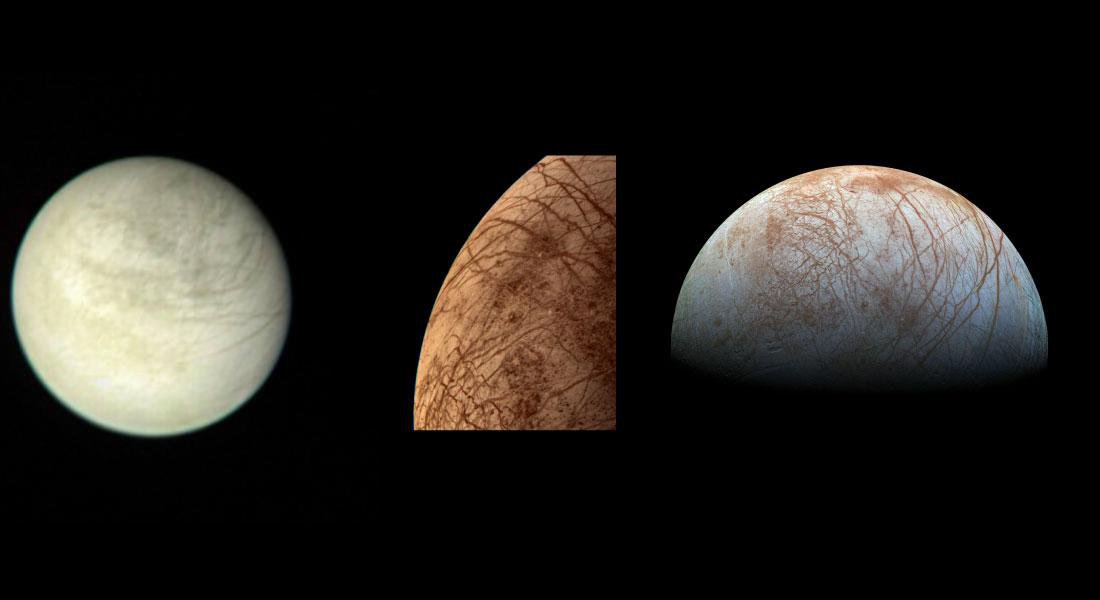
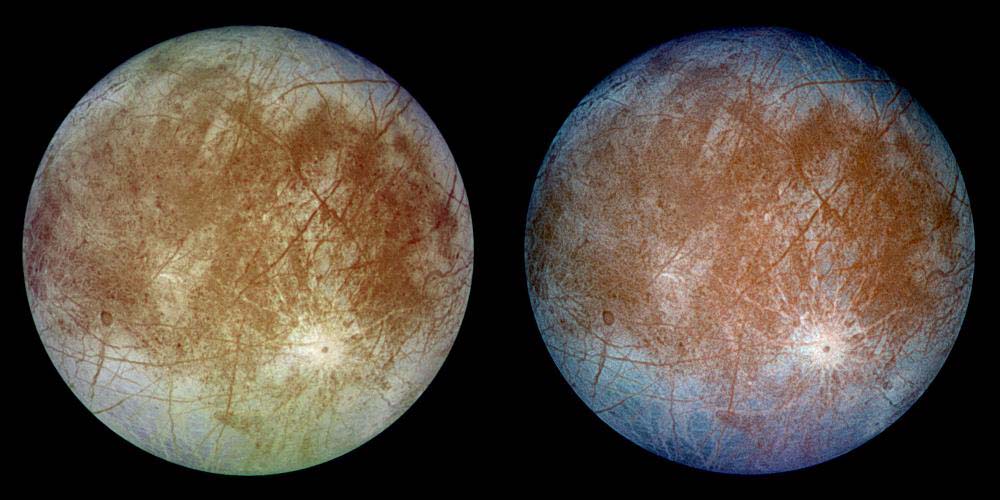
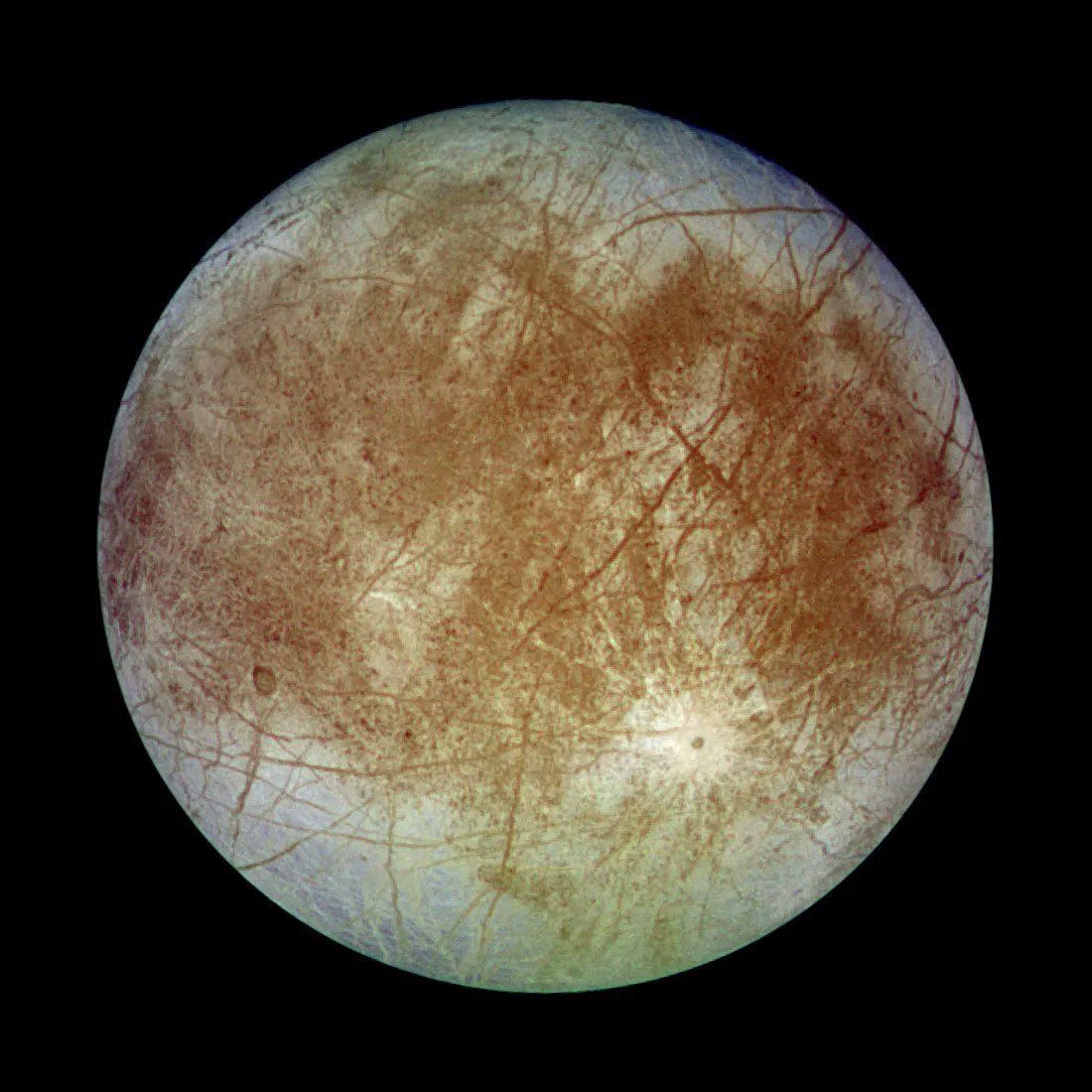
Are we alone? Is there life beyond Earth? These are the questions that plague the very essence of science, and in particular, planetary science. Unfortunately, robotic exploration of exoplanetary systems currently remains out of reach due to the literal astronomical distances to get there. For context, our nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is 4.25 light years away, or a mind-blowing 40,208,000,000,000 km (25,000,000,000,000 miles) from Earth. Finding an intelligent civilization might be out of reach for now but searching for any forms of life beyond Earth is very much possible within the confines of our own solar system.
Continue reading “What’s the Right Depth to Search for Life on Icy Worlds?”Shallow Pockets of Water Under the ice on Europa Could Bring Life Close to its Surface
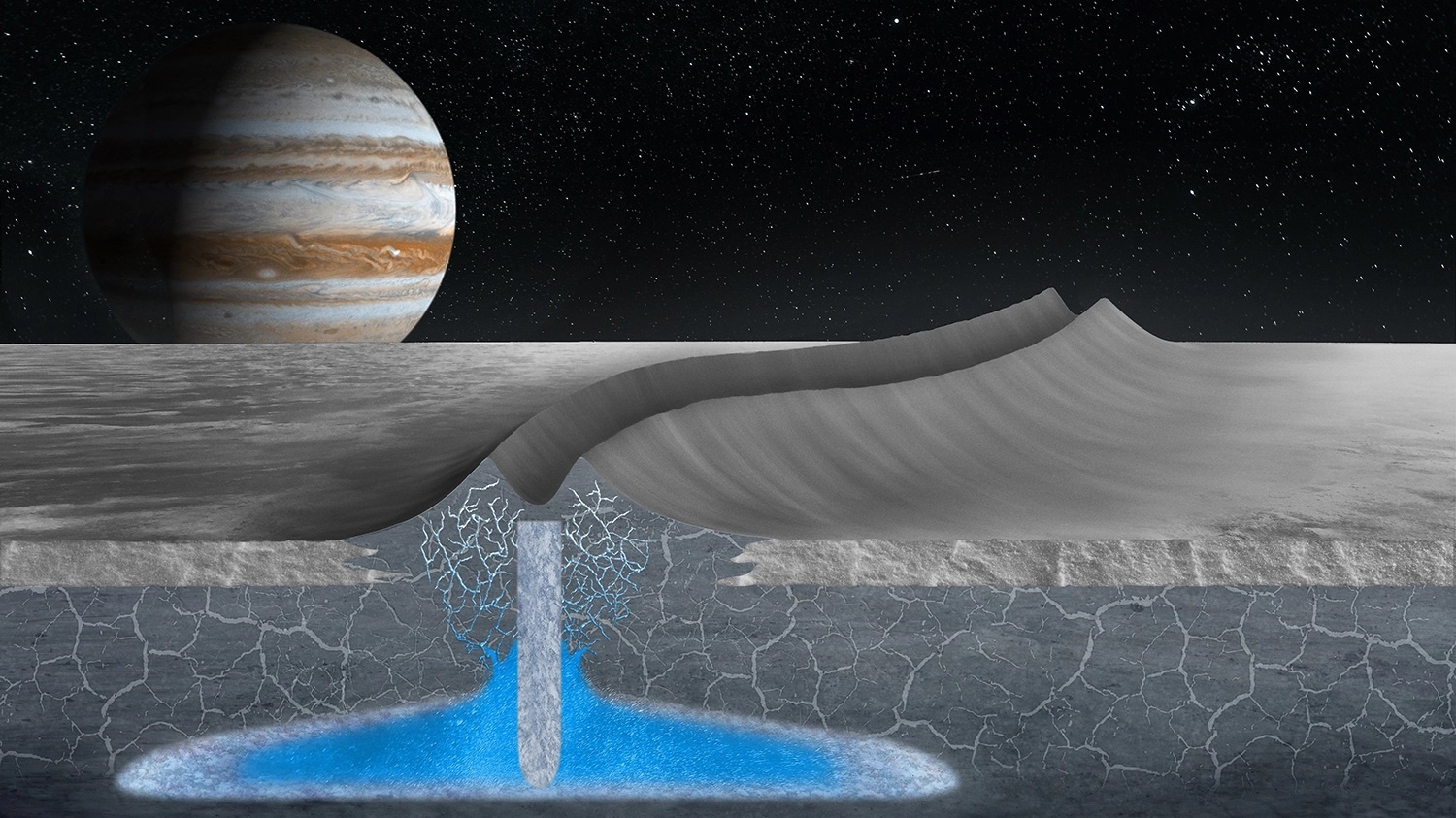
Beneath the surface of Jupiter’s icy moon Europa, there’s an ocean up to 100 km (62 mi) deep that has two to three times the volume of every ocean on Earth combined. Even more exciting is how this ocean is subject to hydrothermal activity, which means it may have all the necessary ingredients for life. Because of this, Europa is considered one of the most likely places for extraterrestrial life (beyond Mars). Hence, mission planners and astrobiologists are eager to send a mission there to study it closer.
Unfortunately, Europa’s icy surface makes the possibility of sampling this ocean rather difficult. According to the two predominant models for Europa’s structure, the ice sheet could be a few hundred meters to several dozen kilometers thick. Luckily, new research by a team from Stanford University has shown that Europa’s icy shell may have an abundance of water pockets inside, as indicated by features on the surface that look remarkably like icy ridges here on Earth.
Continue reading “Shallow Pockets of Water Under the ice on Europa Could Bring Life Close to its Surface”Europa Could be Pulling Oxygen Down Below the Ice to Feed Life
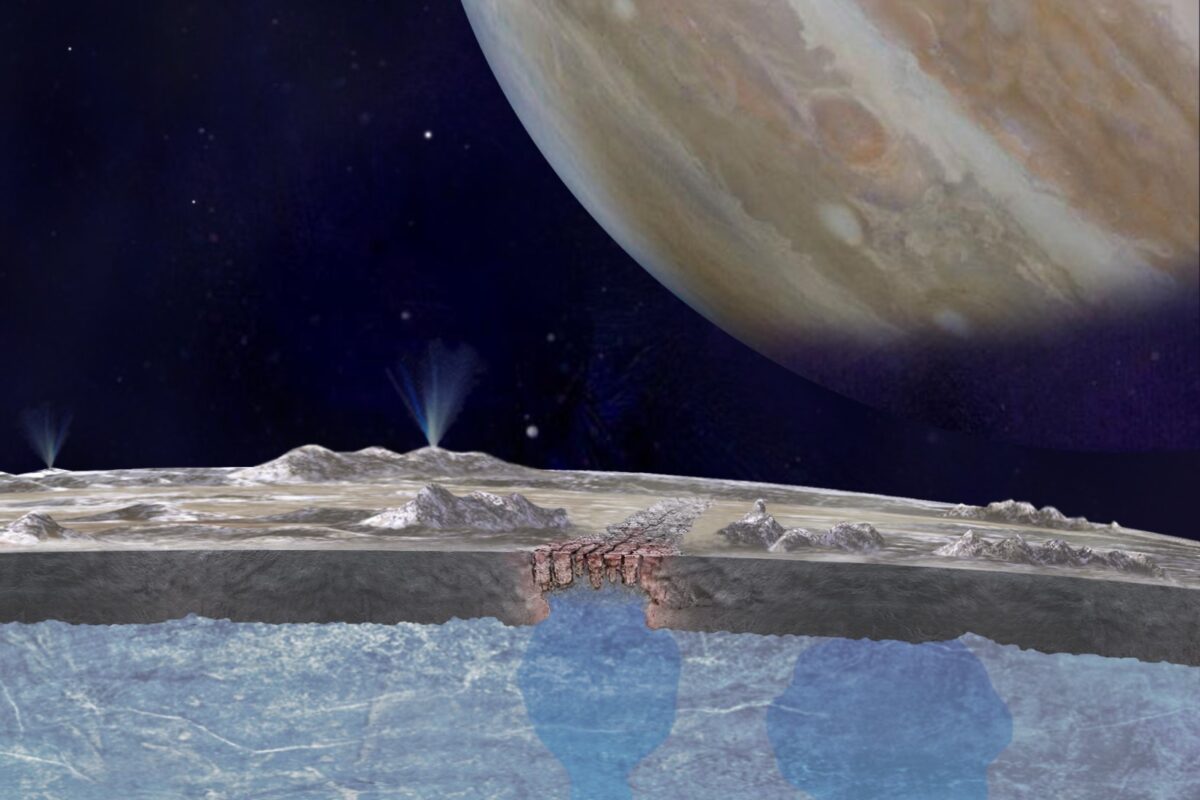

Jupiter’s moon Europa is a prime candidate in the search for life. The frozen moon has a subsurface ocean, and evidence indicates it’s warm, salty, and rich in life-enabling chemistry.
New research shows that the moon is pulling oxygen down below its icy shell, where it could be feeding simple life.
Continue reading “Europa Could be Pulling Oxygen Down Below the Ice to Feed Life”Here are the 7 Best Places to Search for Life in the Solar System
If humanity is ever going to find life on another planet in the solar system, it’s probably best to know where to look. Plenty of scientists have spent many, many hours pondering precisely that question, and plenty have come up with justifications for backing a particular place in the solar system as the most likely to hold the potential for harboring life as we know it. Thanks to a team led by Dimitra Atri of NYU Abu Dhabi, we now have a methodology by which to rank them.
Continue reading “Here are the 7 Best Places to Search for Life in the Solar System”The Europa Clipper is Coming Together, Launching in 2024
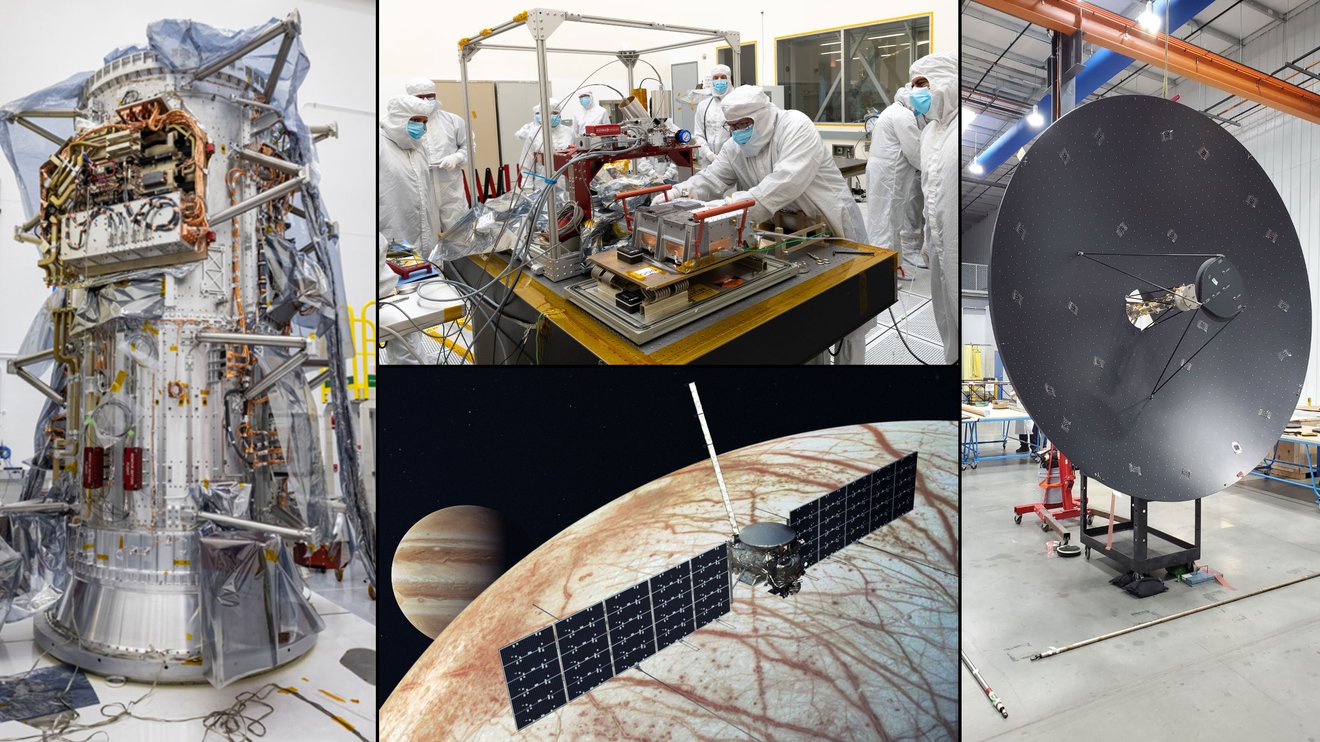

Who is excited to send a spacecraft to Europa? Every person I’ve talked to who is even remotely interested in planetary exploration is incredibly enthusiastic about the upcoming Europa Clipper mission to explore Jupiter’s icy moon. With strong evidence of a subsurface liquid ocean, Europa is considered by many to be the most likely place in our Solar System – besides Earth — which might harbor life. The many mysteries about this moon make it a compelling place to explore.
Continue reading “The Europa Clipper is Coming Together, Launching in 2024”If There are Water Plumes on Europa, Here’s how Europa Clipper Will Study Them
NASA’s Europa Clipper is one of the most anticipated missions of the coming decade, in large part because its target, the large Jovian moon Europa, is considered one of the most likely places in our solar system that extraterrestrial life might exist. If Europa is harboring alien microbes, however, they’re likely to be buried deep beneath the moon’s thick icy crust in a vast subsurface ocean. Unlocking the secrets of this water world isn’t going to be easy, but the Clipper team has a plan to make the most of the opportunity they have: If you can’t get to the ocean, let the ocean come to you.
Continue reading “If There are Water Plumes on Europa, Here’s how Europa Clipper Will Study Them”Europa has Water in its Atmosphere
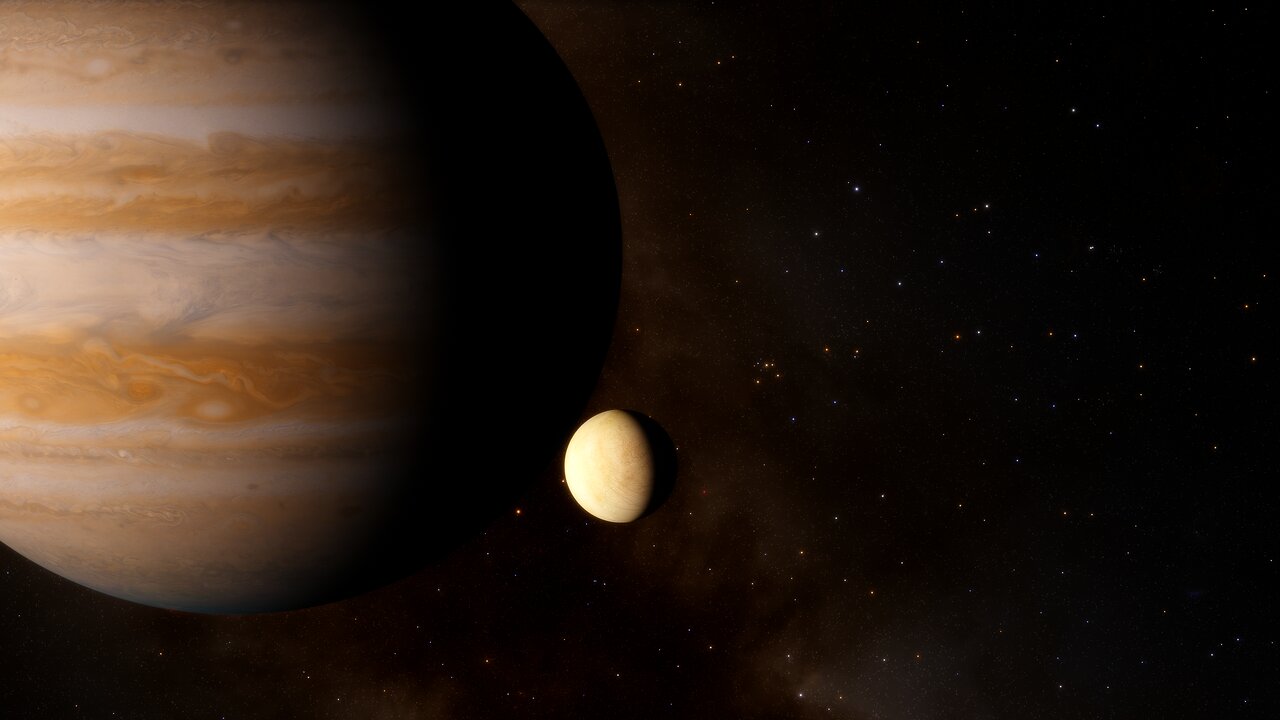

Since the Voyager probes passed through the Jupiter system in 1979, scientists have been intrigued and mystified by its moon Europa. Once the images these probes acquired of the moon’s icy surface returned to Earth, scientists began to speculate about the possibility of a subsurface ocean. Since then, the detection of plume activity and other lines of evidence have bolstered this theory and fed speculation that there could be life beneath Europa’s icy surface.
According to new research, another critical piece of evidence of Europa’s watery nature has at least been confirmed. Using a similar technique that confirmed the presence of atmospheric water vapor in Jupiter’s moon Ganymede, Lorenz Roth of the KTH Royal Institute of Technology confirmed that Europa has water vapor in its atmosphere. This discovery could lead to a greater understanding of Europa’s atmosphere and surface environment, informing missions headed there in the near future.
Continue reading “Europa has Water in its Atmosphere”Why Visit Just one Moon When you Could Explore Them all?
The Solar System’s moons are intriguing objects for exploration. Especially moons like Europa and Enceladus. Their subsurface oceans make them primary targets in the search for life.
But why not send one spacecraft to visit several moons? NASA’s about to launch its Lucy mission which will visit 8 separate asteroids. Could the same be done for a mission to multiple moons?
For a spacecraft to do that, it would have to do a little dance with the notorious three-body problem, which makes a stubborn partner. A new study presents a possible way to do that.
Continue reading “Why Visit Just one Moon When you Could Explore Them all?”Greenland’s Ice Sheet is Similar in Many Ways to the Solar System’s Icy Worlds and Can Teach Us How to Search for Life
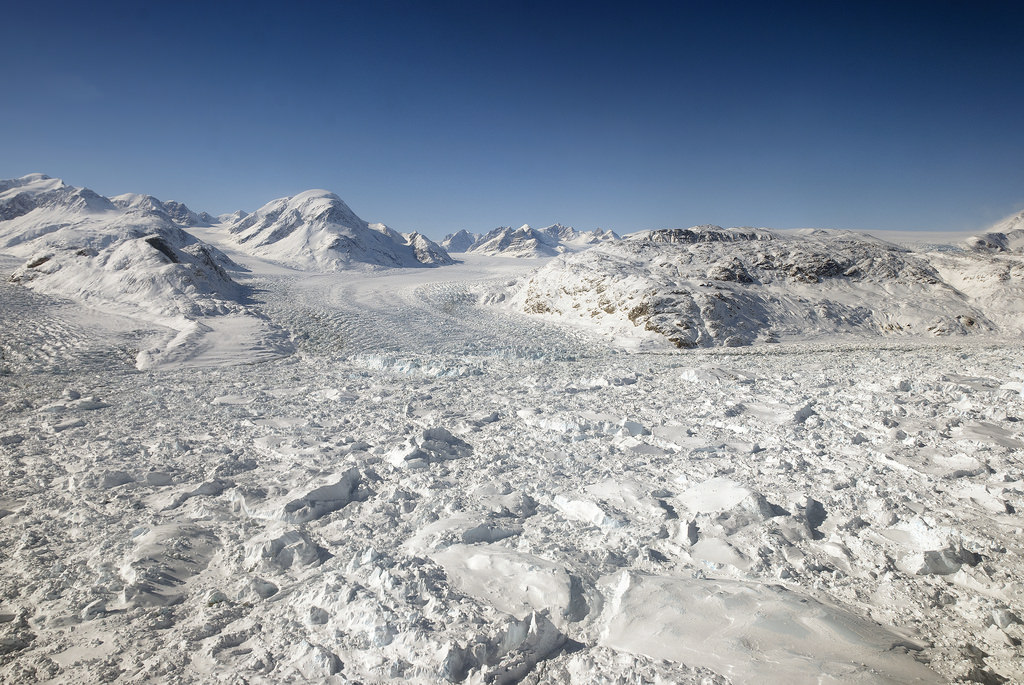

Many regions on Earth are temperate, nutrient-rich, stable environments where life seems to thrive effortlessly. But not all of Earth. Some parts, like Greenland’s ice sheet, are inhospitable.
In our nascent search for life elsewhere in the Solar System, it stands to reason that we’ll be looking at worlds that are marginal and inhospitable. Icy worlds like Jupiter’s moon Europa and Saturn’s moon Enceladus are our most likely targets. These frozen worlds have warm oceans under layers of ice.
What can Greenland’s cryo-ecosystems tell us about searching for life on icy bodies like Europa and Enceladus?
Continue reading “Greenland’s Ice Sheet is Similar in Many Ways to the Solar System’s Icy Worlds and Can Teach Us How to Search for Life”Micrometeorites Churn up the Surface of Europa. If you Want to Find Life, You’ll Need to dig Down a Meter or So
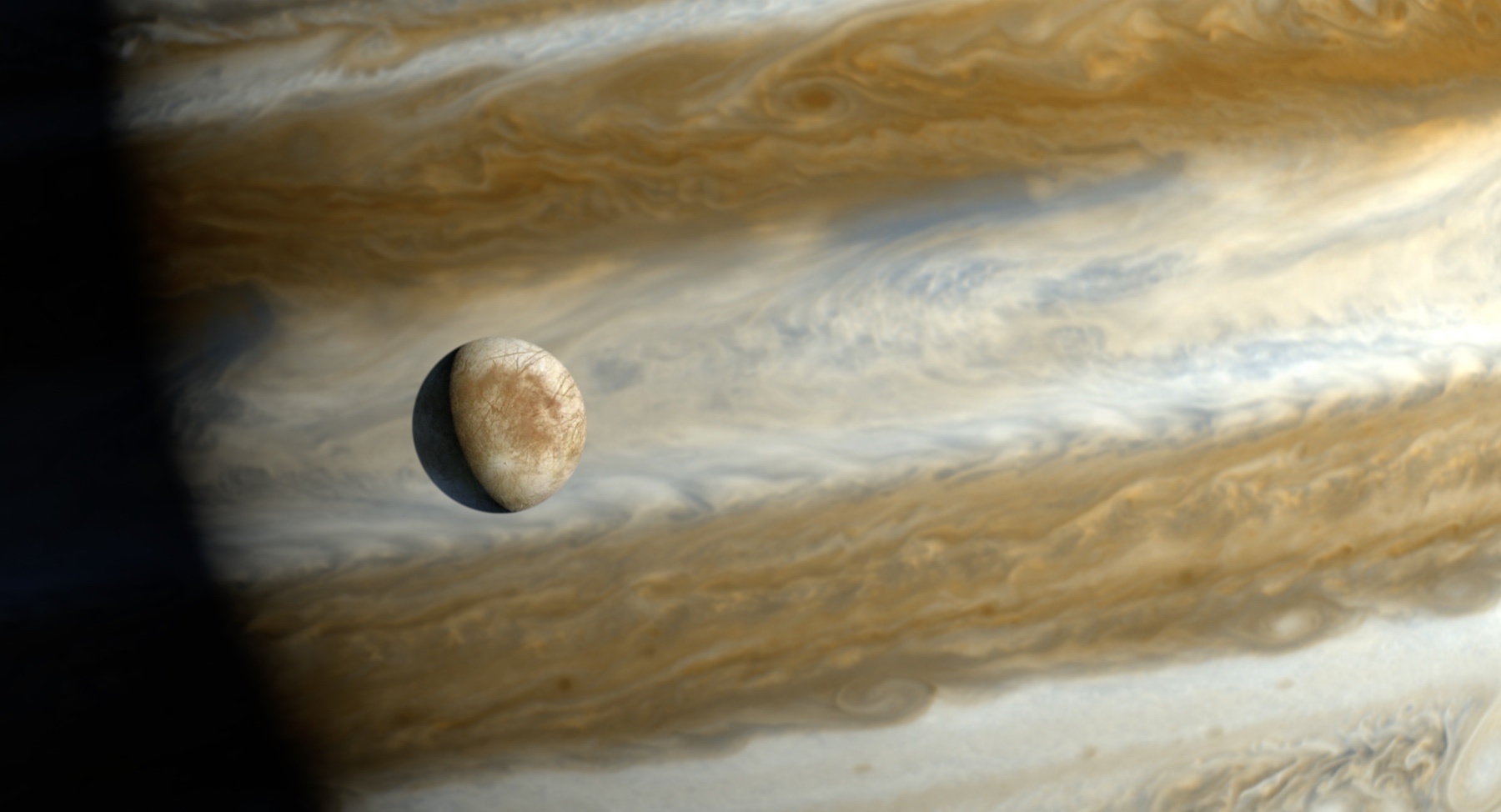

In the coming decade, NASA and the ESA will be sending two dedicated missions that will explore Jupiter’s moon Europa. These missions are known as the Europa Clipper and the JUpiter ICy moons Explorer (JUICE) missions, which will fulfill a dream that has been decades in the making – searching for possible evidence of life inside Europa. Since the 1970s, astronomers have theorized that this satellite contains a warm-water ocean that could support life.
The case for life in Europa has only been bolstered thanks to multiple flybys and observation campaigns that have been mounted since. According to new research led by the University of Hawaii at Manoa, the best way to look for potential signs of life (aka. biosignatures) would be to analyze small impact craters on Europa’s surface. These patches of exposed subsurface ice could point the way towards life that might exist deeper in the moon’s interior.
Continue reading “Micrometeorites Churn up the Surface of Europa. If you Want to Find Life, You’ll Need to dig Down a Meter or So”