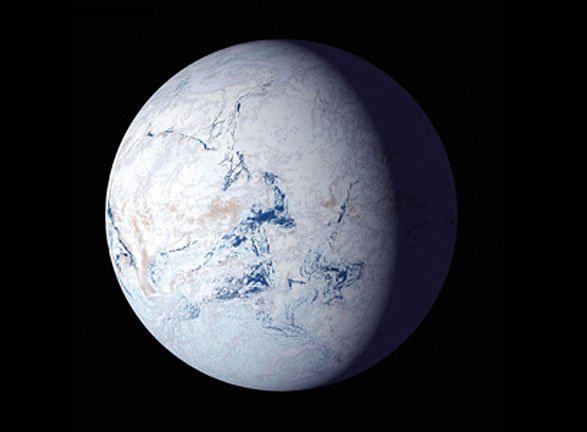
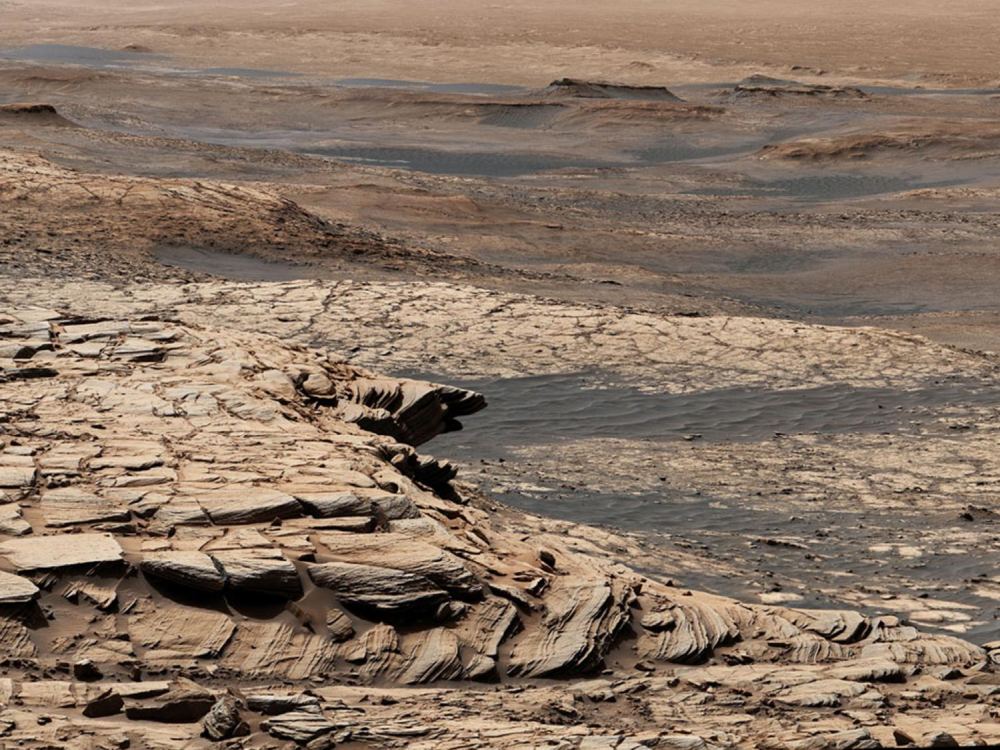
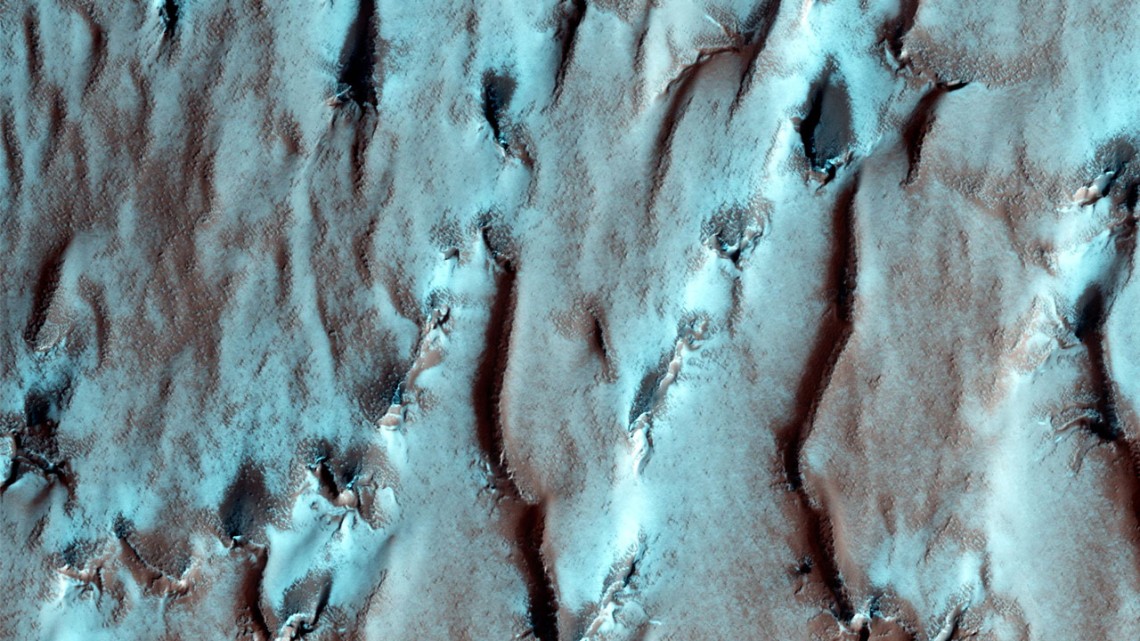
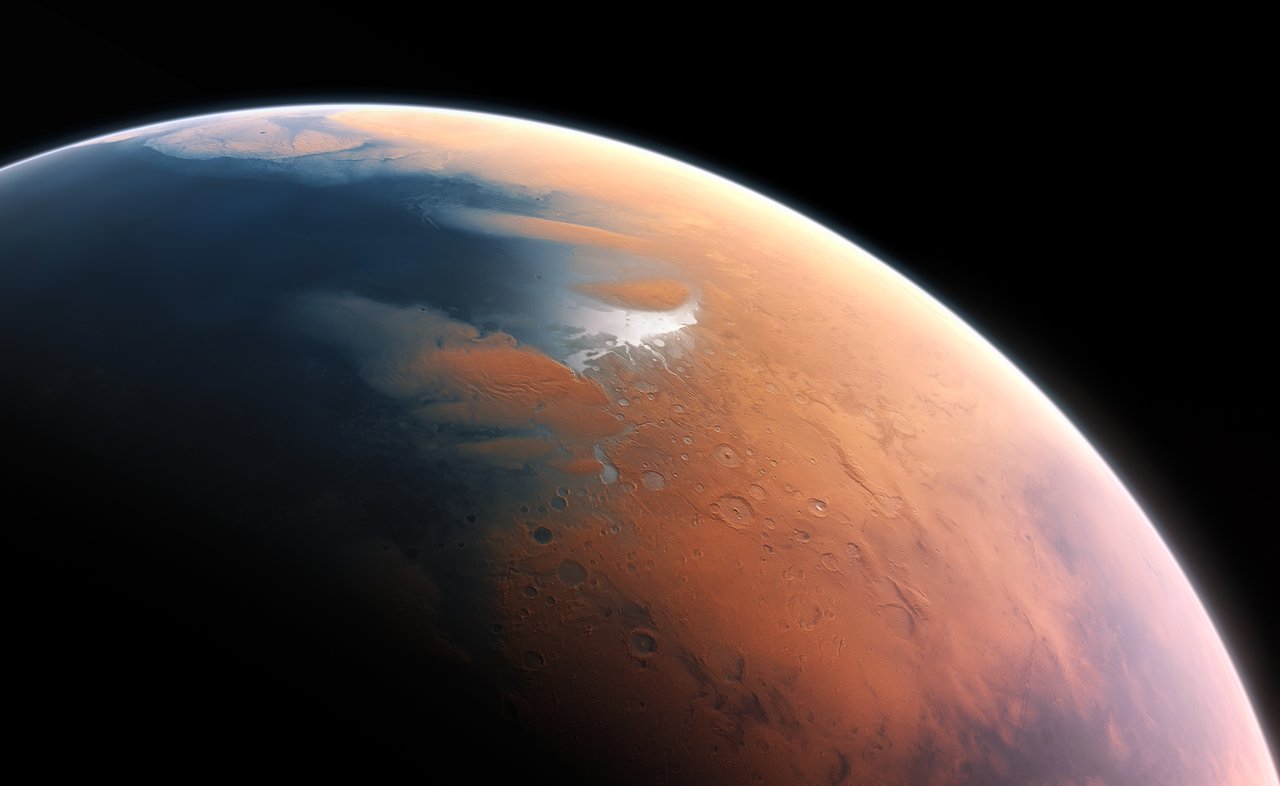
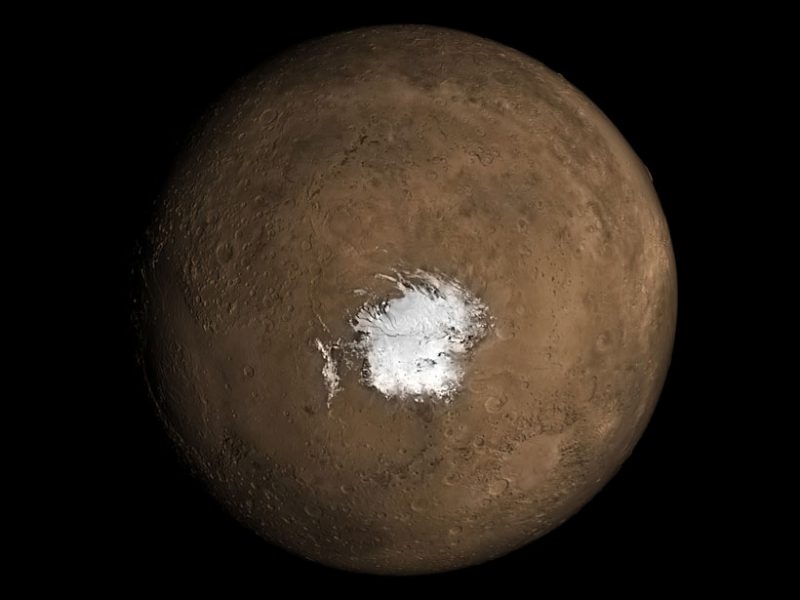
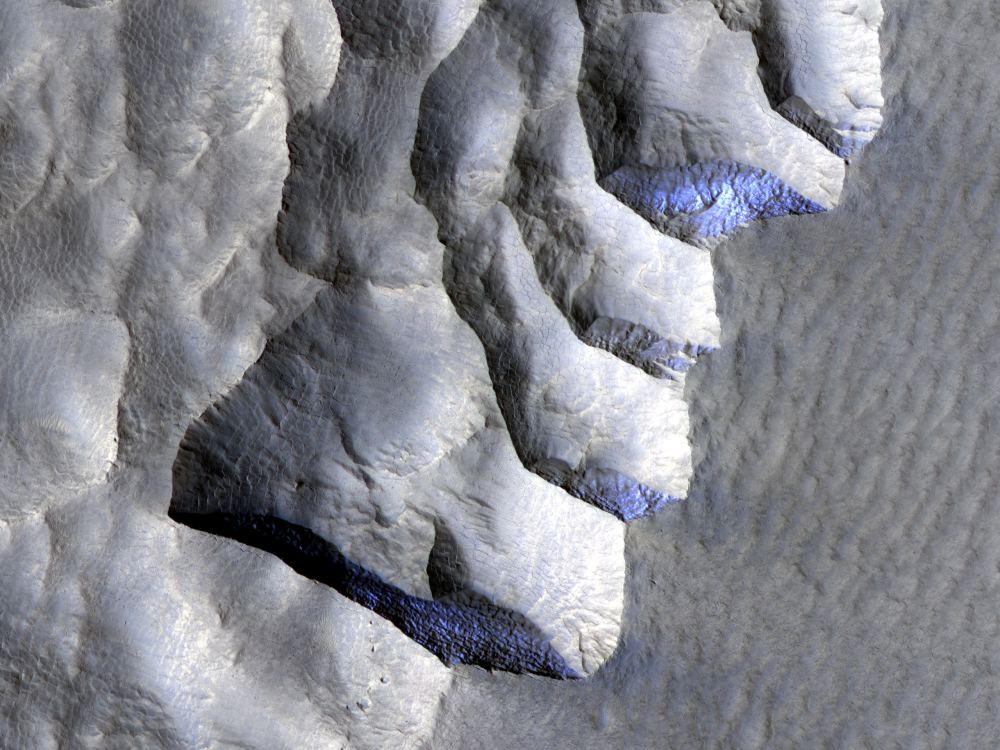
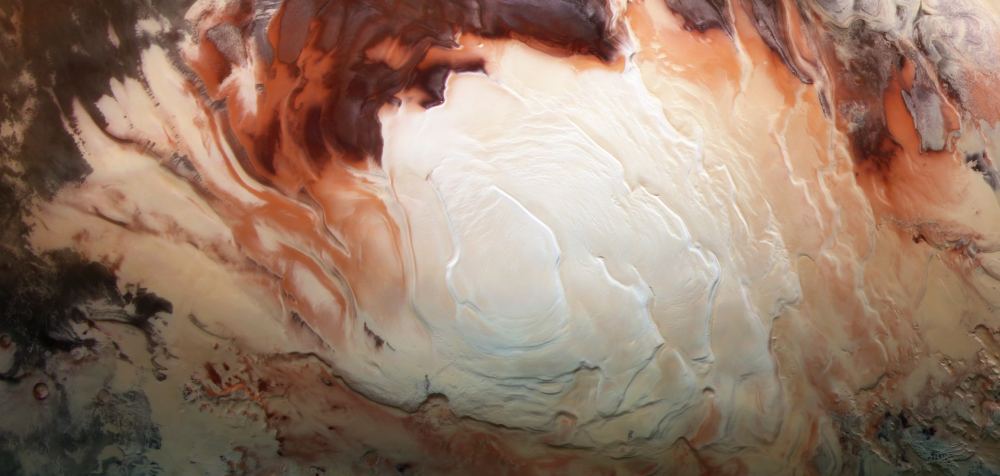
When planning crewed missions to Mars, the key phrase is “follow the water.” When astronauts set down on the Red Planet in the next decade, they will need access to water to meet their basic needs. Following the water is also crucial to our ongoing exploration of Mars and learning more about its past. While all of the water on the Martian surface exists as ice today (the majority locked away in the polar ice caps), it is now known that rivers, lakes, and an ocean covered much of the planet billions of years ago.
Determining where this water went is essential to learning how Mars underwent its historic transformation to become the dry and cold place it is today. Close to twenty years ago, the ESA’s Mars Express orbiter made a huge discovery when it detected what appeared to be a massive deposit of water ice beneath the southern polar region. However, recent findings by a team of researchers from Cornell University indicate that the radar reflections from the South Pole Layered Deposit (SPLD) may be the result of geological layering.
Continue reading “Underground Liquid Water Detected on Mars? Maybe not”