[/caption]
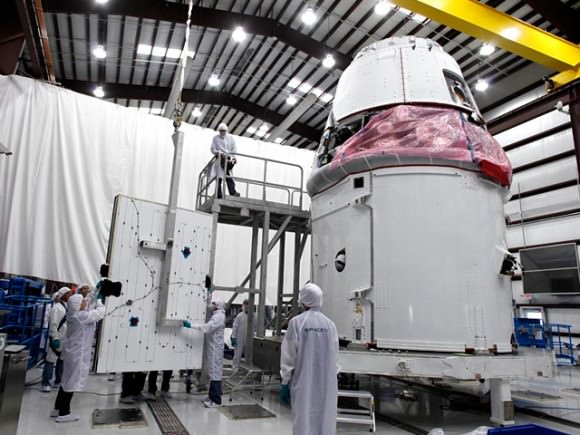
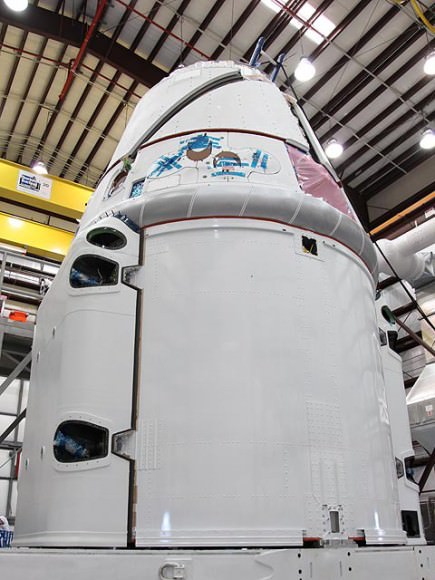
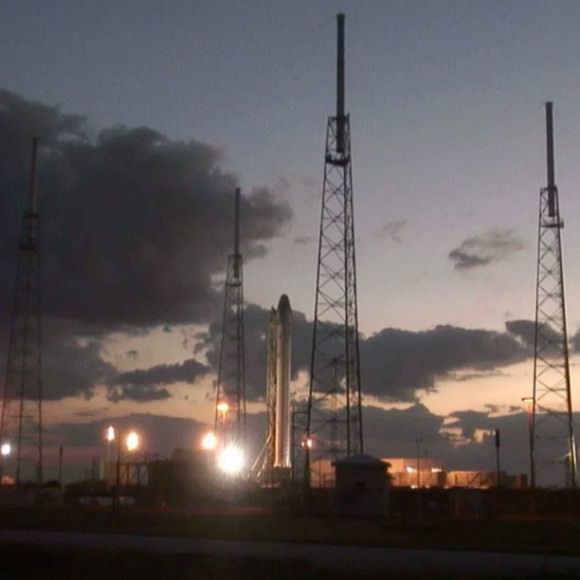
SpaceX successfully completed a key test of the Falcon 9 rocket that will fly the first commercial flight to the International Space Station. Called a ‘wet dress rehearsal,’ SpaceX brought the Falcon 9 “stack” with the Dragon capsule atop to the launch pad at Cape Canaveral on March 1, and loaded it with 76,000 gallons of highly refined kerosene and liquid oxygen fuel. Pre-liftoff operations were conducted as engineers went through a full count-down simulation, stopping at 5 seconds before ‘launch.’
SpaceX said the test was a success and was an important step on the road to the Space Station. “The test went well,” said SpaceX spokeswoman Kirstin Grantham. “Over the coming days, we will continue to review the data as we prepare for our upcoming mission.”
The launch of this historic flight will likely be April 20, or later, depending on the results of this and other tests.
After the wet dress rehearsal, the fuel was drained, and the rocket was later rolled off the launch pad on March 2, and the SpaceX said Dragon will be taken off for additional testing.

Additionally, on March 2, SpaceX conducted another test, called a 9-engine test, firing the engines for a future Falcon 9 rocket. This took place near McGregor, Texas.
As the “real” launch date approaches for the current rocket, the Falcon 9 will again be brought to the Launchpad to fire the nine first-stage engines and practice late packing of cargo in the Dragon.
“These rehearsals allow SpaceX to test out both the vehicle and the ground systems before launch,” Grantham said.
SpaceX is working towards becoming the first commercial spacecraft to dock with the ISS under NASA’s commercial orbital transportation services (COTS) commercial crew development (CCDev) programs. Later this year, another COTS company, Orbital Sciences hopes to launch their Antares rocket and Cygnus capsule from Wallops Island, Virginia.