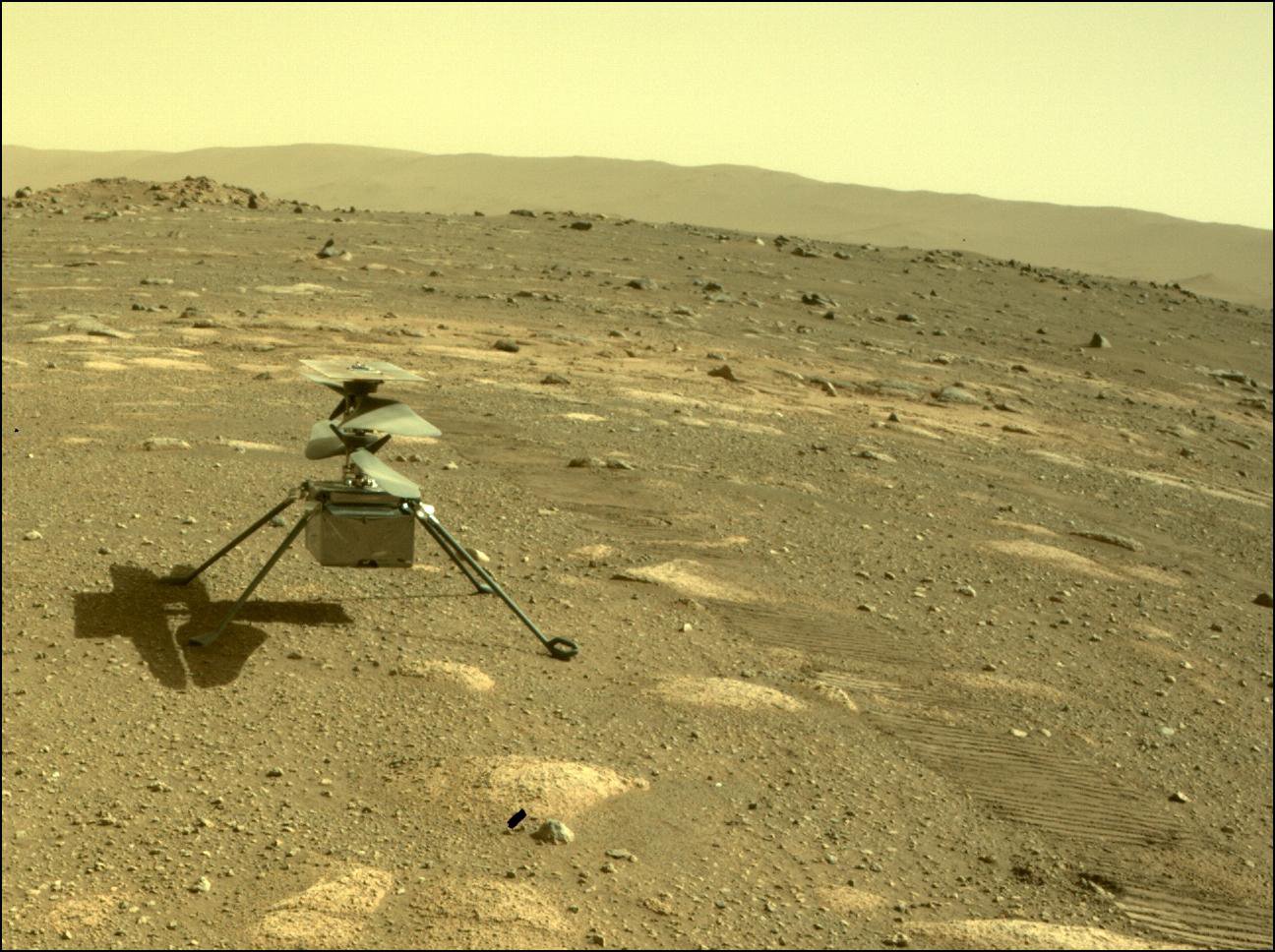
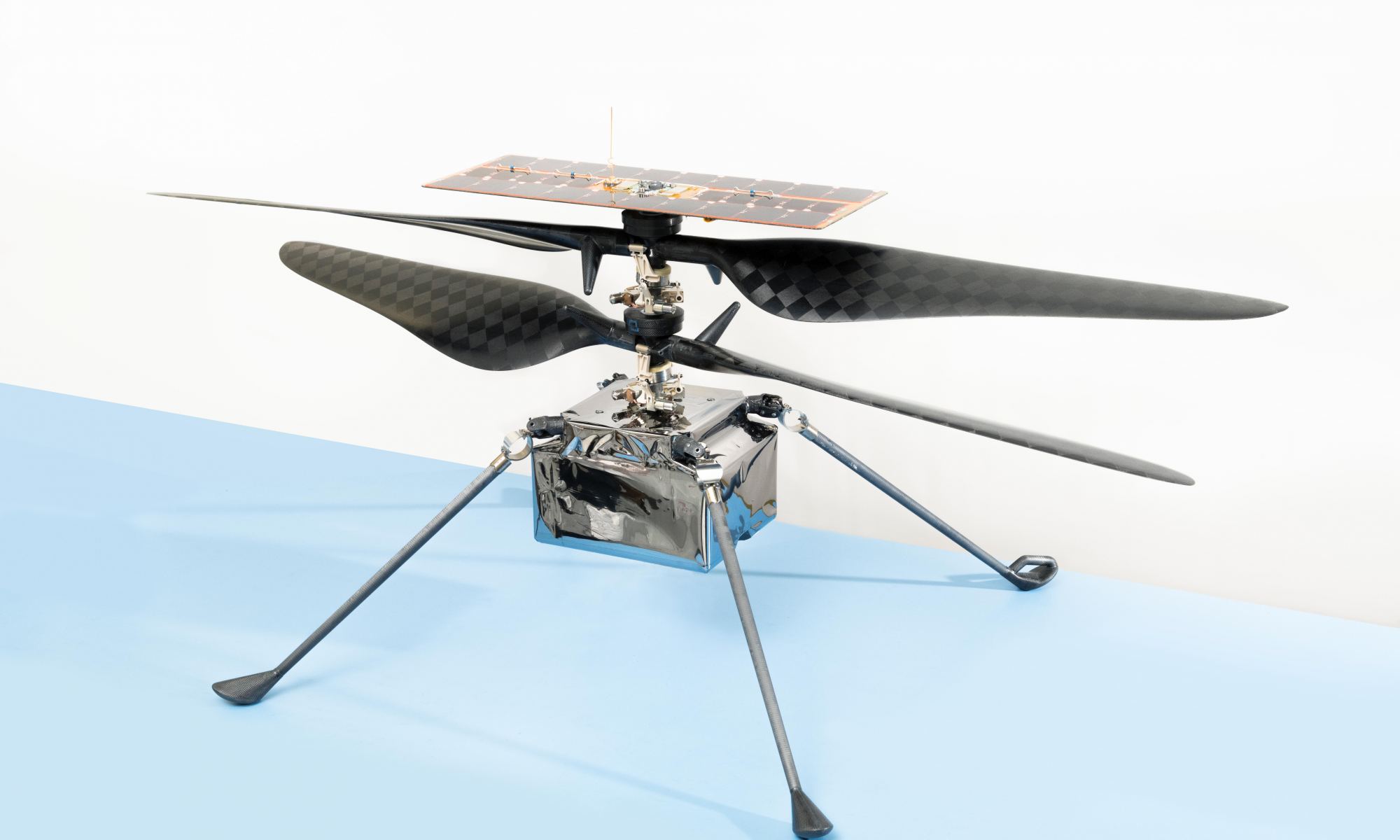
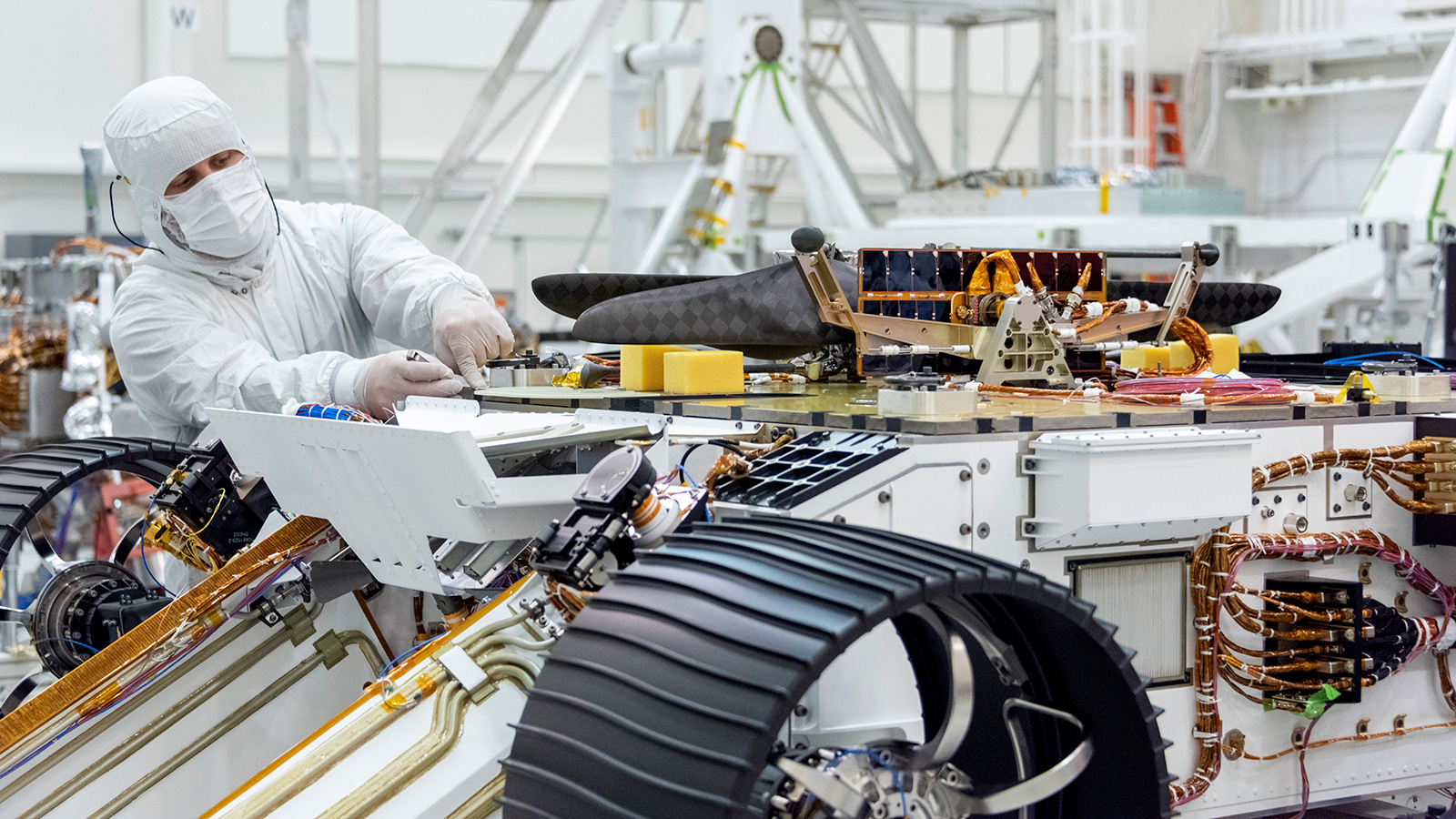
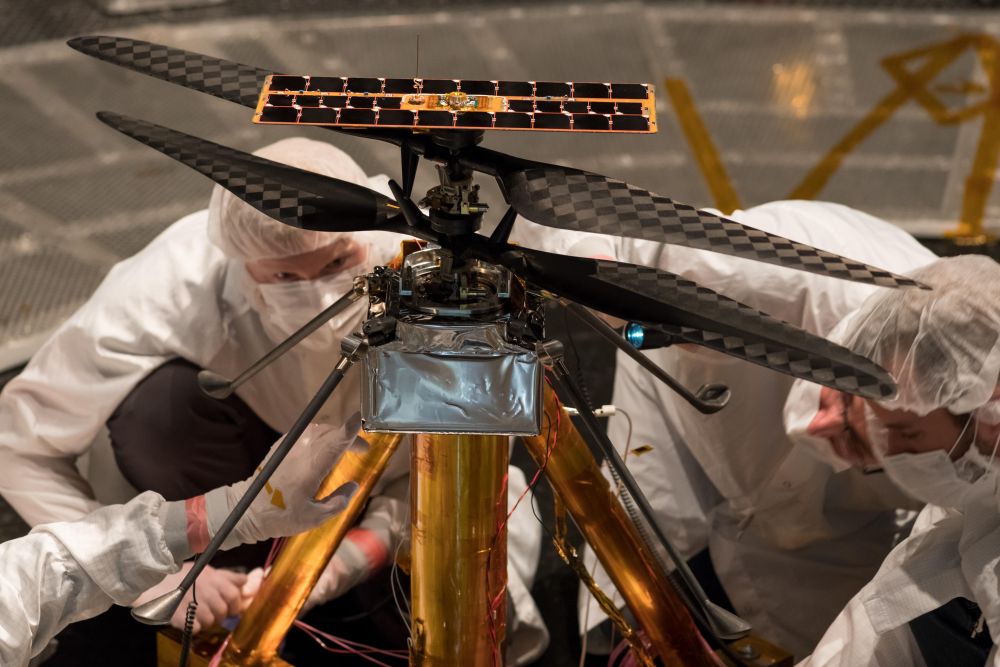
While NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter continues to break records for both airspeed and altitude while it explores Jezero Crater on the Red Planet, NASA engineers back on Earth are hard at work testing carbon fiber blades for next-generation Mars helicopters that could exceed the performance of Ingenuity on future missions to Mars, specifically with the planned Mars Sample Return mission that NASA hopes to accomplish sometime in the 2030s.
Continue reading “NASA Tests its Next-Generation Mars Helicopter Blades”NASA Tests its Next-Generation Mars Helicopter Blades