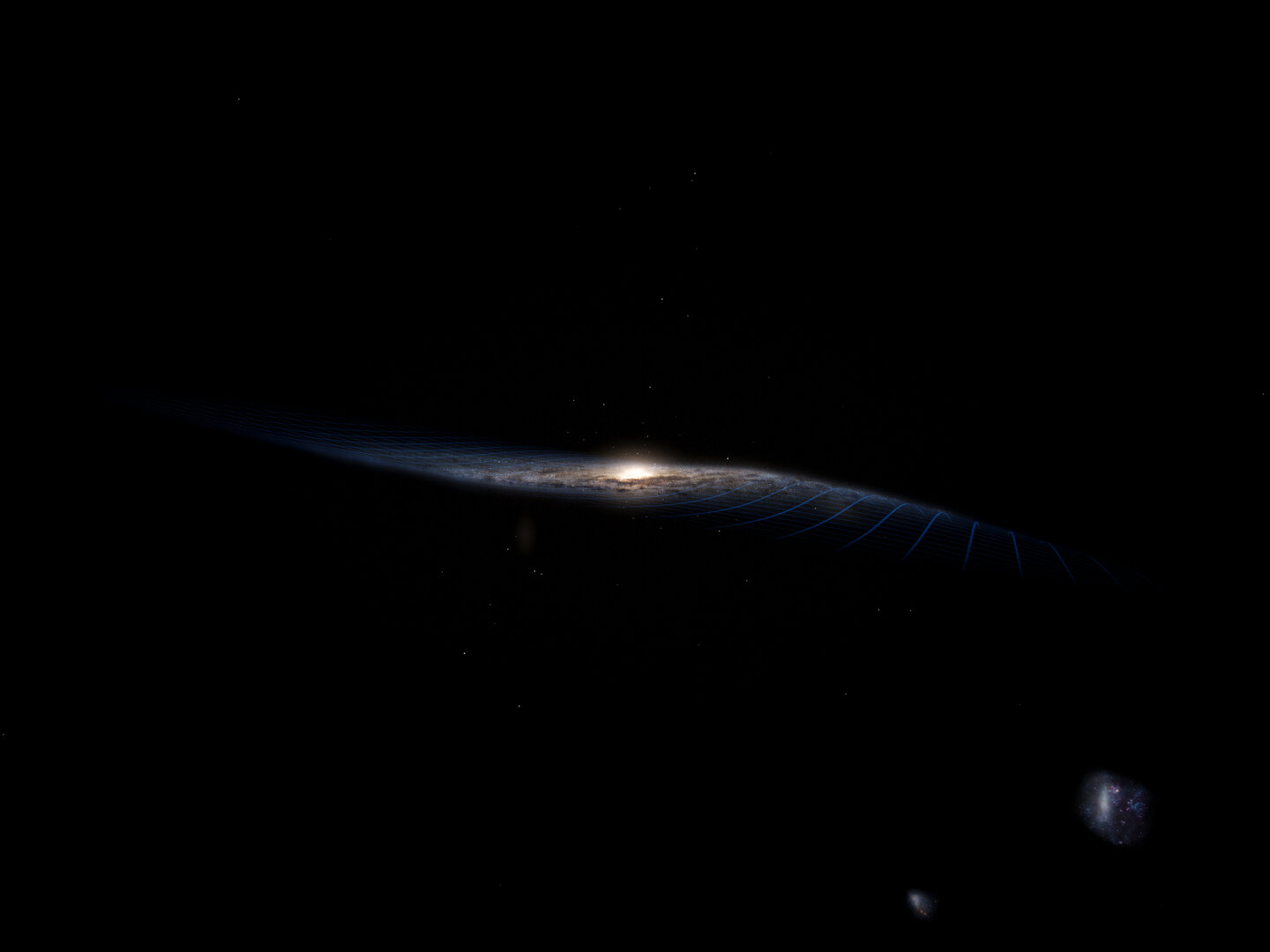
For decades, astronomers have been trying to understand why the Milky Way galaxy is warped the way it is. In recent years, astronomers have theorized that it could be our neighbors, the Magellanic Clouds, that are responsible for this phenomenon. According to this theory, these dwarf galaxies pull on the Milky Way’s dark matter, causing oscillations that pull on our galaxy’s supply of hydrogen gas.
However, according to new data from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) star-mapping Gaia Observatory, it is possible that this warp is the result of an ongoing collision with a smaller galaxy. These findings confirm that the warp in our galaxy is not static, but subject to change over time (aka. precession), and that this process is happening faster than anyone would have thought!
Continue reading “The Disk of the Milky Way is Warped Because it Already Collided With Another Galaxy”