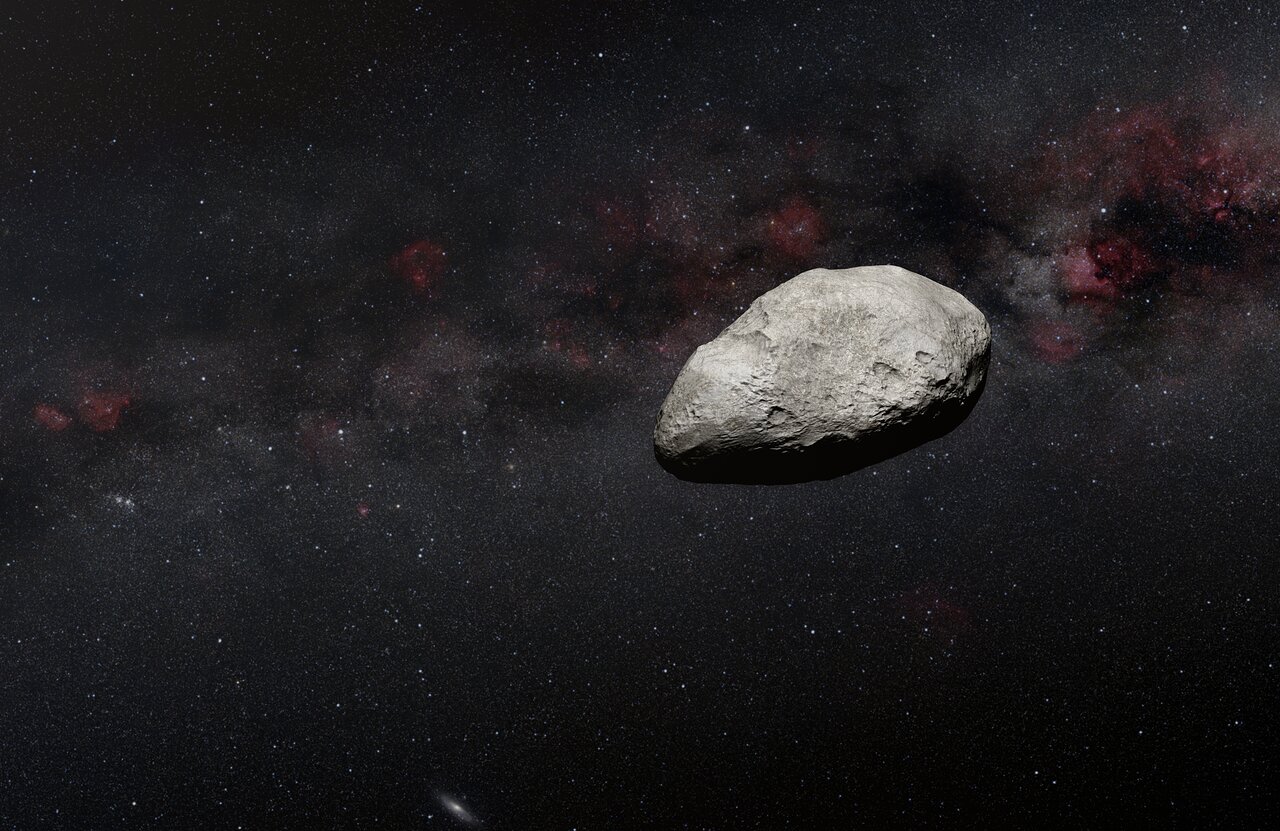
While astronomers and engineers were trying to calibrate one of the James Webb Space Telescope’s instruments last summer, they serendipitously found a previously unknown small 100–200-meter (300-600 ft) asteroid in the main asteroid belt. Originally, the astronomers deemed the calibrations as a failed attempt because of technical glitches. But they noticed the asteroid while going through their data from the Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI), and ended up finding what is likely the smallest object observed to date by JWST. It is also one of the smallest objects ever detected in our Solar System’s main belt of asteroids.
“We — completely unexpectedly — detected a small asteroid in publicly available MIRI calibration observations,” explained Thomas Müller, an astronomer at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany, in a press release. “The measurements are some of the first MIRI measurements targeting the ecliptic plane and our work suggests that many, new objects will be detected with this instrument.”
Continue reading “JWST Unexpectedly Finds a Small Asteroid During ‘Failed’ Observations”