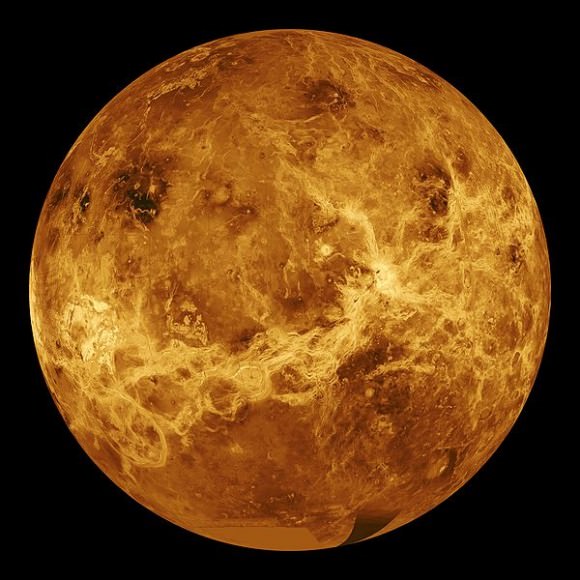
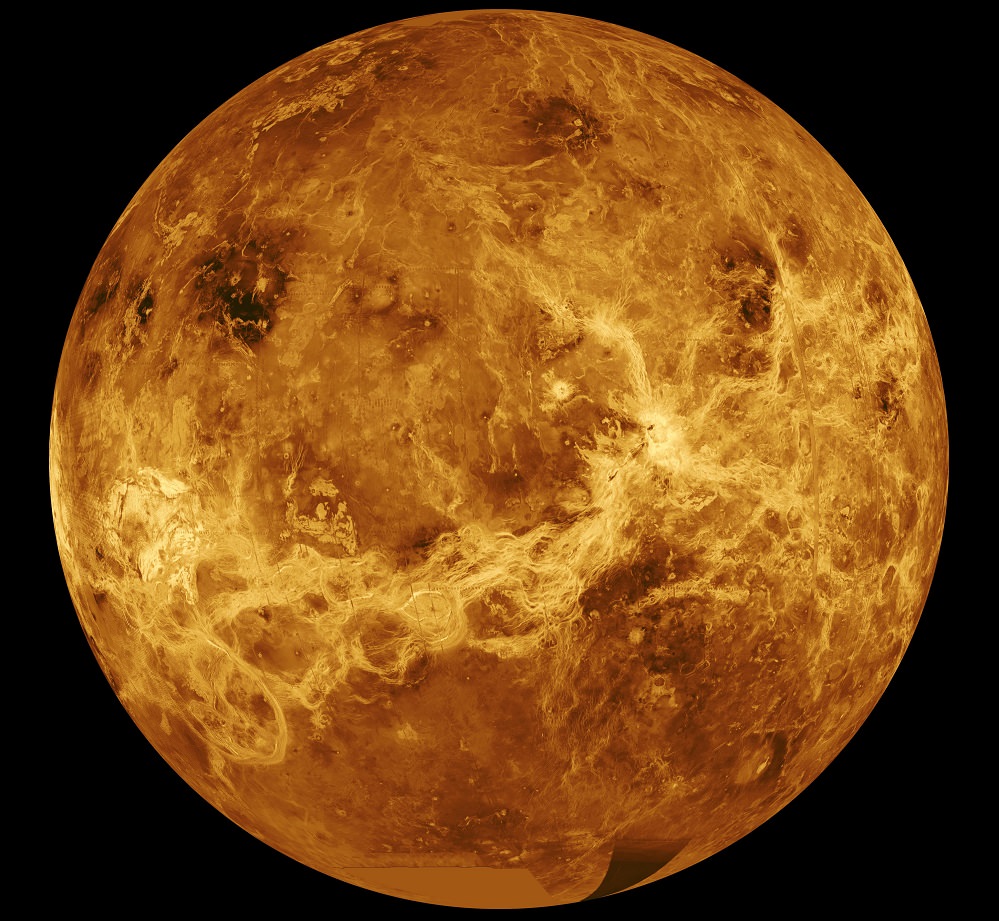
The first spacecraft to reach the surface of another world was the Soviet Venera 3 probe. Venera 3 crash-landed on the surface of Venus on March 1, 1966, 50 years ago. It was the 3rd in the series of Venera probes, but the first two never made it.
Venera 3 didn’t last long. It survived Venus’ blistering heat and crushing atmospheric pressure for only 57 minutes. But because of that 57 minutes, its place in history is cemented.
With a temperature of 462 degree C. (863 F.,) and a surface pressure 90 times greater than Earth’s, Venus’ atmosphere is the most hostile one in the Solar System. But Venus is still a tantalizing target for exploration, and rather than letting the difficult conditions deter them, Venus is a target that NASA thinks it can hit.
The Venus Landsail—called Zephyr—could be the first craft to survive the hostile environment on Venus. If approved, it would launch in 2023, and spend 50 days on the surface of Venus. But to do so, it has to meet several challenges.
NASA thinks they have the electronics that can withstand the heat, pressure, and corrosive atmosphere of Venus. Their development of sensors that can function inside jet engines proves this, and is the kind of breakthrough that really helps to advance space exploration. They also have solar cells that should function on the surface of Venus.
But the thick cloud cover will prevent the Zephyr’s solar cells from generating much electricity; certainly not enough for mobility. They needed another solution for traversing the surface of Venus: the land sail.
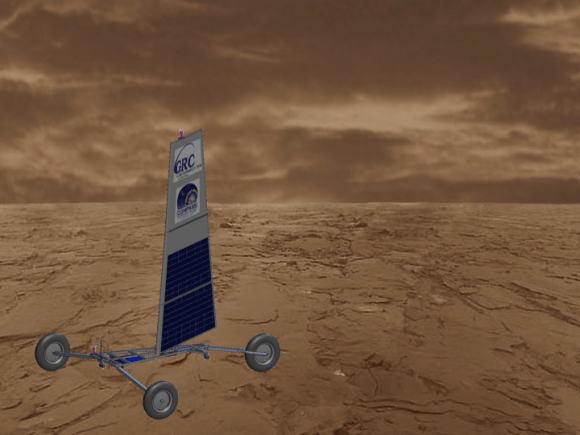
Venus has very slow winds—less than one meter per second—but the high density of the atmosphere means that even a slow wind will allow Zephyr to move effectively around the Venusian surface. But a land sail will only work on a surface without large rocks in the way. Thanks to the images of the surface of Venus sent back to Earth from the Venera probes, we know that a land sail will work, at least in some parts of the Venusian surface.
So Venus is back on the menu. With all the missions to other places in the Solar System, Venus is kind of forgotten, right here in our own backyard. But there’s actually a pretty rich history of missions to Venus, even though an extended visit to the surface has been out of reach. Since it’s been 50 years since Venera 3 reached the surface, now is a good time to look back at the history of the exploration of Venus.
The Soviet Union dominated the exploration of Venus. The Venera probes went all the way up to Venera 16, though some were orbiters rather than landers. From one perspective, the whole Venera program was plagued with problems. Many of the craft failed completely, or else had malfunctions that crippled them. But they still returned important information, and achieved many firsts, so the Venera program overall has to be considered a success.
The Soviet Union did not like to acknowledge or talk about space missions that failed. They often changed the name of a mission if it failed, so the names and numbers can get a little confusing.
Venera 4 was actually the first spacecraft to transmit any data from another world. On October 18th, 1967, it transmitted data from Venus’ atmosphere, but none from the surface. There were actually ten Venera missions before it, but most of them didn’t make it to Venus, suffering explosions or failing to leave Earth’s orbit and crashing back to the surface of Earth. Two of the Venera probes, numbers 1 and 2, suffered a loss of communications, so their fate is unknown.
After Venera 4’s relative success, there was another failed craft that fell back to Earth. Then on May 16th, 1969, Venera 5 successfully entered Venus’ atmosphere, and made it to within 26 kilometers of the surface before being crushed by the pressure. The next day—the Soviets often launched missions in pairs—Venera 6 entered the atmosphere of Venus and successfully transmitted data. It made it deeper into the atmosphere before being crushed within 11 kilometers of the surface.
Venera 7 was a successful mission. On December 15th, 1970, it landed on the surface of Venus and survived for 23 minutes. Venera 7 was the very first broadcast from the surface of another planet.
In 1972 Venera 8 survived for 50 minutes on the surface, followed by Venera 9 in 1975. Venera 9 survived for 53 minutes and sent back the first black and white images of the surface of Venus. Venera 10 landed 3 days after Venera 9 and survived 65 minutes, and also sent photos back. Grainy and blurry, but still amazing!


December 1978 saw the arrival of Venera 11 and 12, surviving 95 and 112 minutes respectively. Venera 11’s camera failed, but Venera 12 recorded what is thought to be lightning.
In March 1982, Venera 13 and 14 arrived. 13 took the first color images of the surface of Venus, and both craft took soil samples. Venera 15 and 16—both orbiters—arrived in 1983 and mapped the northern hemisphere.

The Soviet Unions final missions to Venus were Vega 1 and Vega 2, in 1985, which combined landings on Venus and flybys of Halley’s comet into each mission. Vega 1’s surface experiments failed, while Vega 2 transmitted data from the surface for 56 minutes.
The United States has also launched several mission to Venus, though none have been landers. Spacecraft in the Mariner series studied Venus from orbit and during flybys, sometimes getting quite close to the cloud tops.
In 1962 and 1967, Mariner 2 and 5 completed flybys of Venus and transmitted data back to Earth. Mariner 5 came as close as 4094 km of the surface. In February 1974, Mariner 10 approached Venus and came to within 5,768 km. It returned color images of Venus, and then used gravitational assist—the first spacecraft to ever do so—to propel itself to Mercury.
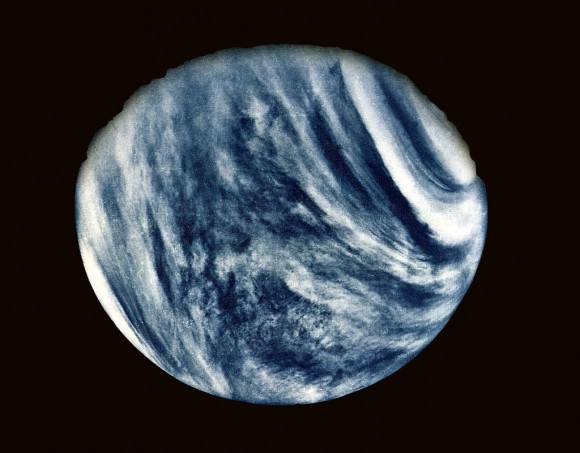
In December 1978, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter reached Venus and studied the atmosphere, surface, and other aspects of Venus. It lasted until August 1992, when its fuel ran out and it was destroyed when it entered the atmosphere.
On August 1990, the Magellan mission reached Venus and used radar to map the surface of the planet. On October 1994, Magellan entered the Venusian atmosphere and was destroyed, but not before successfully mapping over 99% of the planet’s surface.

Messenger was a NASA mission to Mercury that was launched in August 2004. It did two flybys of Venus, in October 2006 and June 2007.
The Venus Express, a European Space Agency mission, orbited Venus and studied the atmosphere and plasma of Venus. Of special interest to Venus Express was the study of what role greenhouse gases played in the formation of the atmosphere.
In 2010, the Japanese Space Agency launched Akatsuki, also known as the Venus Climate Orbiter. It’s role is to orbit Venus and study the atmospheric dynamics. It will also look for evidence of lightning and volcanic activity.
If there’s one thing that space exploration keeps teaching us, it’s to expect the unexpected. Who knows what we’ll find on Venus, if the Land Sail mission is approved, and it survives for its projected 50 days.