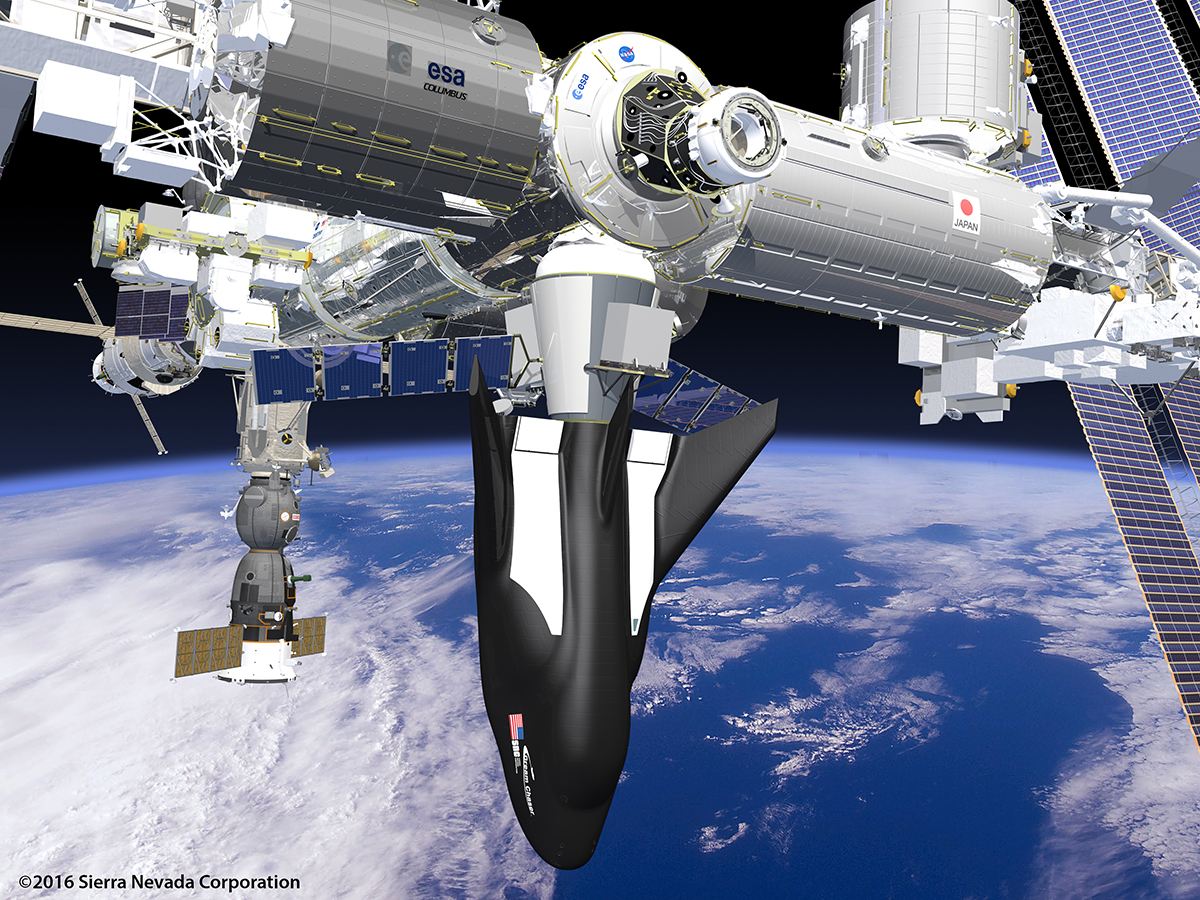
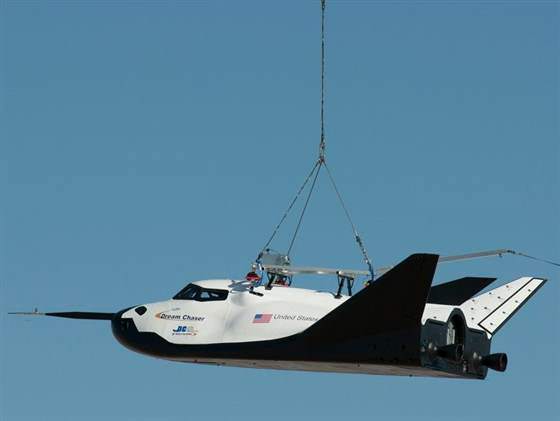
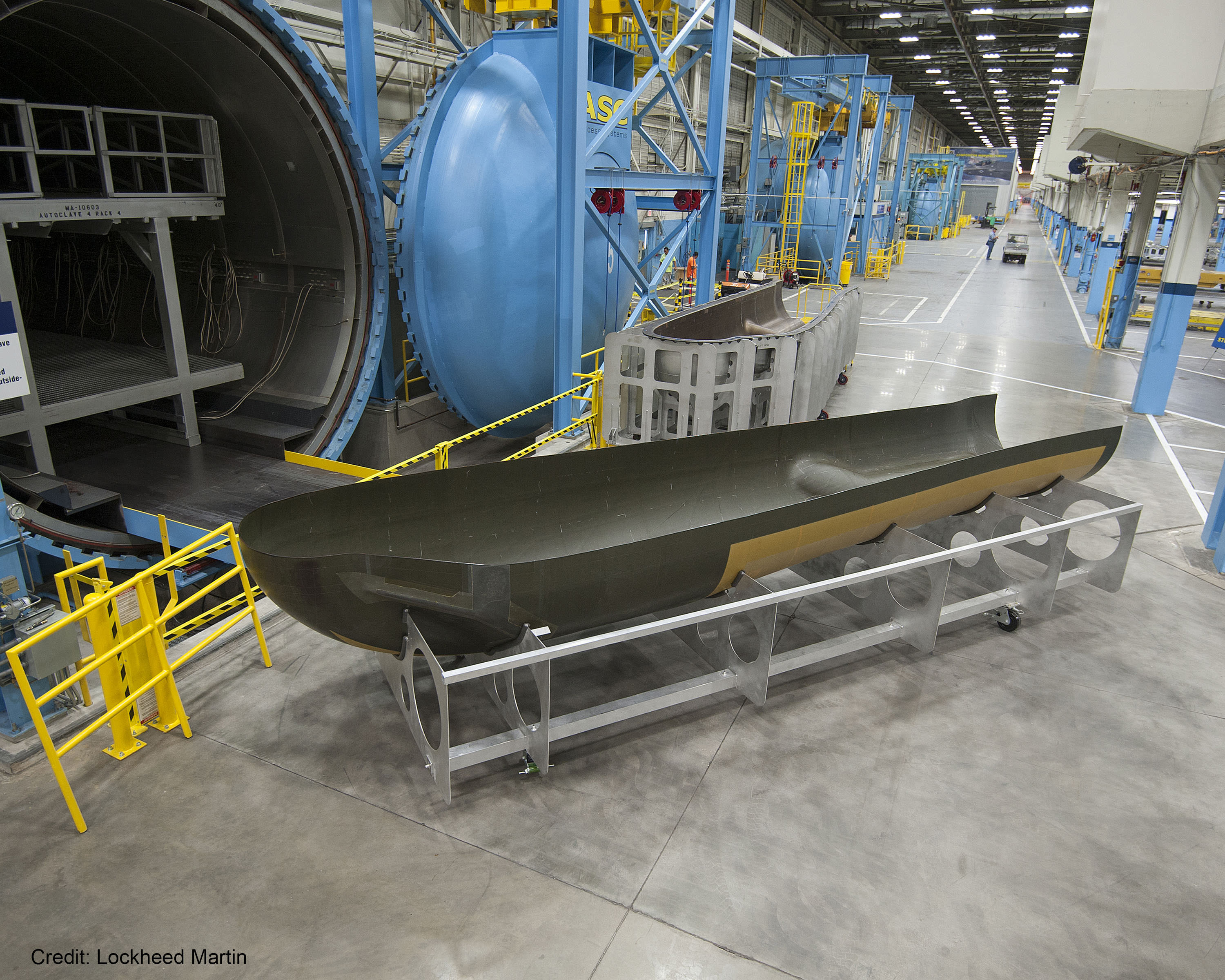
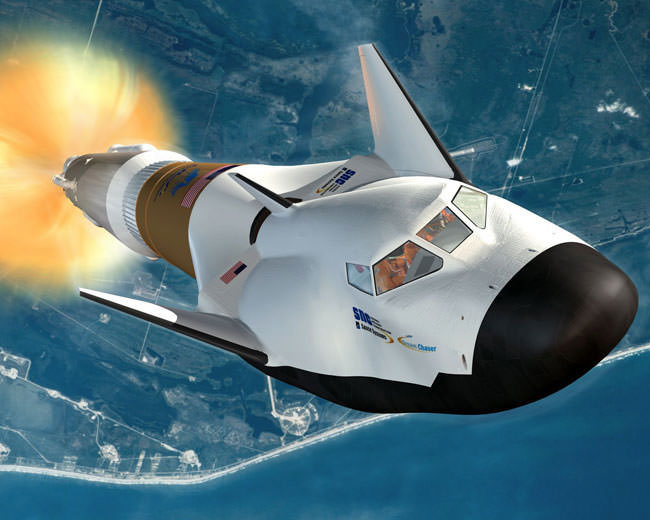
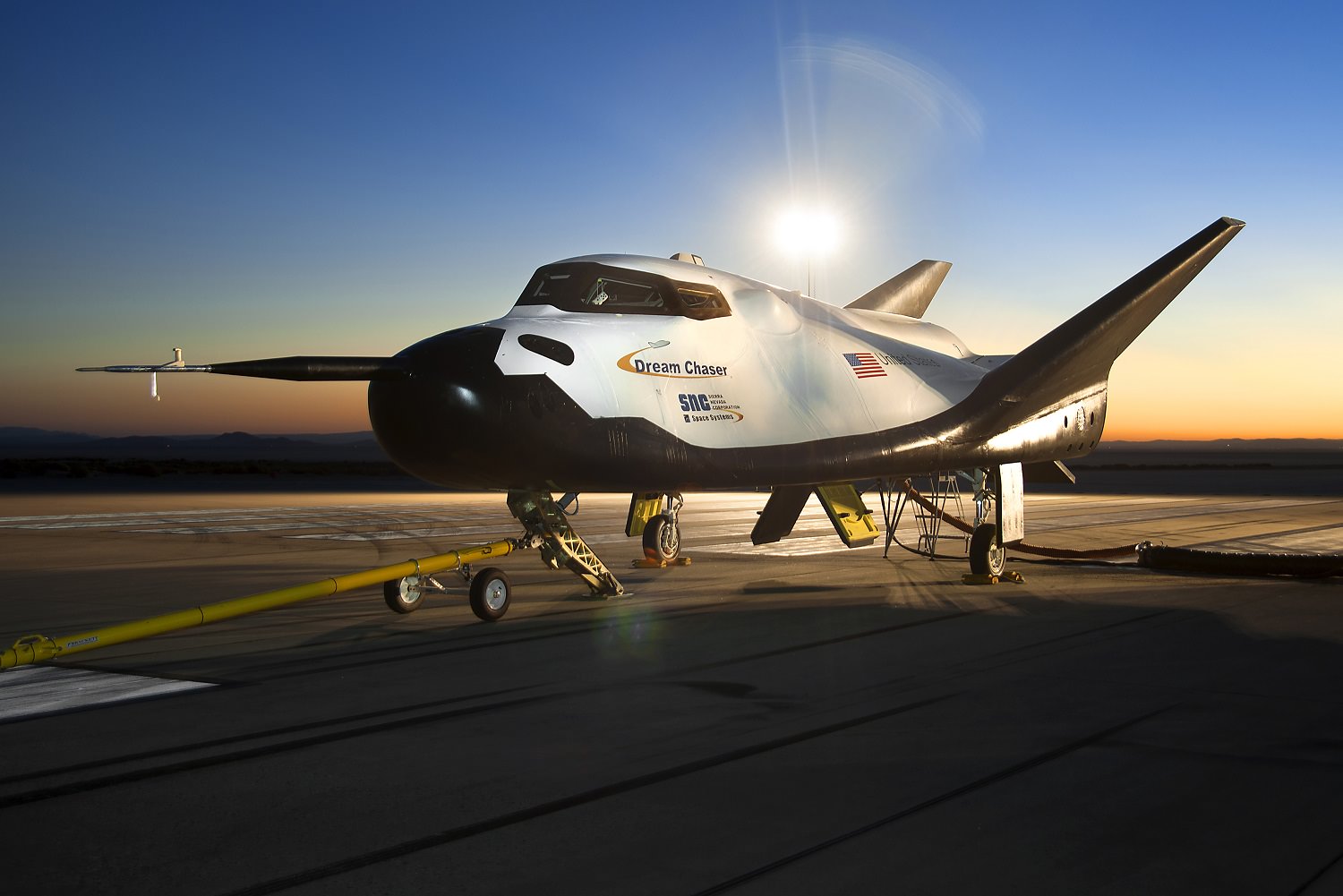
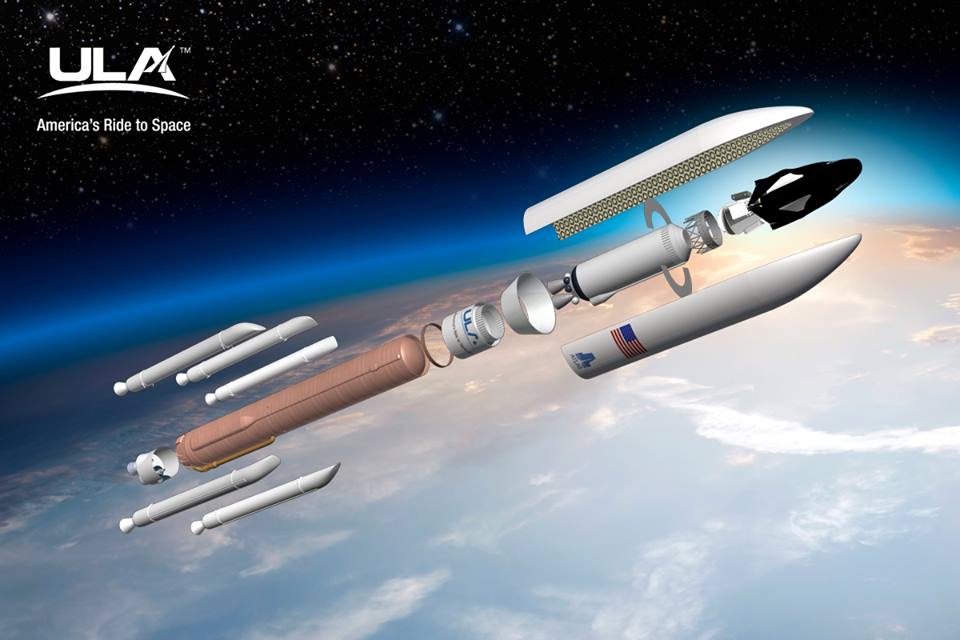
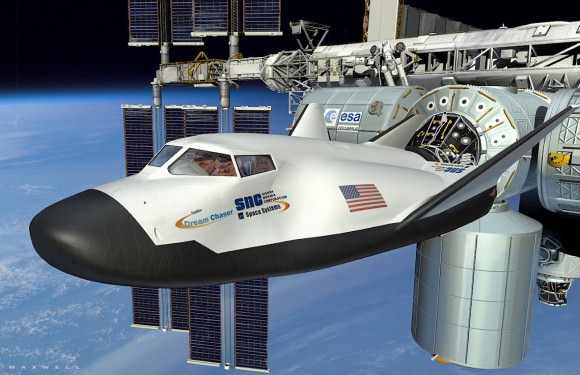
It’s called the Dream Chaser, a reusable spaceplane that will one day transport cargo and crews to the International Space Station. For the past ten years, the Sierra Nevada Corporation and NASA have been developing and testing this next-generation space vehicle. When it is ready, this vehicle will not only provide a more cost-effective way of servicing the ISS, it will also help restore domestic launch capability to the United States.
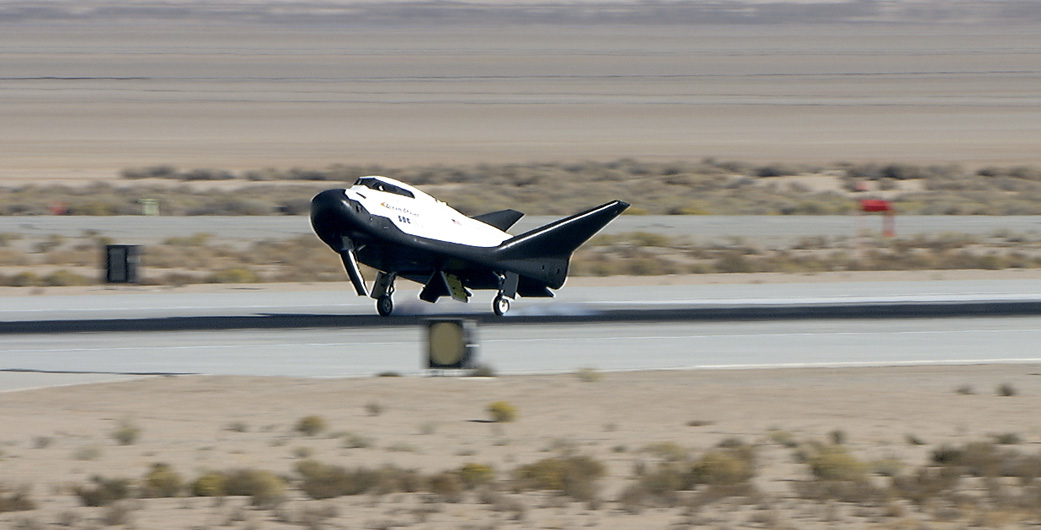
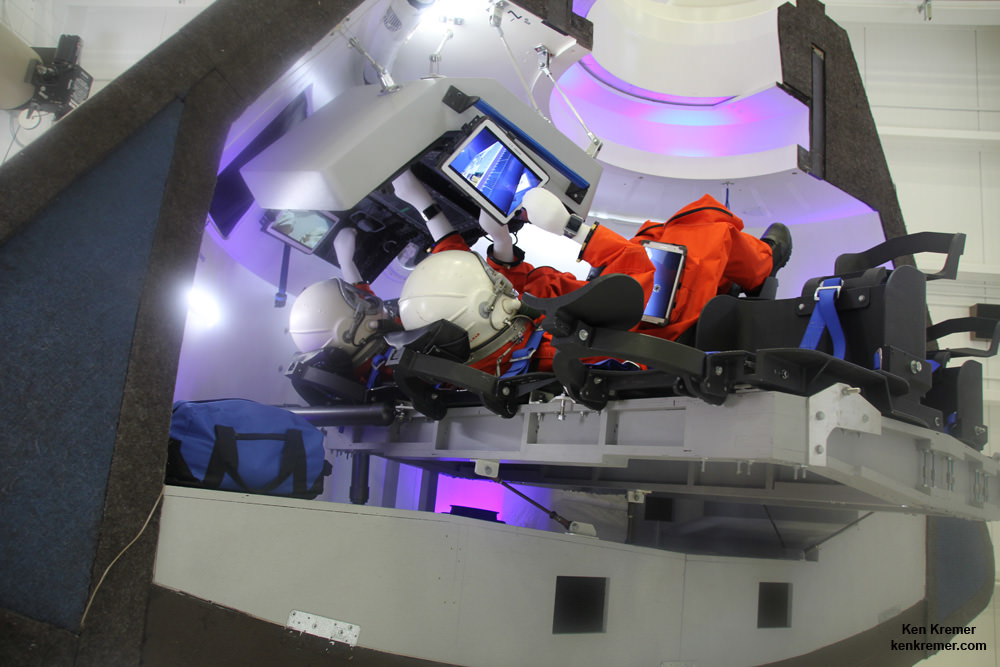
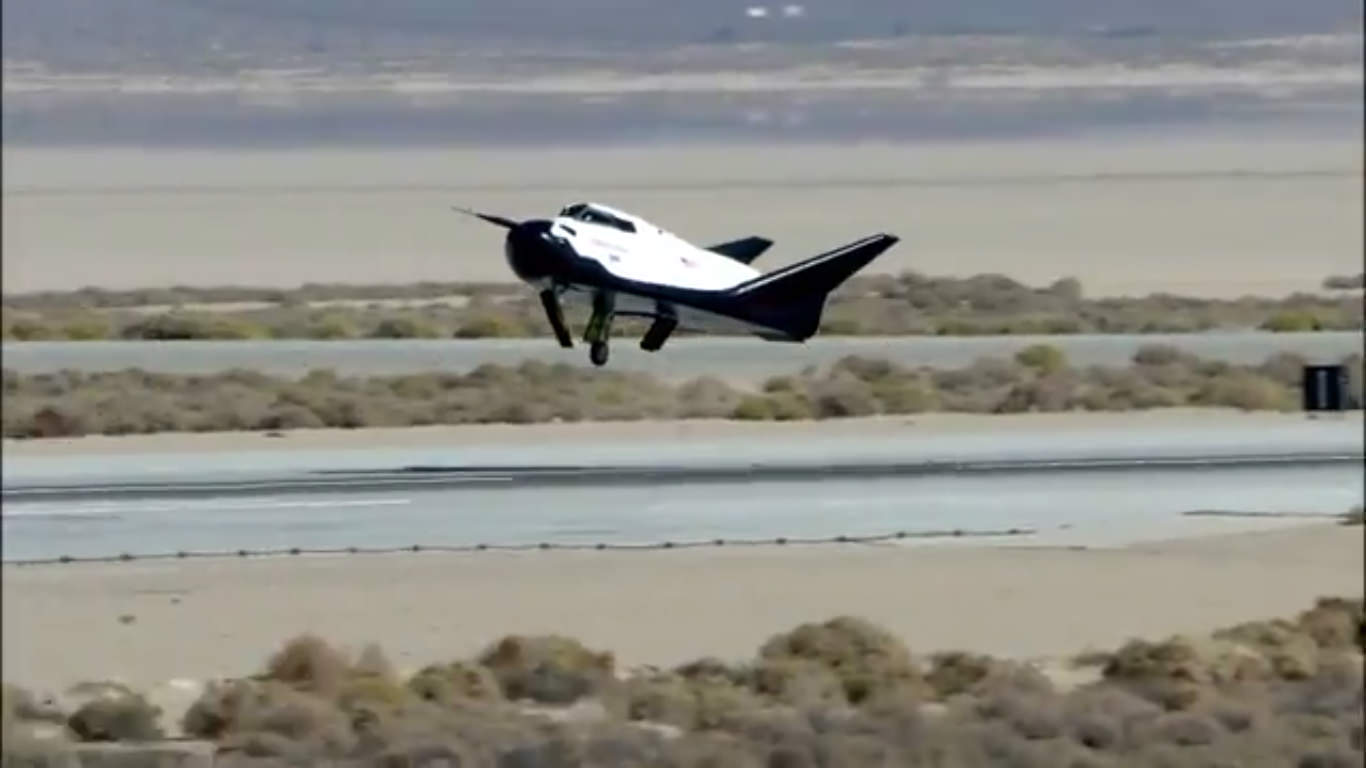
On Saturday, November 11th, the Dream Chaser passed an important milestone by conducting a successful free flight test. This took place at Edwards Air Force Base in California, and verified the spaceplane’s ability to glide and land autonomously. This, in addition to verifying several key avionic and flight systems, is a strong indication that the spaceplane will be capable of conducting runs to and from Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) in the near future.
This test involved the spaceplane being lifted to an altitude of 3,780 meters (12,400 feet) and then let go to glide freely. It then deployed its landing gears and touched down on the Edwards Air Force Base runway before coming to a full stop. This runway, it should be noted, is very similar to the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility runway that the Dream Chaser will land on once it is operational.
https://vimeo.com/242615668
This flight test validated the performance of the Dream Chaser during what is arguably the most critical part of a mission – the approach and landing phase – which will be the final phase of future flights from the ISS. The ability to conduct automated landings is central to the spaceplane’s reusability, which operates in much the same way as the now-retired Space Shuttle did.
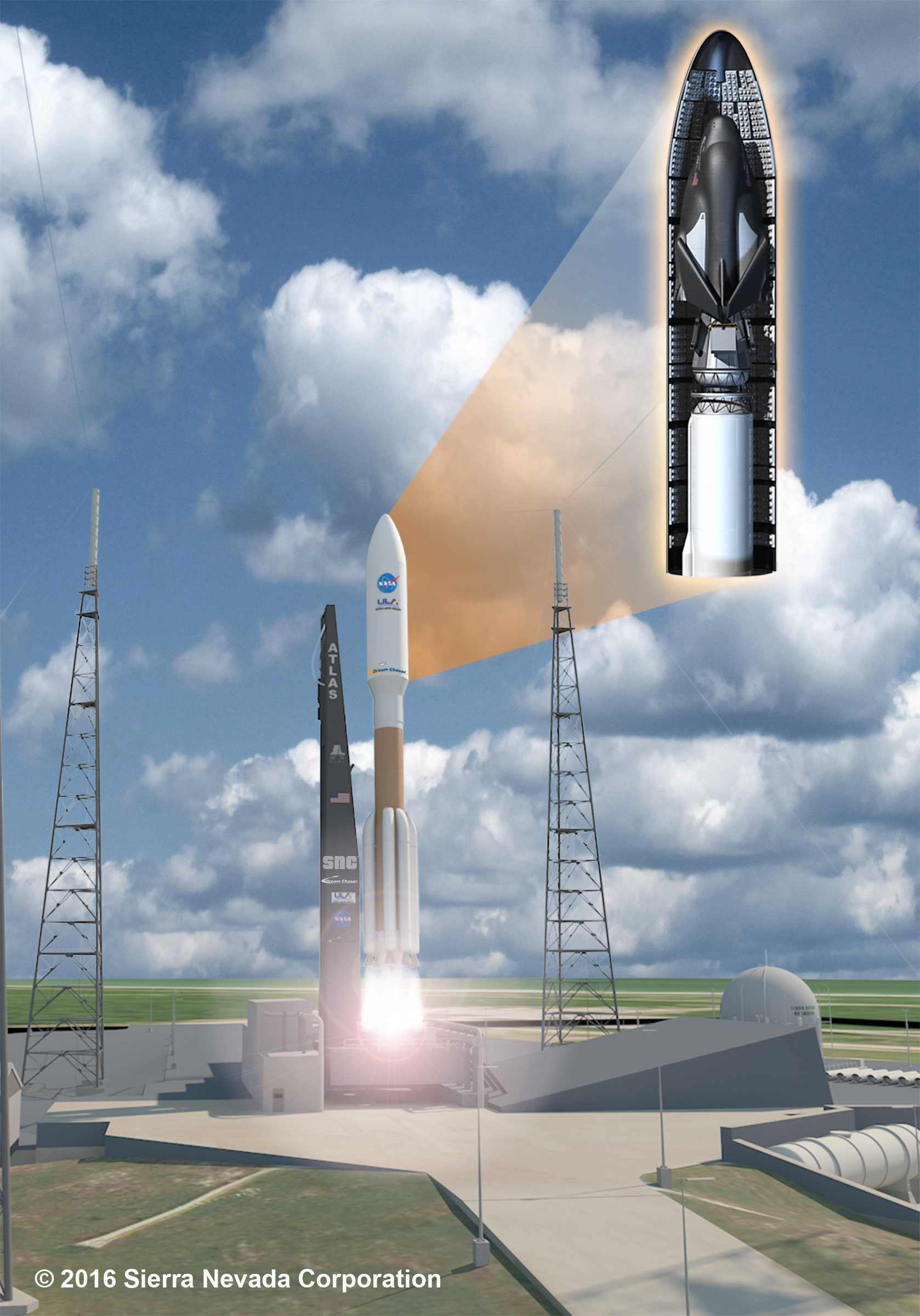
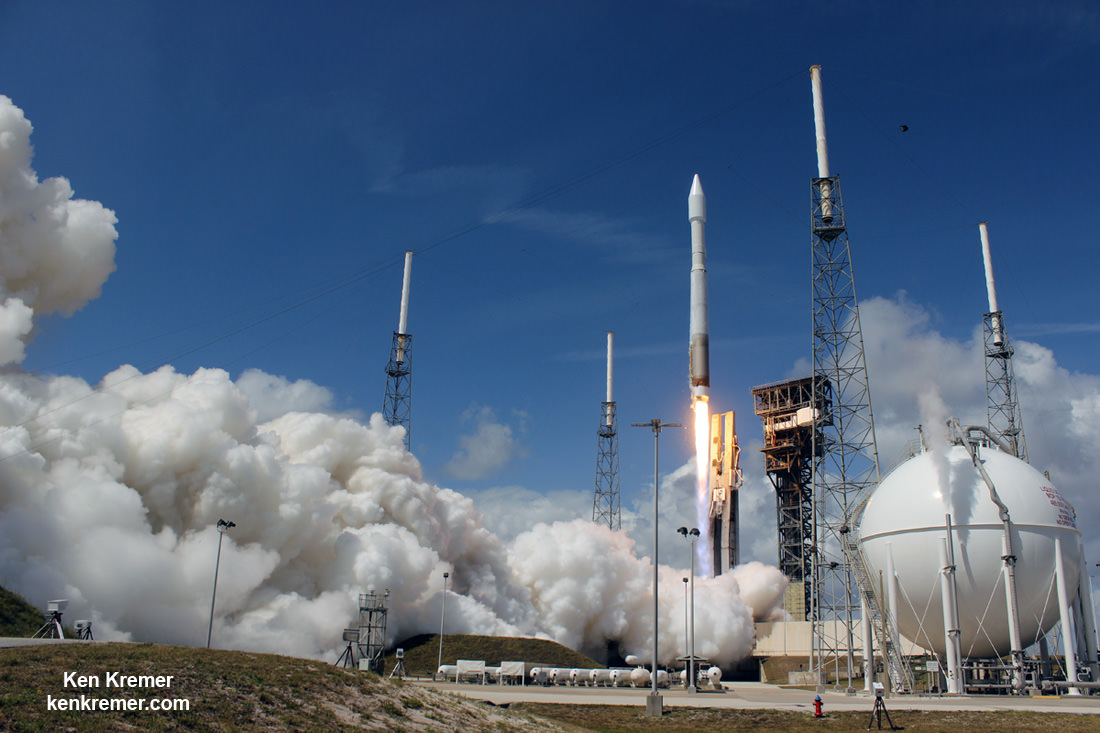
This process entails the craft being launched into orbit aboard a rocket (Atlas V or Ariane 5), maneuvering under its own power while in orbit so that it can dock with the ISS (or other orbiting facilities), and then re-entering the atmosphere and returning to a landing strip. As Mark Sirangelo, the corporate vice president of SNC’s Space System business area, said in a company press release:
“The Dream Chaser flight test demonstrated excellent performance of the spacecraft’s aerodynamic design and the data shows that we are firmly on the path for safe, reliable orbital flight.”
The flight test also helped advance the vehicle as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and prepare it for service under Commercial Resupply Services 2 program. These programs consist of NASA working closely with private aerospace companies to develop new spacecraft and launch systems that will be capable of carrying crews to locations in LEO and to the ISS.
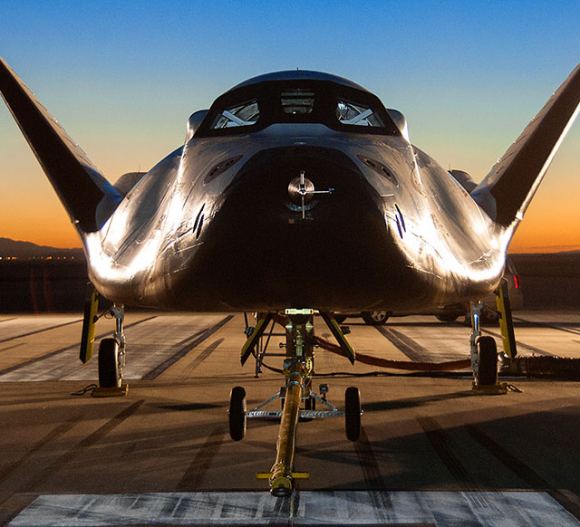

This approach and landing test expands on the phase one flight test, which took place back in October of 2013. For this free-flight test, the vehicle was released from a “skycrane” helicopter and flew a short flight, touching down less than a minute later. Just prior to landing, the left main landing gear failed to deploy resulting in a crash landing. However, the vehicle and its crew compartment were left intact.
For the second flight test, SNC and NASA incorporated orbital vehicle avionics and flight software for the first time. The trajectory also included specific program test inputs which, together with the added software, provided validations for orbital vehicle operations. Over the coming days and weeks, SNC and NASA will be evaluating all the data obtained during the flight, which includes the Dream Chaser aerodynamic and integrated system performance.
The data that SNC gathers from this test campaign will help inform the final design of the cargo Dream Chaser, which will be capable of transporting crews of six astronauts to the ISS. As Fatih Ozmen, the CEO of SNC, exclaimed:
“I’m so proud of the Dream Chaser team for their continued excellence. This spacecraft is the future and has the ability to change the way humans interact with space, and I couldn’t be happier with SNC’s dedicated team and the results of the test.”
If all goes well, SNC and NASA are hoping to begin conducting cargo deliveries by 2019. By 2024, it is hoped that a total of six cargo delivery missions will take place. No indications have been given as to when the crewed variant could start bringing astronauts to the ISS. But once that is possible, NASA will no longer be forced to rely on Roscosmos and their fleet of Soyuz rockets to send astronauts into space.
Be sure to check out this video of the Dream Chaster Cargo System, courtesy of Sierra Nevada Corporation:
https://vimeo.com/199209876
Further Reading: NASA, Sierra Nevada