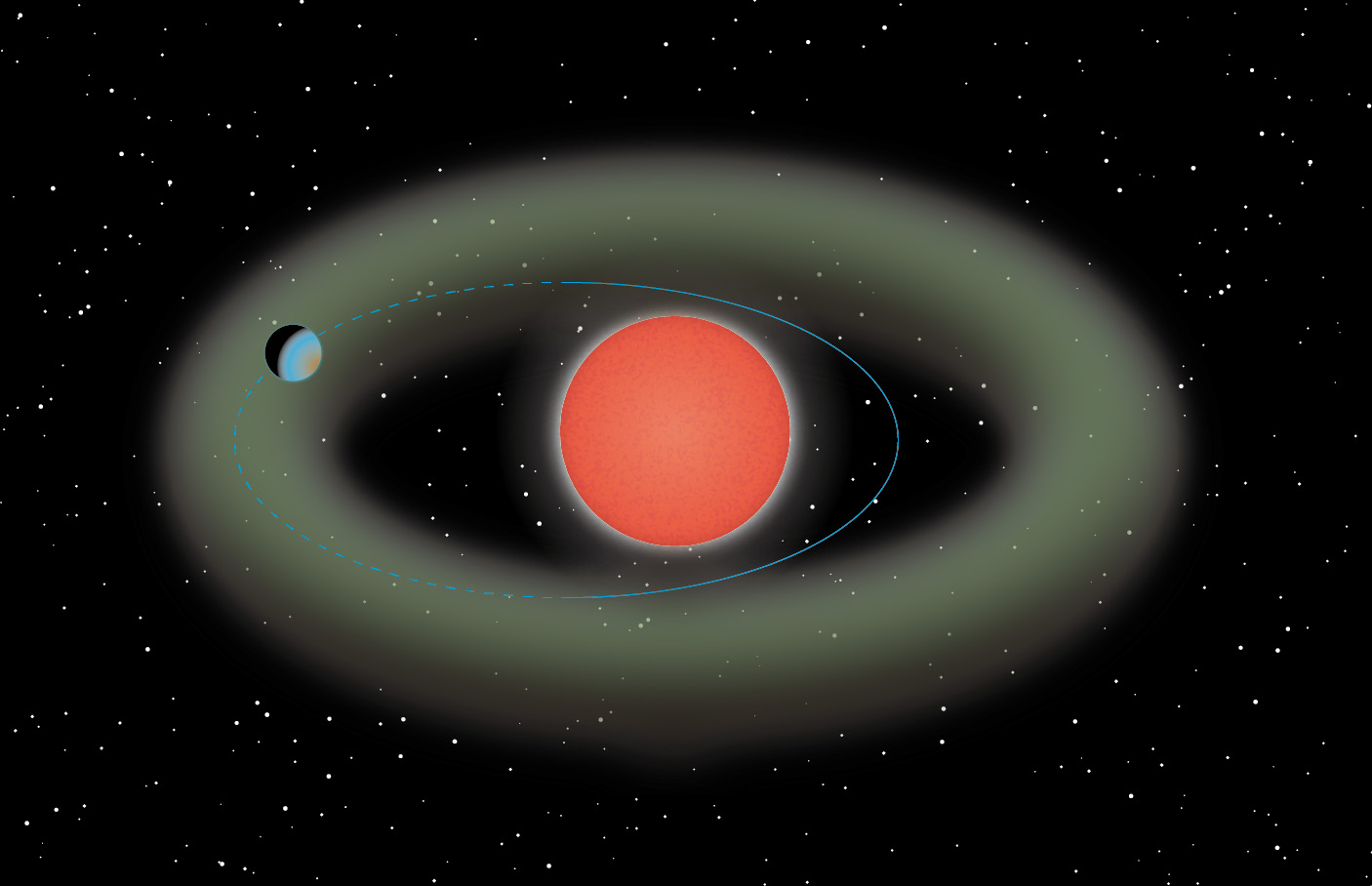
As the planets of our Solar System demonstrate, understanding the solar dynamics of a system is a crucial aspect of determining habitability. Because of its protective magnetic field, Earth has maintained a fluffy atmosphere for billions of years, ensuring a stable climate for life to evolve. In contrast, other rocky planets that orbit our Sun are either airless, have super-dense (Venus), or have very thin atmospheres (Mars) due to their interactions with the Sun.
In recent years, astronomers have been on the lookout for this same process when studying extrasolar planets. For instance, an international team of astronomers led by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) recently conducted follow-up observations of two Super-Earths that orbit very closely to their respective stars. These planets, which have no thick primordial atmospheres, represent a chance to investigate the evolution of atmospheres on hot rocky planets.
Continue reading “Astronomers Look at Super-Earths That had Their Atmospheres Stripped Away by Their Stars”