The EmDrive is a hypothetical rocket that proponents claim can generate thrust with no exhaust. This would violate all known physics. In 2016, a team at NASA’s Eagleworks lab claimed to measure thrust from an EmDrive device, the news of which caused quite a stir. The latest attempt to replicate the shocking results has resulted in a simple answer: the Eagleworks measurement was from heating of the engine mount, not any new physics.
Continue reading “In a Comprehensive new Test, the EmDrive Fails to Generate any Thrust”China’s Super-Heavy Lift Rocket Will Carry 100 Tons to the Moon
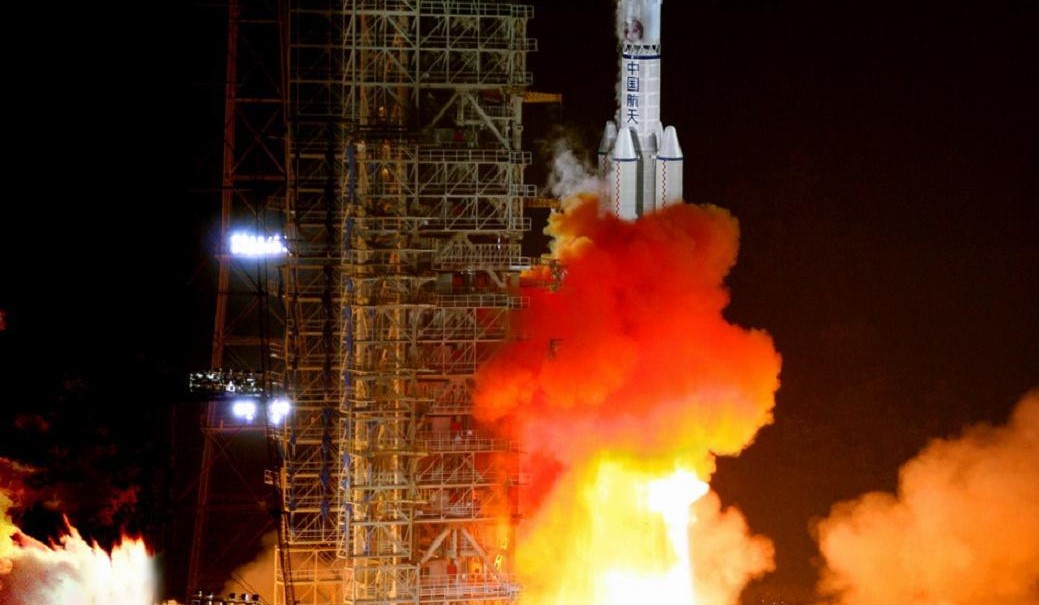
China’s proposed next-generation rocket reached the final stage of feasibility studies this month. The planned launch vehicle, known as the Long March-9, will be capable of sending 100 tons to the Moon, and could see its first launch as early as 2030.
Announced in 2018, the Long March-9 will play a key role in China’s long-term space ambitions. If all goes as planned, its first payload is likely to be a Martian sample return mission, and it would support China’s Lunar ambitions as well. Another proposed use for the super-heavy lift vehicle is to build an experimental space-based solar power station, although plans for that project are still very tentative.
Continue reading “China’s Super-Heavy Lift Rocket Will Carry 100 Tons to the Moon”ESA is Working on its own Reusable Booster Stage
It’s an exciting time for space exploration! All around the world, national space agencies are sending missions to deep-space and preparing to send astronauts to orbit and the Moon. At the same time, the commercial aerospace industry (NewSpace) is expanding to include more launch providers and service new markets. These developments are adding up and making space more cost-effective and accessible.
One such development of the emergence of reusable rockets, which are reducing the cost of individuals launches down considerably. Earlier this month (Dec. 15th), the European Space Agency (ESA) contracted with aerospace giant ArianeGroup to develop a reusable rocket. As part of the Themis Program, the ESA will use this rocket to evaluate the technologies involved for potential use on future European launch vehicles.
Continue reading “ESA is Working on its own Reusable Booster Stage”RocketLab Recovers a First-Stage Booster for the First Time: “Return to Sender”
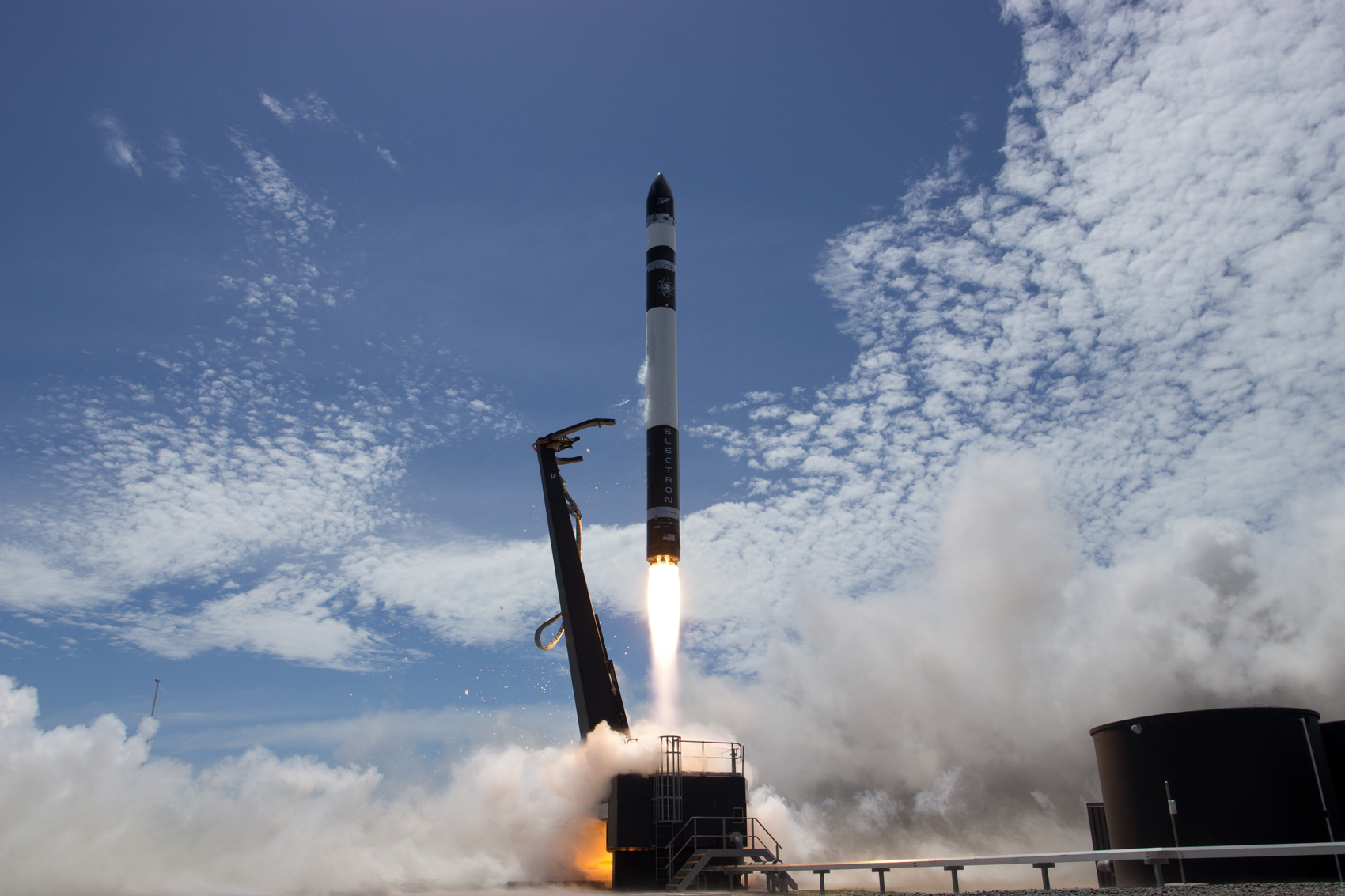
In recent years, one of the most impressive developments for space exploration has been the rise of the commercial space industry (aka. NewSpace). Beyond fulfilling contracts with space agencies like NASA to provide commercial and crewed launch services, private aerospace companies are also fostering innovation that is helping to reduce the cost of sending payloads to space.
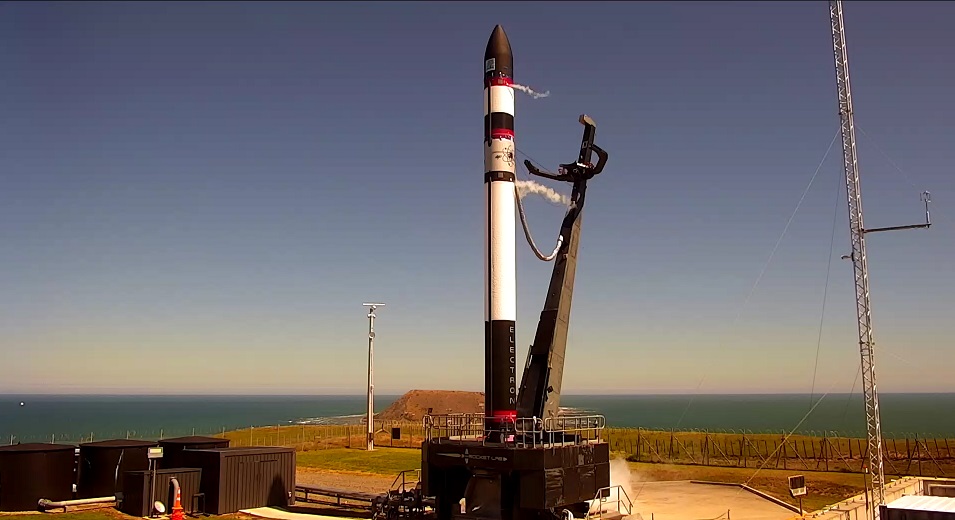
Take RocketLab, the US/NZ-based small satellite launch company that has broken new ground with its Electron rocket. In a further bid to reduce the costs of individual launches, RocketLab announced last year that it would begin recovering and reusing the spent boosters of its rockets. Recently, the company took a big step by successfully retrieving the first stage of an Electron after it delivered a payload to orbit.
Continue reading “RocketLab Recovers a First-Stage Booster for the First Time: “Return to Sender””SpaceX Starship Passes Static Fire Test With Three Raptor Engines, Finally Gets Nose Cone!
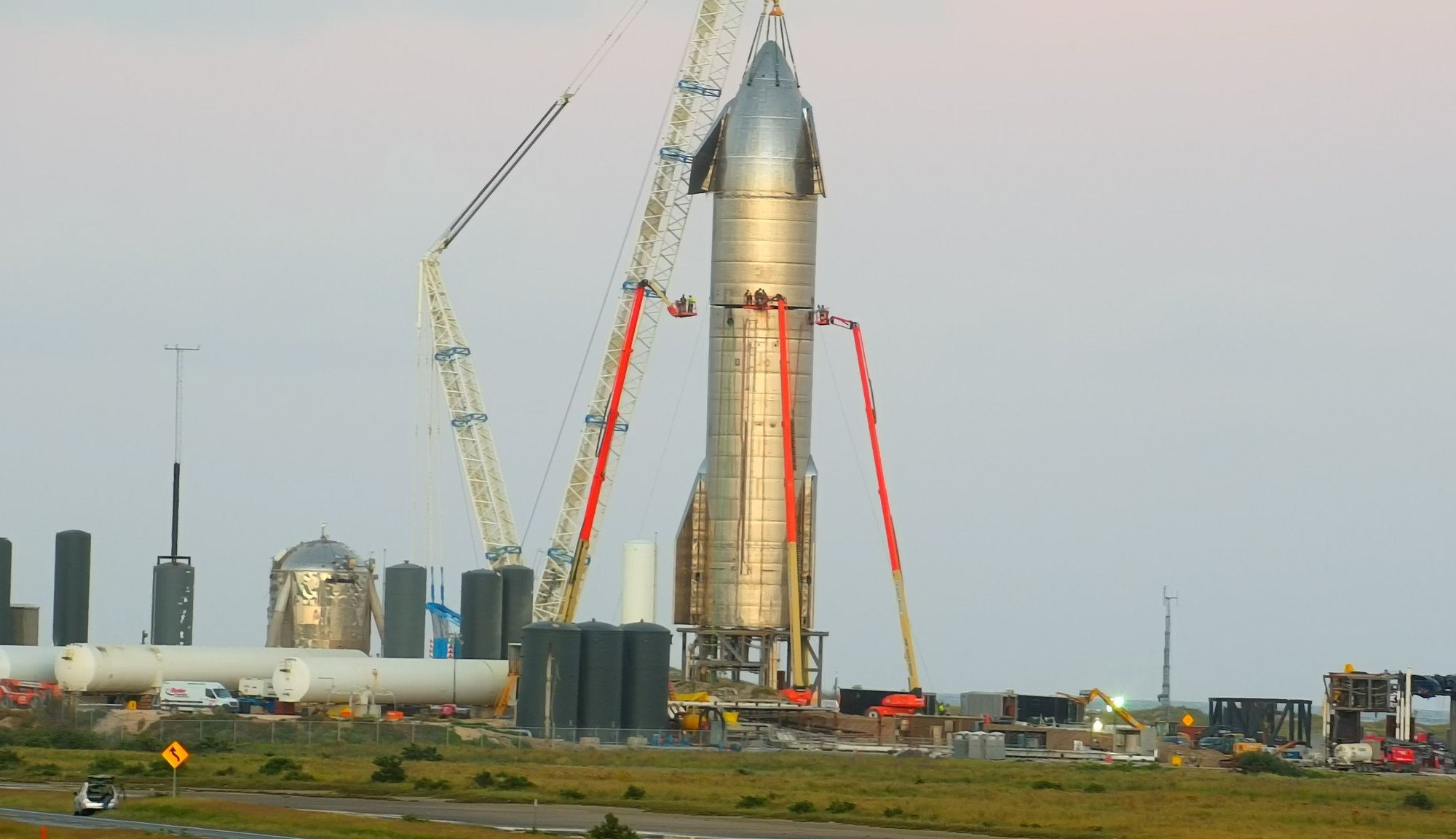
It’s beginning to look like SpaceX will attempt to make the 15 km (9.3 mi) hop test before Christmas! After two successful 150 m (~500 ft) hops with the SN5 and SN6 prototypes, engineers at SpaceX’s Boca Chica launch facility in South Texas rolled out the SN8 – the first Starship prototype to have three Raptor engines. But before the SN8 can conduct a high-altitude test flight, the engineers needed to run a static fire test.
This test is crucial to ensuring that the Starship‘s interior plumbing can handle its cryogenic propellants, and is the last milestone before the Starship can conduct a high-altitude flight. On the evening of Tuesday, October 20th, that’s exactly what they did! At 3:13 AM local time (01:13 AM PDT; 04:13 AM EDT), the SN8 fired up its three Raptor engines and kept firing them for several seconds straight.
Continue reading “SpaceX Starship Passes Static Fire Test With Three Raptor Engines, Finally Gets Nose Cone!”Electron Rocket’s 13th Launch Failed, Destroying its Satellite Payload
This past weekend (June 5th), the California and New Zealand-based aerospace company Rocket Lab suffered a terrible accident. During the 13th launch of their Electron rocket, an anomaly caused the second stage of the rocket to explode in midair. Luckily, there were no injuries, but the explosion did claim the mission payload, which consisted of satellites and commercial payloads for three different companies.
Continue reading “Electron Rocket’s 13th Launch Failed, Destroying its Satellite Payload”Virgin Orbit’s first air-launched rocket launch fails
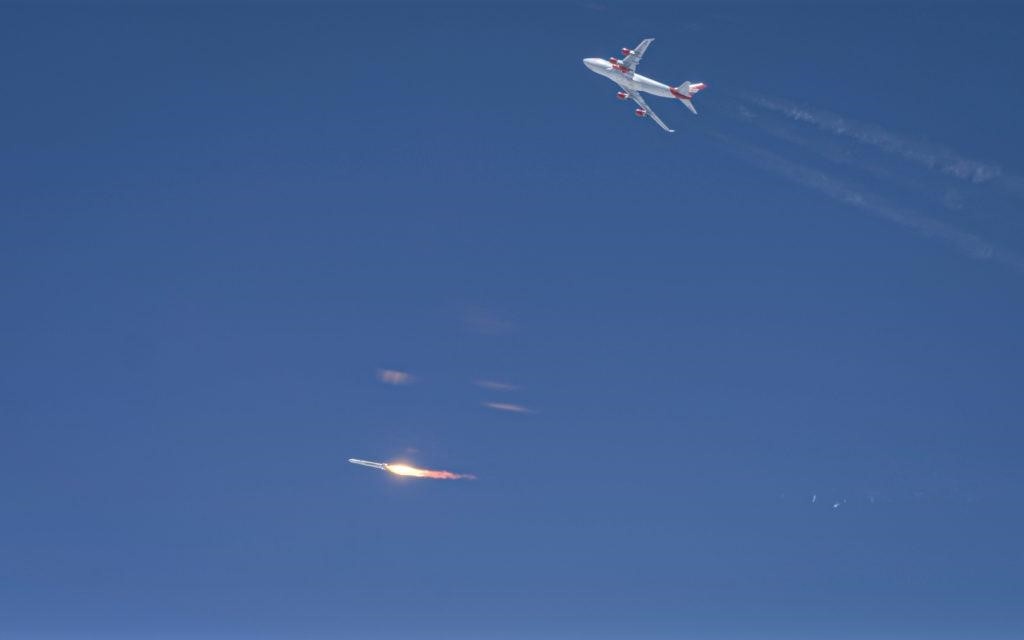
The reason people use the aphorism “it isn’t rocket science” is because rocket science is hard. Virgin Orbit, a spin-off of Virgin Galactic that focuses on small satellite launches, proved that with a recent test of its LauncherOne rocket.
Continue reading “Virgin Orbit’s first air-launched rocket launch fails”This Rocket Engine’s Thrust Chamber was 3D-printed and Only has Three Parts
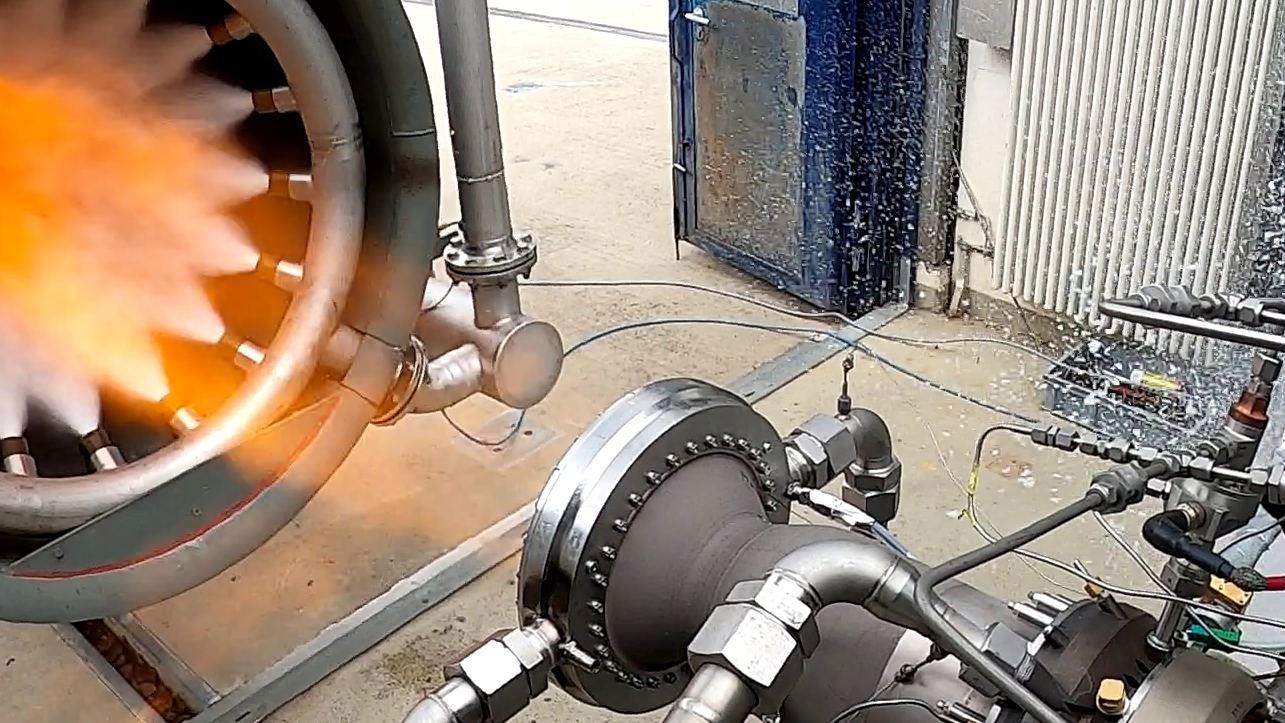

This week, European engineers hot-fire tested a fully 3D-printed thrust chamber that could one day power the upper stages for rockets. The chamber has just three parts, and was constructed using additive layer manufacturing, another name for 3D printing.
This hot-fire test lasted 30 seconds and was carried out on May 26, 2020 at the DLR German Aerospace Center’s Lampoldshausen testing facility. The European Space Agency said that additional tests are planned for next week.
Continue reading “This Rocket Engine’s Thrust Chamber was 3D-printed and Only has Three Parts”If Rockets were Transparent: Video Shows You How Rockets Use up Their Propellant
I always remember hearing the comparison of how the Space Shuttle’s main engines would drain an average family swimming pool in under 25 seconds. Or that the Saturn V used the equivalent of 763 elephants of fuel. But just how much fuel does a rocket burn during its ascent to orbit? As you might expect, the amount varies with different rockets.
A great new video provides an incredible visual of how much fuel is burned by four different rockets, from launch to the various stage separations by showing what rocket launches would look like if the rockets were completely transparent.
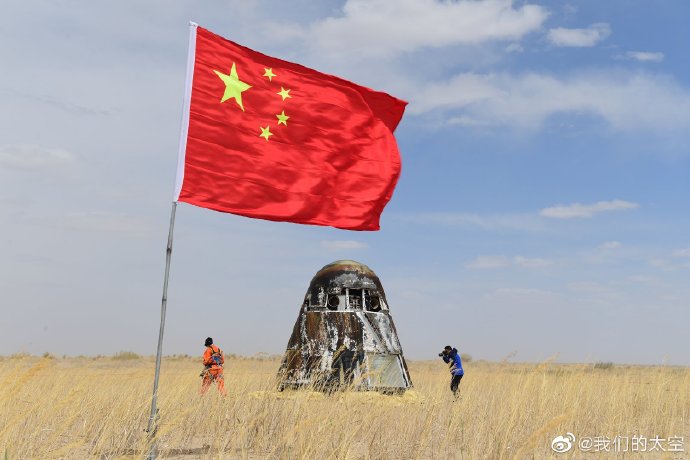
Continue reading “If Rockets were Transparent: Video Shows You How Rockets Use up Their Propellant”China’s New Crew Capsule Just Landed, and so Did Parts of their New Rocket!
China’s next-generation crewed spacecraft, which will replace the venerable Shenzou spacecraft in the coming years, recently returned to Earth after spending almost three days in space. The purpose of this mission was to test the deep space capabilities of the spacecraft that will be sending Chinese astronauts (taikonauts) to orbit, to the Moon, and beyond in the coming years.
In addition, this mission also saw China’s new Long March 5B (CZ-5B) heavy-lift rocket launch a payload to space for the first time. This rocket is the latest installment in the Long March family and will be vital to the creation of the third and largest Chinese space station. These two milestones have brought China a step closer to becoming a full-fledged superpower in space.
Continue reading “China’s New Crew Capsule Just Landed, and so Did Parts of their New Rocket!”