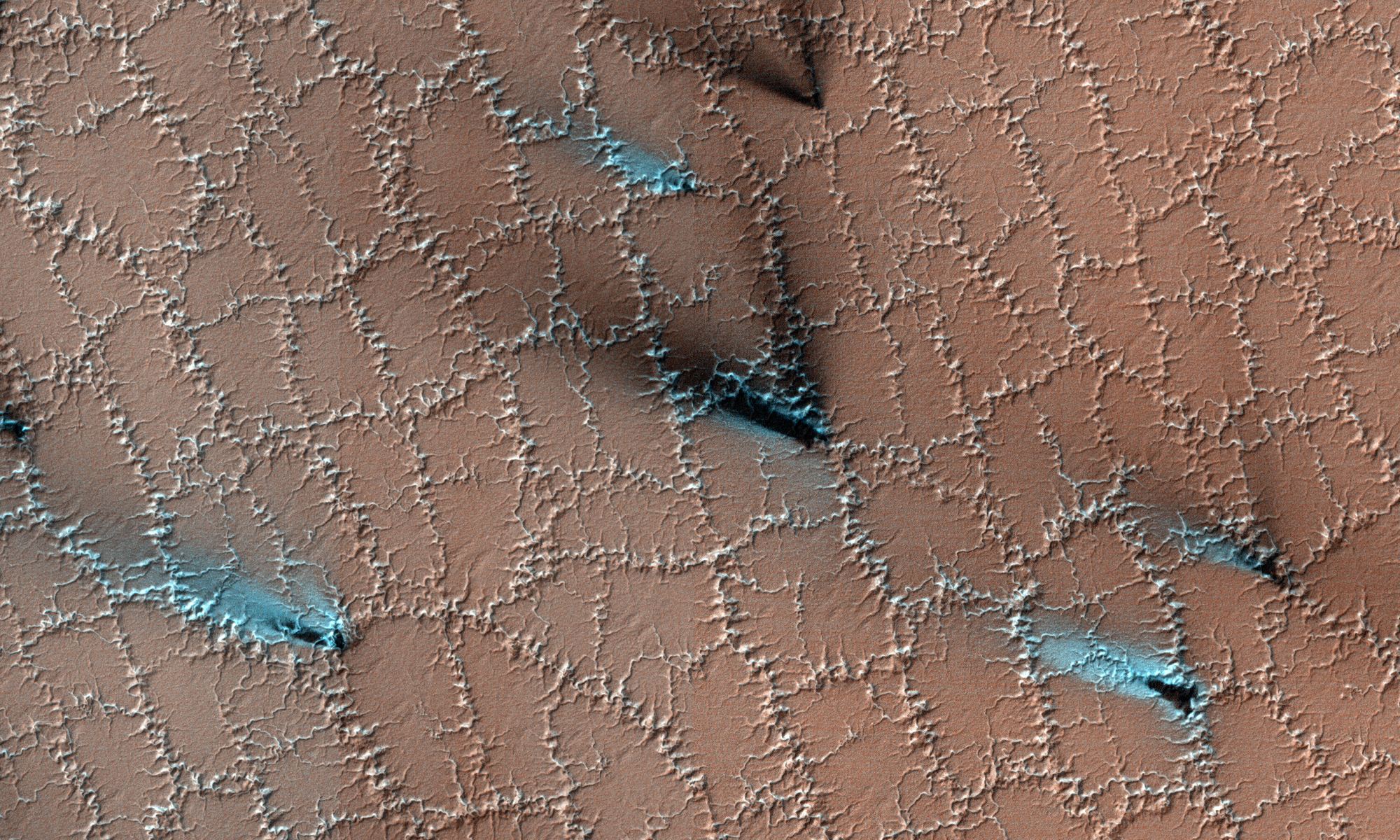
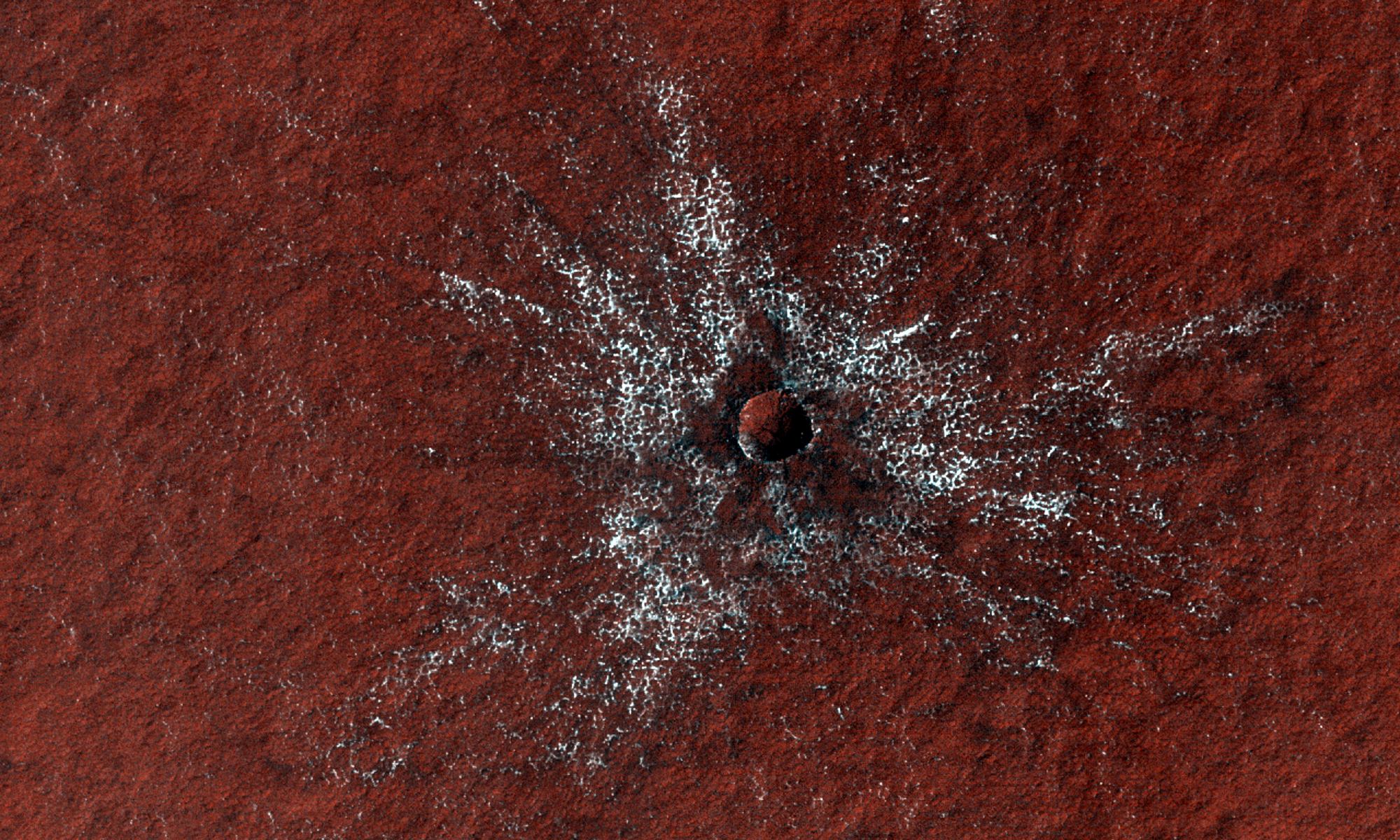
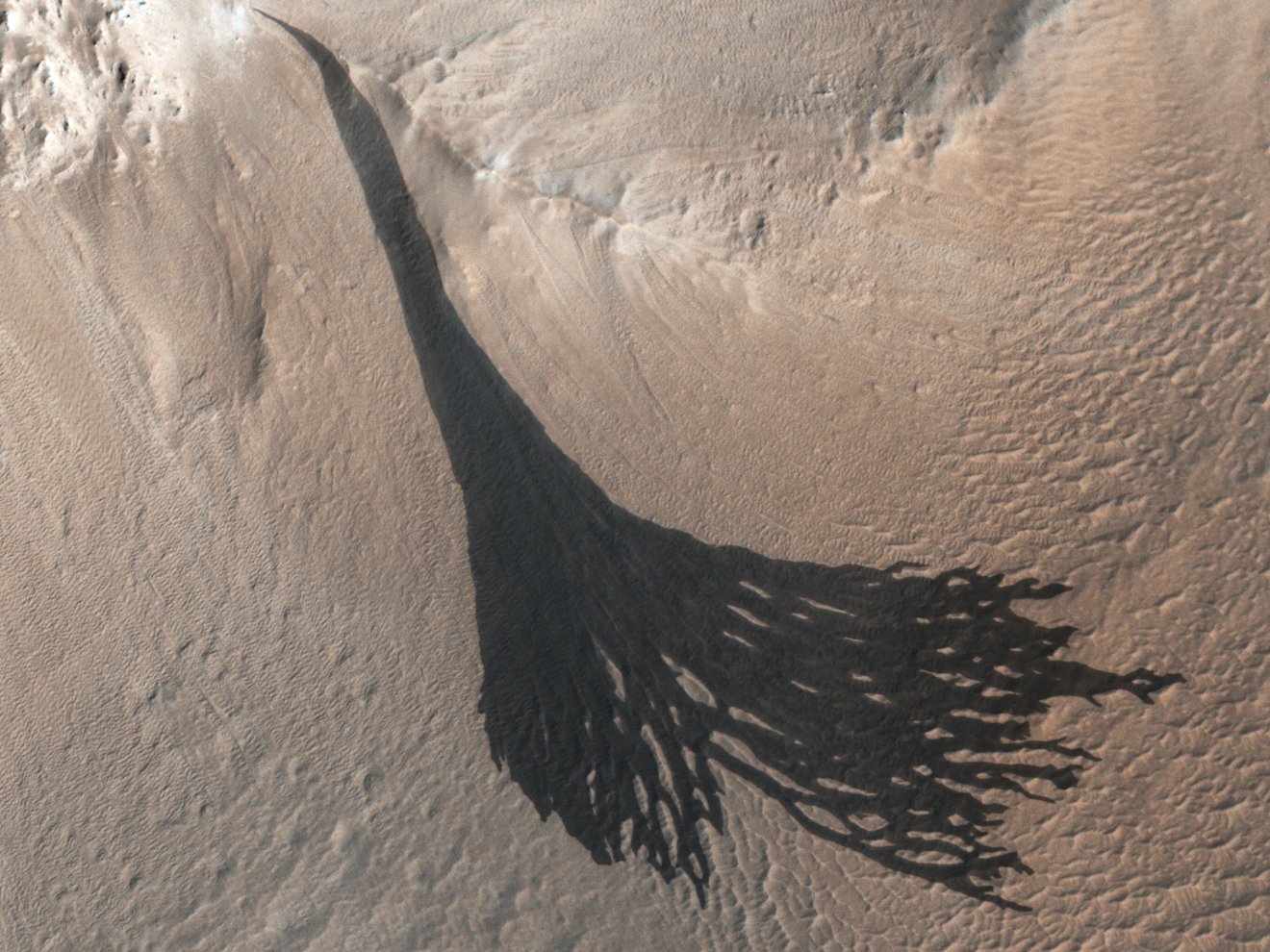
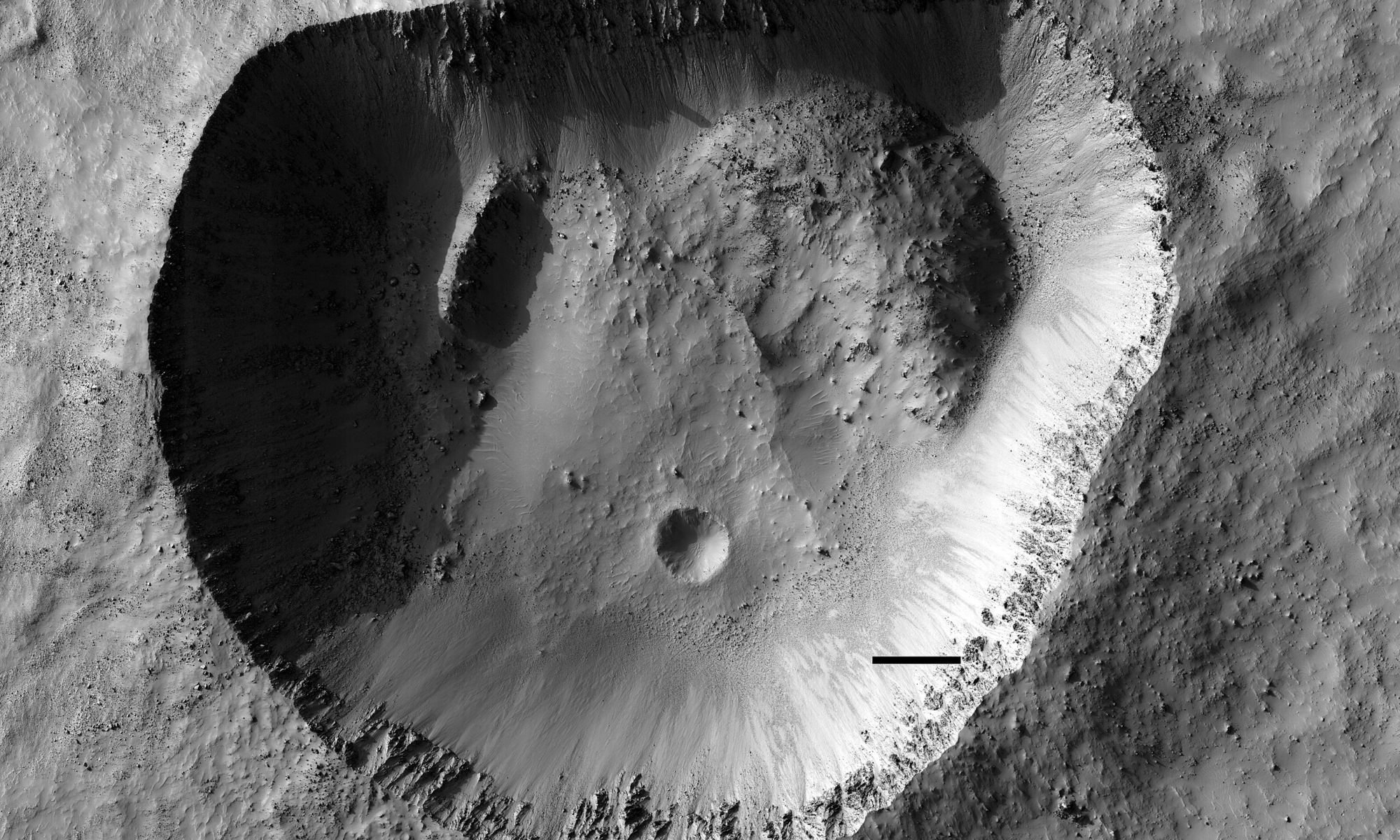
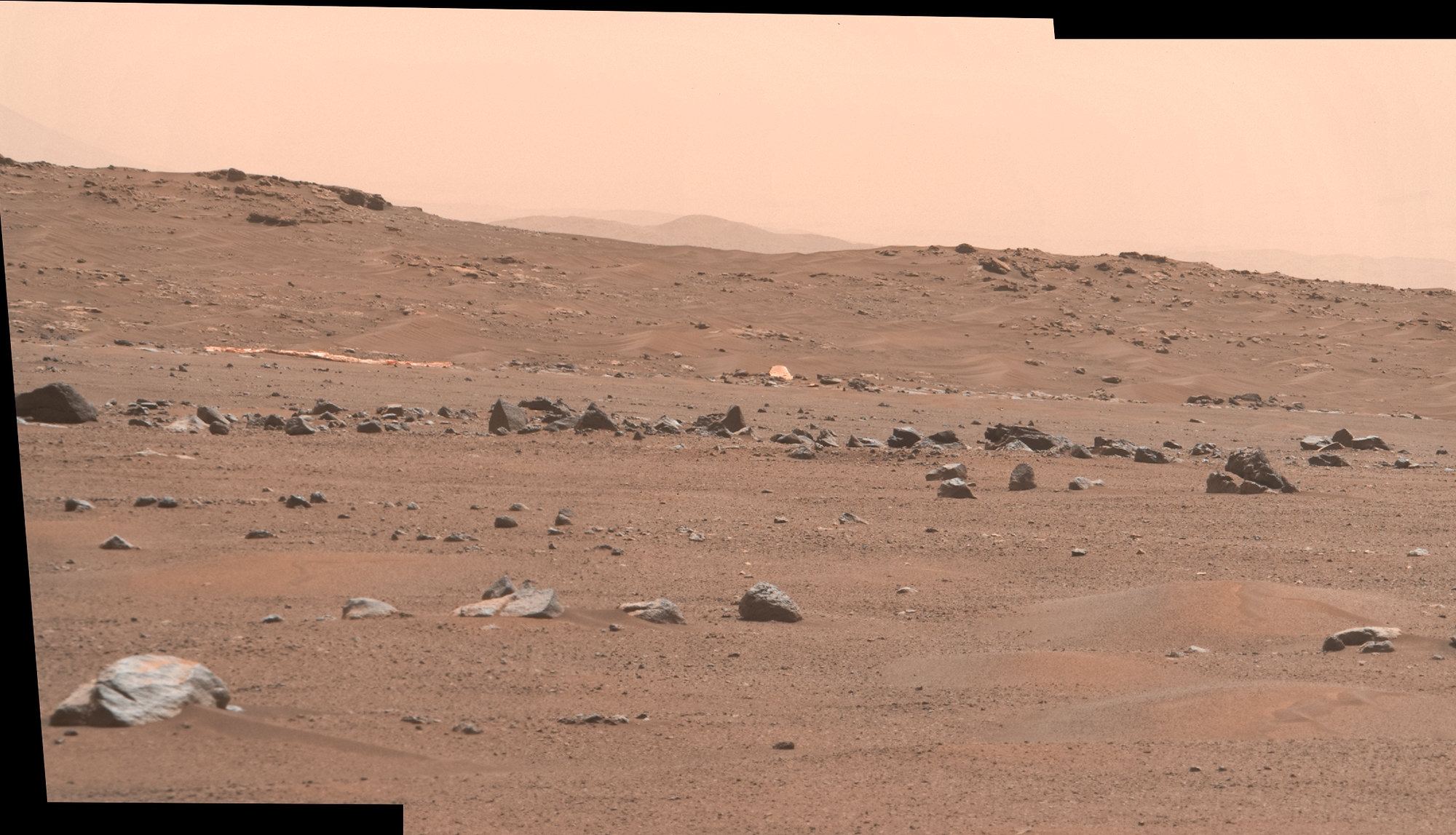
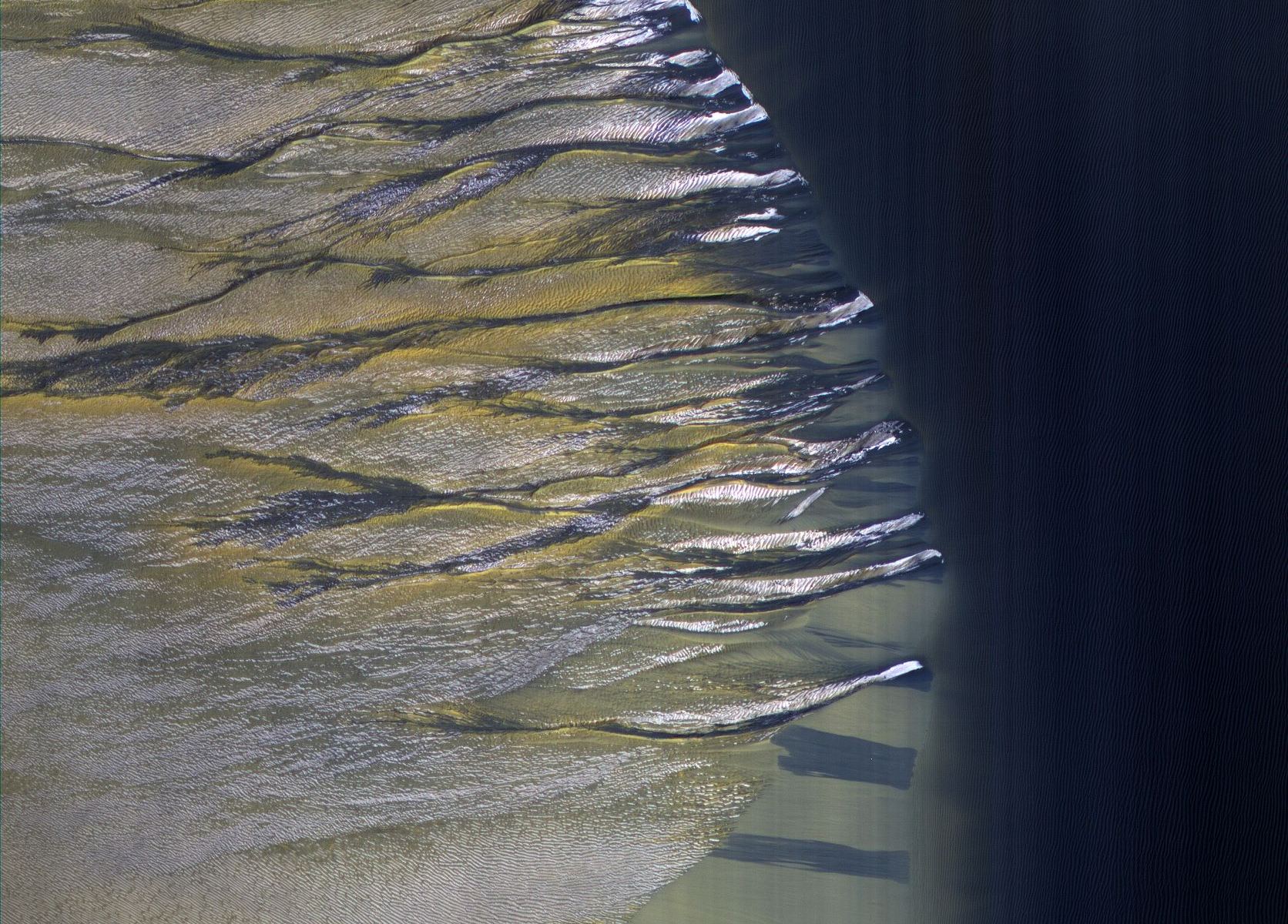
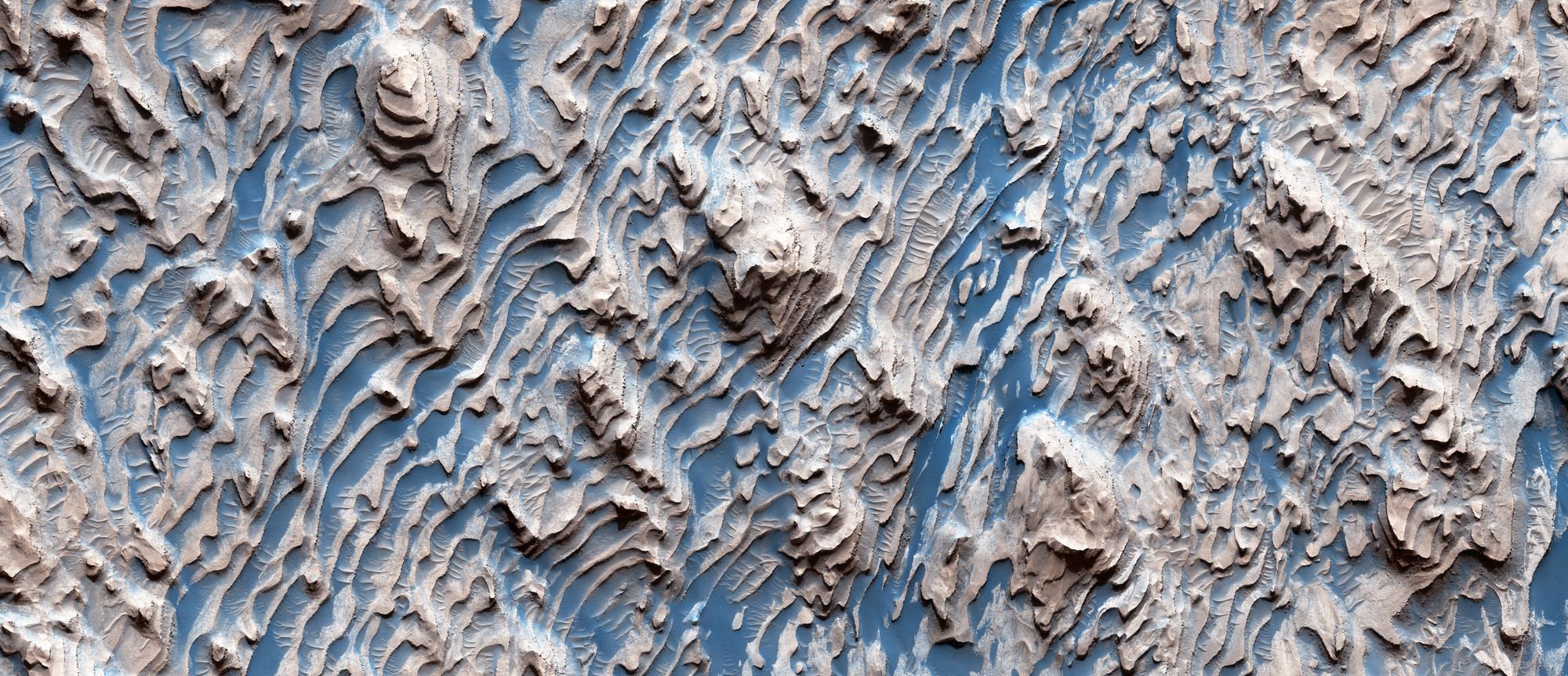
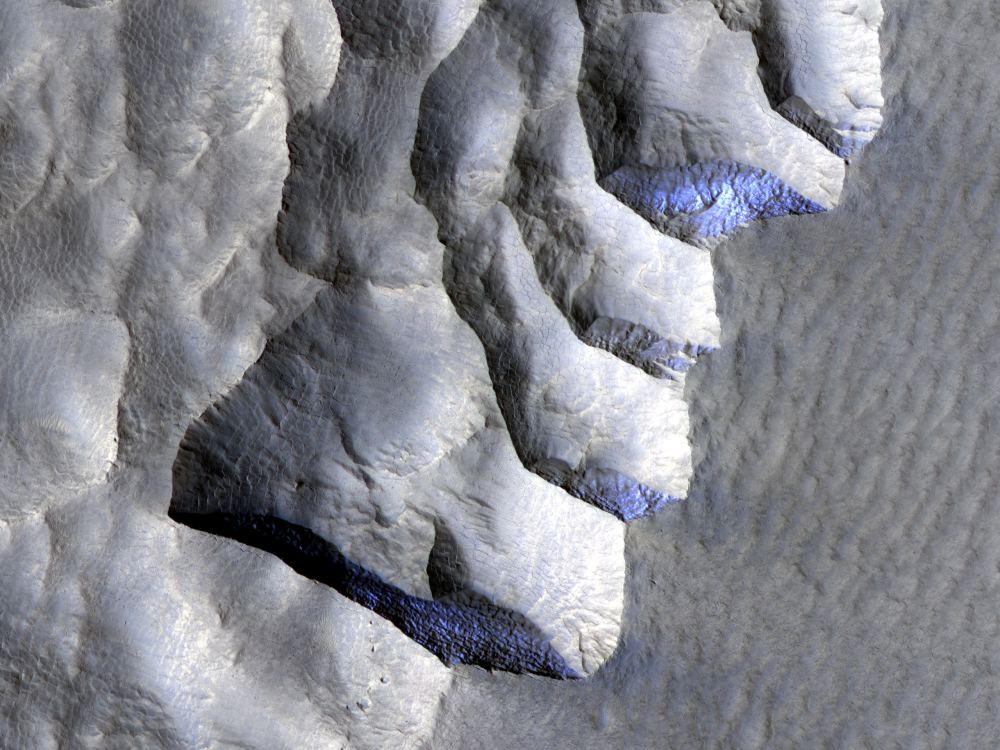
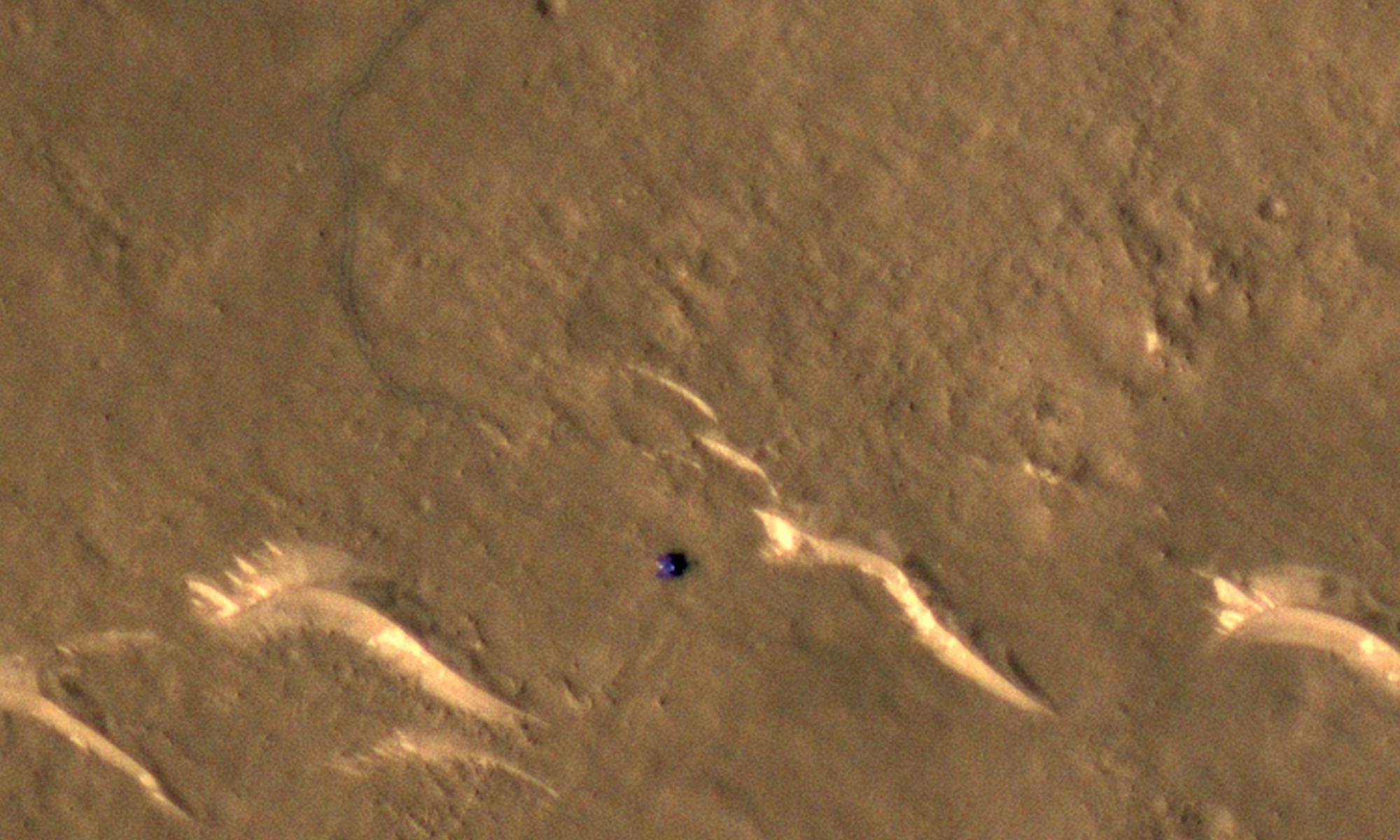
From orbit, this landscape on Mars looks like a lacy honeycomb or a spider web. But the unusual polygon-shaped features aren’t created by Martian bees or spiders; they are actually formed from a ongoing process of seasonal change from created from water ice and carbon dioxide.
Continue reading “This Bizarre Terrain on Mars is Caused by Water Ice and Carbon Dioxide”This Bizarre Terrain on Mars is Caused by Water Ice and Carbon Dioxide