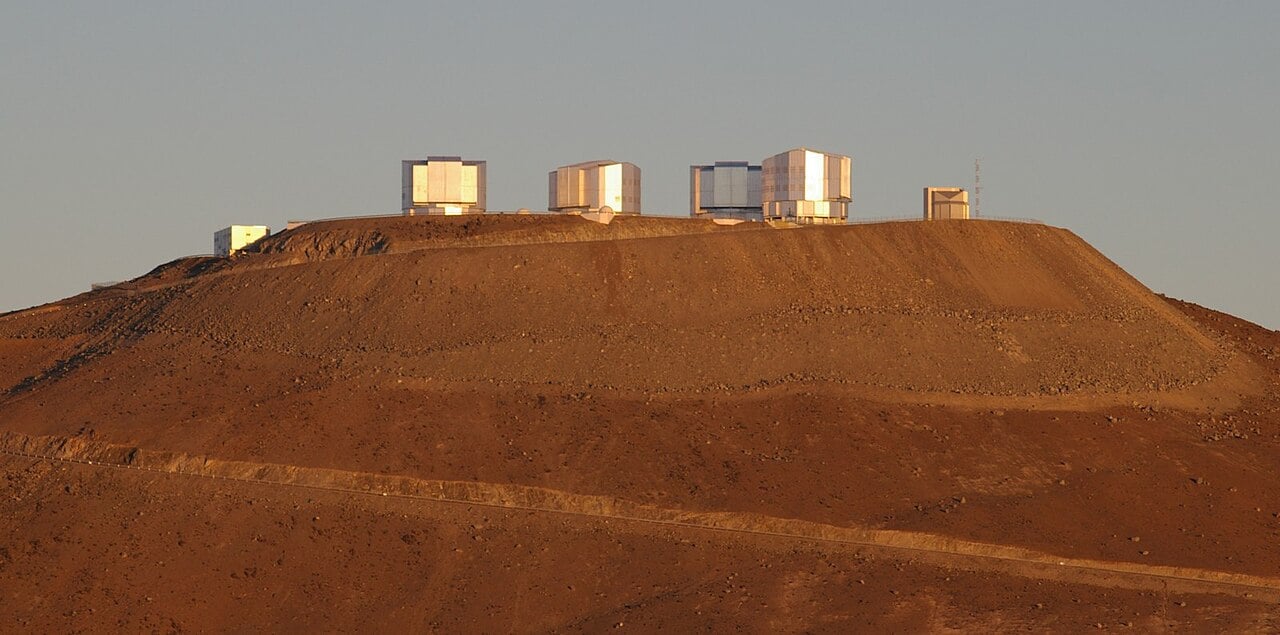
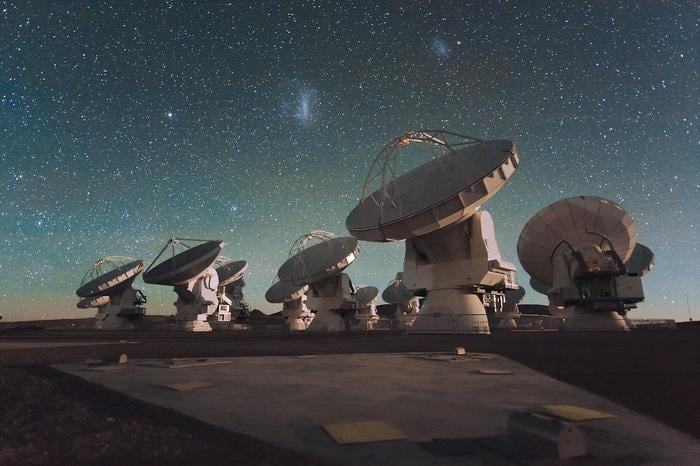
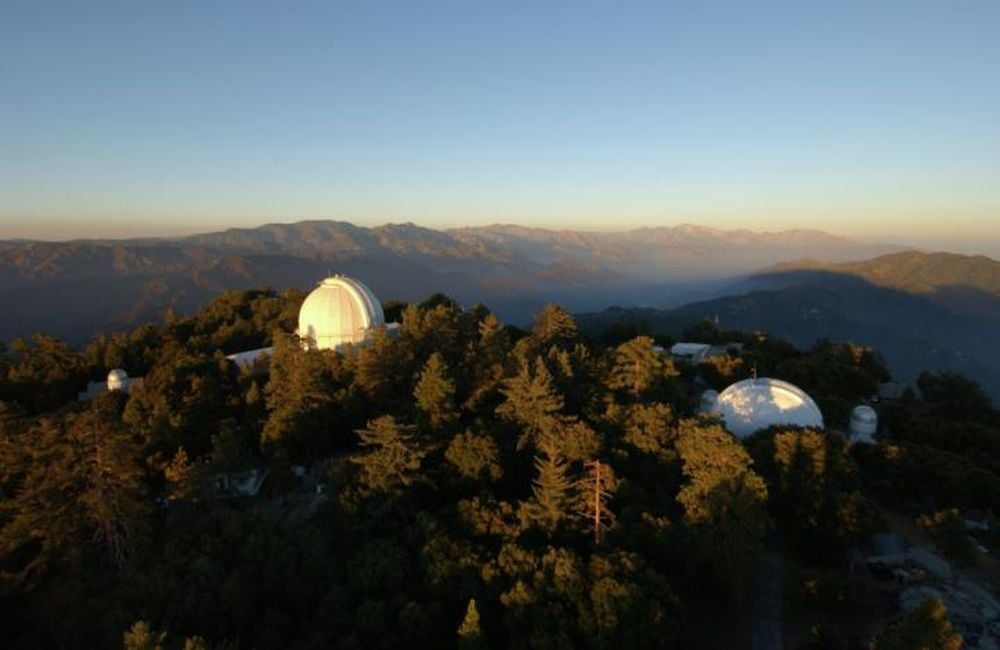
Chile's Paranal Observatory Saved from Industrial Development
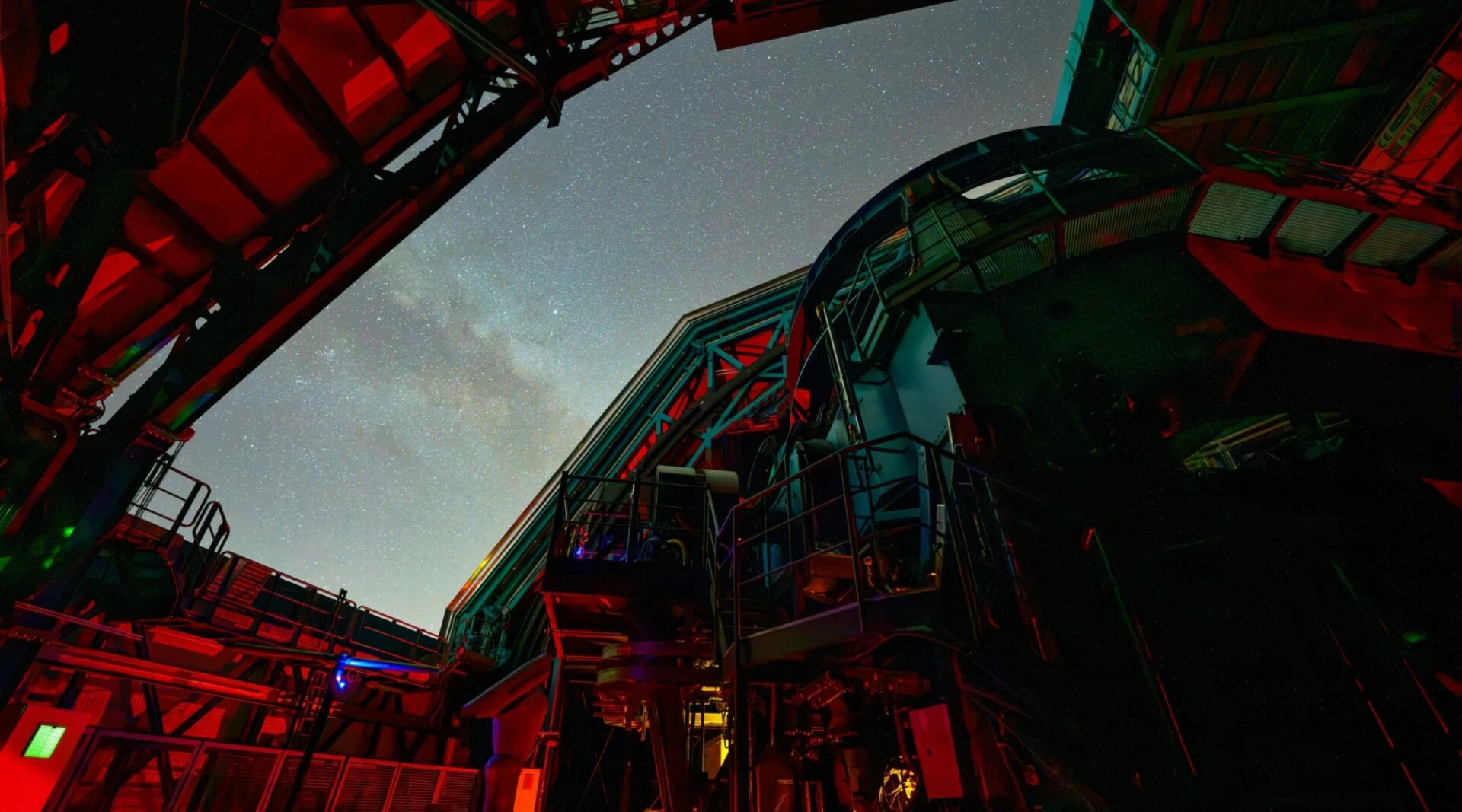
After months of protests led by Nobel laureate Reinhard Genzel, the American energy company AES Andes has abandoned plans to build a massive solar and wind facility just kilometres from one of the world's premier telescope sites. The decision preserves the pristine night skies above Chile's Paranal Observatory, where the European Southern Observatory operates some of humanity's most powerful eyes on the universe.
 Universe Today
Universe Today