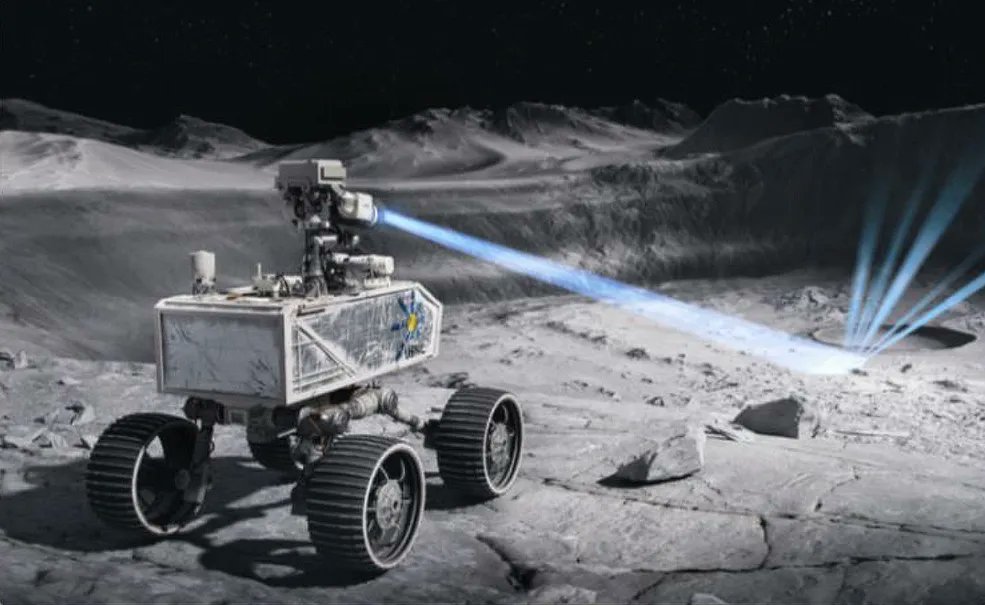
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese National Space Administration recently published a study in the journal Space: Science & Technology outlining how the upcoming Chang’e-7 mission, due to launch in 2026, will use a combination of orbital observations and in-situ analyses to help identify the location, amount, and dispersion of water-ice in the permanently-shadowed regions (PSRs) of the Moon, specifically at the lunar south pole.
Continue reading “China’s Chang’e-7 Will Deploy a Hopper that Jumps into a Crater in Search of Water Ice”NASA Artemis DIMPLE Instrument Suite to Explore Moon’s Mysterious Volcanic Features
NASA recently selected a new science payload that will travel to the Moon through a series of robotic missions via the agency’s Artemis program. This instrument suite, known as the Dating an Irregular Mare Patch with a Lunar Explorer (DIMPLE), will have the task of studying the Ina Irregular Mare Patch, also known as Ina, which is a small depression that could provide insights into the Moon’s volcanic history. It was discovered using orbital images from the Apollo 15 crew, and despite several past studies, its origin remains unclear.
Continue reading “NASA Artemis DIMPLE Instrument Suite to Explore Moon’s Mysterious Volcanic Features”India Launches Chandrayaan-3 to the Moon, Hoping for a Successful Landing
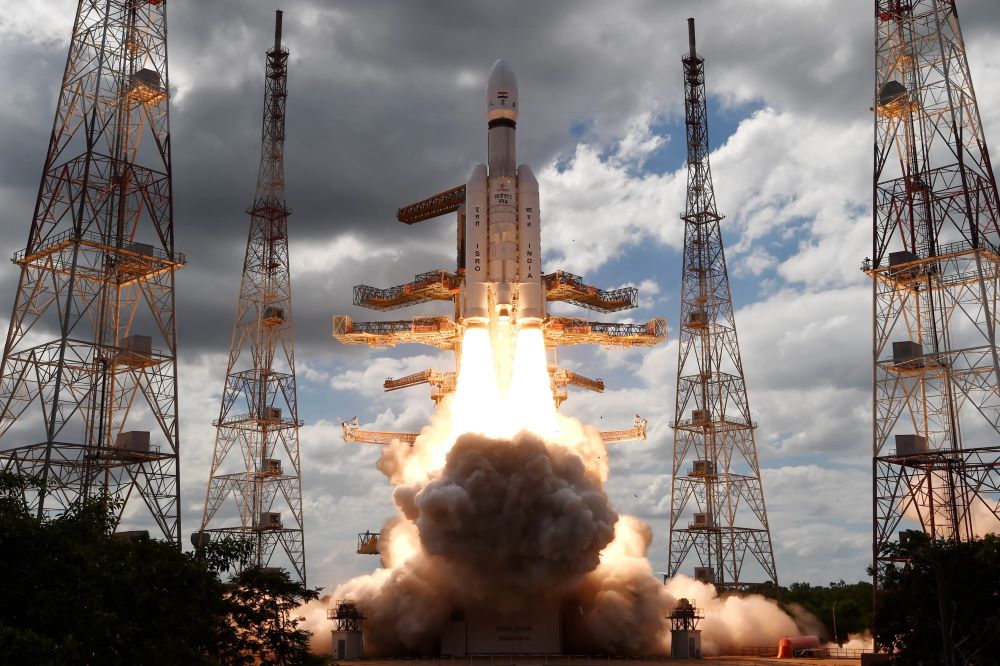

On July 14, 2023, at 2:35 pm Indian Standard Time (5:05 am EST), the Indian Space Resource Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched their Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft from the Satish Dhawan Space Center, which is the primary spaceport of the ISRO. The goal of the mission is to put India’s first lander (Vikram) and rover (Pragyan) on the lunar surface and is scheduled to touch down on the Moon on August 23, 2023. This mission comes after the ISRO’s Chandrayaan-2 Vikram lander crashed on the Moon on September 6, 2019, due to a last-minute guidance software glitch. While the ISRO indicated everything was going according to plan, they unexpectedly lost contact with the Vikram lander approximately 2.1 kilometers (1.3 miles) above the lunar surface.
Continue reading “India Launches Chandrayaan-3 to the Moon, Hoping for a Successful Landing”Volcanic Hotspot Found on the Moon

A recent study published in Nature examines a volcanic hotspot that potentially exists beneath a feature on the Moon’s farside (the side facing away from the Earth) called the Compton-Belkovich Thorium Anomaly. Researchers led by the Planetary Science Institute collected data from the hotspot region using microwave instruments onboard the China National Space Administration’s Chang’e-1 and Chang’e-2 orbiters and holds the potential to help scientists better understand the past volcanic processes on our nearest celestial neighbor, as surface evidence indicates lunar volcanic activity ceased between 3 to 4 billion years ago.
Continue reading “Volcanic Hotspot Found on the Moon”Artemis Accords Adds 25th, 26th, and 27th Signatory Countries
NASA recently welcomed the newest signatories of the Artemis Accords as Spain, Ecuador, and India became the 25th, 26th, and 27th countries, respectively, to sign on to the historic agreement for cooperation and partnership for space exploration, specifically pertaining to NASA’s Artemis program.
Continue reading “Artemis Accords Adds 25th, 26th, and 27th Signatory Countries”NASA Seeks Industry Proposals for Next-Generation Lunar Rover

As Artemis II gets ready to launch in November 2024, NASA recently announced it is pursuing contract proposals from private companies for the development of a next-generation Lunar Terrain Vehicle (LTV) to be used for crewed missions starting with Artemis V, which is currently scheduled for 2029. NASA has set a due date for the proposals of July 10, 2023, at 1:30pm Central Time, with the announcement for rewarded contracts to occur in November 2023.
Continue reading “NASA Seeks Industry Proposals for Next-Generation Lunar Rover”China is Planning to Land Humans on the Moon by 2030 as Part of its Ambitious Lunar Agenda

Weiren Wu, the Chief Designer of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (CLEP), recently announced an ambitious plan to put Chinese footprints on the lunar surface by 2030. This announcement came just prior to this year’s Space Day of China, an annual event celebrated on April 24th meant to showcase the space industry achievements of the China National Space Administration (CNSA).
Continue reading “China is Planning to Land Humans on the Moon by 2030 as Part of its Ambitious Lunar Agenda”Blue Origin is Building Solar Cells out of (Simulated) Lunar Regolith
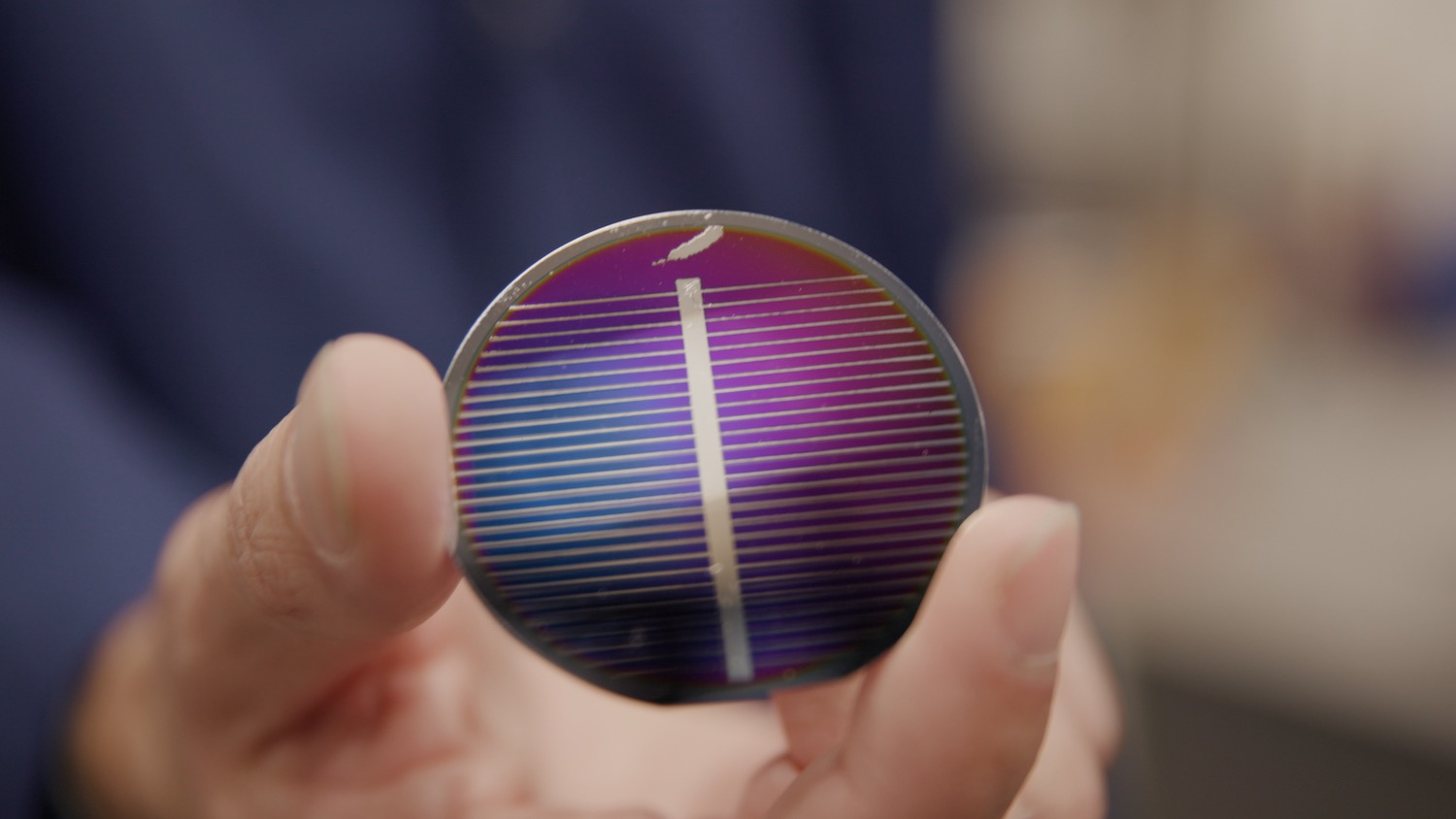
Power infrastructure will be critical for any long-term space colony, and one of the most critical pieces of that power infrastructure, at least in the inner solar system, is solar cells. So in-situ research experts were thrilled when Blue Origin, ostensibly a rocket company, recently announced that they had made functional solar cells entirely out of nothing other than lunar regolith simulant.
Continue reading “Blue Origin is Building Solar Cells out of (Simulated) Lunar Regolith”A new way to Peer Into the Permanently Shadowed Craters on the Moon, Searching for Deposits of Water ice
Not all flashlights are created equal. Some are stronger, consume more power, or have features such as blinking or strobes. Some aren’t even meant for humans, such as a new project that recently received funding from a NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts (NIAC) Phase I award. Designed by the Ultra Safe Nuclear Corporation (USNC), this flashlight doesn’t emit visible light, but it does emit x-rays and gamma rays, and the researchers on the project think it could be useful for finding resources on the Moon.
Continue reading “A new way to Peer Into the Permanently Shadowed Craters on the Moon, Searching for Deposits of Water ice”Artemis Astronauts Could Rely on Solar Cells Made out of Moon Dust
Within the next decade, several space agencies and commercial space partners will send crewed missions to the Moon. Unlike the “footprints and flags” missions of the Apollo Era, these missions are aimed at creating a “sustained program of lunar exploration.” In other words, we’re going back to the Moon with the intent to stay, which means that infrastructure needs to be created. This includes spacecraft, landers, habitats, landing and launch pads, transportation, food, water, and power systems. As always, space agencies are looking for ways to leverage local resources to meet these needs.
This process is known as in-situ resource utilization (ISRU), which reduces costs by limiting the number of payloads that need to be launched from Earth. Thanks to new research by a team from the Tallinn University of Technology (TalTech) in Estonia, it may be possible for astronauts to produce solar cells using locally-sources regolith (moon dust) to create a promising material known as pyrite. These findings could be a game-changer for missions in the near future, which include the ESA’s Moon Village, NASA’s Artemis Program, and the Sino-Russian International Lunar Research Station (ILRS).
Continue reading “Artemis Astronauts Could Rely on Solar Cells Made out of Moon Dust”