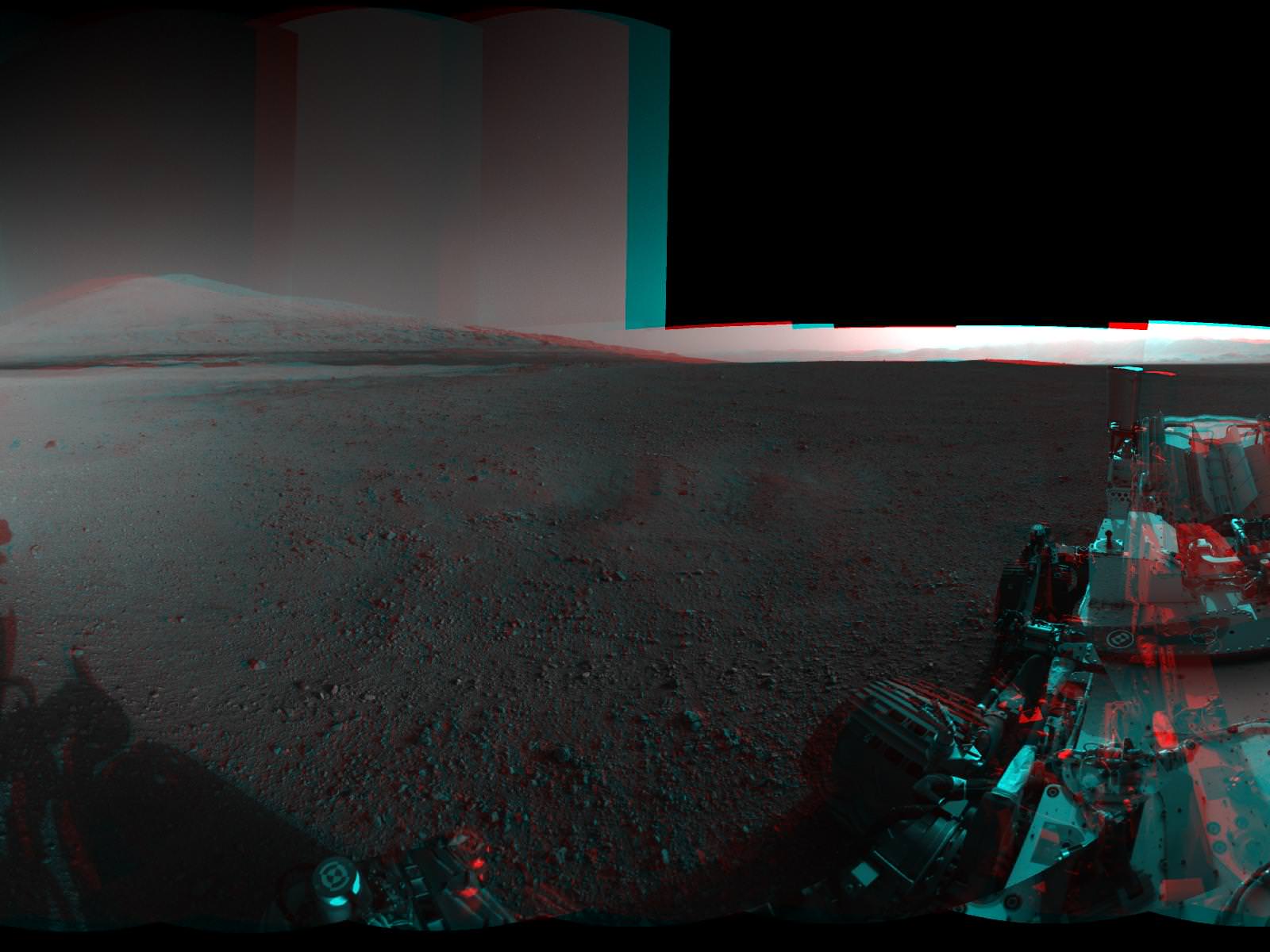
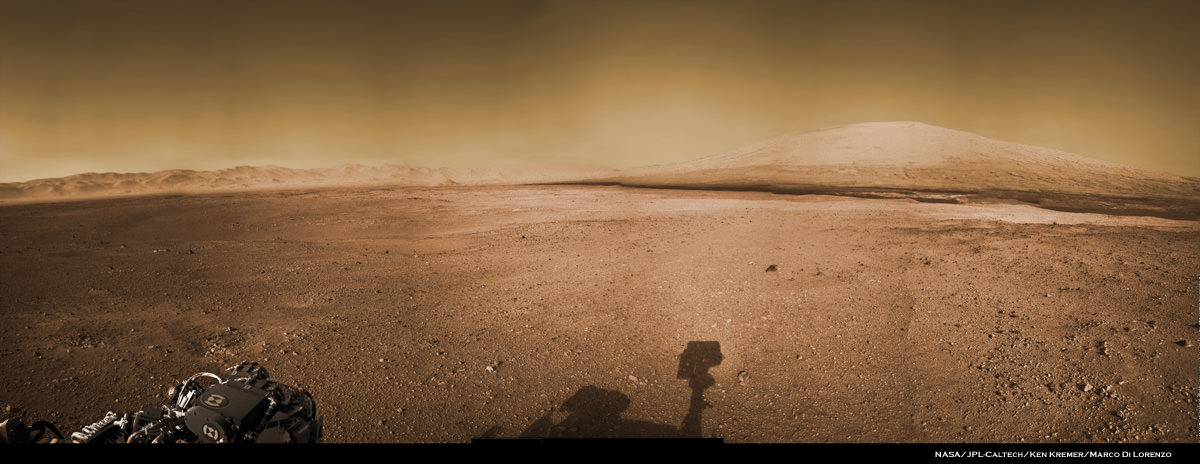
Image Caption: Panoramic mosaic shows gorgeous Glenelg snapped by Curiosity on Sol 64 (Oct. 10) with eroded crater rim and base of Mount Sharp in the distance. This is a cropped version of the full mosaic as assembled from 75 images acquired by the Mastcam 100 camera. See full mosaic below. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
NASA’s 1 ton mega rover Curiosity is simultaneously eating Martian dirt and busily snapping hundreds of critical high resolution color photos of her surroundings at the gorgeous locale of tasty terrain of outcrops the scientists call the ‘Promised Land’ – a place that will help unveil the watery mysteries of ancient Mars.
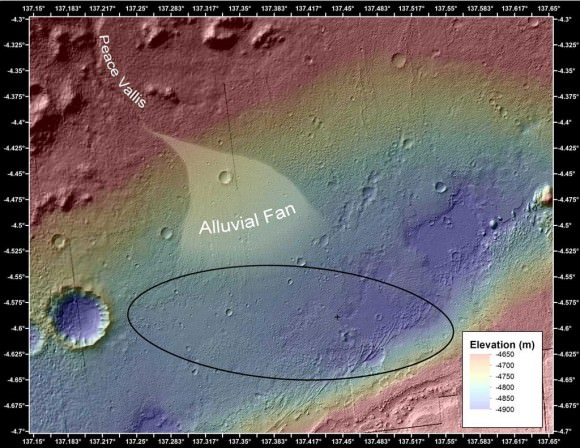
11 weeks into Curiosity’s 2 year primary mission she finds herself at a spot dubbed Glenelg – her first major science destination – and which lies at the natural junction of three types of geologically varied terrain.
See our detailed color panoramic mosaics of the road ahead inside Glenelg as the robot methodically scans around at the inviting mix of geologic features never before investigated by a robotic emissary from Earth.
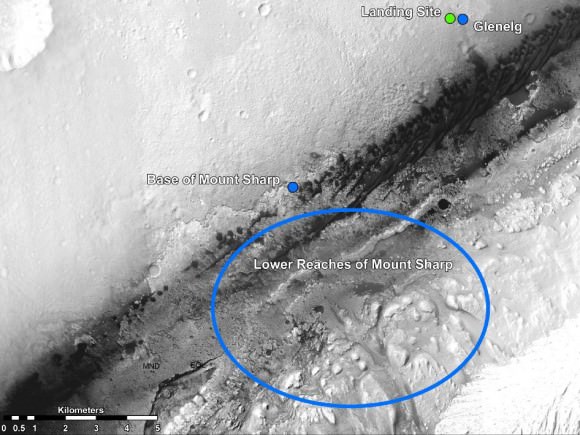
Glenelg offers an unprecedented opportunity for a boon of discoveries to the rover science team long before she arrives at her ultimate destination – the 3.4 mile (5.5 km) high layered mountain named Mount Sharp.
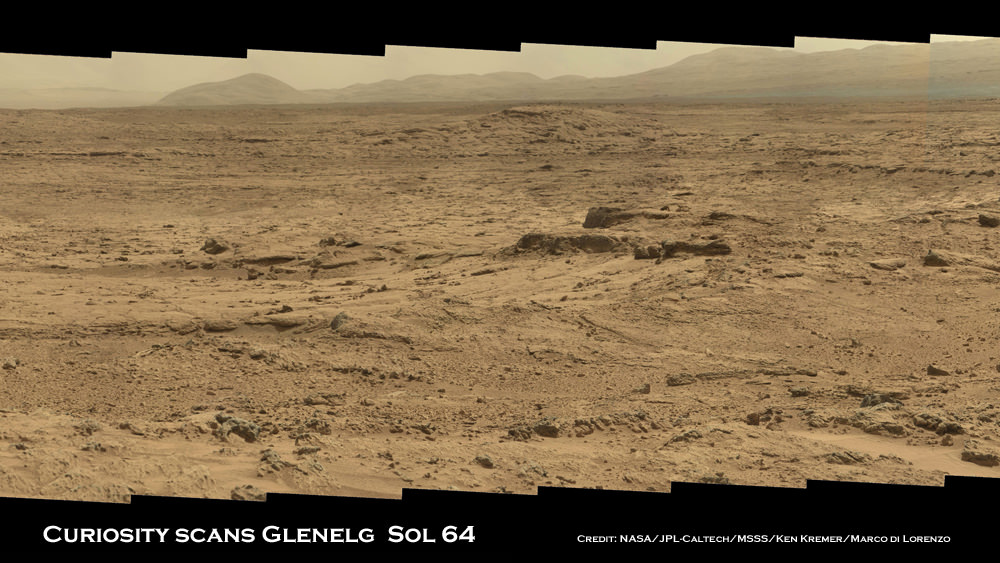
Image Caption: Panoramic mosaic shows gorgeous Glenelg snapped by Curiosity from Rocknest windblown dune on Sol 64 (Oct. 10) with eroded crater rim and base of Mount Sharp in the distance. This mosaic as assembled from 75 images acquired by the high resolution Mastcam 100 camera on Sol 64. Click to enlarge. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
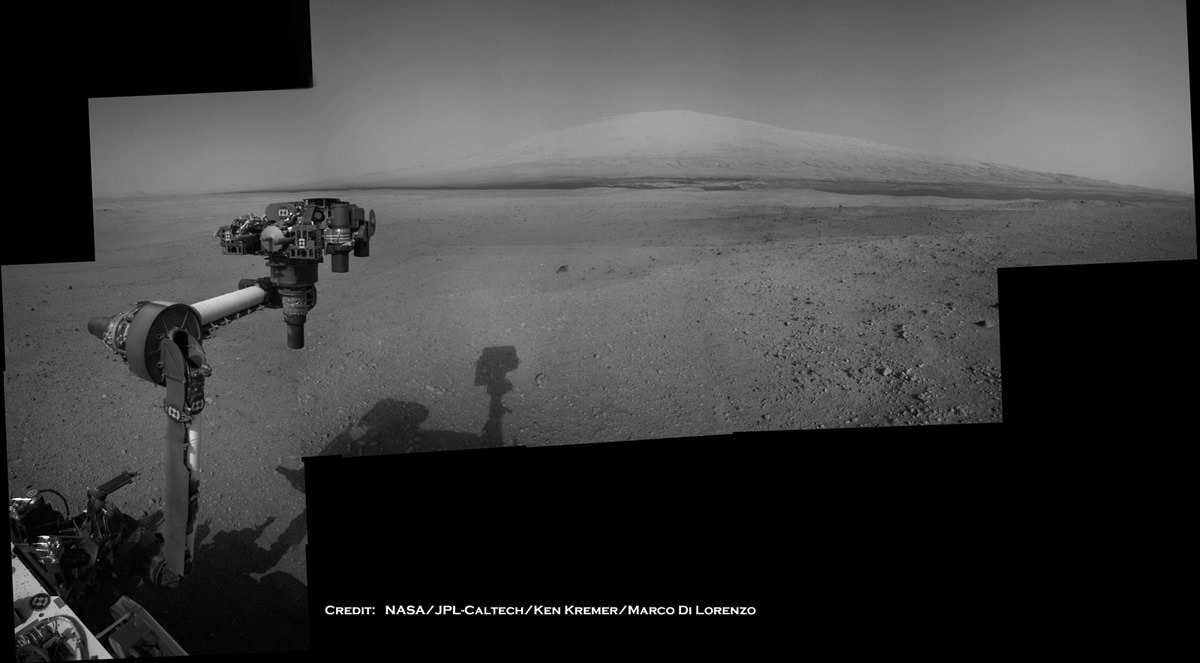
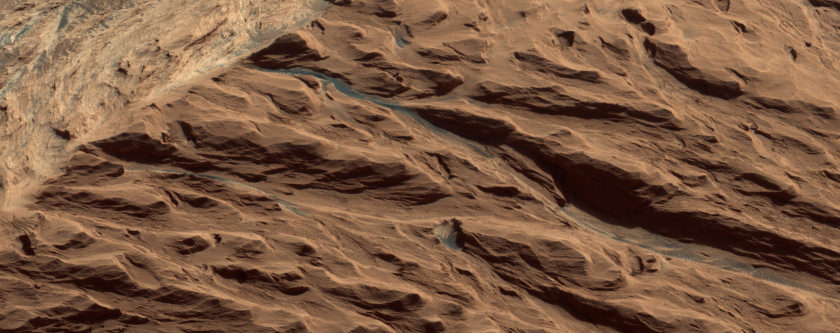
Image Caption: Panorama shows beautiful vista of distant eroded rim of Gale Crater and breathtaking foreground terrain. This mosaic was assembled from high resolution Mastcam 100 images taken by Curiosity on Sol 50 (Sep. 26). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
Curiosity Project Scientist John Grotzinger scientist explained to me that the team is using the Mastcam 100 imagery to come up with options for the upcoming driving and exploration plan to be carried out over at least the next few weeks.
“We are at Glenelg and consider ourselves to be in the ‘Promised Land’. We took the images in the direction we will be traveling,” said Curiosity Project Scientist John Grotzinger of the California Institute of Technology during a media teleconference on Oct. 18.
“We mostly see outcrops there and that’s the reason we took those prioritized images,” he said about the Mastcam 100 imagery from Sols 64 and 66.
“These images will help guide us and give the team options in terms of what I am calling ‘tours’. The team comes up with hypothesis based on the images about observations they would like to make and where they would like to drive.”.
“Then we will integrate the different observations to come up with a model we hope for how the Glenelg area was put together geologically. And then that will inform ultimately our selection for which rock to drill into for the first time,” explained Grotzinger.
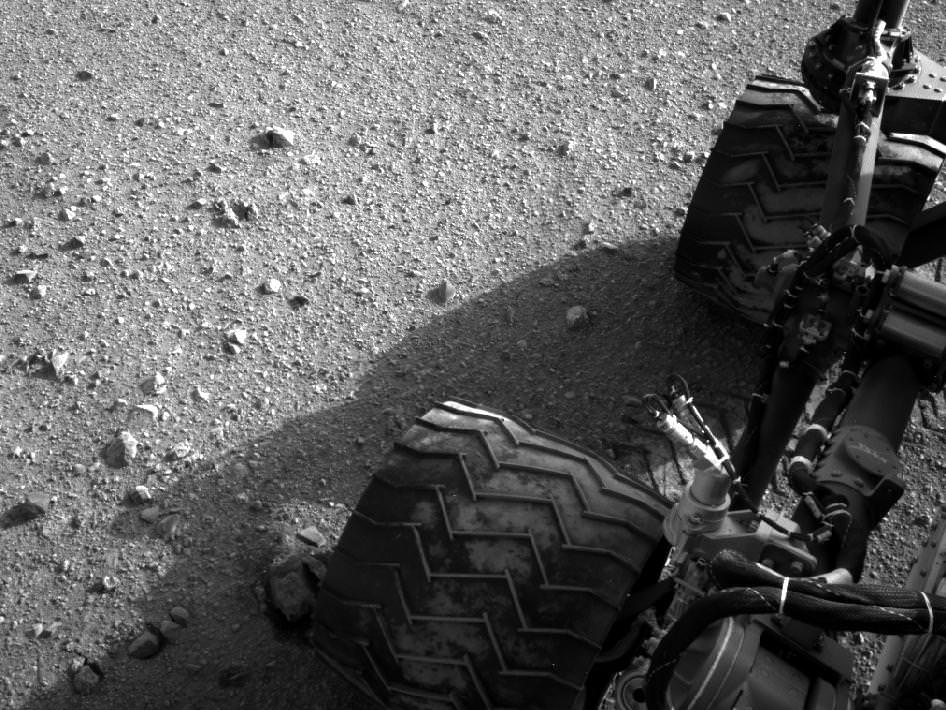
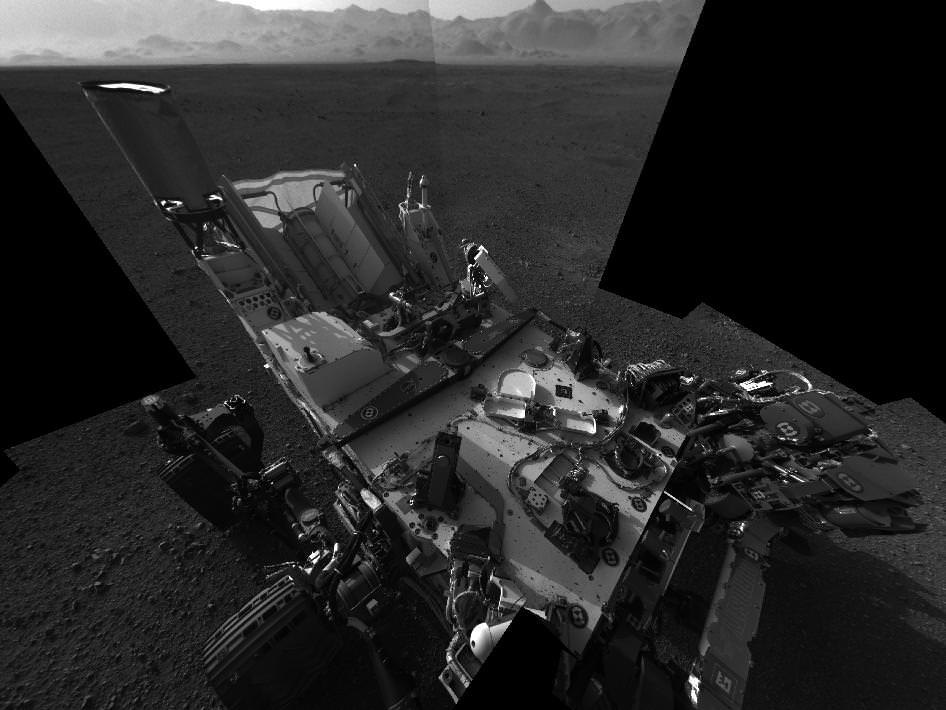
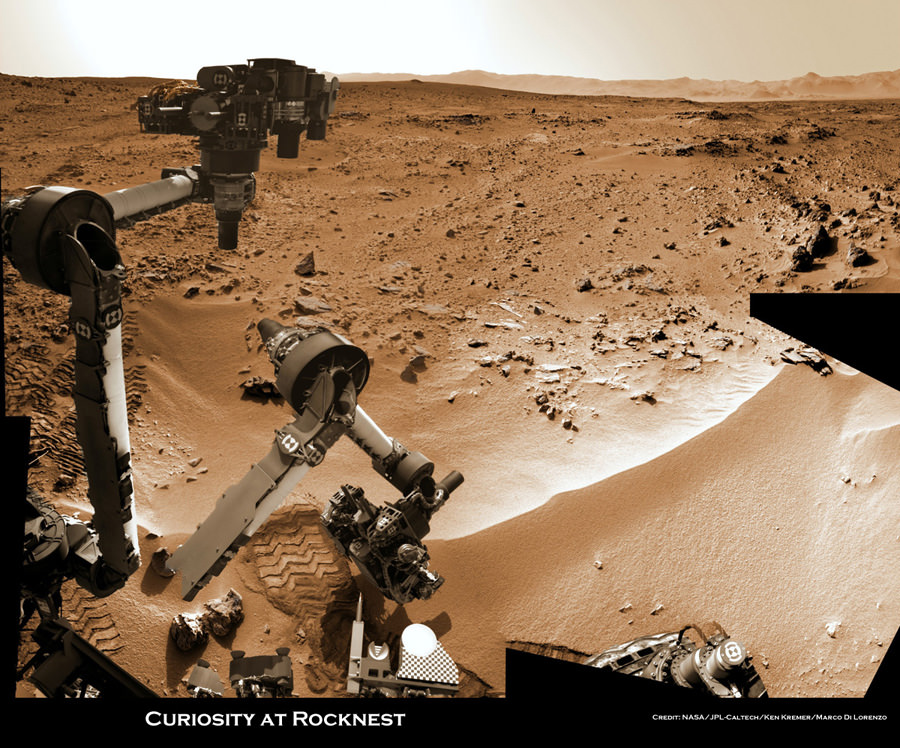
Image Caption: Curiosity scoops up Martian soil sample on Sol 66 (Oct 12. 2012). Navcam camera image mosaic shows the robotic arm at work during scooping operations. Curiosity later delivered the first soil sample to the circular CheMin sample inlet at the center on the rover deck. Tiny trenches measure about 1.8 inches (4.5 centimeters) wide. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
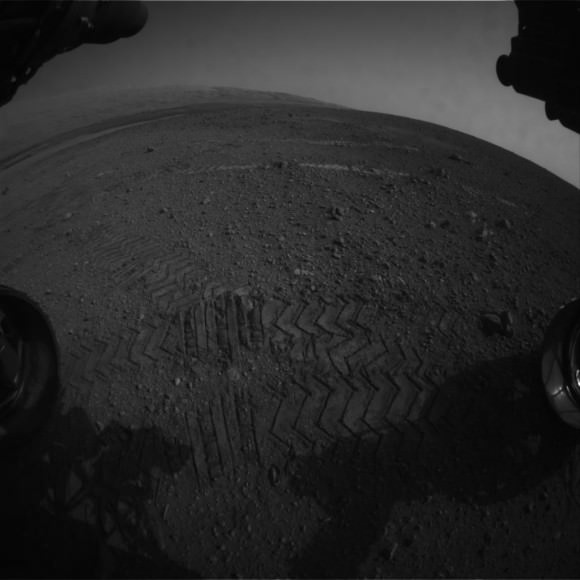
Image caption: Three bite marks left in the Martian ground by the scoop on the robotic arm of NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity are visible in this image taken by the rover’s right Navigation Camera during the mission’s 69th Martian day, or sol (Oct. 15, 2012). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Curiosity is currently parked at a windblown ripple named ‘Rocknest’. It afforded the perfect type of dusty martian material to first test out the scoop and clean the sample processing system twice before finally inhaling the first sample of Martian sand into the robots Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin) analytical instrument several sols ago to determine what minerals it contains.
Results from the Red Planet soil poured into the CheMin experiment located on the rover’s deck are expected in the coming week or so.
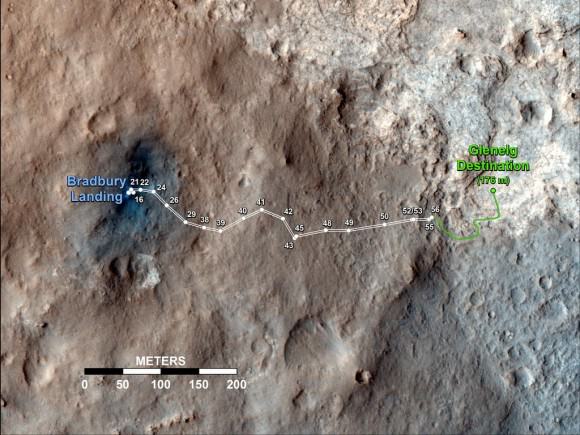
Tosol is Sol 75. Curiosity has taken nearly 20,000 pictures so far and driven a total distance of about 1,590 feet (484 meters).
See more of our Curiosity Mars mosaics by Ken Kremer & Marco Di Lorenzo at NBC News Cosmic log
…..
Nov. 16: Free Public Lecture by Ken Kremer about “Curiosity and the Search for Life in 3 D” and more at Union County College and Amateur Astronomers Inc in Cranford, NJ.





![698428main_Grotzinger-1pia16231-946[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/698428main_Grotzinger-1pia16231-9461-580x435.jpg)

![697173main_pia16229-43_946-710[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/697173main_pia16229-43_946-7101-580x435.jpg)
![697185main_pia16230-43_946-710[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/697185main_pia16230-43_946-7101-580x435.jpg)




![692089main_Grotzinger-1-pia16156-43_800-600[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/692089main_Grotzinger-1-pia16156-43_800-6001-580x435.jpg)