On October 19th, 2017, the Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System-1 (Pan-STARRS-1) in Hawaii announced the first-ever detection of an interstellar asteroid, named 1I/2017 U1 (aka. ‘Oumuamua). Based on subsequent measurements of its shape (highly elongated and thin), there was some speculation that it might actually be an interstellar spacecraft (the name “Rama” ring a bell?).
For this reason, there are those who would like to study this object before it heads back out into interstellar space. While groups like Project Lyra propose sending a mission to rendezvous with it, Breakthrough Initiatives (BI) also announced its plans to study the object using Breakthrough Listen. As part of its mission to search for extra-terrestrial communications, this project will use the Greenbank Radio Telescope to listen to ‘Oumuamua for signs of radio transmissions.
Observations of ‘Oumuamua’s orbit revealed that it made its closest pass to our Sun back in September of 2017, and has been on its way back to interstellar space ever since. When it was observed back in October, it was passing Earth at a distance of about 85 times the distance between Earth and the Moon, and was traveling at a peak velocity of about 315,430 km/h (196,000 mph).
This indicated that, unlike the many Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) that periodically cross Earth’s orbit, this asteroid was not gravitationally bound to the Sun. In November, astronomers using the ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) at the Paranal Observatory in Chile were also able to determine the brightness and color of the asteroid, which allowed for precise calculations of its size and shape.
Basically, they determined that it was 400 meters (1312 ft) long and very narrow, indicating that it was shaped somewhat like a cigar. What’s more, the idea of a cigar or needle-shaped spacecraft is a time-honored concept when it comes to science fiction and space exploration. Such a ship would minimize friction and damage from interstellar gas and dust, and could rotate to provide artificial gravity.
For all of these reasons, it is understandable why some responded to news of this asteroid by making comparisons to a certain science fiction novel. That would be Arthur C. Clarke’s Rendezvous with Rama, a story of a cylindrical space ship that travels through the Solar System while on its way to another star. While a natural origin is the more likely scenario, there is no consensus on what the origin this object might be – other than the theory that it came from the direction of Vega.
Hence why Breakthrough Listen intends to explore ‘Oumuamua to determine whether it is truly an asteroid or an artifact. Established in January of 2016, Listen is the largest scientific research program aimed at finding evidence of extra-terrestrial intelligence with established SETI methods. These include using radio observatories to survey 1,000,000 of the closest stars (and 100 of the closest galaxies) to Earth over the course of ten years.

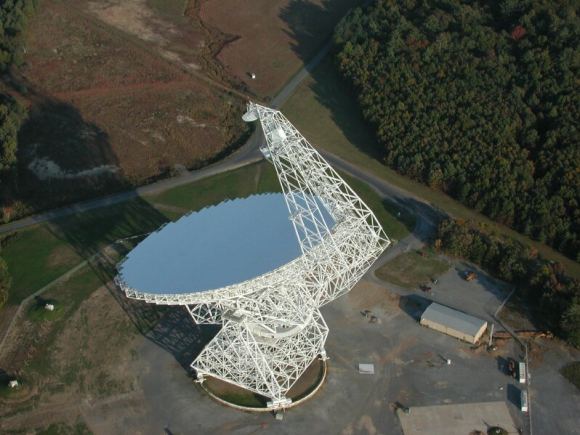
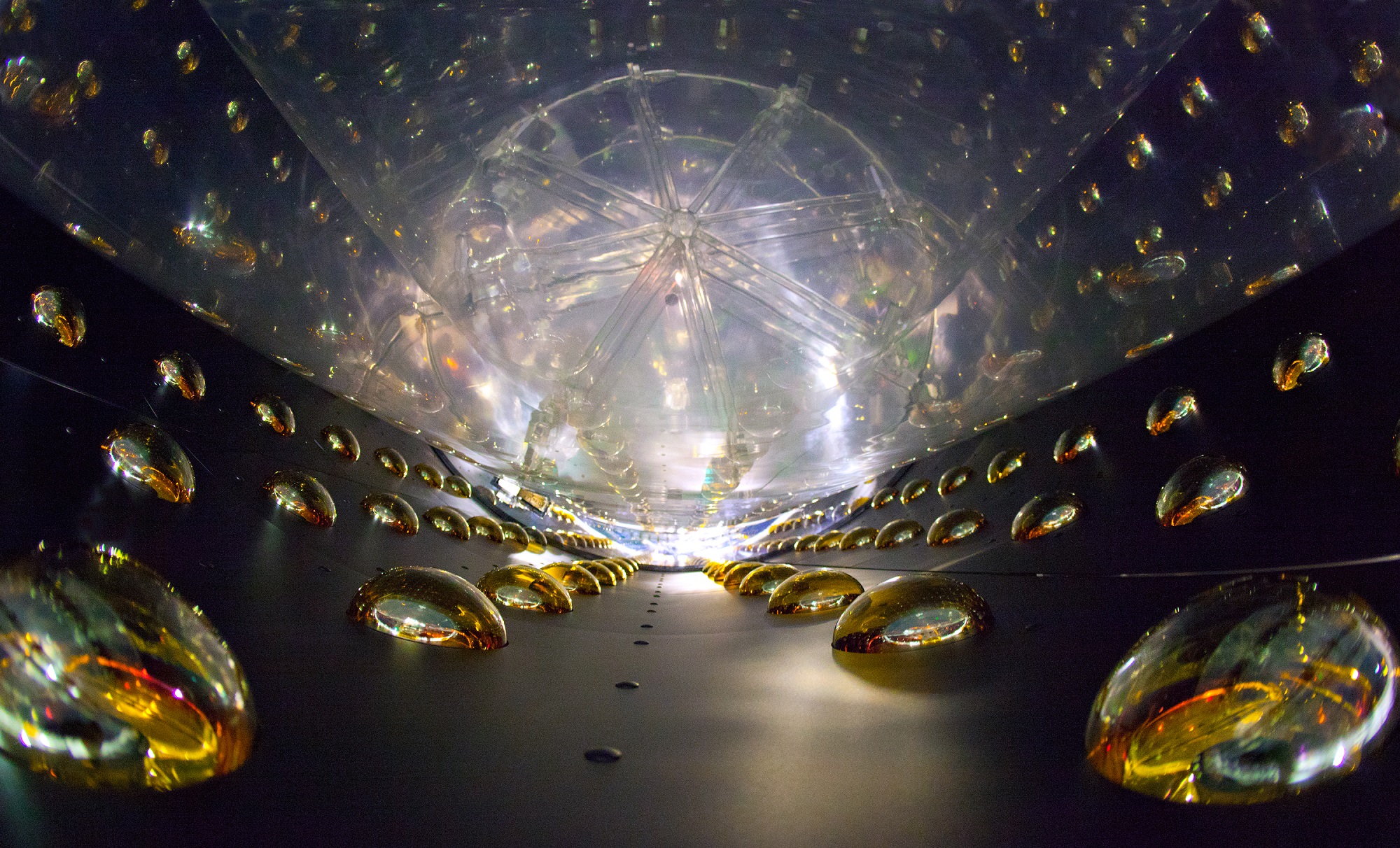
Listen’s observation campaign will begin on Wednesday, December 13th, at 3:00 pm EST (12:00 PST), using the Greenbank Radio Telescope. This 100-meter telescope is the world’s premiere single-dish radio telescope and is capable of operating at millimeter and submillimeter wavelengths. It is also the mainstay of the NSF-funded Green Bank Observatory, located in West Virginia.
The first phase of observations will last a total of 10 hours, ranging from the 1 to 12 GHz bands, and will broken down into four “epochs” (based on the object’s rotational period). At present, ‘Oumuamua is about 2 astronomical units (AUs) – or 299,200,000 km; 185,900,000 mi – away from Earth, putting it at twice the distance between the Earth and the Sun. This places it well beyond the orbit of Mars, and over halfway between Mars and Jupiter.
At this distance, the Green Bank Telescope will take less than a minute to detect an omni-directional transmitter with the power of a cellphone. In other words, if there is a alien signal coming from this object, Breakthrough Listen is sure to sniff it out in no time! As Andrew Siemion, Director of Berkeley SETI Research Center and a member of Breakthrough Listen, explained in a BI press statement:
“‘Oumuamua’s presence within our solar system affords Breakthrough Listen an opportunity to reach unprecedented sensitivities to possible artificial transmitters and demonstrate our ability to track nearby, fast-moving objects. Whether this object turns out to be artificial or natural, it’s a great target for Listen.”
Even if there are no signals to be heard, and no other evidence of extra-terrestrial intelligence is detected, the observations themselves are a opportunity for scientists and the field of radio astronomy in general. The project will observe ‘Oumuamua in portions of the radio spectrum that it has not yet been observed at, and is expected to yield information about the possibility of water ice or the presence of a “coma” (i.e. gaseous envelop) around the object.
During the previous survey, data gathered using the VLT’s FOcal Reducer and low dispersion Spectrograph (FORS) indicated that ‘Oumuamua was likely a dense and rocky asteroid with a high metal content and little in the way of water ice. Updated information provided by the Greenbank Telescope could therefore confirm or cast doubt on this, thus reopening the possibility that it is actually a comet.
Regardless of what it finds, this survey is likely to be a feather in the cap of Breakthrough Listen, which already demonstrated it’s worth in terms of non-SETI astronomy this past summer. At that time, and using the Green Bank Radio Telescope, the Listen science team at UC Berkeley observed 15 Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) for the fist time coming from a dwarf galaxy three billion light-years from Earth.
Still, I think we can all agree that an extra-terrestrial spaceship would be the most exciting possibility (and perhaps the most frightening!). And it is very safe to say that some of us will be awaiting the results of the survey with baited breath. Luckily, we’ll only have to wait two more days to see if humanity is still alone in the Universe or not! Stay tuned!
Further Reading: Breakthrough Initiatives