[/caption]
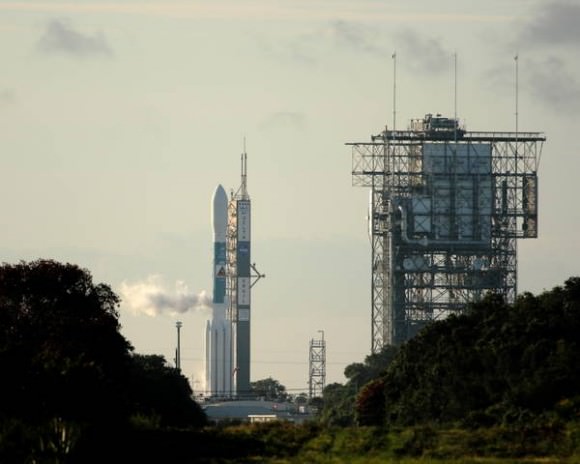
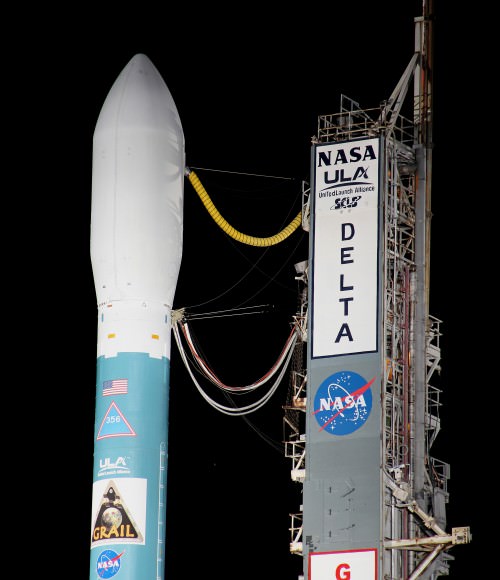
NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) moon mapping twins and the mighty Delta II rocket that will blast the high tech physics experiment to space on a lunar science trek were magnificently unveiled in the overnight darkness in anticipation of a liftoff that had originally been planned for the morning of Sept. 8.
Excessively high upper level winds ultimately thwarted Thursday’s launch attempt.
NASA late today has just announced a further postponement by another day to Saturday Sept. 10 to allow engineers additional time to review propulsion system data from Thursday’s detanking operation after the launch attempt was scrubbed to Friday. Additional time is needed by the launch team to review the pertinent data to ensure a safe blastoff of the $496 Million GRAIL mission.
There are two instantaneous launch opportunities at 8:29:45 a.m. and 9:08:52 a.m. EDT at Cape Canaveral, eight minutes earlier than was planned on Sept. 8. The weather forecast for Sept. 10 still shows a 60 percent chance of favorable conditions for a launch attempt.

Credit: Ken Kremer (kenkremer.com)
Despite a rather poor weather prognosis, the heavy space coast cloud cover had almost completely cleared out in the final hours before launch, the surface winds were quite calm and we all expected to witness a thunderous liftoff. But measurements from weather balloons sent aloft indicated that the upper level winds were “red” and violated the launch criteria.

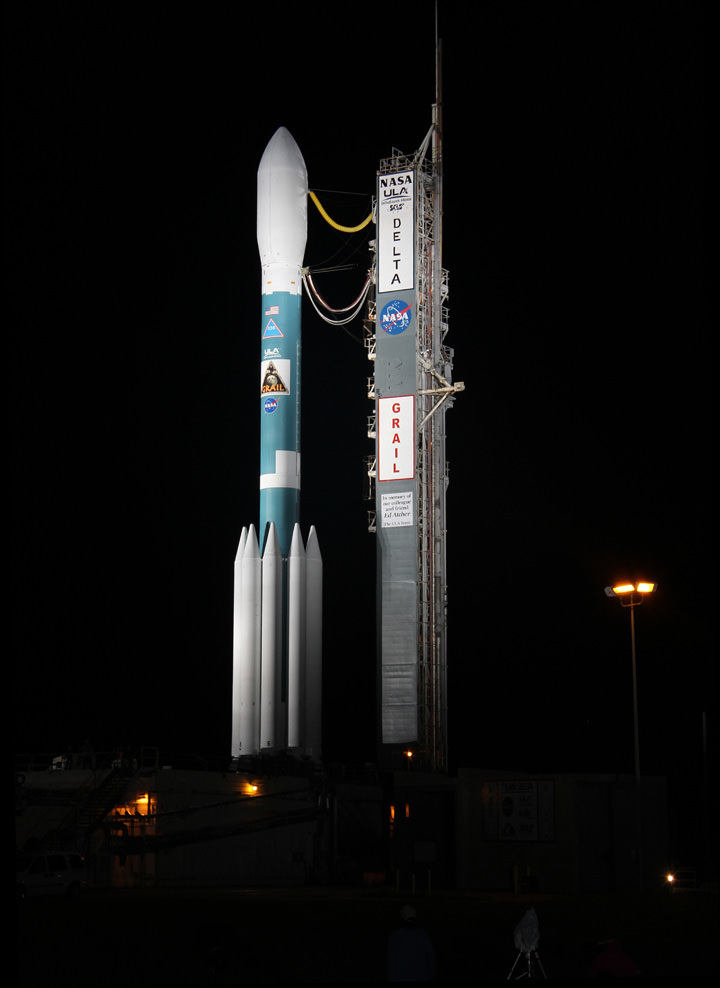
As the launch gantry was quickly retracted at Launch Complex 17B on Sept. 7, the Delta was bathed in xenon spotlights that provided a breathtaking light show as the service structure moved a few hundred feet along rails.
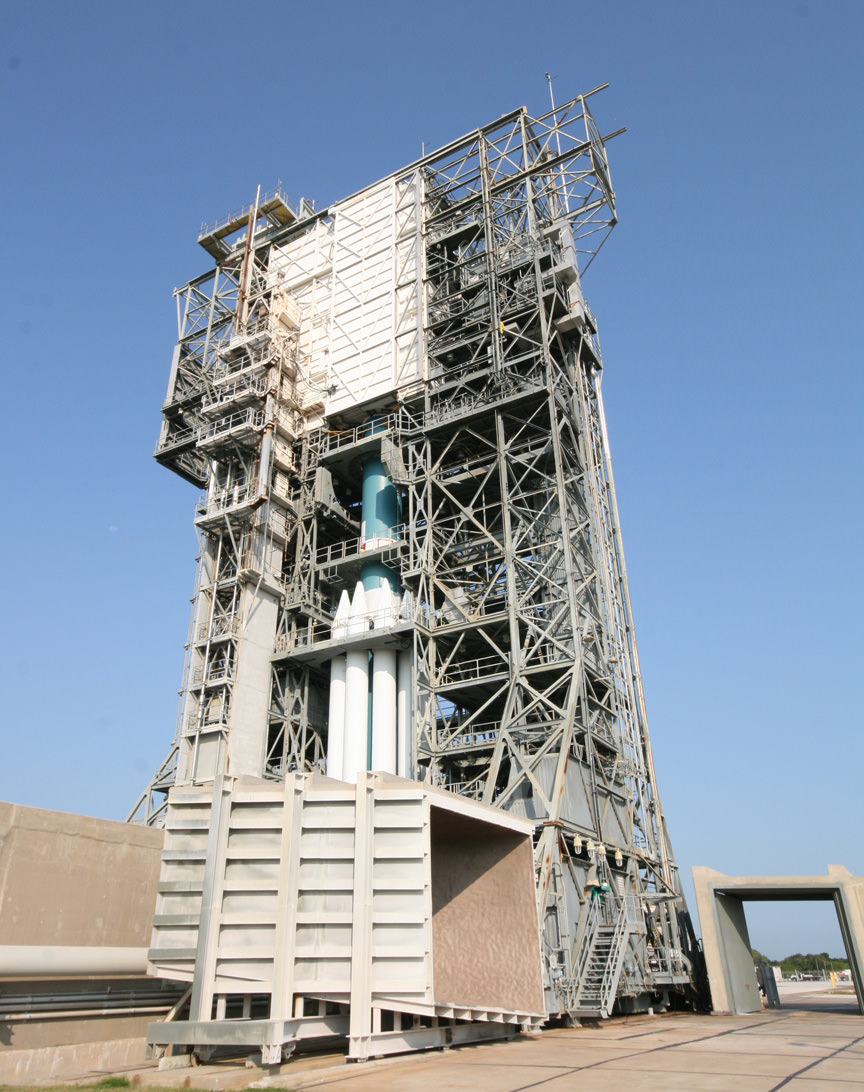
The cocoon like Mobile Service Tower (MST) provides platforms to access the rocket at multiple levels to prepare the vehicle and spacecraft for flight. The MST also protects the rocket from weather and impacts from foreign debris.
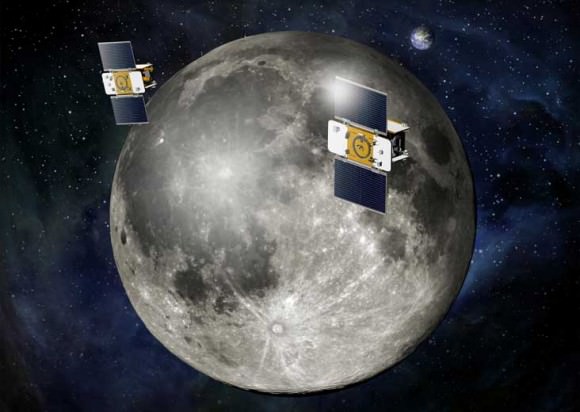
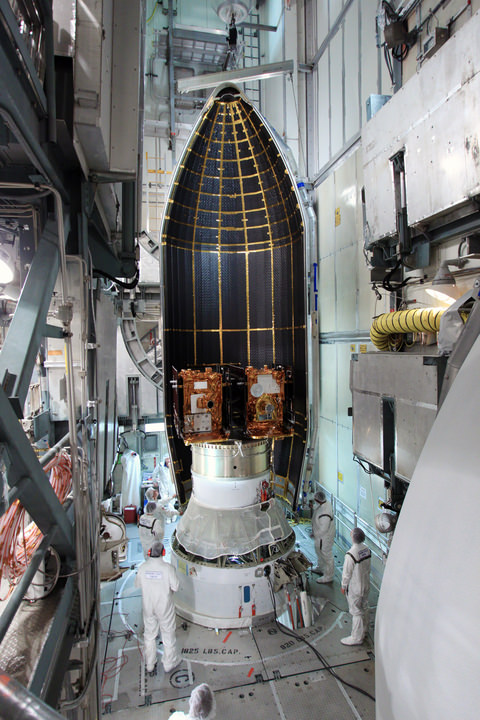
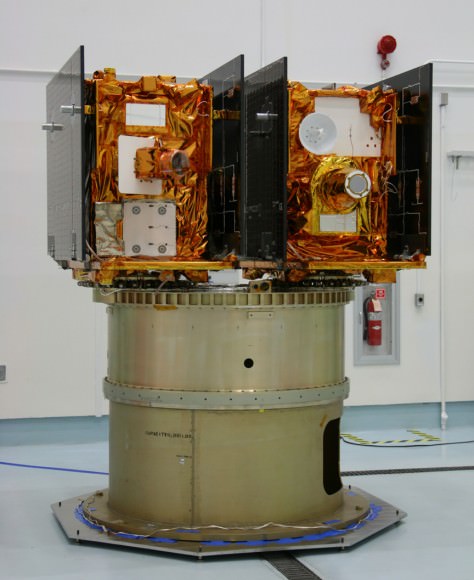
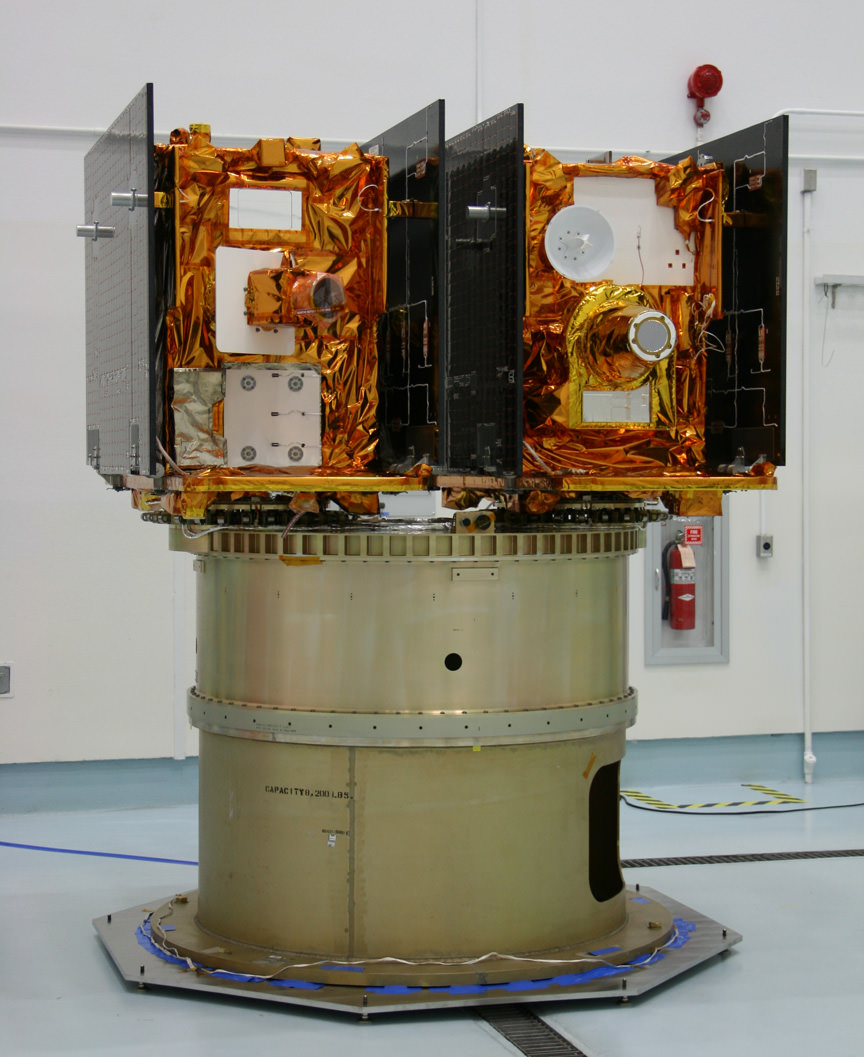
The GRAIL A and B mirror image twins ride side by side to space atop the Delta rocket. The washing machine spacecraft weigh about 677 pounds (307 kg) each.
The Delta II rocket stands 128 feet tall and is 8 feet in diameter. The first stage liquid and solid rocket fueled engines will generate about 1.3 million pounds of thrust.
During the Terminal Countdown, the first stage is fueled with cryogenic liquid oxygen and highly refined kerosene (RP-1).
GRAIL is an extraordinary first ever journey to the center of the moon that will — with its instruments from orbit — peer into the moons interior from crust to core and map its gravity field by 100 to 1000 times better than ever before. The mission employs two satellites flying in tandem formation some 50 km in near circular polar orbit above the lunar surface.
GRAIL A and B will perform high precision range-rate measurements between them using a Ka-band instrument. The mission will provide unprecedented insight into the formation and thermal evolution of the moon that can be applied to the other rocky planets in our solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
After a 3.5 month journey to the moon, the probes will arrive about a day apart on New Year’s Eve and New Year’s Day 2012 for an 82 day science mapping phase as the moon rotates three times beneath the GRAIL orbit.

Credit: Ken Kremer

Read Ken’s continuing features about GRAIL
Last Delta II Rocket to Launch Extraordinary Journey to the Center of the Moon on Sept. 8
NASAs Lunar Mapping Duo Encapsulated and Ready for Sept. 8 Liftoff
GRAIL Lunar Twins Mated to Delta Rocket at Launch Pad
GRAIL Twins ready for NASA Science Expedition to the Moon: Photo Gallery