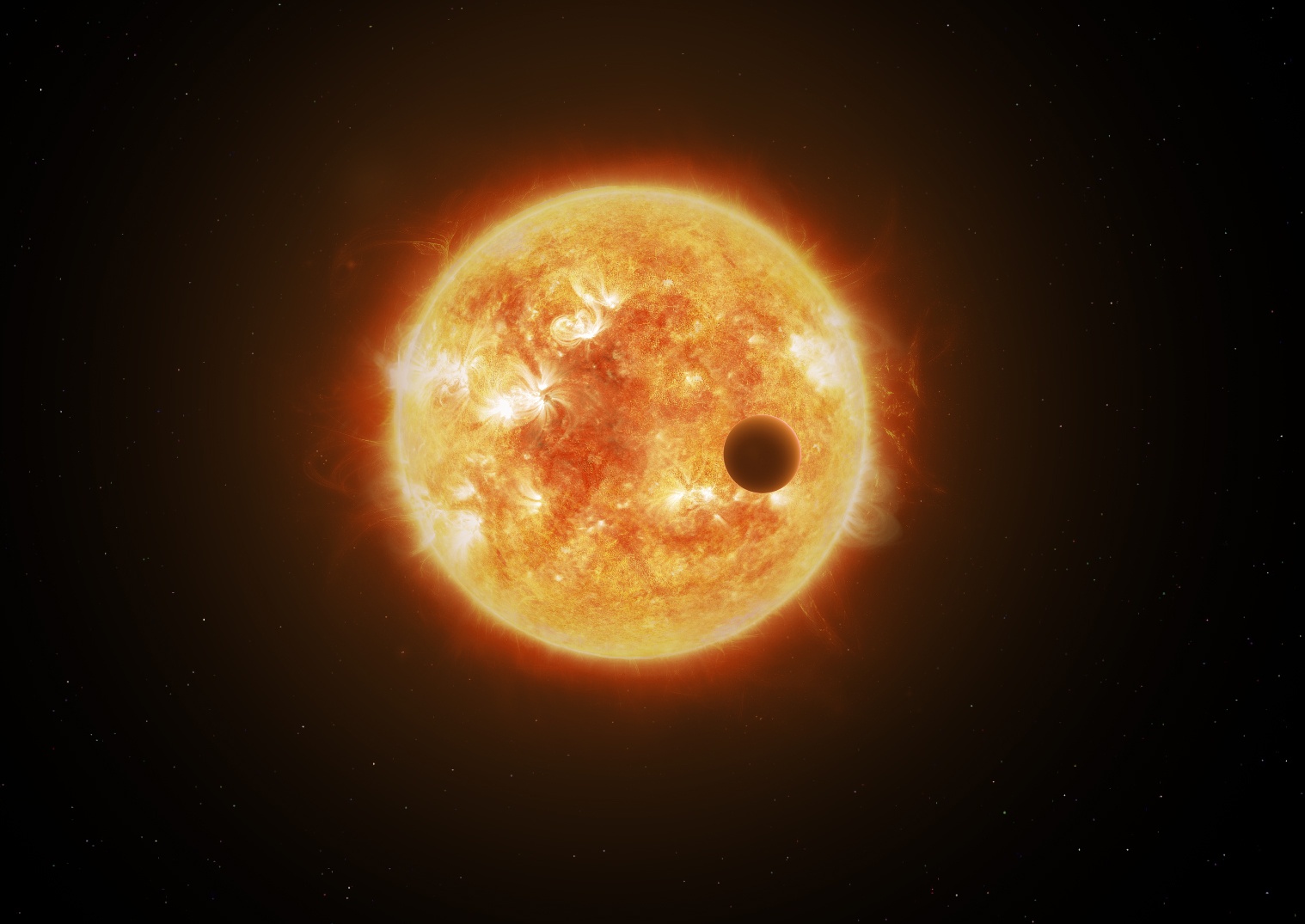
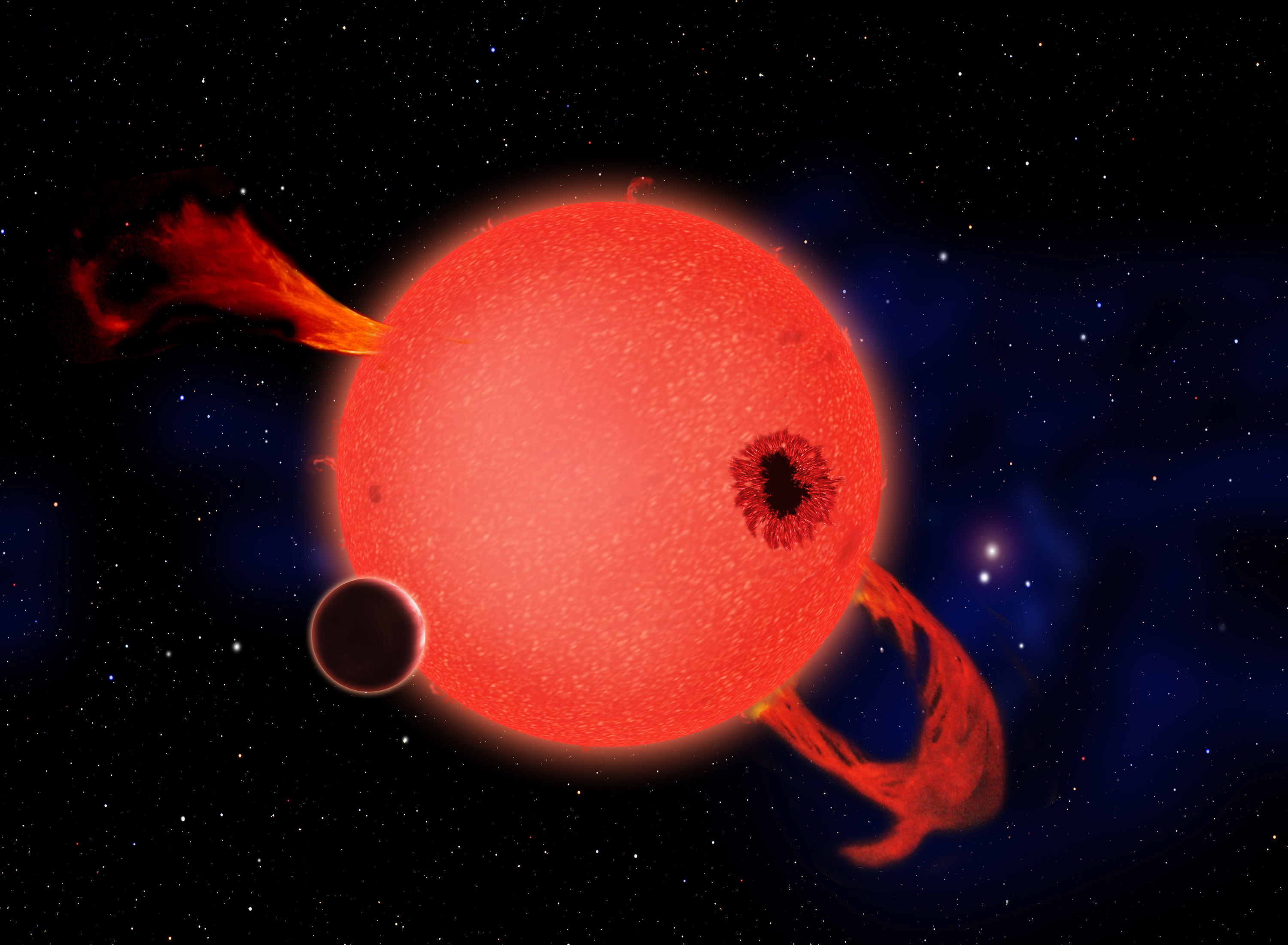
Back in 2020 astronomers observed a Red Nova, which while enormously powerful, is on the low side of energetic events in the universe. Now an astronomer has studied the event in close detail and has come to the conclusion that we have just witnessed a star destroying its own planet.
Continue reading “Astronomers Find a “Red Nova”: A Main-Sequence Star Just Eating its Planet”Astronomers are Starting to Find the Wreckage Left Over from the First Stars in the Universe
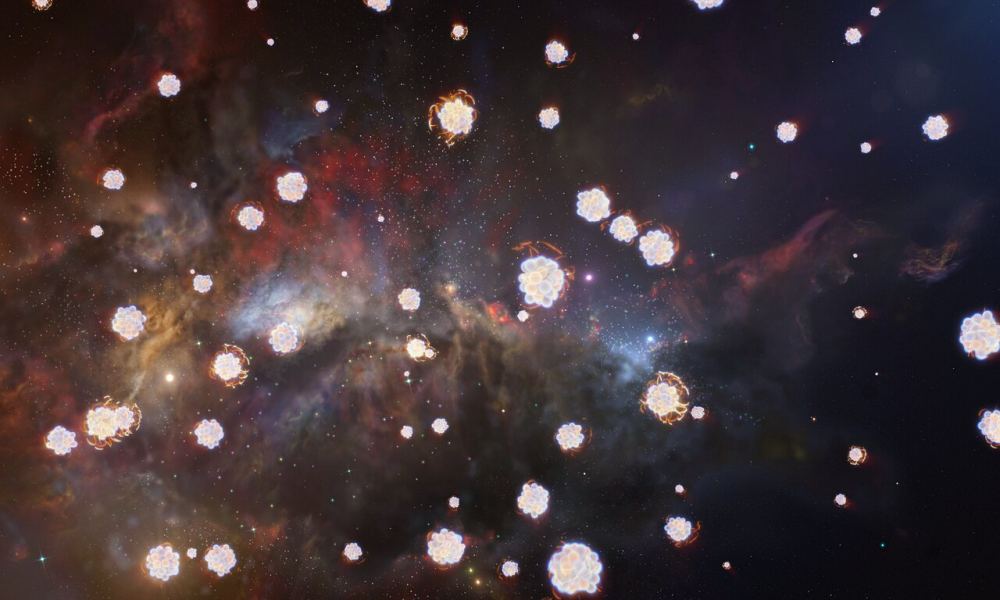

The first stars were odd ducks. Nobody’s observed them yet (although astronomers are hopeful JWST might spot them someday) but their ghosts remain. Born more than 13.5 billion years ago, they were very different from most of those we know today. These were massive monsters made mostly of hydrogen and helium. And, when they exploded as supernovae, their “starstuff” got scattered to space. Astronomers have now found the chemical remains of those stars in three distant gas clouds observed by European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope.
Continue reading “Astronomers are Starting to Find the Wreckage Left Over from the First Stars in the Universe”The Discovery of a Hot Neptune that Shouldn’t Exist
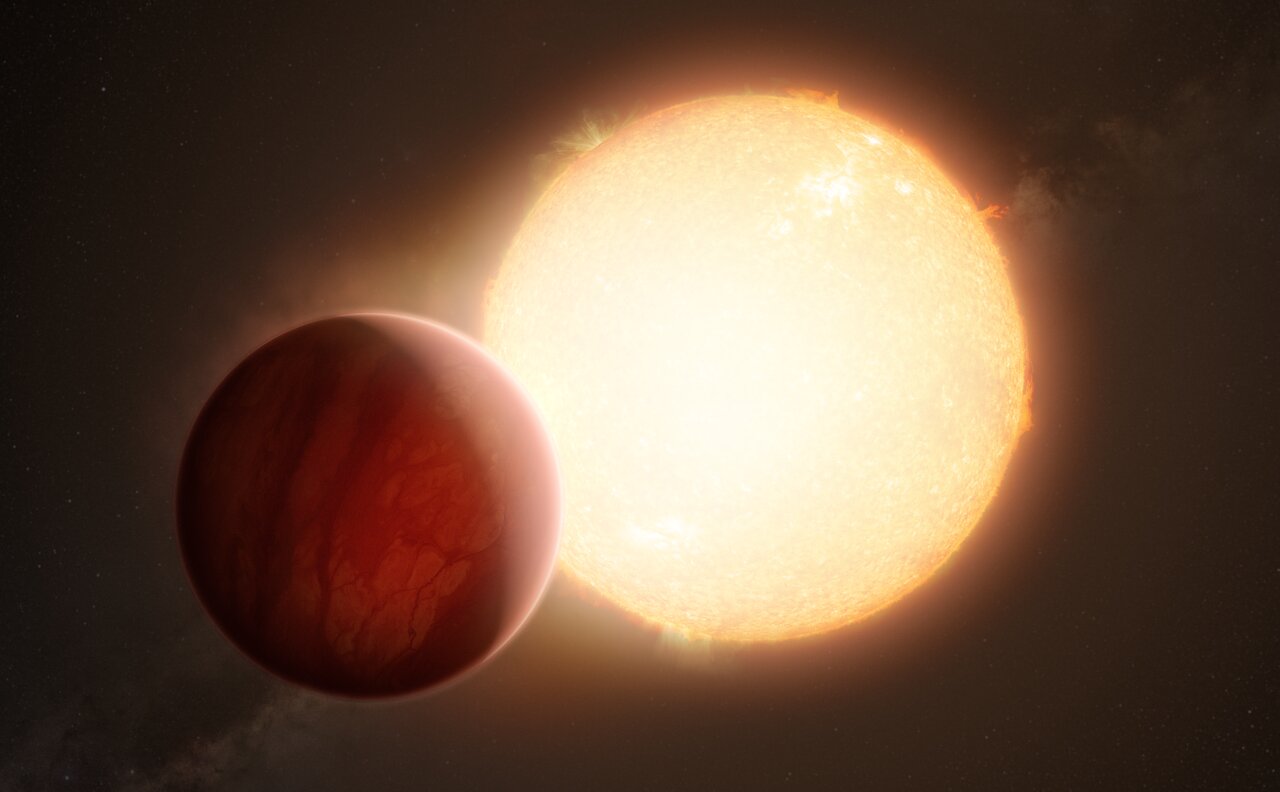

1800 light-years away, an unlikely survivor orbits an aged star. This rare planet is called a hot Neptune, and it’s one of only a small handful of hot Neptunes astronomers have found. Hot Neptunes are so close to their stars that the overpowering stellar radiation should’ve stripped away their atmospheres, leaving only a planetary core behind.
But this planet held onto its atmosphere somehow.
Continue reading “The Discovery of a Hot Neptune that Shouldn’t Exist”JWST Sees Organic Molecules Swirling Around a Newborn Star

One of the most interesting questions we can ask is, “How did life form?”. To answer it, scientists go back to look at the basic chemical building blocks of life. Those are water, carbon-based organic molecules, silicates, and others. The James Webb Space Telescope offered a peek at the gases, ice particles, and dust surrounding a newborn star and found organic molecules exist there.
Continue reading “JWST Sees Organic Molecules Swirling Around a Newborn Star”Some Elements Arrived on Earth by Surfing Supernova Shock Waves
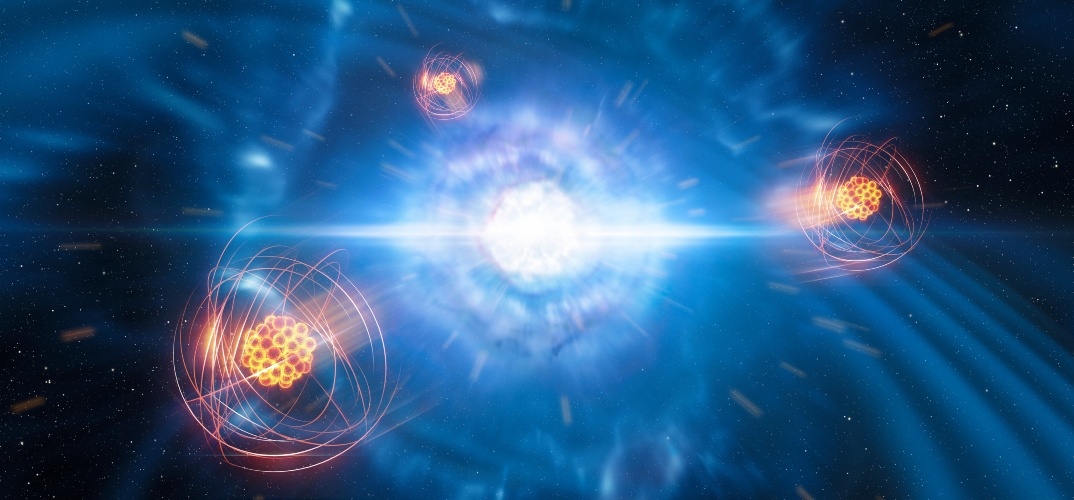

When stars die, they spread the elements they’ve created in their cores out to space. But, other objects and processes in space also create elements. Eventually, that “star stuff” scatters across the galaxy in giant debris clouds. Later on—sometimes millions of years later—it settles onto planets. What’s the missing link between element creation and deposition on some distant world?
Continue reading “Some Elements Arrived on Earth by Surfing Supernova Shock Waves”Astronomers Spot Three Interacting Systems with Twin Discs
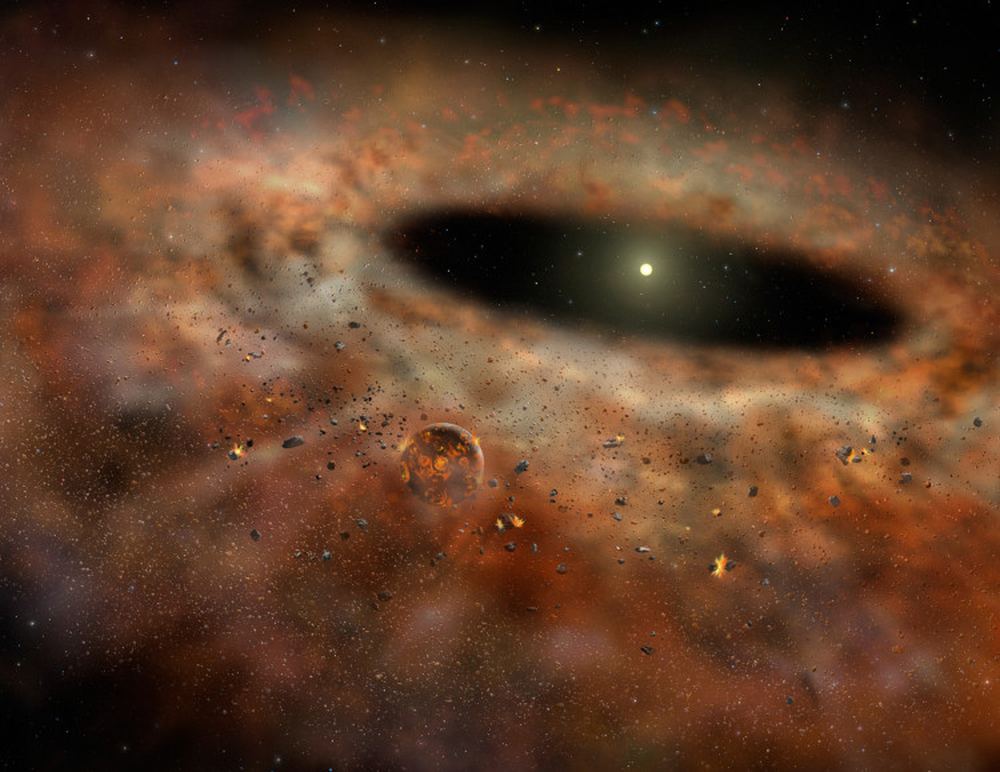

According to the most widely-accepted theory about star formation (Nebular Hypothesis), stars and planets form from huge clouds of dust and gas. These clouds undergo gravitational collapse at their center, leading to the birth of new stars, while the rest of the material forms disks around it. Over time, these disks become ring structures that accrete to form systems of planets, planetoids, asteroid belts, and Kuiper belts. For some time, astronomers have questioned how interactions between early stellar environments may affect their formation and evolution.
For instance, it has been theorized that gravitational interactions with a passing star or shock waves from a supernova might have triggered the core collapse that led to our Sun. To investigate this possibility, an international team of astronomers observed three interacting twin disc systems using the Spectro-Polarimetric High-contrast Exoplanet REsearch (SPHERE) on the ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT). Their findings show that due to their dense stellar environments, gravitational encounters between early-stage star systems play a significant role in their evolution.
Continue reading “Astronomers Spot Three Interacting Systems with Twin Discs”The Latest JWST Image Shows a Star in the Earliest Stage of Formation
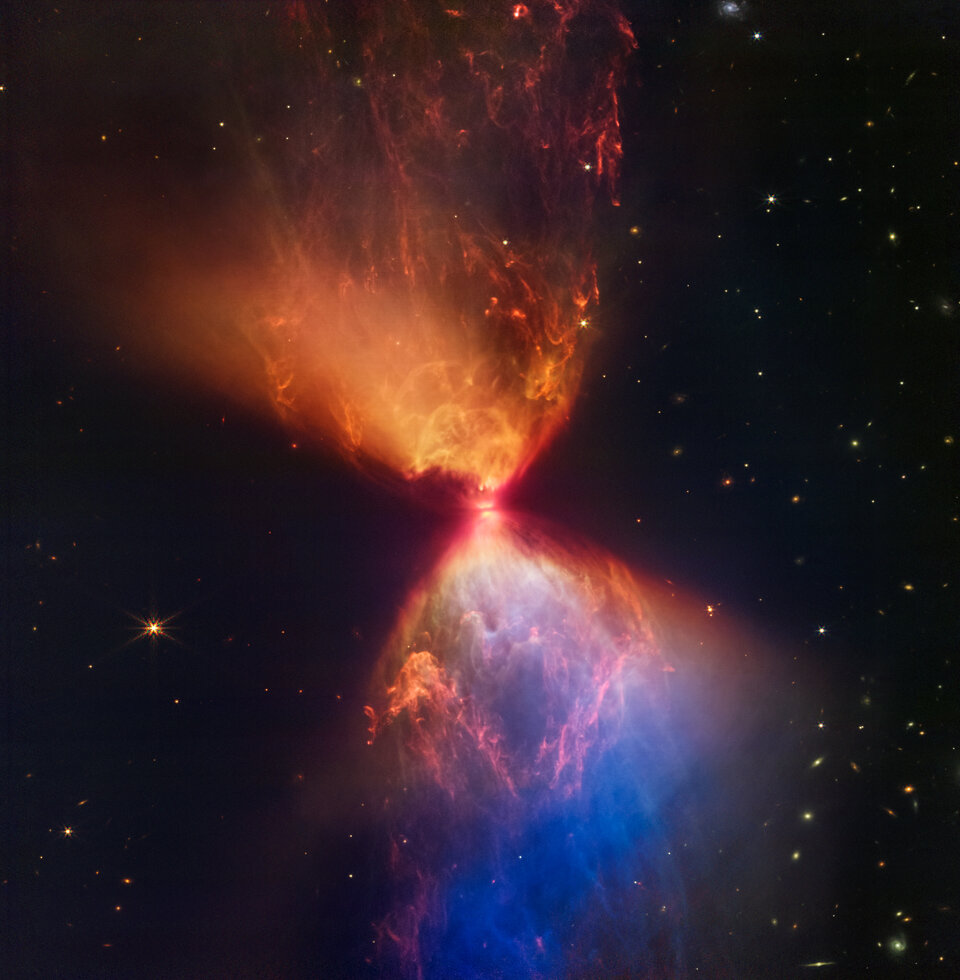

What’s the most exciting thing about the James Webb Space Telescope? The stunning images? The completion of its torturous path from concept to launch?
Or is it because it provides such compelling visual evidence of objects and processes long theorized about but difficult to observe?
Continue reading “The Latest JWST Image Shows a Star in the Earliest Stage of Formation”Hubble saw the Same Supernova at Three Different Times Thanks to Gravitational Lensing
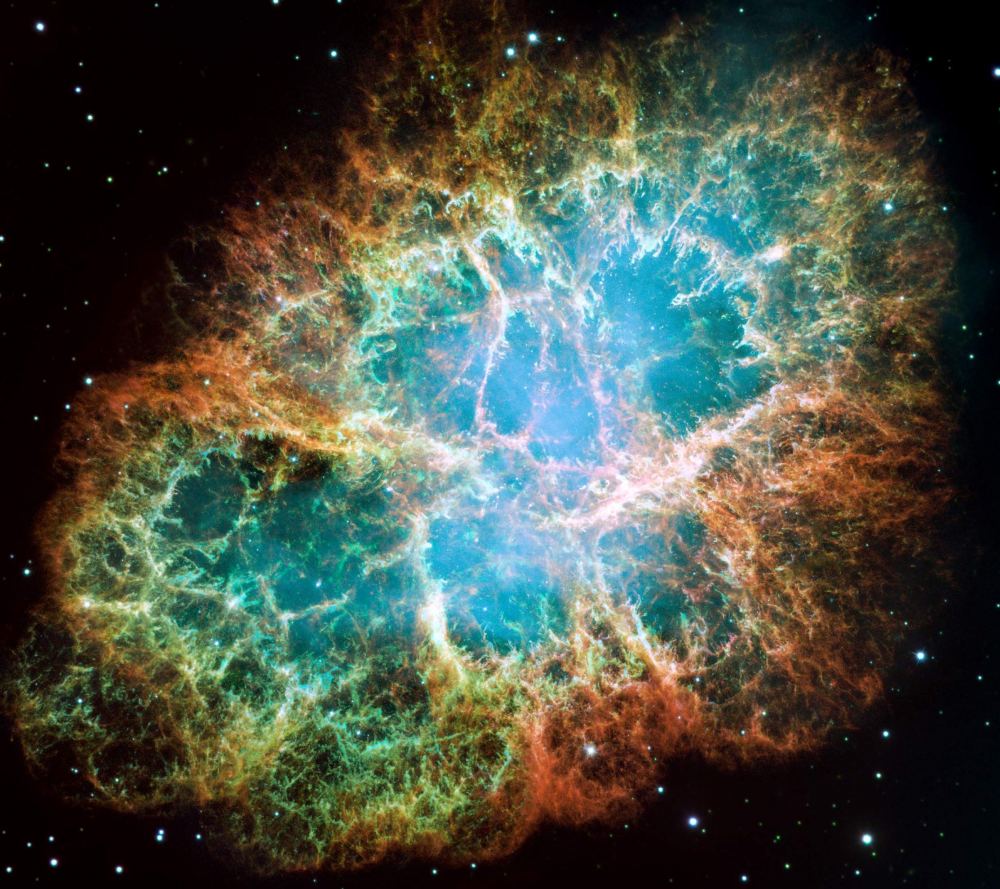

As cosmic events go, supernova explosions epitomize the saying, “Live fast, die young, and leave a good-looking corpse.” They’re the deaths of stars so massive that they tear through their fuel in a short time. Then, they explode and create gorgeous scenes of stellar destruction. These seminal events enrich the universe with chemical elements for new generations of stars and planets.
Continue reading “Hubble saw the Same Supernova at Three Different Times Thanks to Gravitational Lensing”It’s Tough to Find Evidence of Stars Eating Planets
Tragically sometimes stars engulf their own planets. While most stars are able to quickly cover up the evidence for their crime, a new study by astronomers has revealed that in some cases the evidence can linger for up to two billion years.
Continue reading “It’s Tough to Find Evidence of Stars Eating Planets”ESO Finds the Ghostly Image of a Dying Star

Astronomical images never cease to delight, and the European Southern Observatory’s image of the Vela nebula is no exception.
Continue reading “ESO Finds the Ghostly Image of a Dying Star”