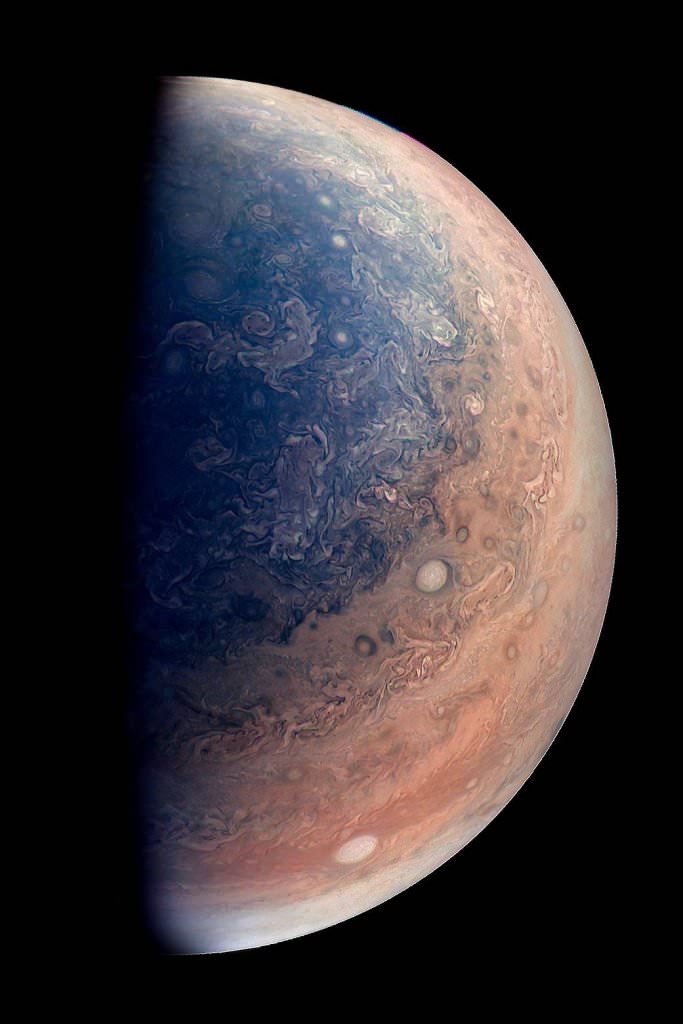
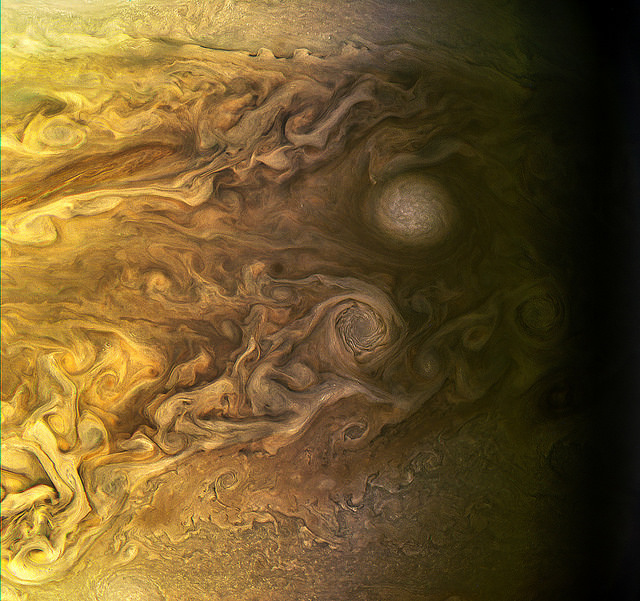
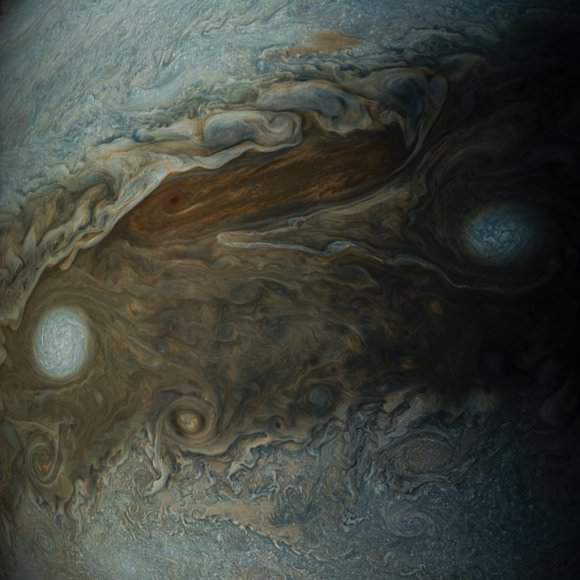
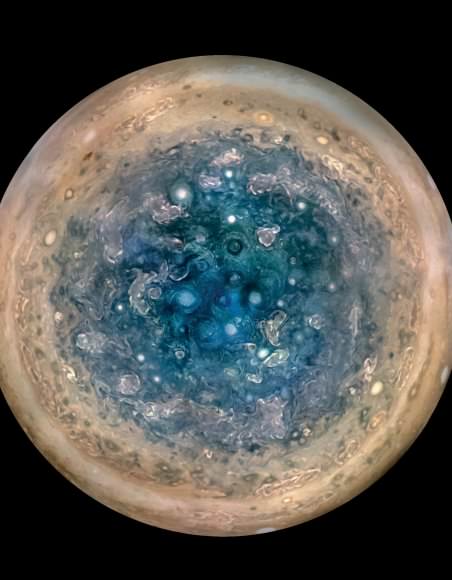
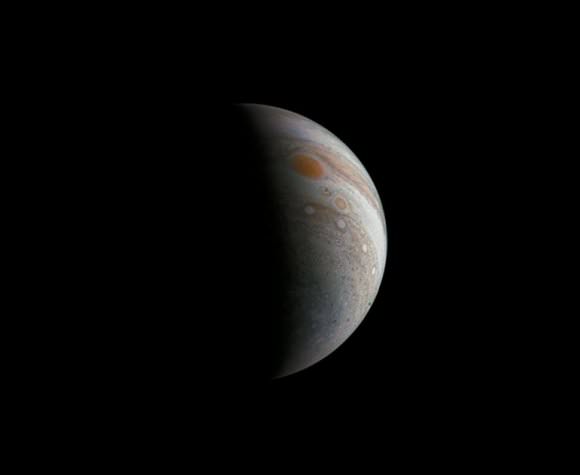
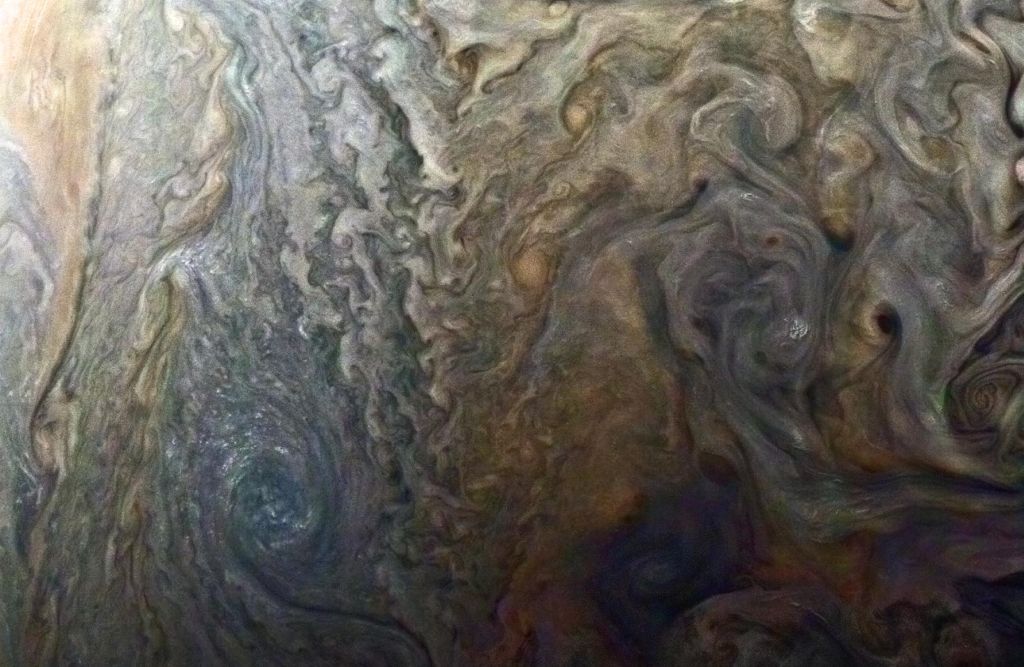
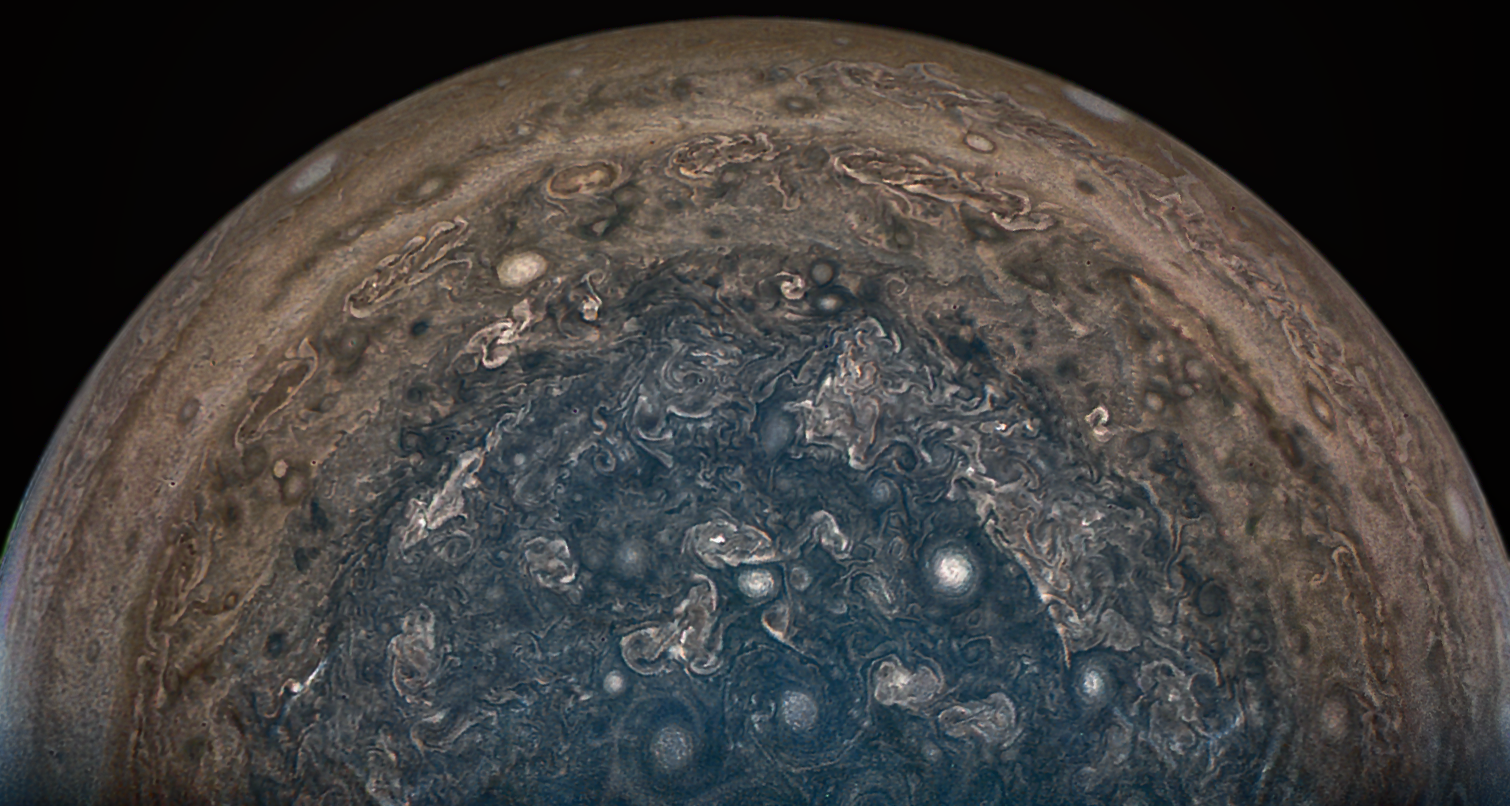
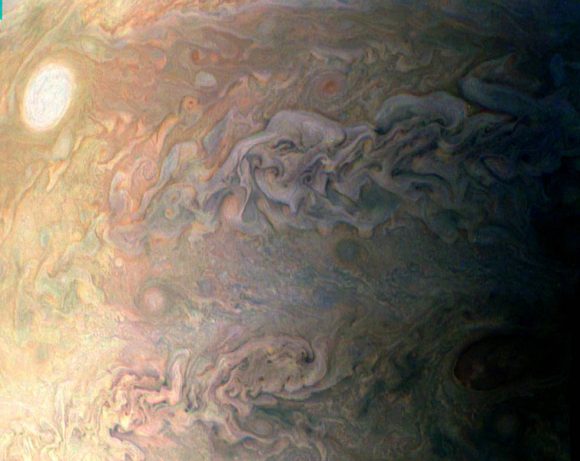
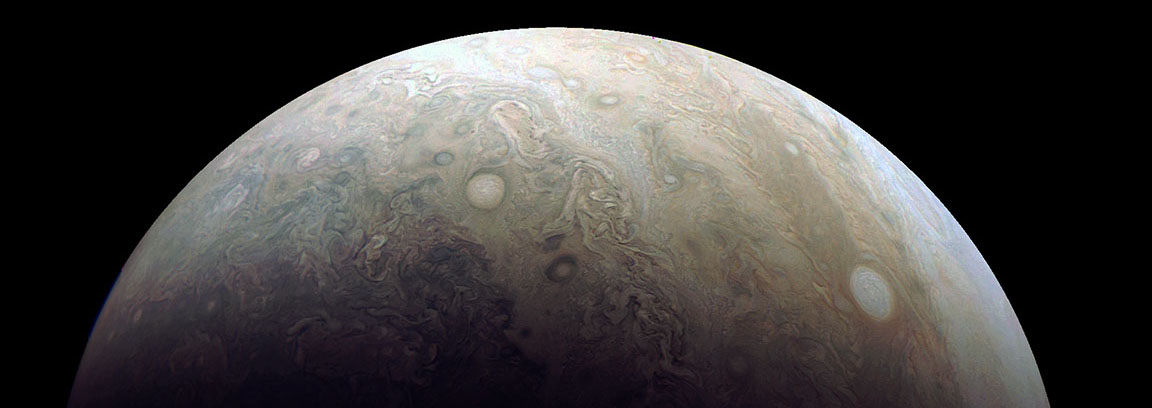
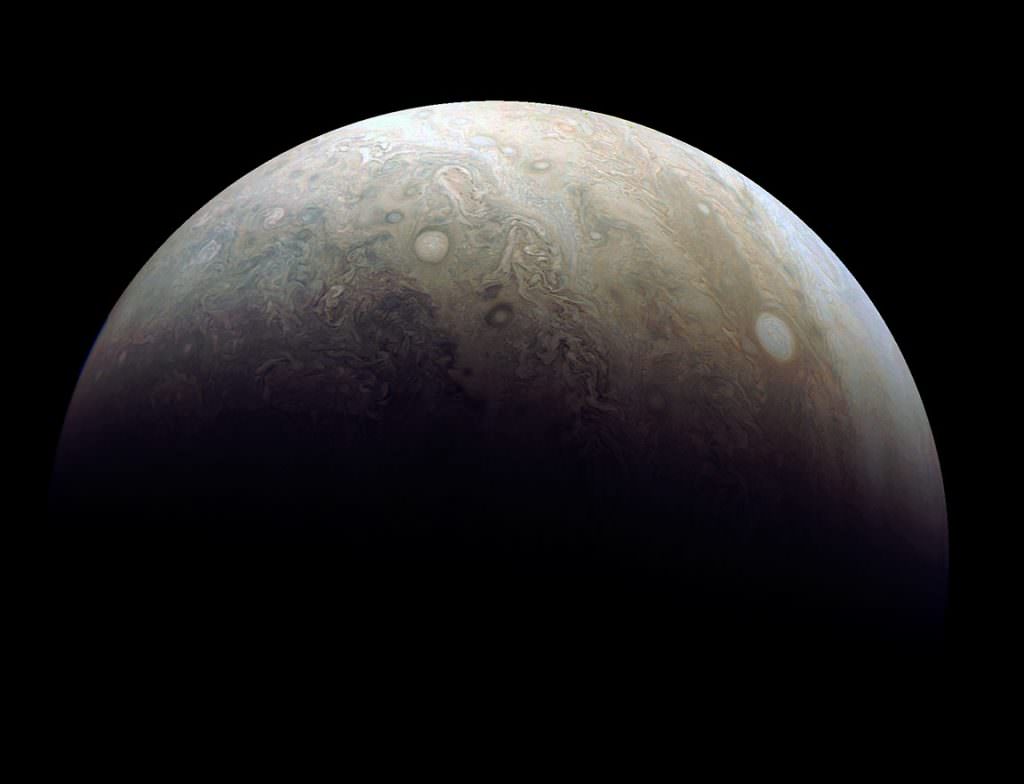
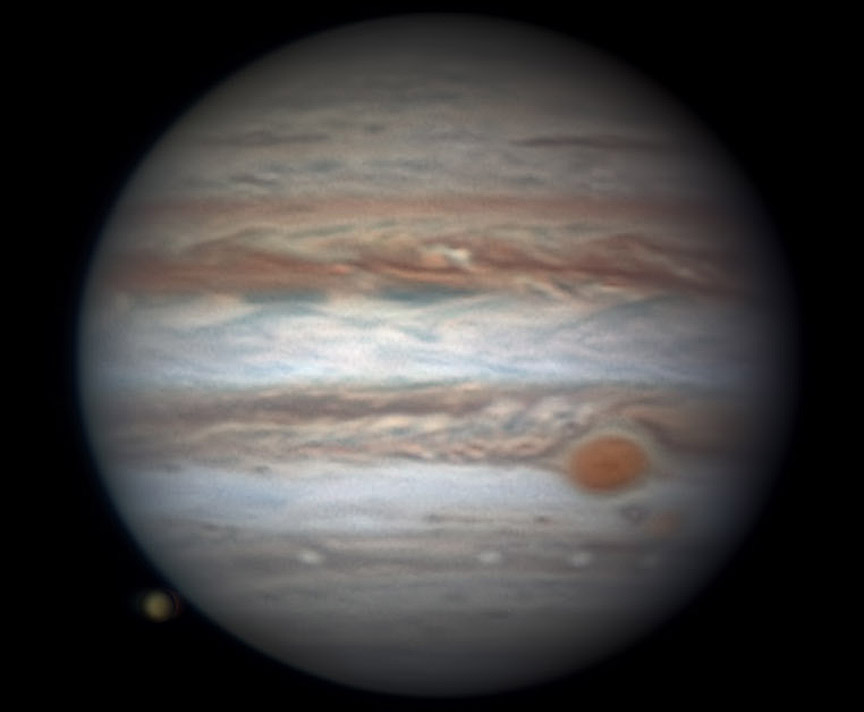
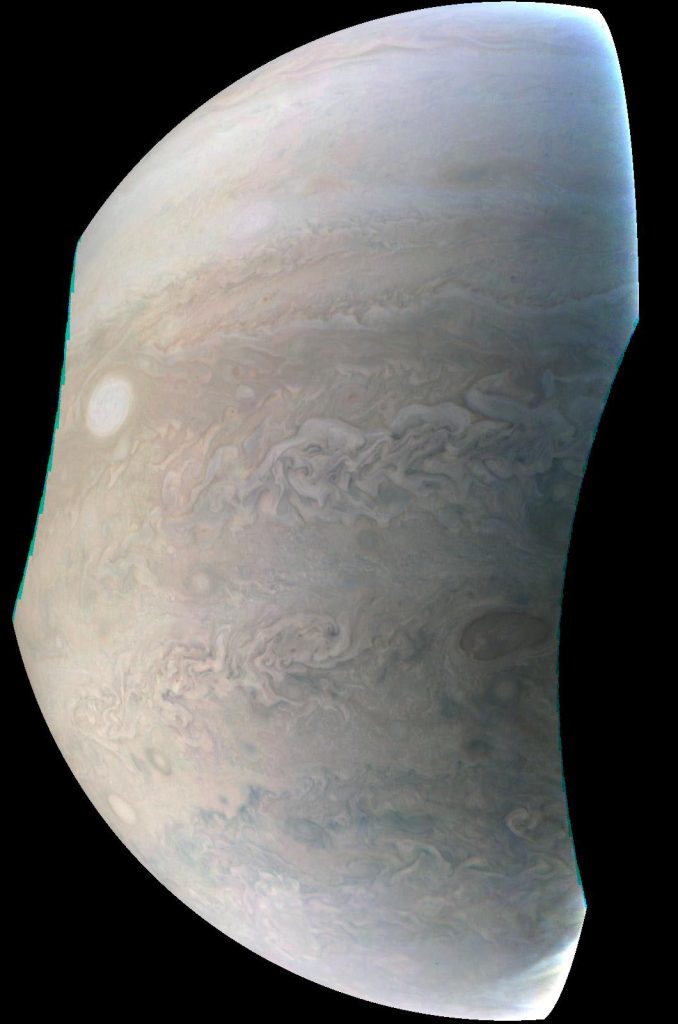
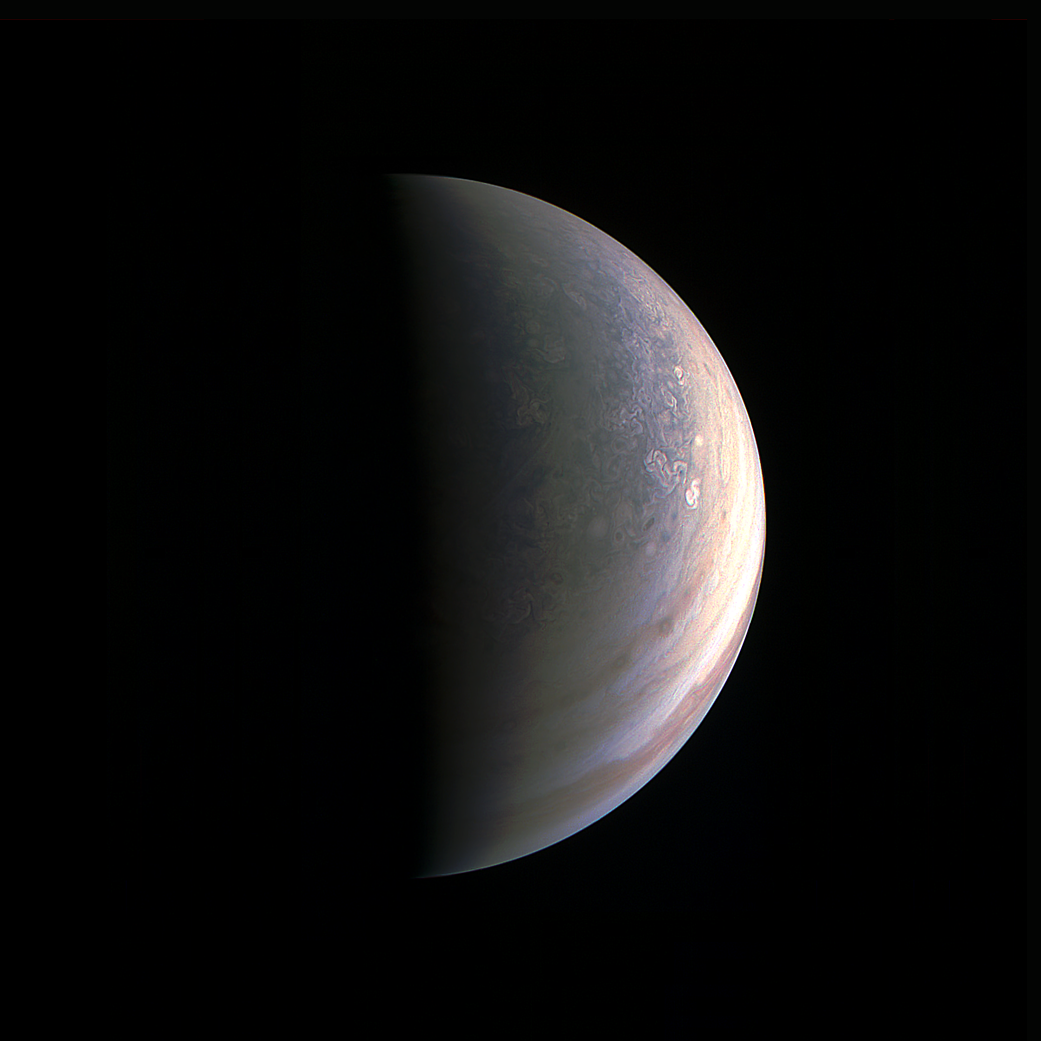
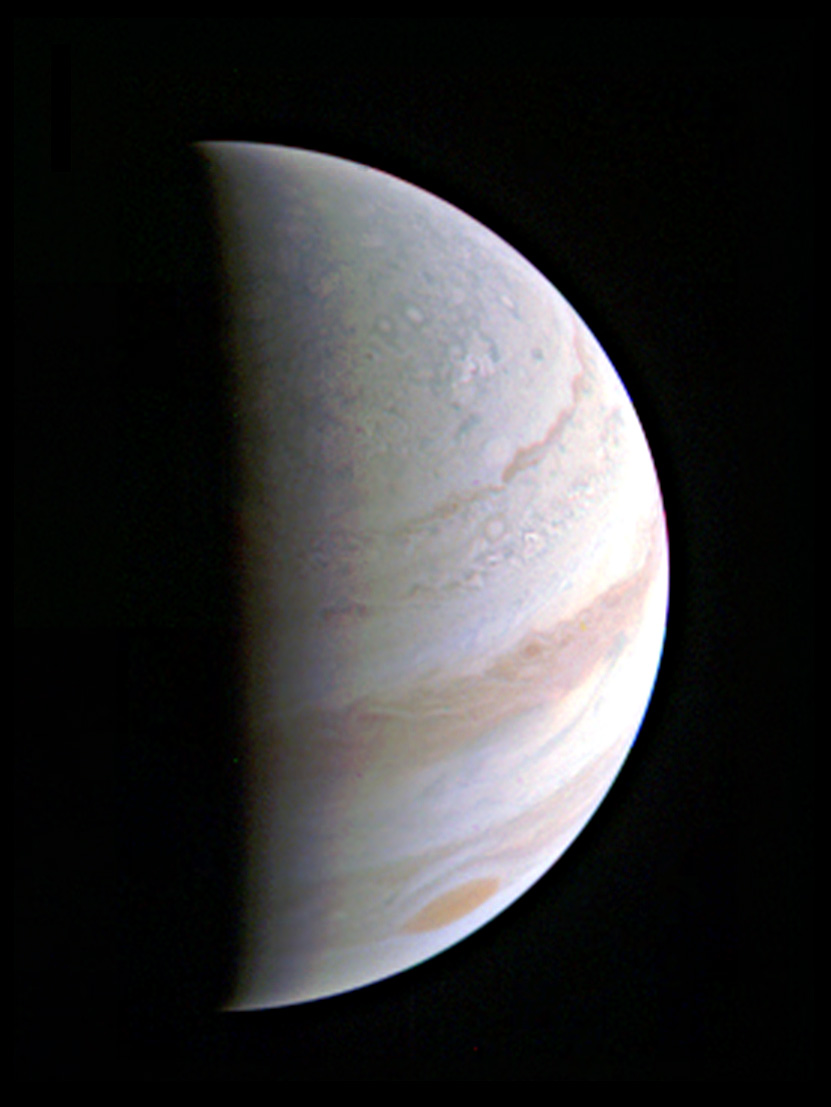
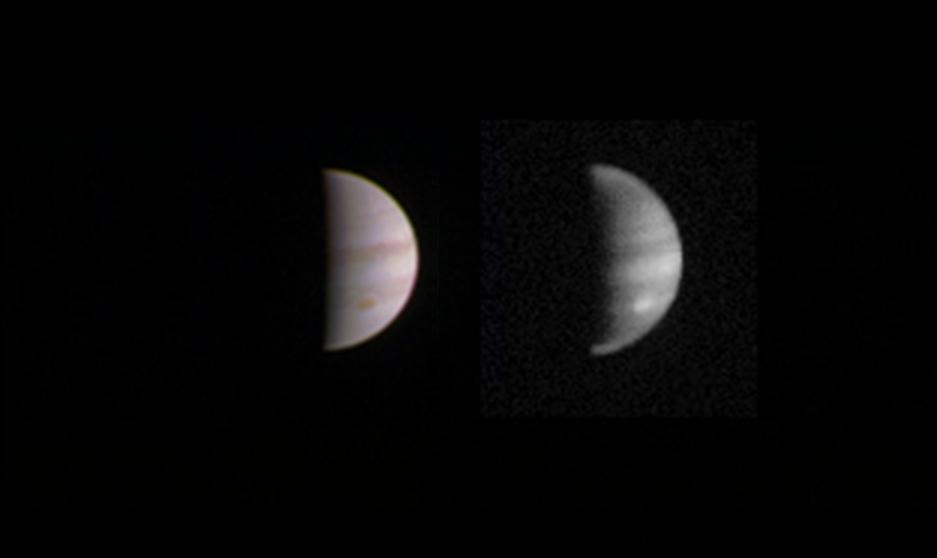
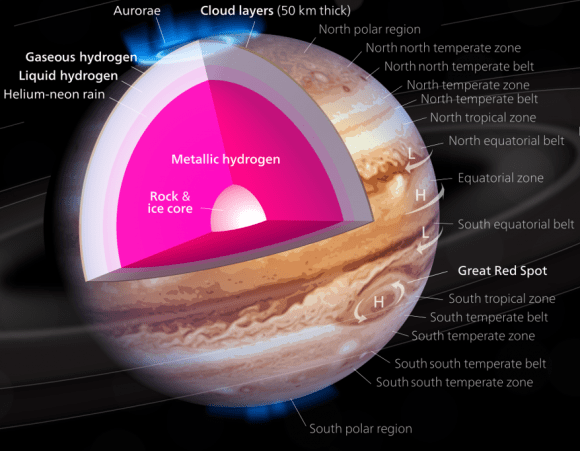
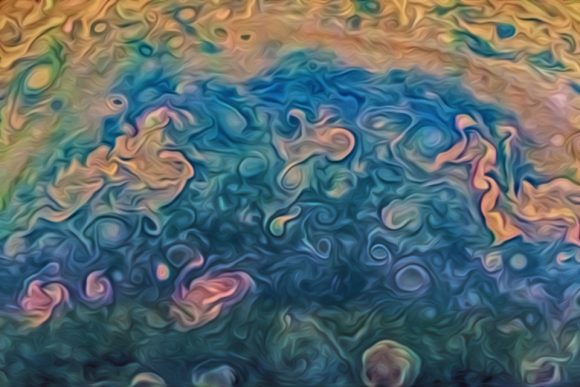
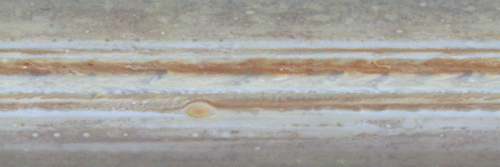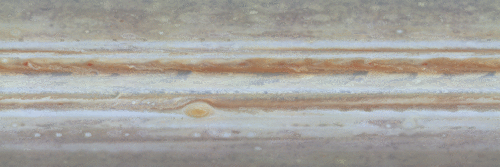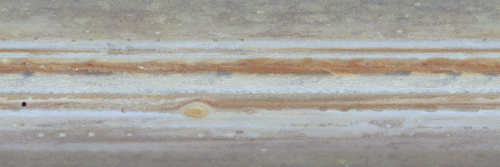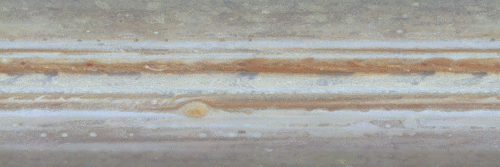
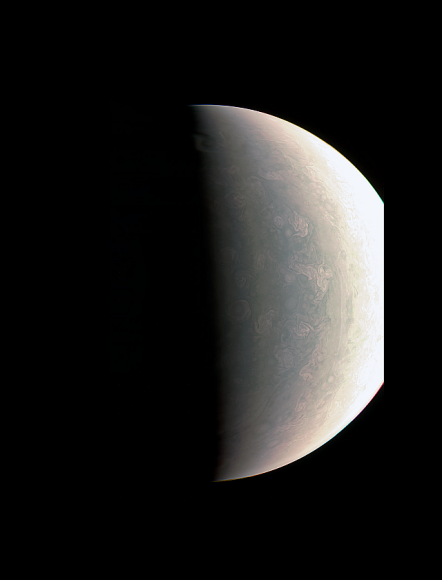
The original plans for the Juno mission to Jupiter didn’t include a color camera. You don’t need color images when the mission’s main goals are to map Jupiter’s magnetic and gravity fields, determine the planet’s internal composition, and explore the magnetosphere.
But a camera was added to the manifest, and the incredible images from the JunoCam have been grabbing the spotlight.
As an instrument where students and the public can choose the targets, JunoCam is a “public outreach” camera, meant to educate and captivate everyday people.
“The whole endeavor of JunoCam was to get the public to participate in a meaningful way,” said Candy Hansen, Juno co-investigator at the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, speaking at a press conference last week to showcase Juno’s science and images.
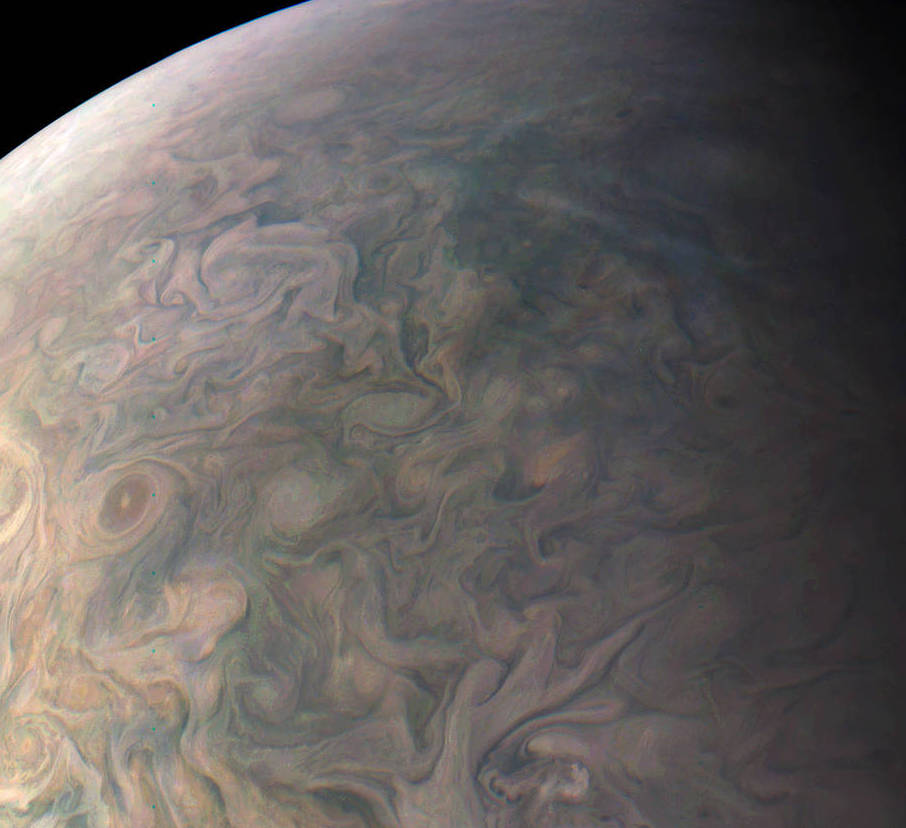
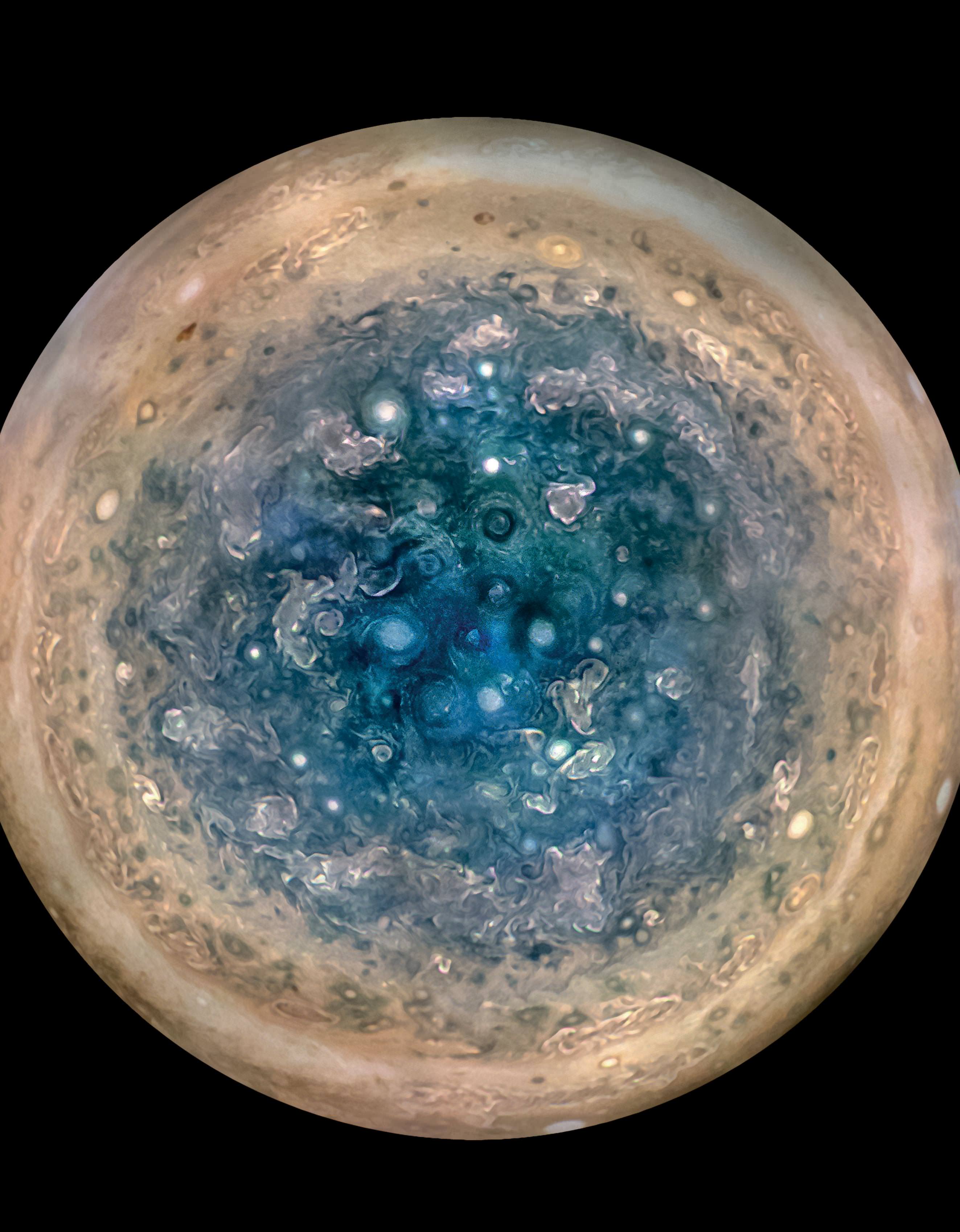
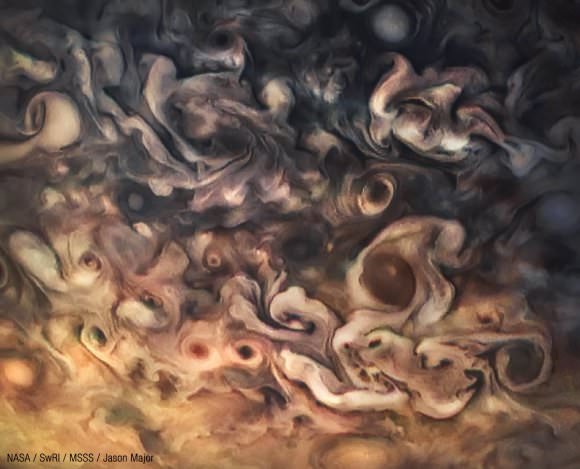
And participate they have. Hundreds of ‘amateur’ image processing enthusiasts have been processing raw data from the JunoCam, turning them into stunning images, many reminiscent of a swirling Van Gogh ‘starry night’ or a cloudscape by Monet.

“The contributions of the amateurs are essential,” Hansen said. “I cannot overstate how important the contributions are. We don’t have a way to plan our data without the contributions of the amateur astronomers. We don’t have a big image processing team, so we are completely relying on the help of our citizen scientists.”

Click on this image to have access to a 125 Megapixel upscaled print portrait.
Featured here are images processed by Seán Doran, Sophia Nasr, Kevin Gill and Jason Major. Like hundreds of others around the world, they anxiously await for data to arrive to Earth, where it is uploaded to the public Juno website. Then they set to work to turn the data into images.
“What I find the most phenomenal of all is that this takes real work,” Hansen said. “When you download a JunoCam image and process it, it’s not something you do in five minutes. The pictures that we get that people upload back onto our site, they’ve invested hours and hours of their own time, and then generously returned that to us.”
This video shows Juno’s trajectory from Perijove 6, and is based on work by Gerald Eichstädt, compiled and edited by Seán Doran. “This is real imagery projected along orbit trajectory,” Doran explained on Twitter.
Many of the images are shared on social media, but you can see the entire gallery of processed JunoCam images here. The Planetary Society also has a wonderful gallery of images processed by people around the world.

NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI /MSSS/Kevin M. Gill.

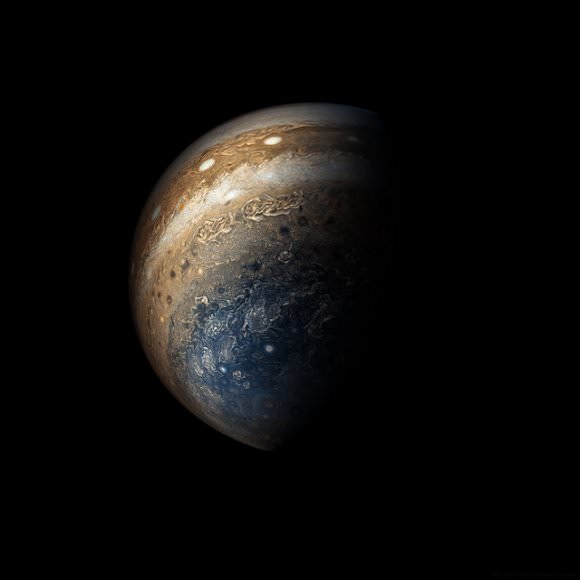
NASA / SwRI / MSSS / Gerald Eichstädt / Seán Doran.
JunoCam was built by Malin Space Science Systems, which has cameras on previous missions like the Curiosity Mars Rover, the Mars Global Surveyor and the Mars Color Imager on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. To withstand the harsh radiation environment at Jupiter, the camera required special protection and a reinforced lens.
Whenever new images arrive, many of us feel exactly like editing enthusiast Björn Jónsson:
I never expected I'd ever say this but: The latest @NASAJuno images of Jupiter are the most spectacular images of Jupiter I've ever seen. pic.twitter.com/7HawZ9RSwe
— Björn Jónsson (@bjorn_jons) May 25, 2017
Even the science team has expressed their amazement at these images.
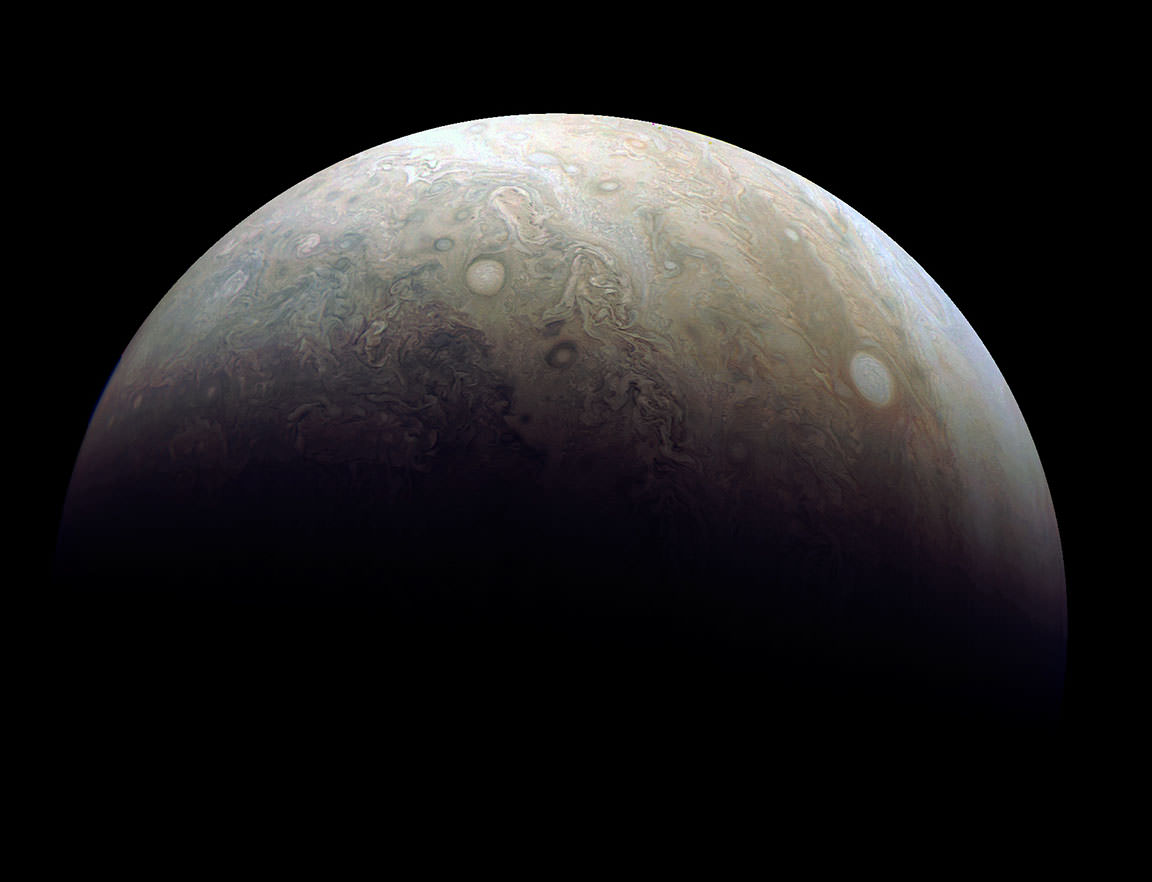
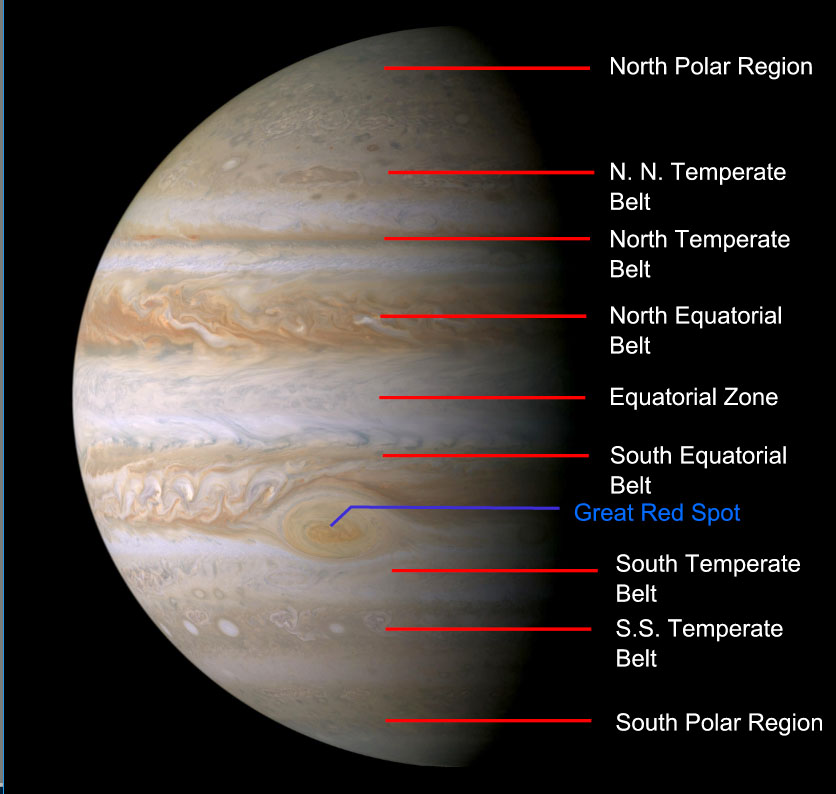
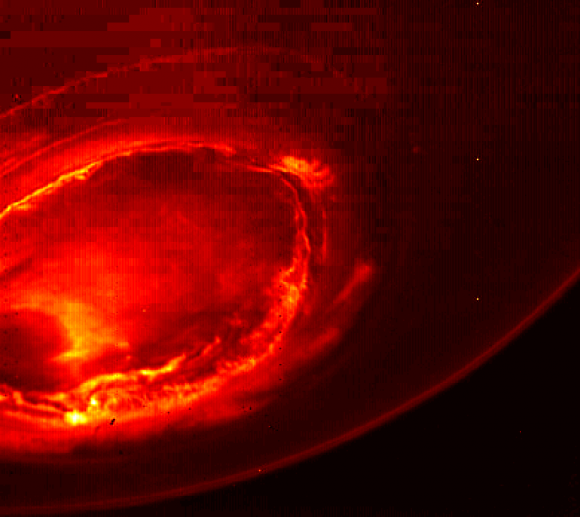
“Jupiter looks different than what we expected,” said Scott Bolton, Juno’s principal investigator at the Southwest Research Institute. “Jupiter from the poles doesn’t look anything like it does from the equator. And the fact the north and south pole don’t look like each other, makes us wonder if the storms are stable, if they going to stay that way for years and years like the the Great Red Spot. Only time will tell us what is true.”
Read our article about the science findings from Juno.

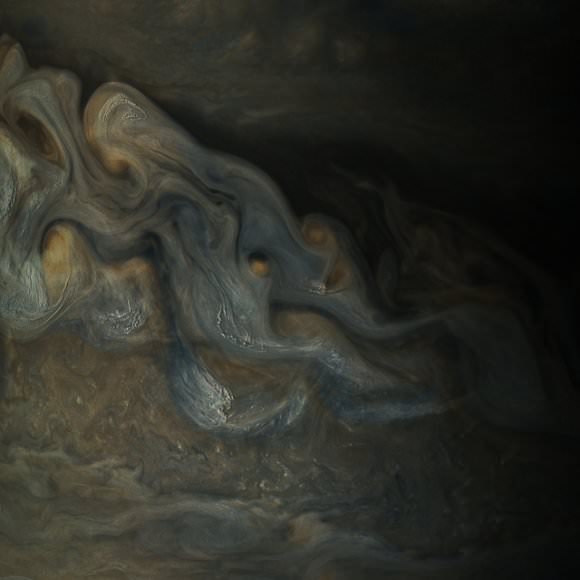
NASA / SwRI / MSSS / Gerald Eichstädt / Seán Doran.
Part of what makes these images so stunning is that Juno is closer to Jupiter than any previous spacecraft.
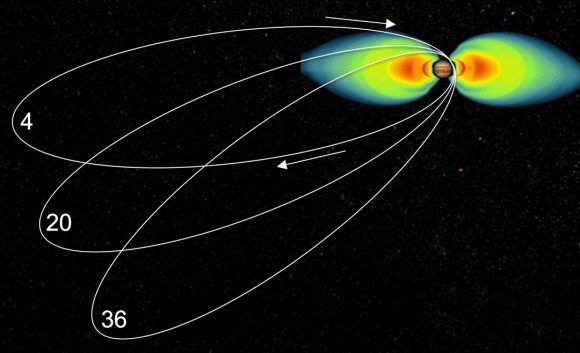
“Juno has an elliptical orbit that brings it between the inner edges of Jupiter’s radiation belt and the planet, passing only 5,000 km above the cloud tops,” Juno Project Manager Rick Nybakken told me in my book ‘Incredible Stories From Space: A Behind-the-Scenes Look at the Missions Changing Our View of the Cosmos.’ “This close proximity to Jupiter is unprecedented, as no other mission has conducted their science mission this close to the planet. We’re right on top of Jupiter, so to speak.”
Juno engineers designed the mission to enable the use of solar panels, which prior to Juno, have never been used on a spacecraft going so far from the Sun. Juno orbits Jupiter in a way that the solar panels are always pointed towards the Sun and the spacecraft never goes behind the planet. Juno’s orbital design not only enabled an historic solar-powered mission, it also established Juno’s unique science orbit.
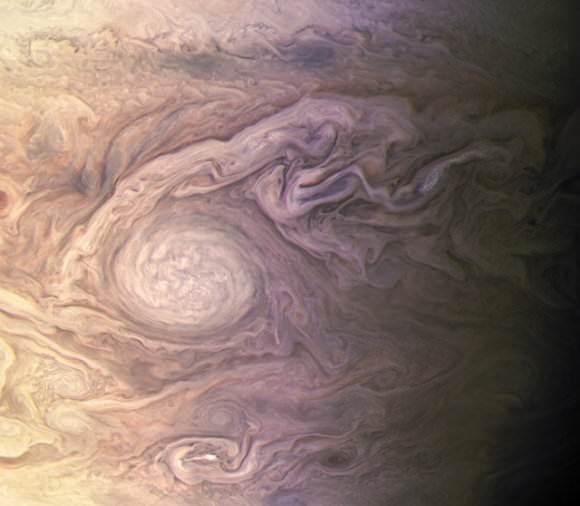

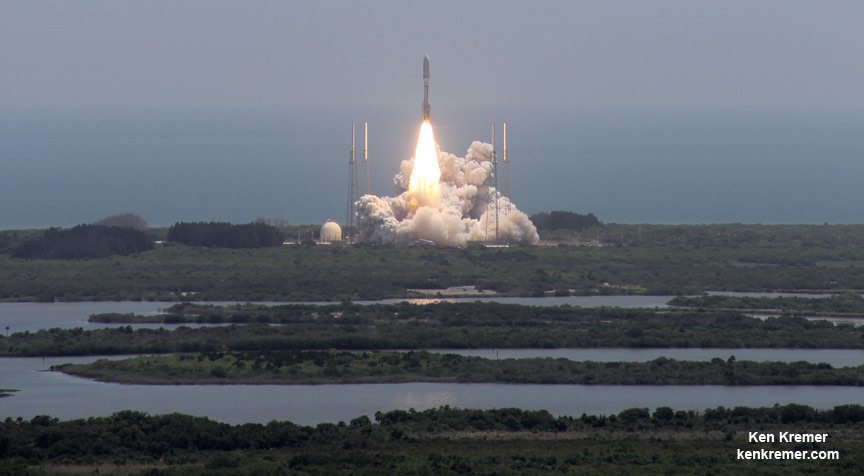
Juno spacecraft launched from Cape Canaveral on August 5, 2011. After traveling five years and 1.7 billion miles Juno arrived in orbit at Jupiter on July 4, 2016. The mission will last until at least February 2018, making 11 science orbits around Jupiter, instead of the 32 laps originally planned. Last year, engineers detected a problem with check valves in the propulsion system, and NASA decided to forego an engine burn to move Juno into a tighter 14-day orbit around Jupiter. The current 53.4 day orbit will be maintained, but depending on how the spacecraft responds, NASA could extend the mission another three years to give Juno more flybys near Jupiter.
The next science flyby will occur on July 11, when Juno will get some close-up views of the famous Great Red Spot.
Thanks to everyone who works on these images.