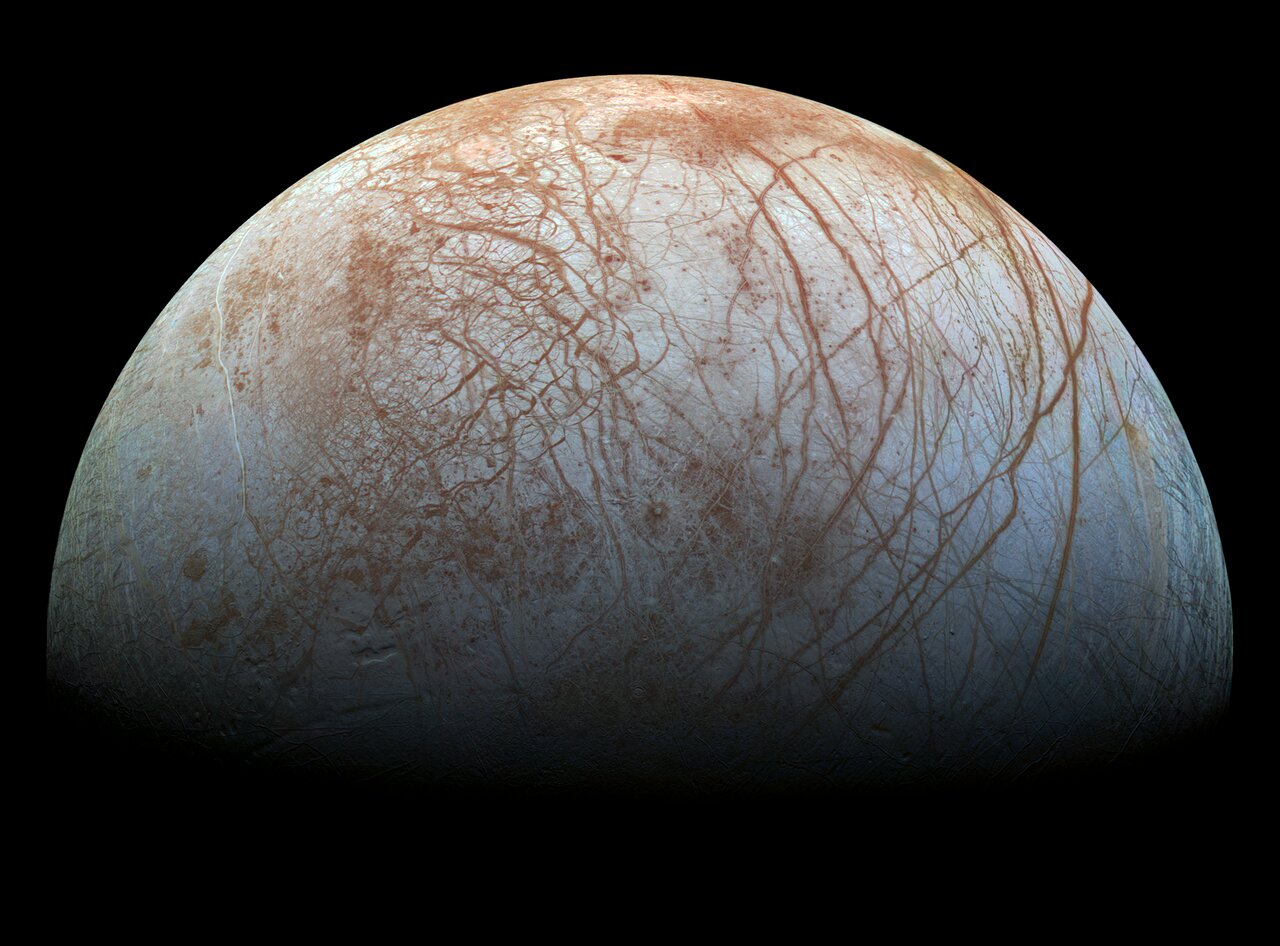
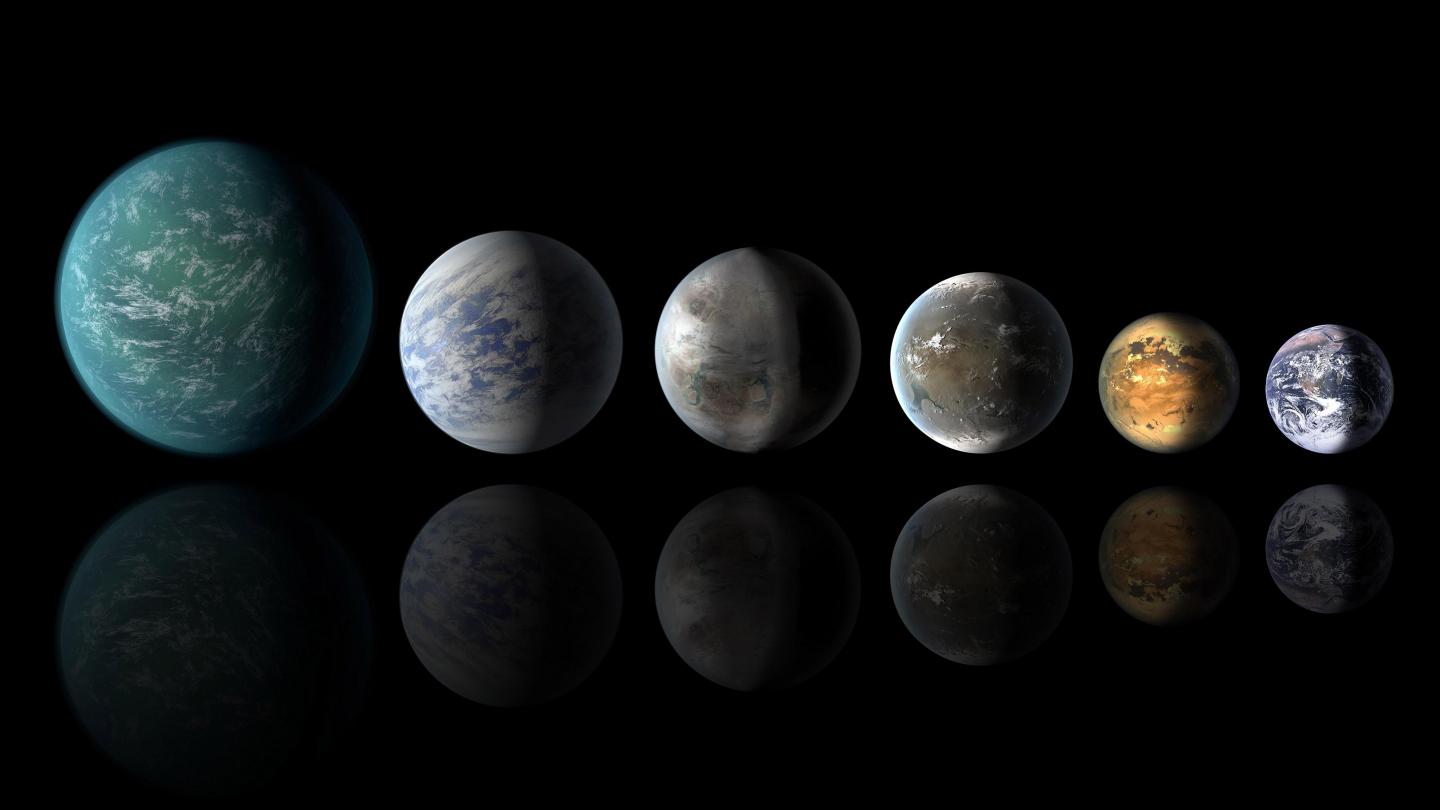
Evolution has produced a wondrously diverse variety of lifeforms here on Earth. It just so happens that talking primates with opposable thumbs rose to the top and are building a spacefaring civilization. And we’re land-dwellers. But what about other planets? If the dominant species on an ocean world builds a technological civilization of some sort, would they be able to escape their ocean home and explore space?
Continue reading “Some Intelligent Civilizations Will Be Trapped on their Worlds”Some Intelligent Civilizations Will Be Trapped on their Worlds