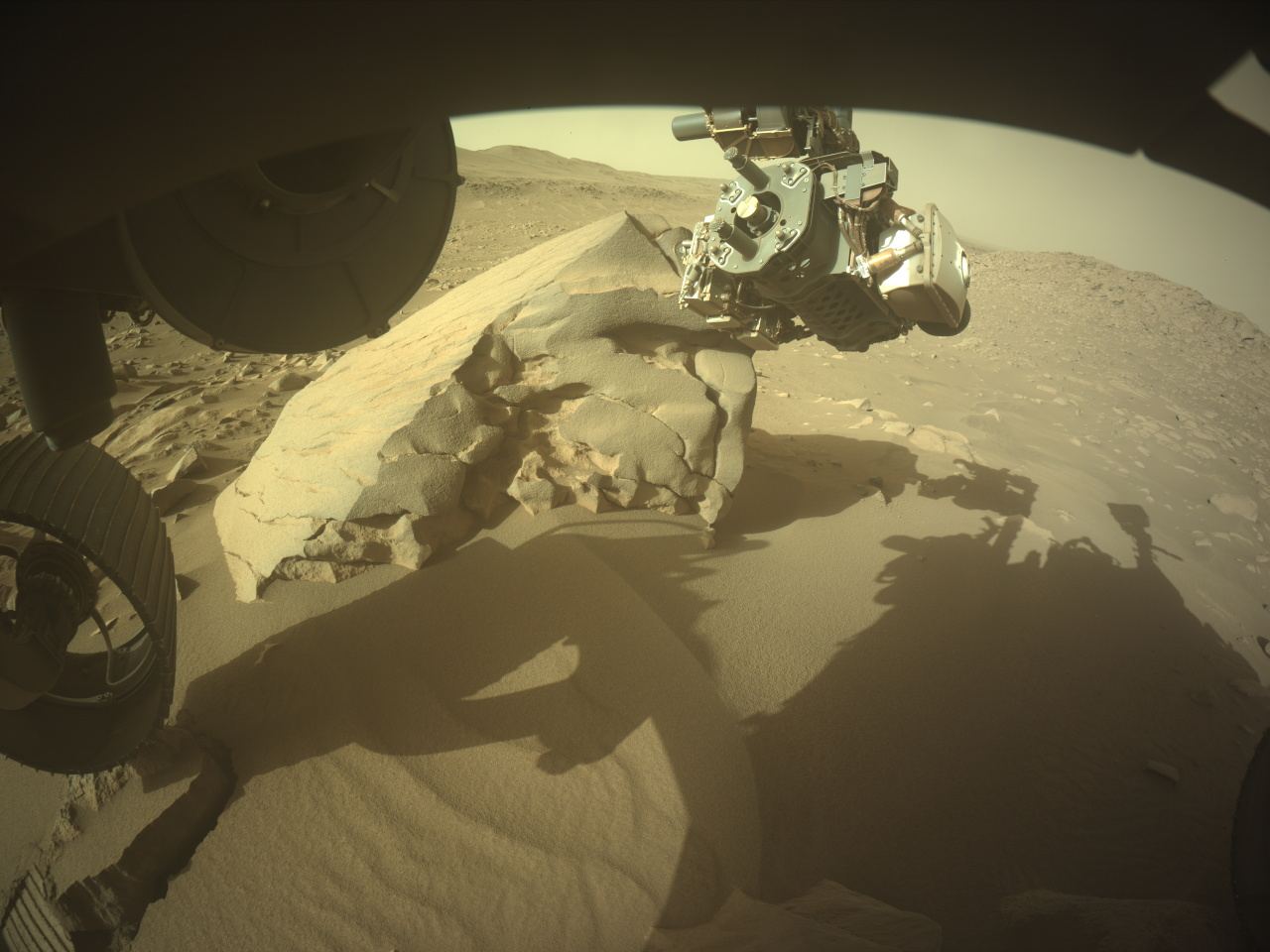
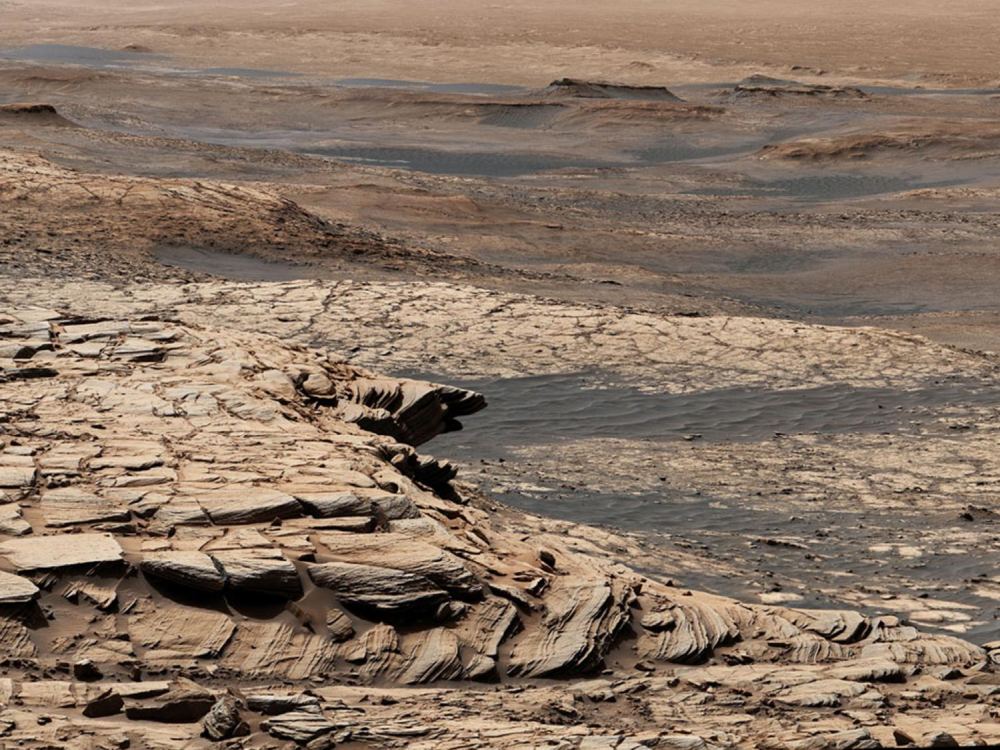
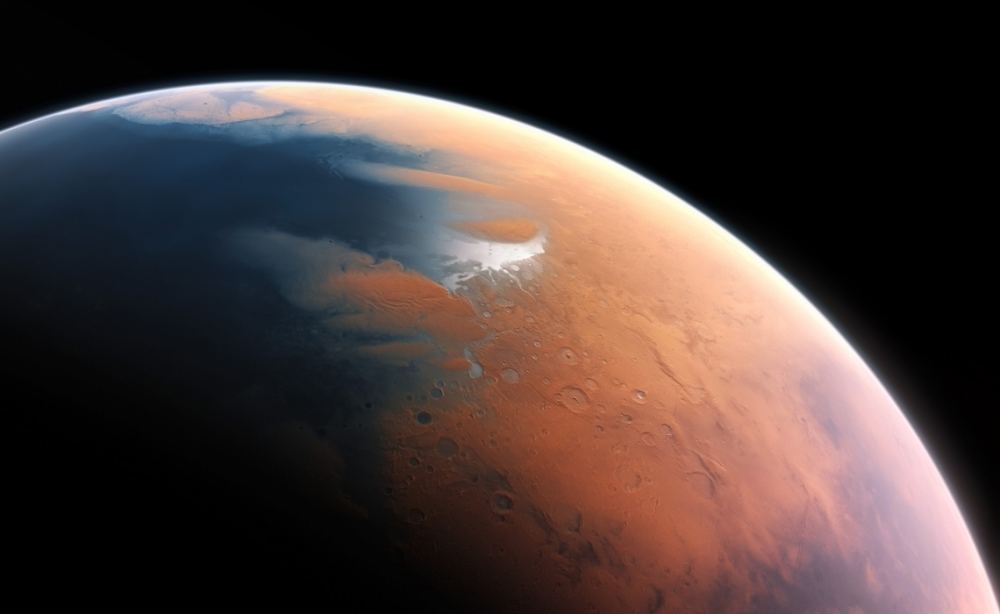
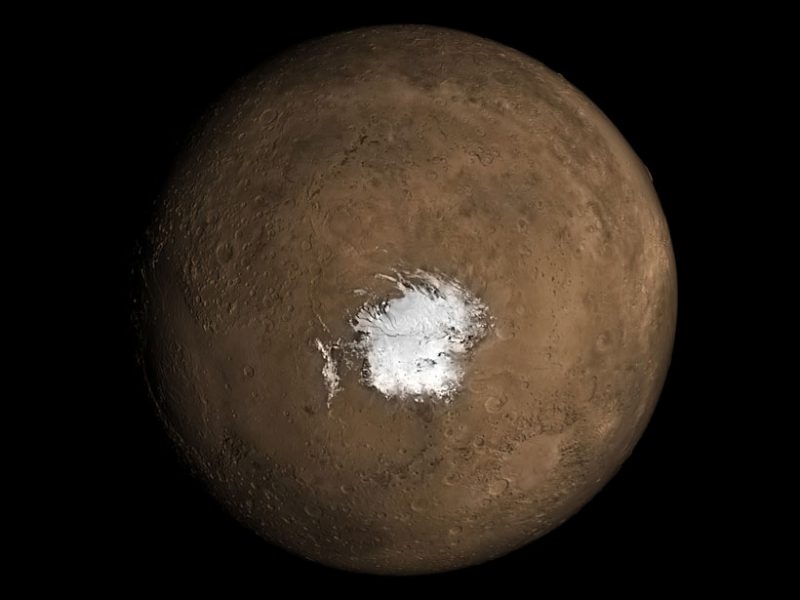
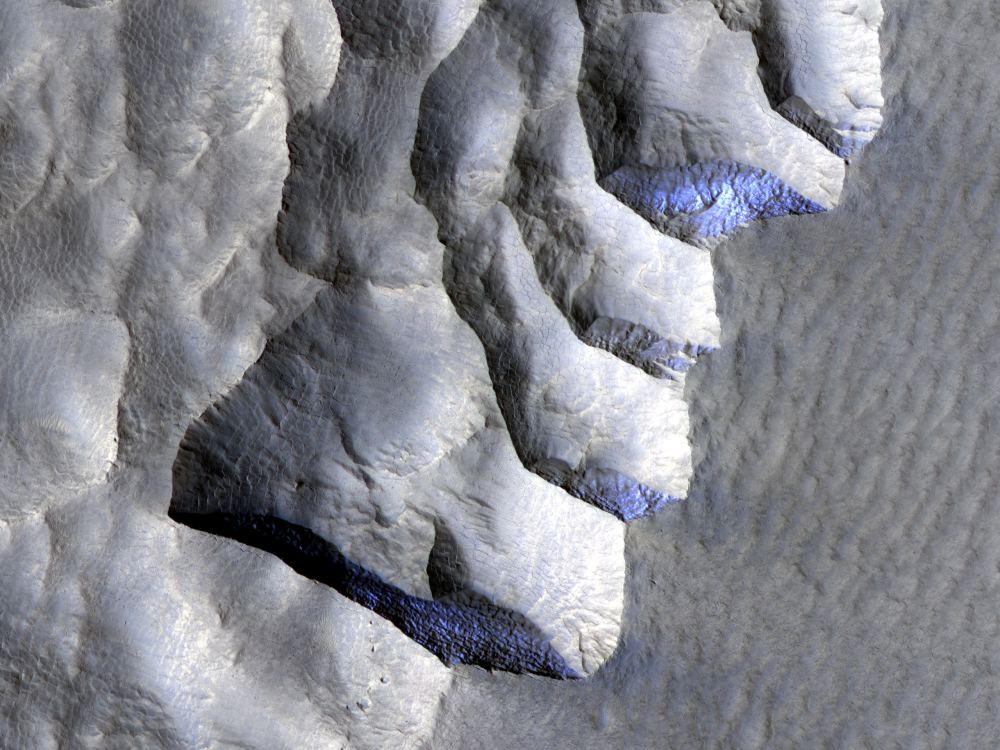
The ESA’s Mars Express orbiter captured an image of the remains of a vast ancient lake on Mars. The remnant lake bed has been weathered and altered by the passing of billions of years. In the planet’s distant past, scientists say, it held enough water to fill Earth’s Caspian Sea almost three times over.
Continue reading “An Ancient Martian Lake Was Larger Than Any Lake on Earth”An Ancient Martian Lake Was Larger Than Any Lake on Earth