the clearest evidence yet that magnetars can indeed power some of these extreme events, and they did it by detecting something unexpected, the "heartbeat" of a newborn star.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today