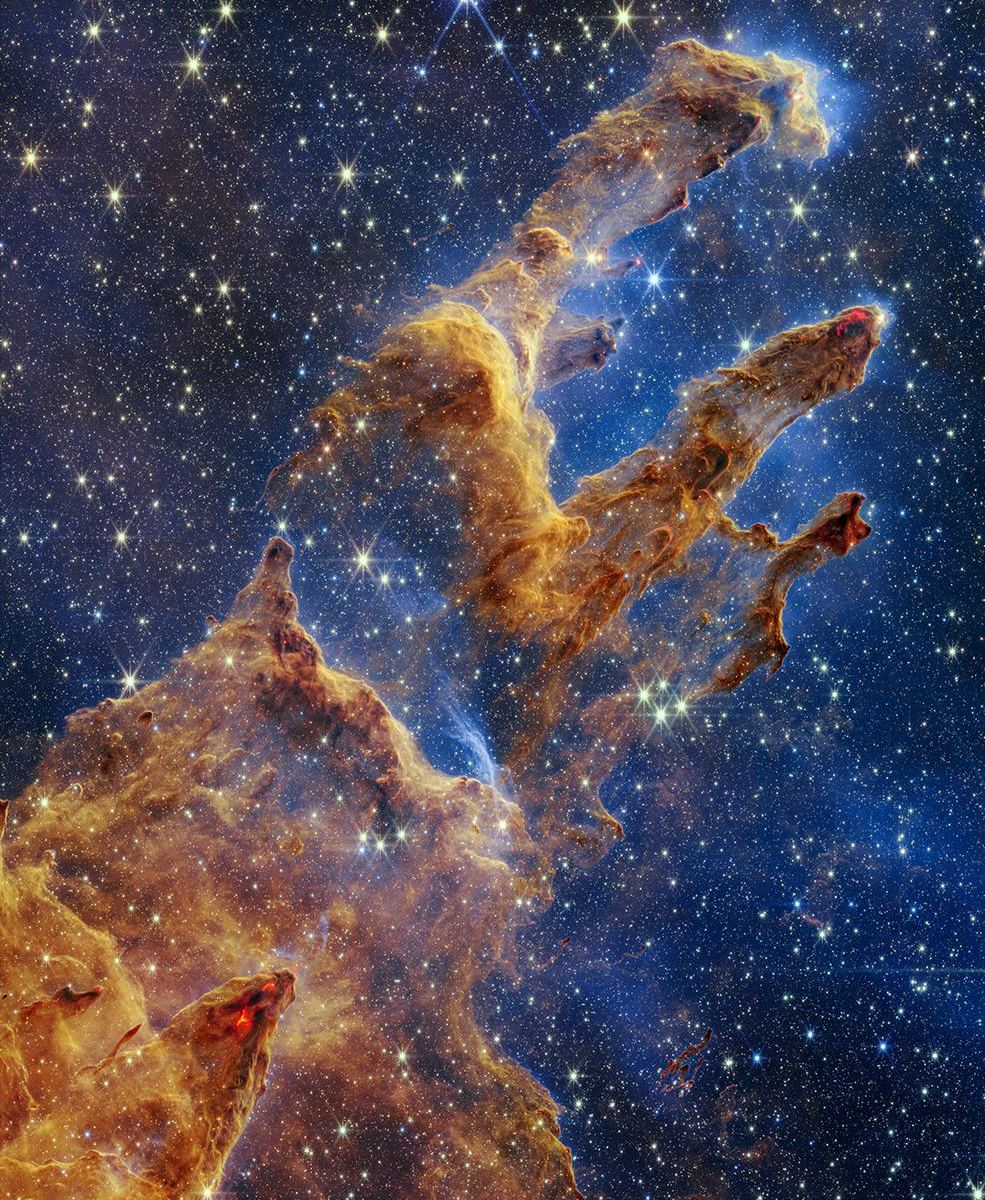
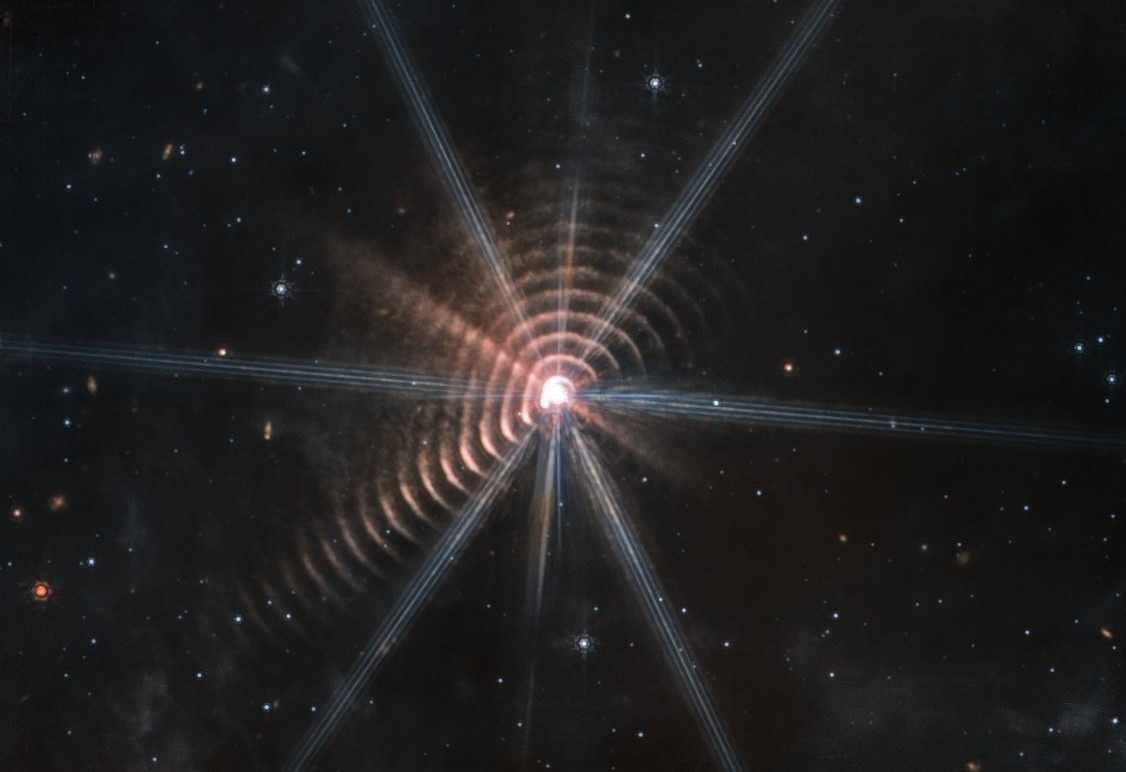
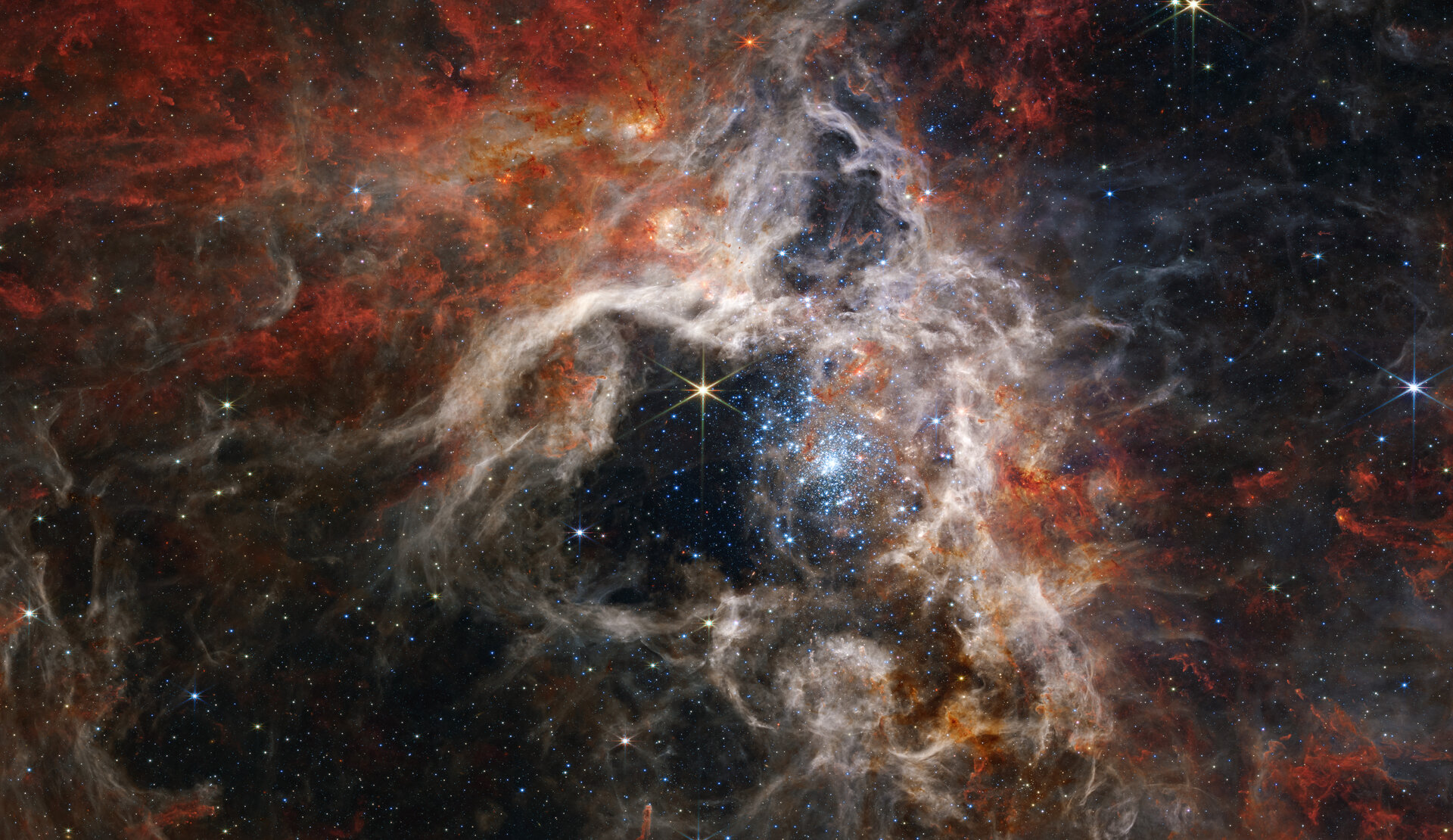
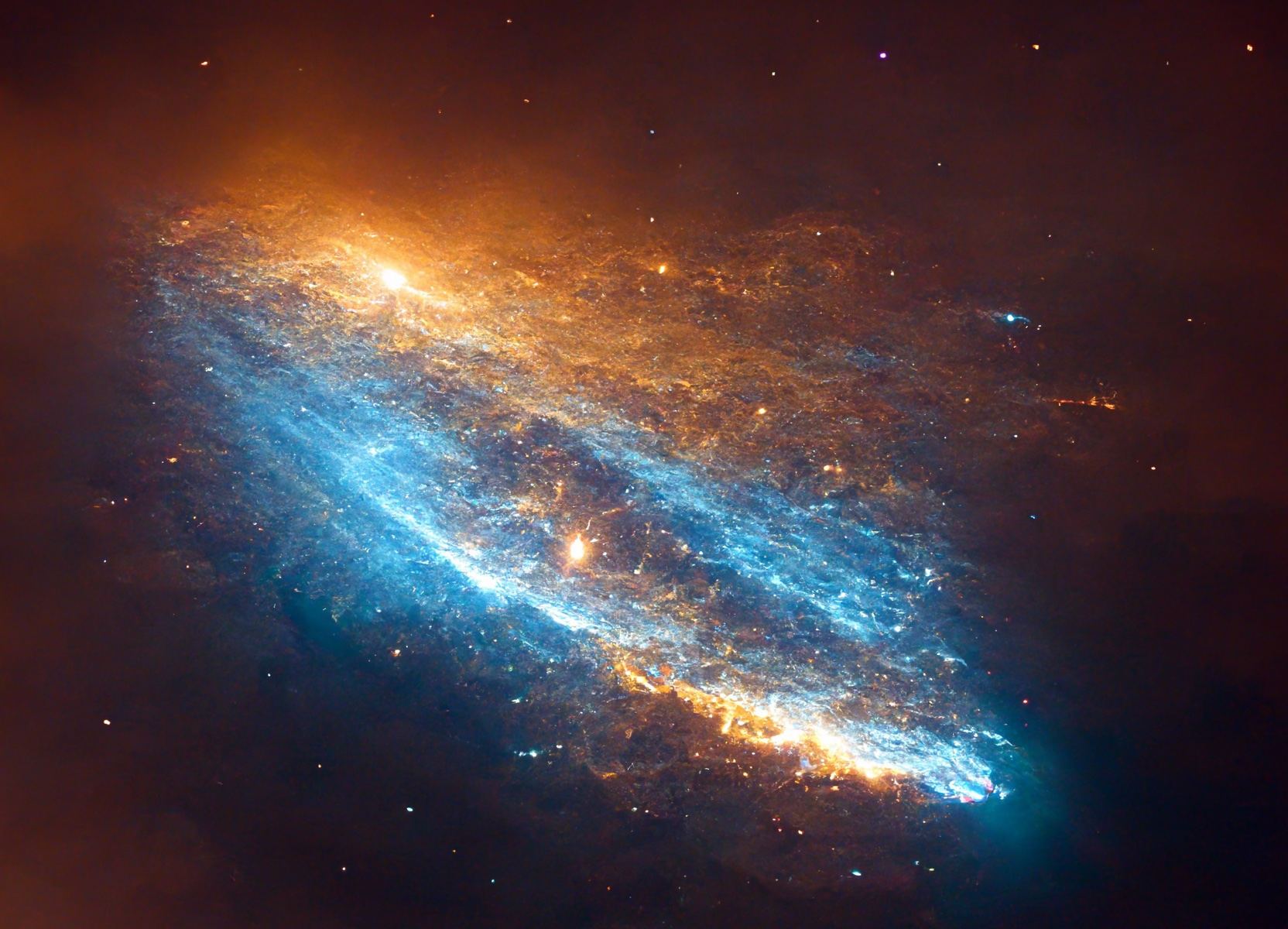
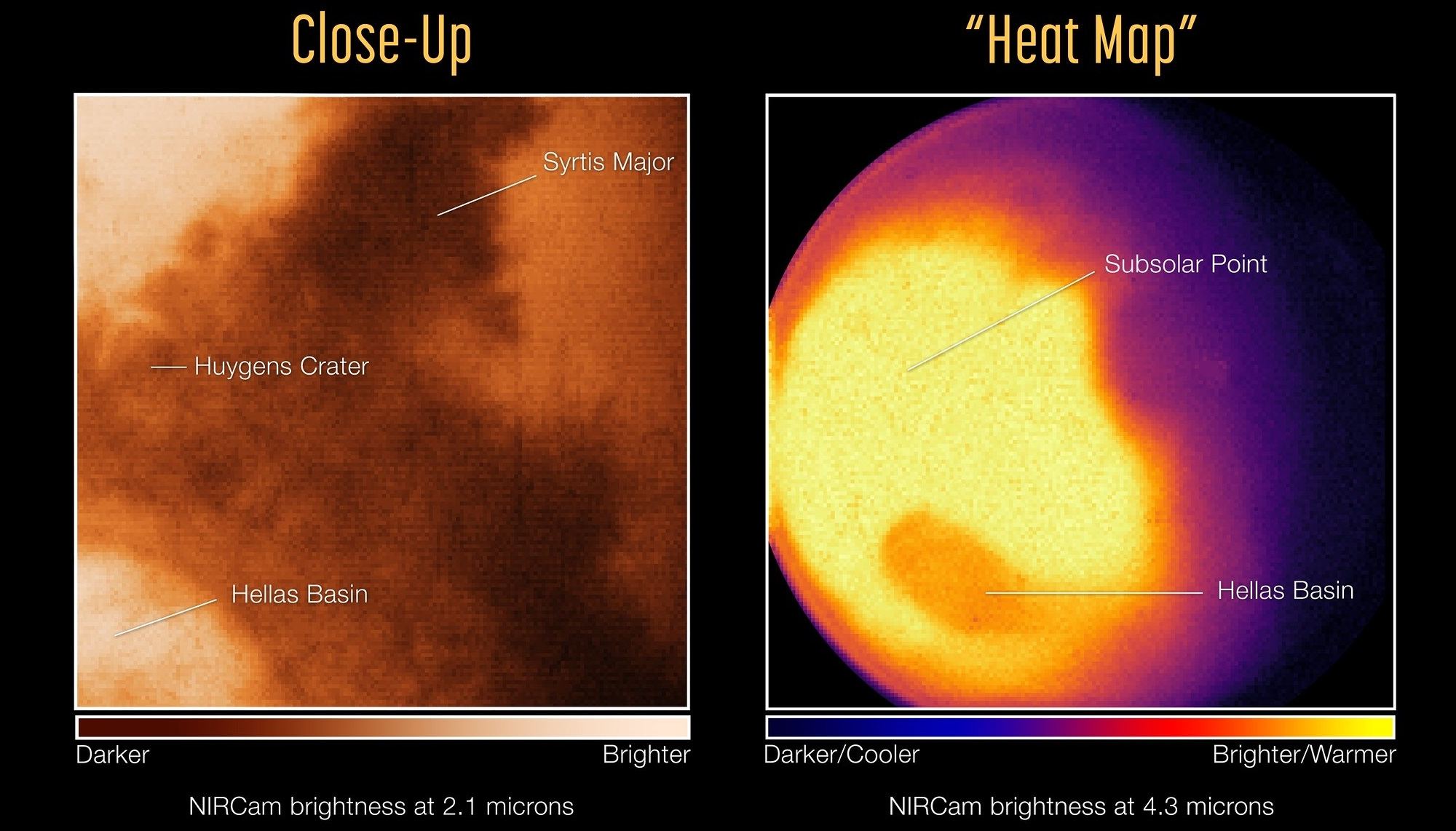
MEMPHIS, Tenn. — Side-by-side pictures from NASA’s 32-year-old Hubble Space Telescope and the brand-new James Webb Space Telescope may draw oohs and ahhs, but they don’t give you a full sense of just how much more astronomers are getting from the new kid on the cosmic block.
Fortunately, new tools for data visualization can get you closer to the sense of wonder those astronomers are feeling.
“The public is just presented with these beautiful pictures, and they think, ‘Oh, wow, that’s great,'” says Harvard astronomer Alyssa Goodman. “But in my opinion, they could learn a lot more from these images.”
Goodman laid out strategies for getting a better appreciation of JWST — and a better appreciation of the technologies that are transforming modern astronomy — this week at the ScienceWriters 2022 conference in Memphis.
Continue reading “How to See the Bigger Picture From NASA’s Webb Space Telescope”