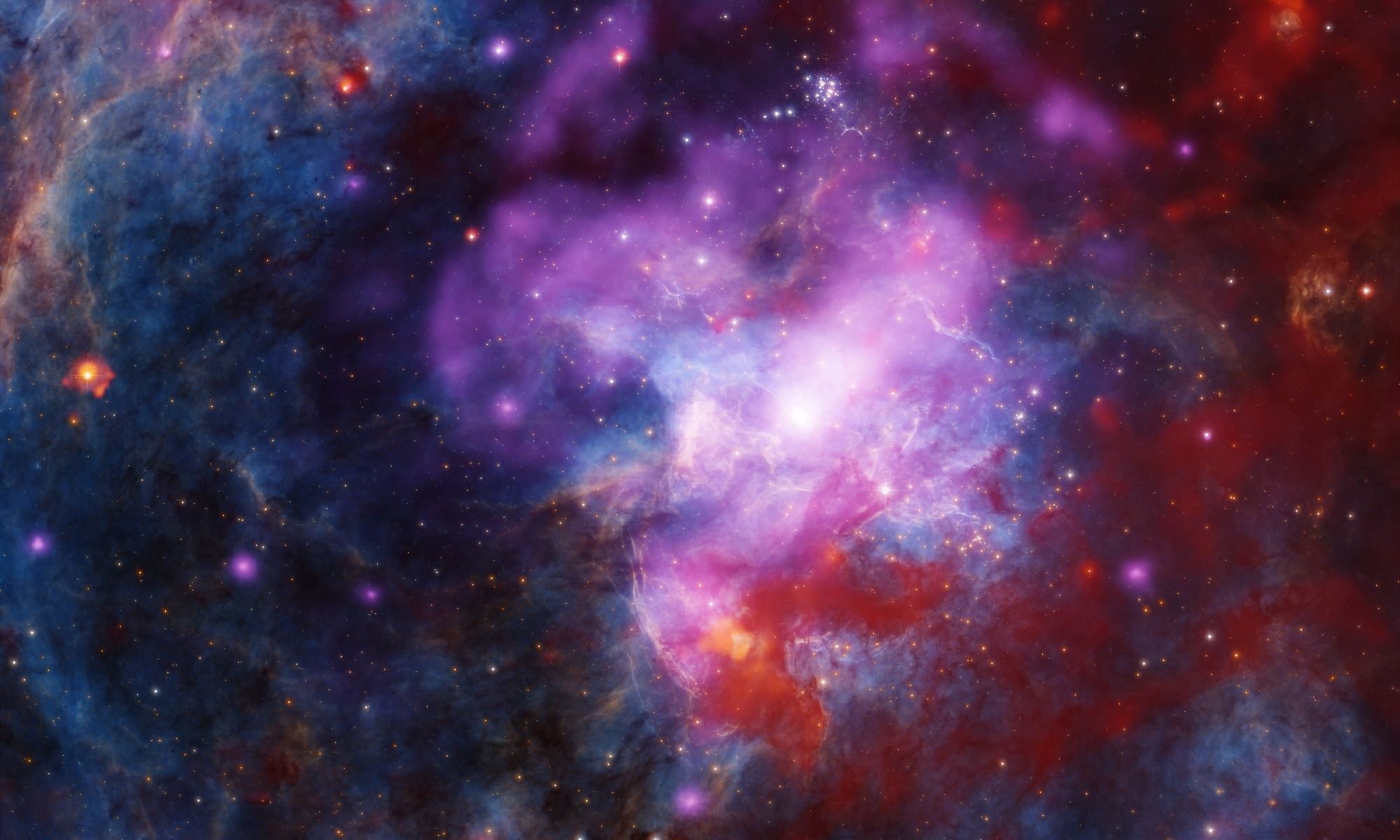
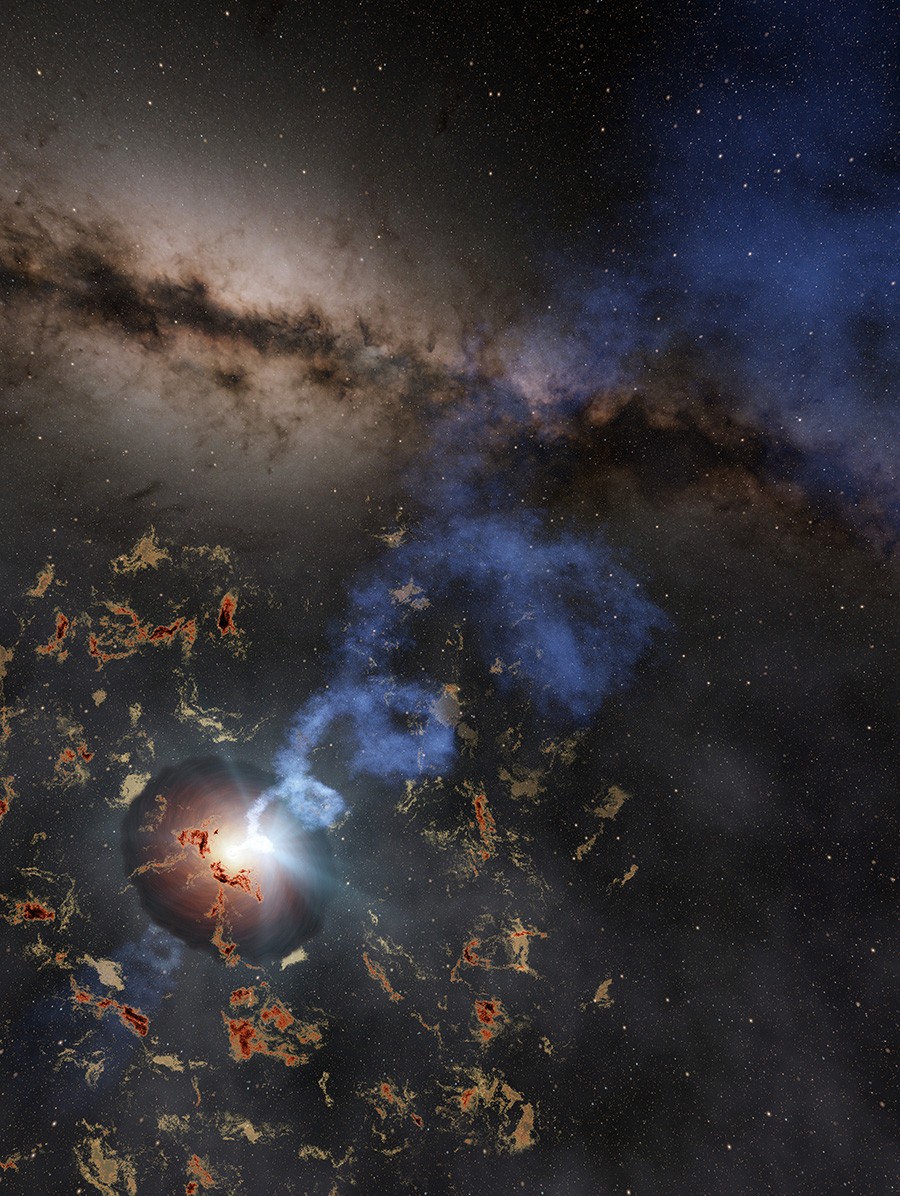
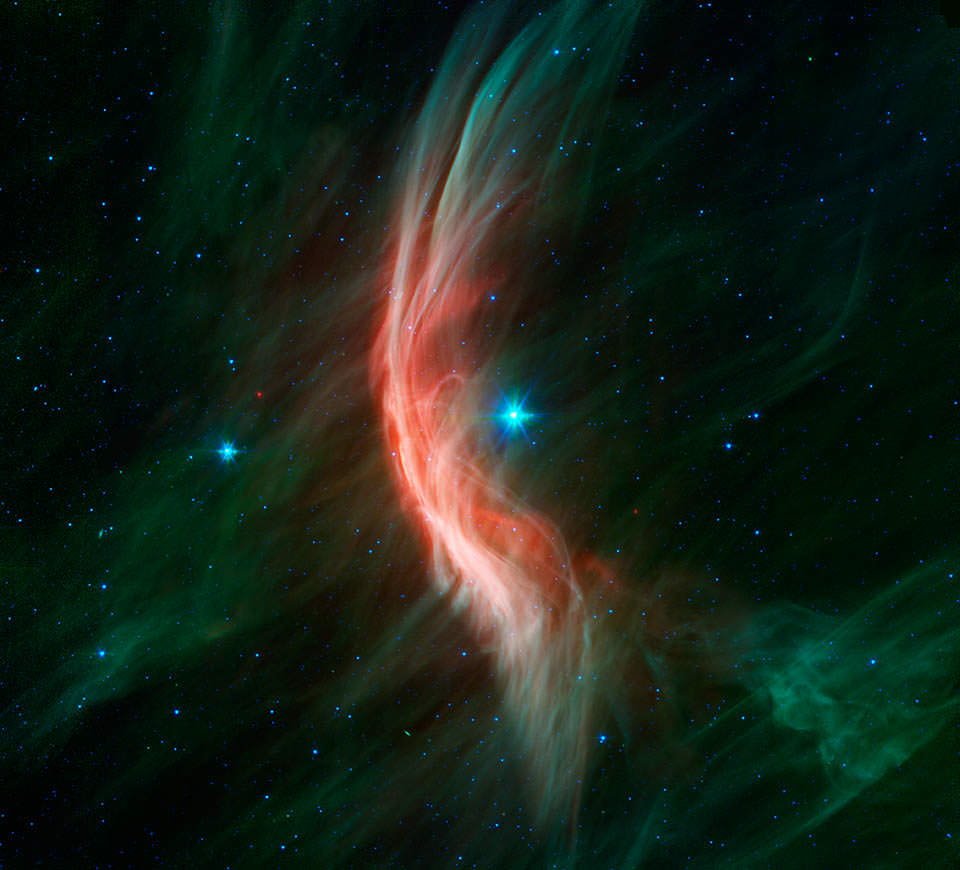
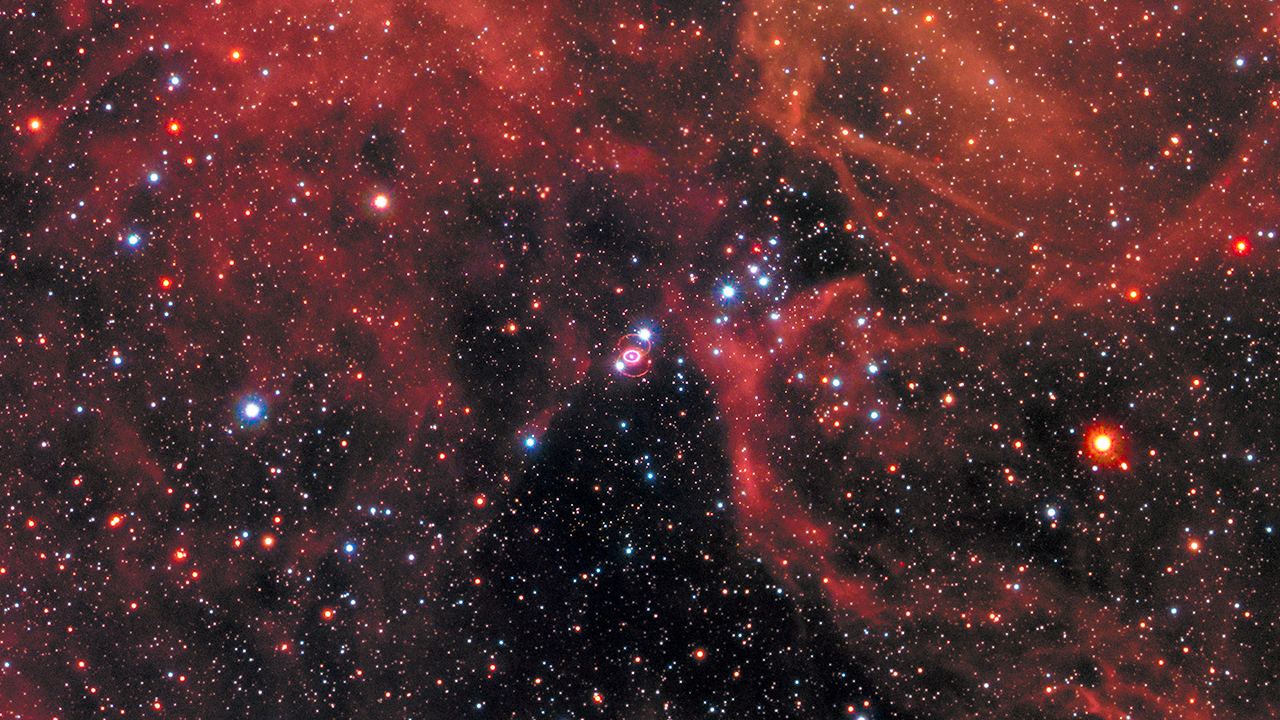
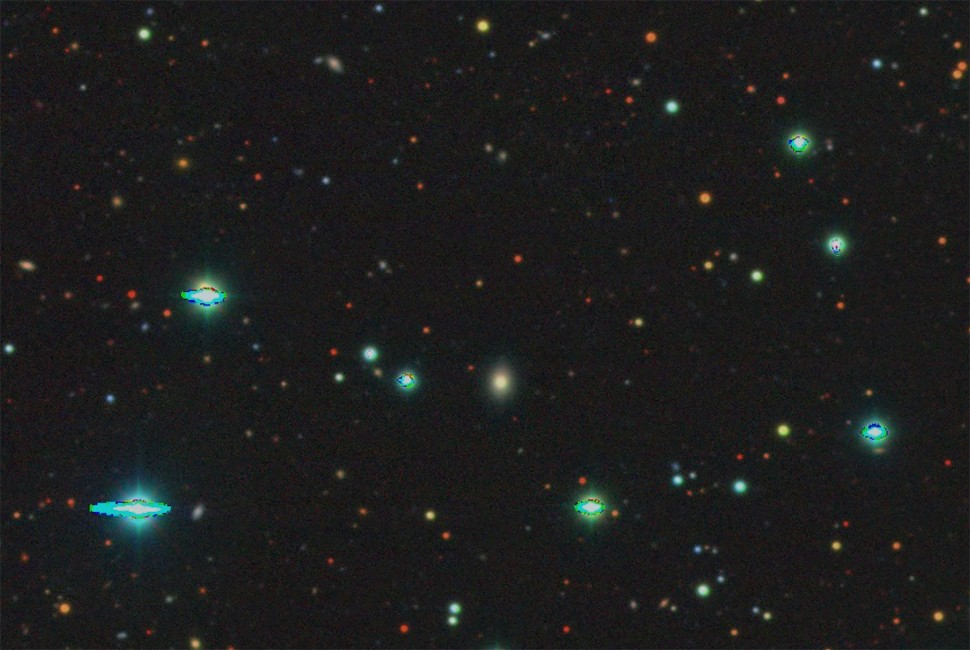
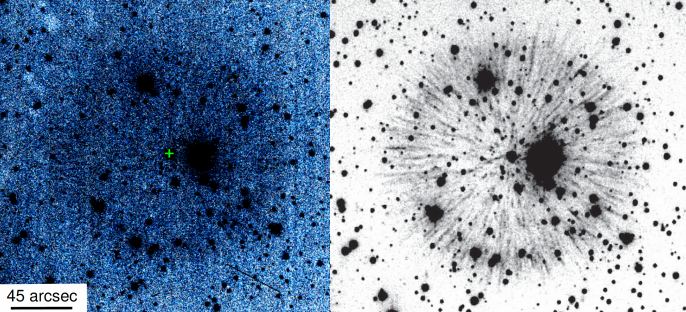
The key to astronomy is careful observation. Unlike many sciences, astronomers can’t often do their work in a lab. Sure, they can build space telescopes and large ground observatories, but even with tools as simple as sticks and stones astronomers were able to change our understanding of the Universe with patience and observation. That tradition still holds true today, as a recent study in The Astronomical Journal shows.
Continue reading “Multiple Supernova Remnants Merging in a Distant Nebula”Multiple Supernova Remnants Merging in a Distant Nebula