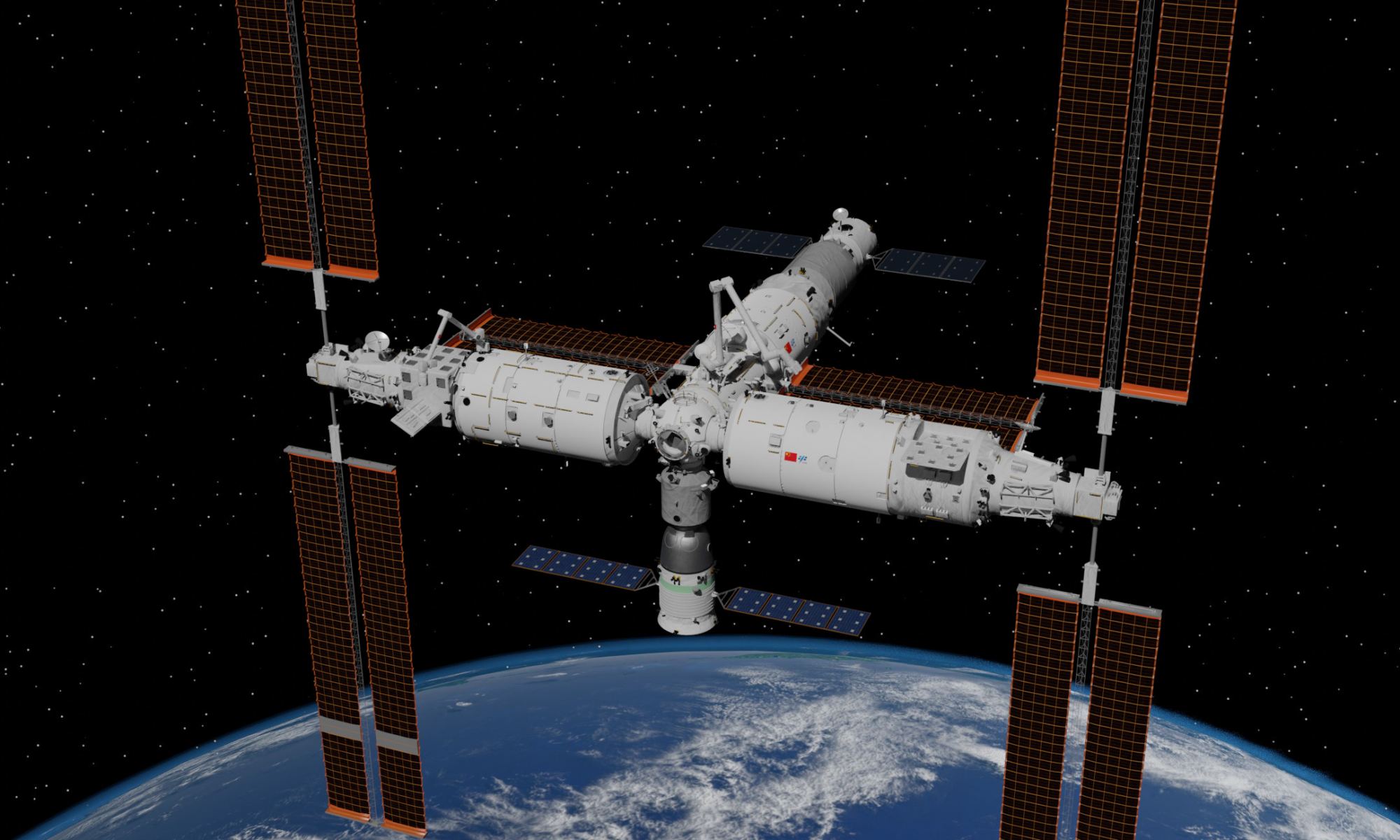
China continues to establish new milestones in space. In recent years, the China National Space Agency (CNSA) has begun assembling the Long March-9 (CZ-9), the country’s first reusable super-heavy launch vehicle; the Tianwen-1 mission became the first Chinese orbiter, lander, and rover combination to reach Mars, and their super-secret spaceplane completed its second flight (after spending 276 days in space). China has also made significant progress in terms of human spaceflight, especially where the Tiangong space station is concerned.
Earlier this week (Tues. May 30th), the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) took another major step when it launched the country’s sixteenth mission (Shenzou-16) to Tiangong atop a Long March-2F (CZ-2F) rocket. This mission delivered three taikonauts to the space station and performed the most complicated docking maneuver ever attempted. The mission highlights included successfully testing the Shenzou’s upgraded instruments and systems, which allowed the spacecraft to autonomously rendezvous with the station under less-than-ideal conditions.
Continue reading “Three New Astronauts Arrive at the Chinese Space Station, Including the Country's First Civilian”