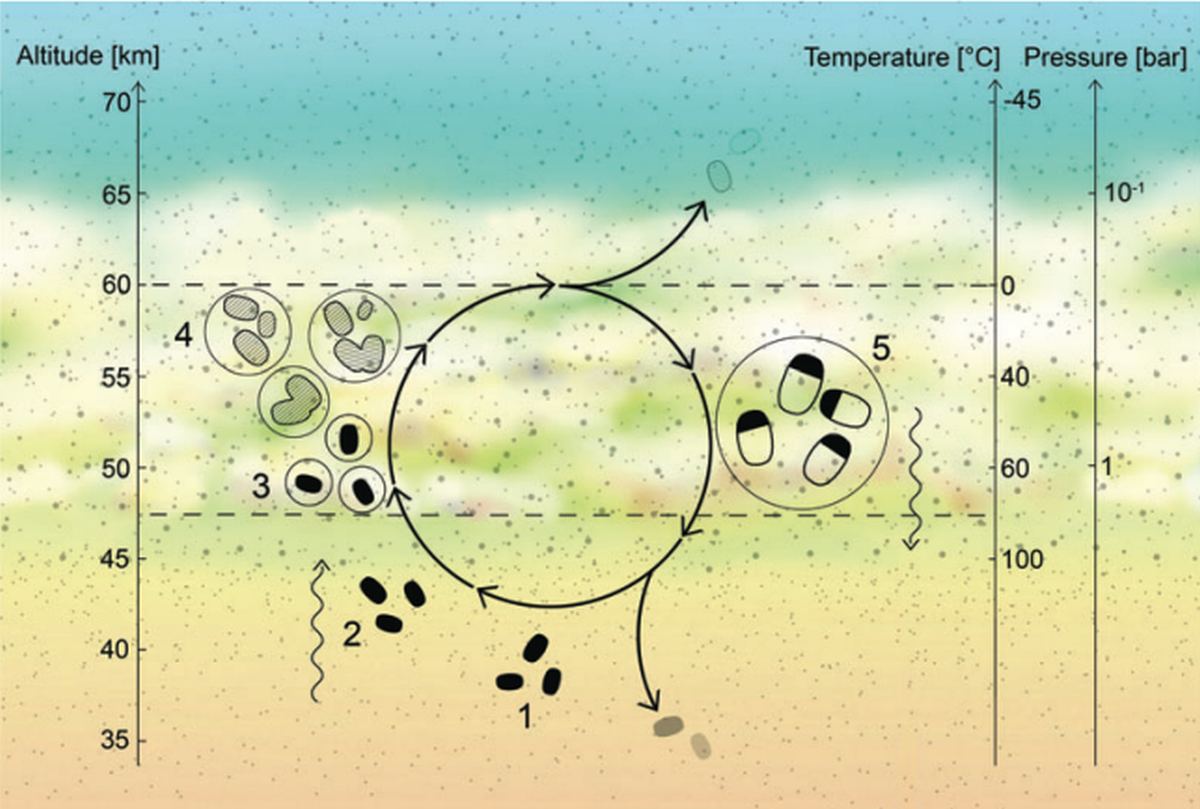
It’s a measure of human ingenuity and curiosity that scientists debate the possibility of life on Venus. They established long ago that Venus’ surface is absolutely hostile to life. But didn’t scientists find a biomarker in the planet’s clouds? Could life exist there, never touching the planet’s sweltering surface?
It seems to depend on who you ask.
Continue reading “Could Life Exist in Water Droplet Worlds in Venus’ Atmosphere?”