On October 5th, 2017, Vice President Mike Pence announced the Trump administration’s plan to return astronauts to the Moon. Looking to the long-term, NASA and several other space agencies are also intent on establishing a permanent lunar base there. This base will not only provide opportunities for lunar science, but will facilitate missions to Mars and beyond.
The only question is, where should such a base be built? For many years, NASA, the ESA and other agencies have been exploring the possibility of stable lava tubes as a potential site. According to new study by a team of international scientists, the presence of such a tube has now been confirmed in the Marius Hills region. This location is likely to be the site of future lunar missions, and could even be the site of a future lunar habitat.
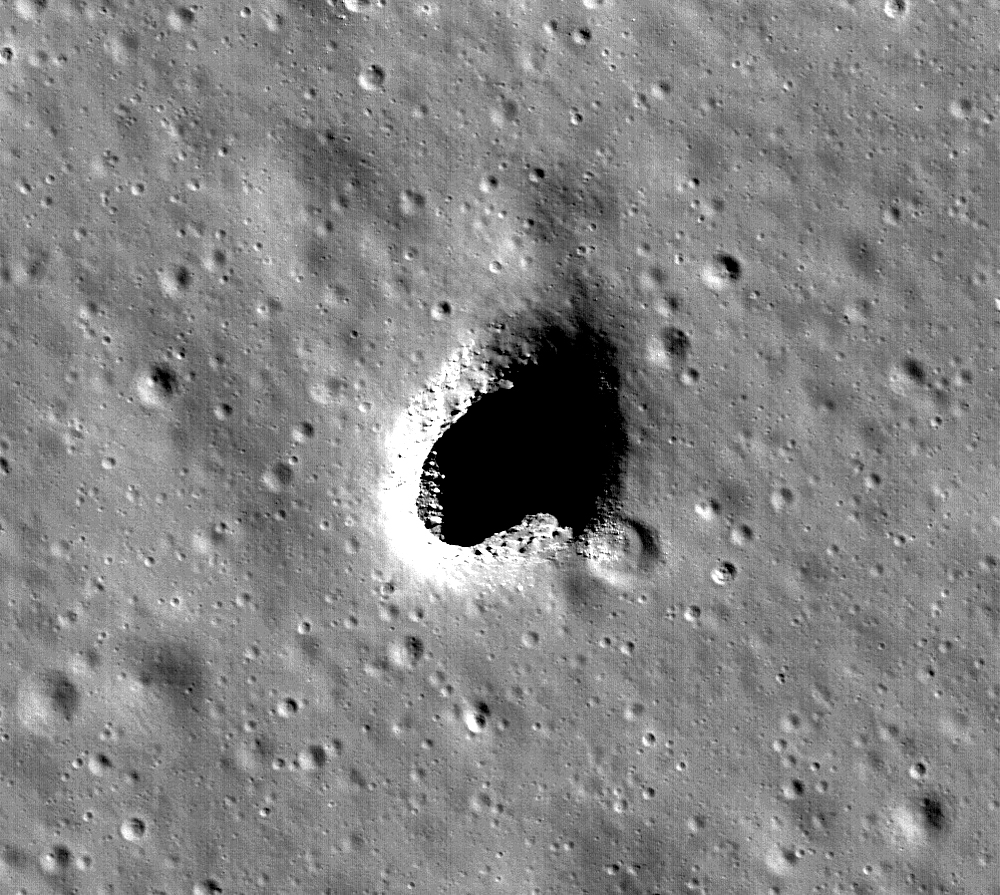
In 2009, data provided by the Terrain Camera aboard JAXA’s SELENE spacecraft indicated the presence of three huge pits on the Moon. These pits (aka. “skylights”) were of particular interest since they were seen as possible openings to subsurface lava channels. Since then, the Marius Hills region (where they were found) has been a focal point for astronomers and planetary scientists hoping to confirm the existence of lava tubes.

The recent study, titled “Detection of intact lava tubes at Marius Hills on the Moon by SELENE (Kaguya) Lunar Radar Sounder“, recently appeared in the journal Geophysical Research Letters. The team consisted of members from JAXA’s Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), Purdue University, the University of Alabama, AstroLabs, the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NOAJ) and multiple Japanese Universities.
Together, they examined data from the SELENE mission’s Lunar Radar Sounder (LRS) from locations that were close to the Marius Hills Hole (MHH) to determine if the region hosted stable lava tubes. Such tubes are a remnant from the Moon’s past, when it was still volcanically active. These underground channels are believed to be an ideal location for a lunar colony, and for several reasons.
For starters, their thick roofs would provide natural shielding from solar radiation, cosmic rays, meteoric impacts, and the Moon’s extremes in temperature. These tubes, once enclosed, could also be pressurized to create a breathable environment. As such, finding an entrance to a stable lava tube would the first step towards selecting a possible site for such a colony.
As Junichi Haruyama, a senior researcher at JAXA and one of the co-authors on the study, explained in a University of Purdue press release:
“It’s important to know where and how big lunar lava tubes are if we’re ever going to construct a lunar base. But knowing these things is also important for basic science. We might get new types of rock samples, heat flow data and lunar quake observation data.”

Granted, the LRS was not specifically designed to detect lava tubes, but to characterize the origins of the Moon and its geologic evolution. For this reason, it did not fly close enough to the Moon to obtain extremely accurate information on the subsurface. Nevertheless, as SELENE passed near the Marius Hills Hole, the instrument picked up a distinctive echo pattern.
This pattern was characterized by a decrease in echo power followed by a large second echo peak. These two echoes correspond to radar reflections from the Moon’s surface, as well as the floor and ceiling of the open lava tube. When they analyzed this pattern, the research team interpreted it is evidence of a tube. They found similar echo patterns at several locations around the hole, which could indicate that there is more than one lava tube in the region.
To confirm their findings, the team also consulted data from NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission. Consisting of two spacecraft, this collaborative effort collected high-quality data on the Moon’s gravitational field between 2011 and 2012. By using GRAIL data that identified mass deficits under the surface, which are evidence of caverns, the team was able to narrow down their search.
Jay Melosh, a GRAIL co-investigator and Distinguished Professor of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences at Purdue University, was also a co-author on the paper. As he explained:
“They knew about the skylight in the Marius Hills, but they didn’t have any idea how far that underground cavity might have gone. Our group at Purdue used the gravity data over that area to infer that the opening was part of a larger system. By using this complimentary technique of radar, they were able to figure out how deep and high the cavities are.”

On Earth, stable lava tubes have been found that can extend for dozens of kilometers. To date, the longest and deepest to be discovered is the Kazumura Cave in Hawaii, which is over a kilometer (3,614 feet) deep and 65.5 km (40.7 mi) long. On the Moon, however, lava tubes are much larger, due to the fact that the Moon has only a fraction of the Earth’s gravity (0.1654 g to be exact).
For a lava tube to be detecting using gravity data, it would need to be several kilometers in length and at least one kilometer in height and width. Since the tube in Marius Hills was detectable, it is likely big enough to house a major city. In fact, during a presentation at the 47th Lunar and Planetary Conference, researchers from Purdue University showed GRAIL data that indicated how the tube beneath the MHH could be large enough to house Philadelphia.
This most recent study was also the subject of a presentation at the 48th Lunar and Planetary Conference. Similar evidence of possible stable lava tubes in the Sea of Tranquility was also obtained by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) back in 2010. However, this latest combination of radar and gravity data has provided the clearest picture yet of what a stable lava tube looks like.
Similar evidence of lava tubes has also been discovered on Mars, and possible even Mercury. On Mars in particular, chains of pit craters, broad lava fans, skylights and partially collapsed lava tubes all indicate the presence of stable tubes. Based on this latest study, future mission to the Red Planet (which could include the creation of a habitat) might also entail the investigation of these features.
In fact, lava tubes could become the means through which a human presence is established throughout the Solar System someday!
Further Reading: Purdue University, Geophysical Research Letters