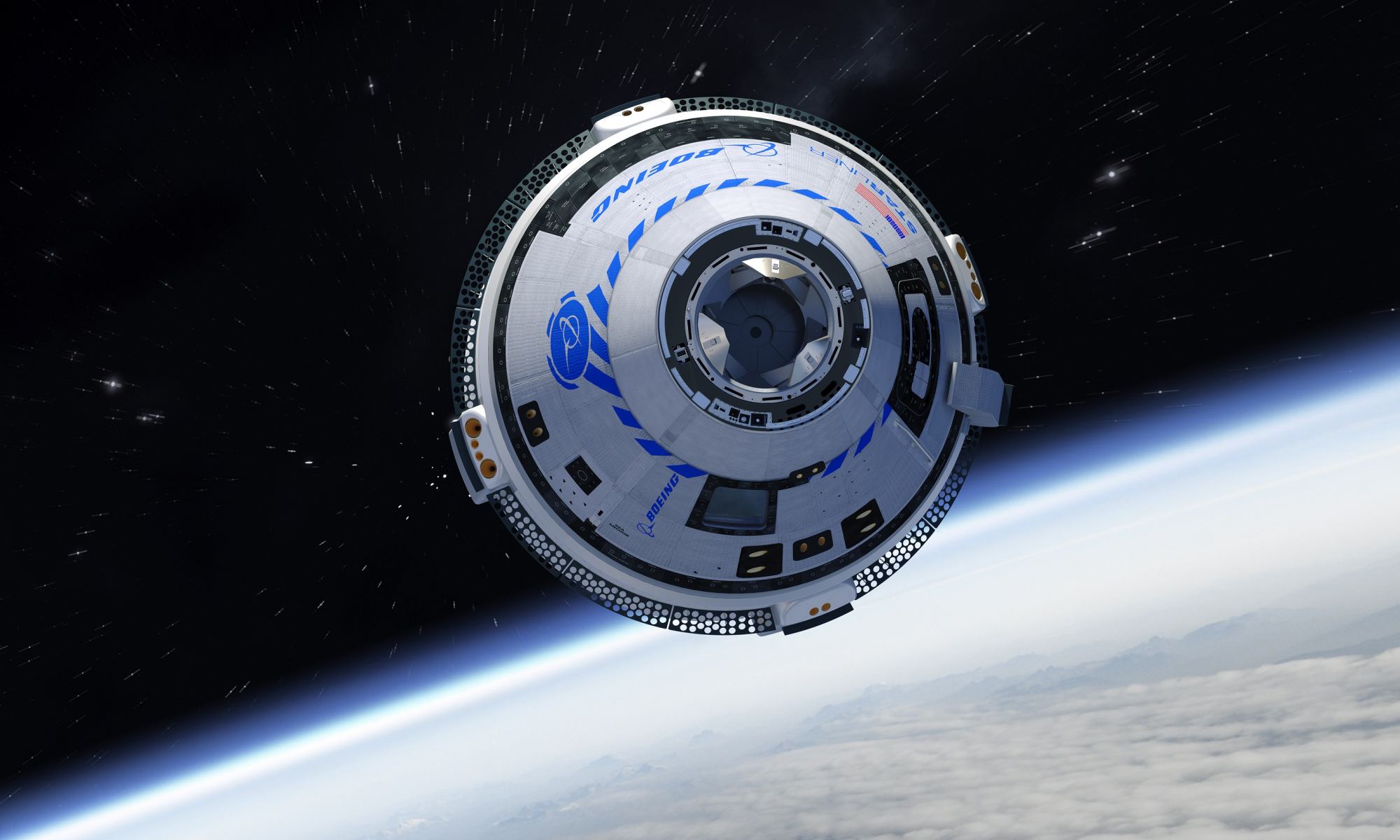
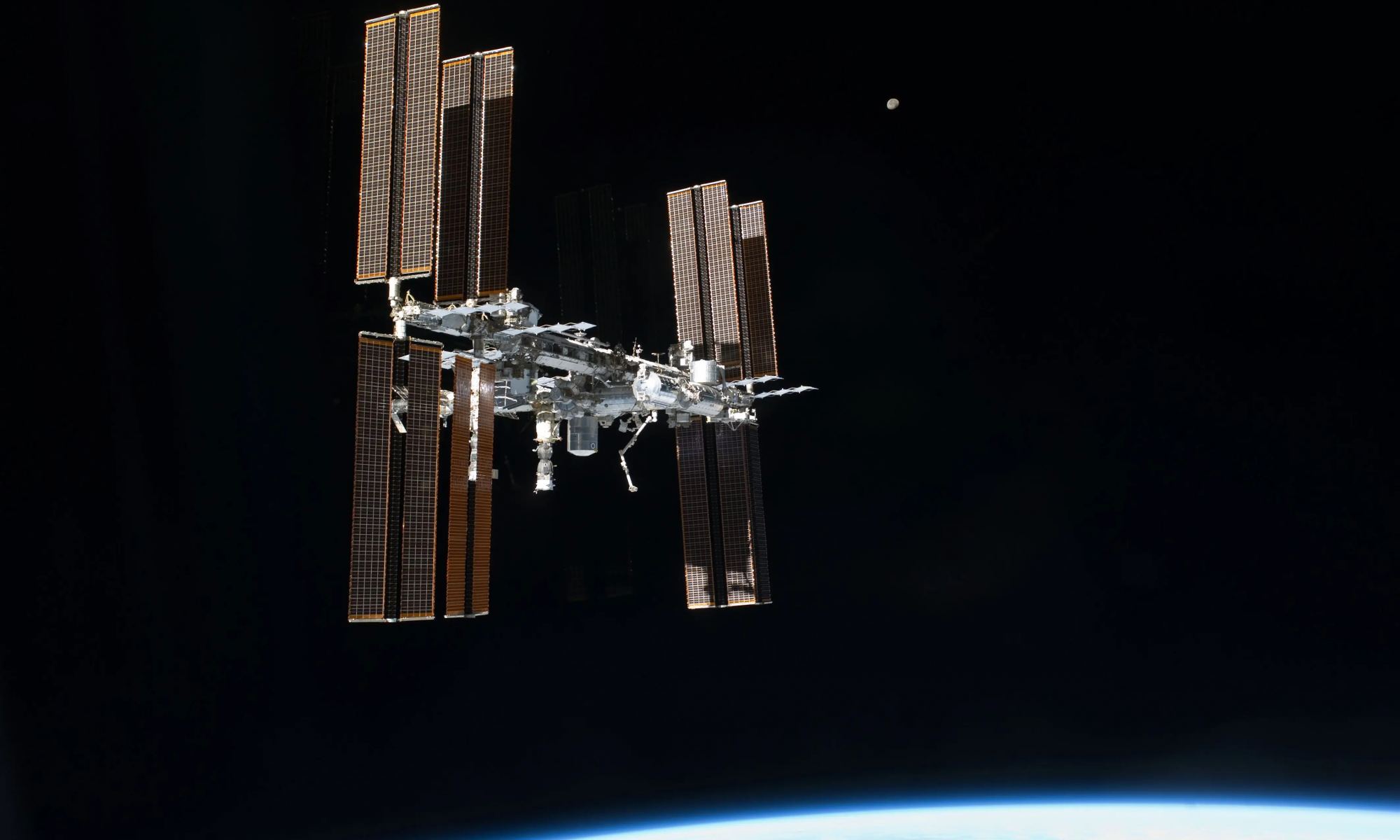
On July 28th, the International Space Station (ISS) suffered a mishap after a new Russian module (named Nauka) fired its thrusters just hours after arriving. As a result, the entire station was temporarily pushed out of position, forcibly delaying the Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) mission. This would have been Boeing’s CT-100 Starliner’s second attempt to rendezvous with the ISS as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP).
The ISS managed to correct its orbit shortly thereafter, while the OFT-2 launch was delayed until the next available opportunity (Wednesday, Aug. 4th). Unfortunately, the mission was delayed again due to an issue with one of the valves on the spacecraft’s propulsion system. This prompted the ground crews to move the Starliner and Atlas V launch vehicle back into Vertical Integration Facility (VIF), so they can look for the source of the problem more closely.
Continue reading “Russia’s new Module Kicks the Station out of Position, Causes a Delay for Starliner”