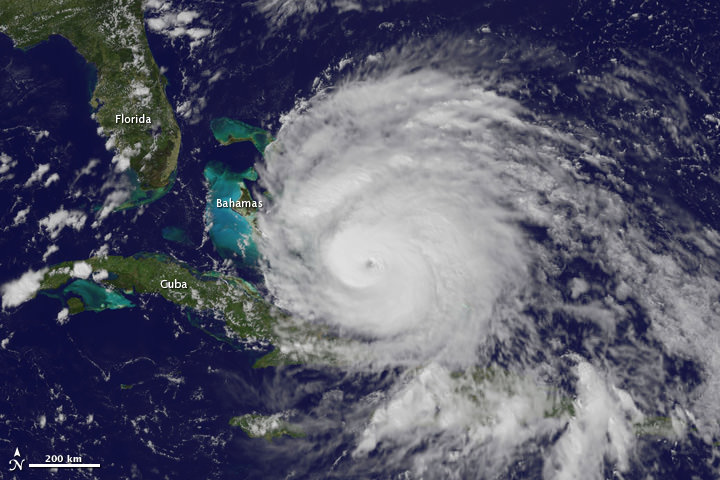
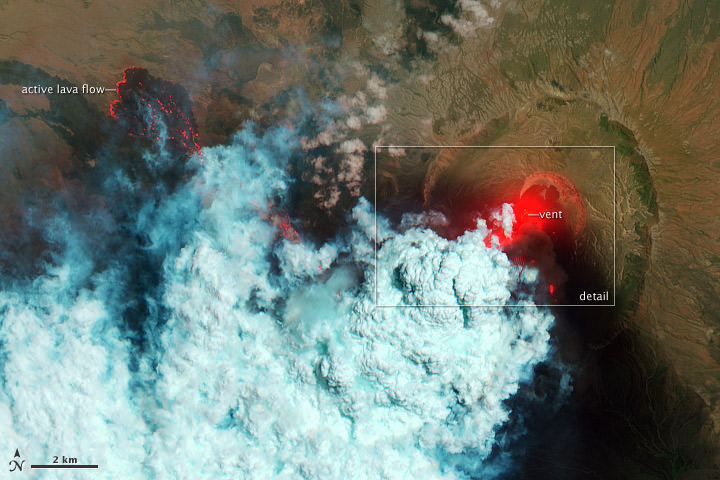
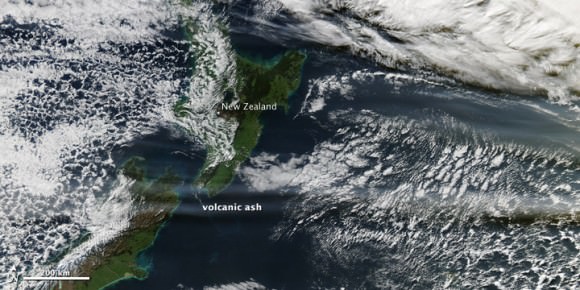
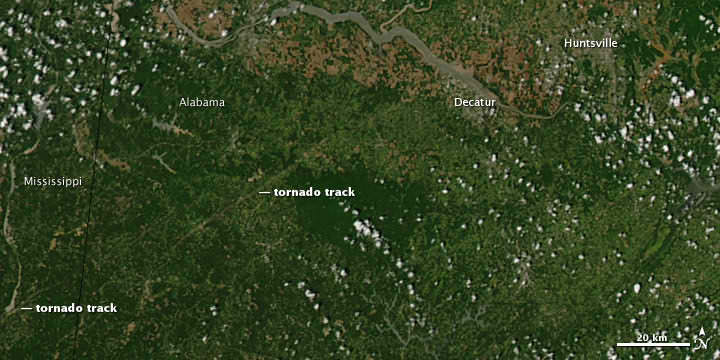
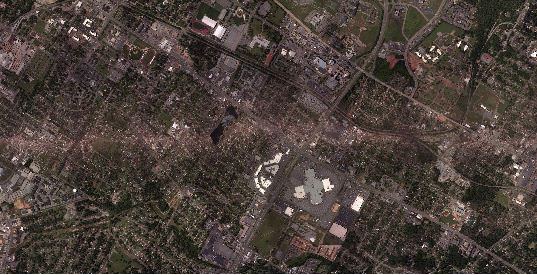
Here are several different views of Hurricane Irene: from 230 miles above the Earth, cameras on the International Space Station captured several views of powerful Hurricane Irene as it churned over the Bahamas at 3:10 p.m. EDT on August 24, 2011. Irene is moving to the northwest as a Category 3 hurricane, packing winds of 120 miles an hour. Irene is expected to strengthen to a Category 4 storm as it heads toward the Outer Banks of North Carolina, the Eastern Seaboard and the middle Atlantic and New England states.
See more from other satellites, below:
[/caption]
This view of Irene was taken by the GOES satellite at 2:55 p.m. Eastern Daylight Time on August 24, 2011. Irene now has a distinct eye and the clouds spiraling around the center are becoming more compact. The image also shows how large Irene has become, measuring several hundred kilometers across.
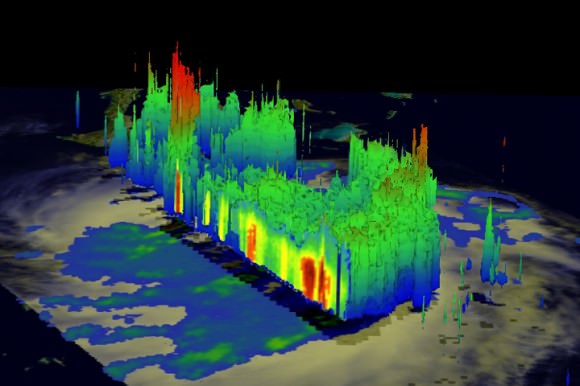
This image was taken on August 22, but is a really nifty, three-dimensional view of the precipitation from Irene, as seen by the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission. It reveals an area of deep convection (shown in red) near the storm’s center where precipitation-sized particles are being carried aloft. These tall towers are associated with strong thunderstorms responsible for the area of intense rain near the center of Irene seen in the previous image. They can be a precursor to strengthening as they indicate areas within a storm where vast amounts of heat are being released. This heating, known as latent heating, is what is drives a storm’s circulation and intensification.
Here’s the latest view of Irene from WeatherBug:

As of 8 a.m. EDT on August 25, Hurricane Irene was located near 25.5 N and 76.5 W, or 65 miles east-southeast of Nassau, Bahamas. This places it about 670 miles south of Cape Hatteras, N.C. Irene`s top sustained winds remain at 115 mph, and is moving to the northwest at 13 mph.
Sources: NASA Multimedia,