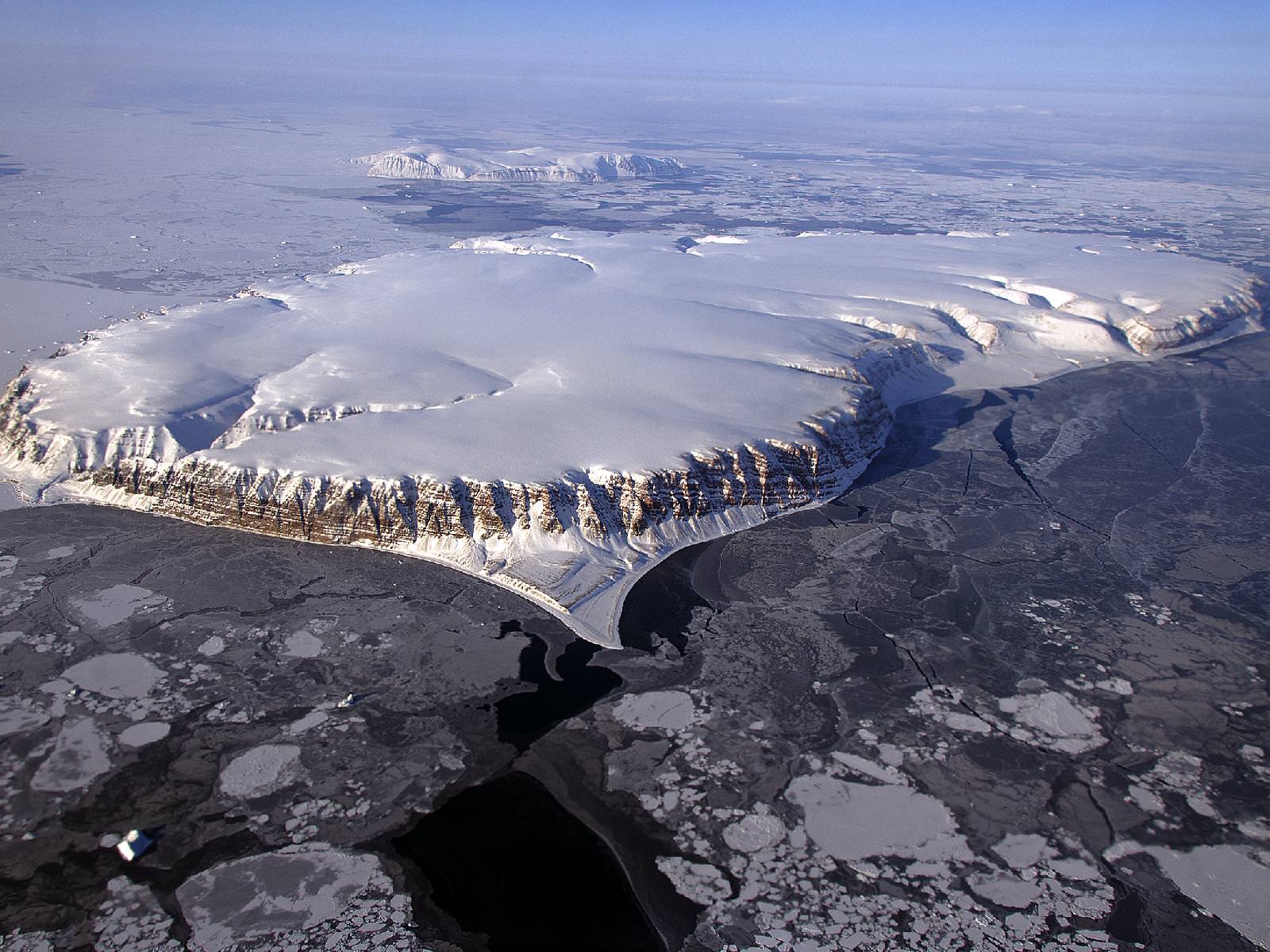
It’s quite a long way from Mars, but I can’t help but be reminded of the Red Planet’s ice-covered north pole when looking at this photo taken by Michael Studinger earlier this month, during a recent IceBridge survey flight over Greenland.
Called Saunders Island (also Appat Island) the 82-square-mile frozen slab of rock rises from the sea off the coast of northwestern Greenland, one of many islands within the Wolstenholme (Uummannaq) Fjord on the shore of Baffin Bay. Operation IceBridge, a six-year aerial survey of the changing ice coverage at our planet’s poles, is run by NASA to provide valuable ground-level information to supplement satellite data.
To me, the shape of the island’s steep rock faces and rugged inlets slice into its interior bear a striking resemblance to Mars’ ice cap.
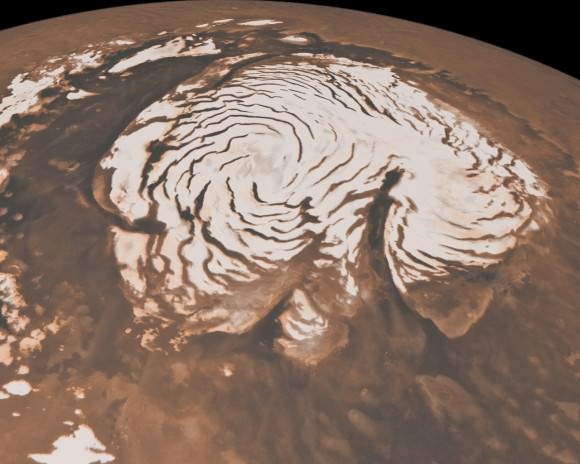
While Mars’ ice cap is shaped by very different processes — and obviously much bigger — you might see the connection too!
But rather than dark Martian dunes, sea ice can be seen surrounding the islands in varying thicknesses in the IceBridge photo above. Sea ice coverage in the fjord ranges from thicker, white ice in the background to thinner “grease” ice and leads with dark, open ocean water in the foreground.

As the amount of darker, ice-free water surfaces increase over the course of the year due to rising global temperatures, the more heat from solar radiation is collected in the ocean — thus speeding up the process of seasonal sea ice loss and overall Arctic warming.
Read more about the IceBridge mission here, and see a collection of more photos from this season’s flights here.
NASA’s Operation IceBridge images Earth’s polar ice in unprecedented detail to better understand processes that connect the polar regions with the global climate system. IceBridge utilizes a highly specialized fleet of research aircraft and the most sophisticated suite of innovative science instruments ever assembled to characterize annual changes in thickness of sea ice, glaciers, and ice sheets. In addition, IceBridge collects critical data used to predict the response of earth’s polar ice to climate change and resulting sea-level rise.

